{{ searchResult.title }}

Wandering Albatross
Diomedea exulans
Known for its majestic wingspan and far-ranging travels, the Wandering Albatross is a captivating presence in the Southern Ocean's expanse. As the bird with the widest wingspan globally, this remarkable creature glides effortlessly across vast oceanic distances, its brilliant white plumage and solitary habits making it a unique symbol of the wild, open sea.
On this page
Appearance and Identification
Vocalization and sounds, behavior and social structure, distribution and habitat, lifespan and life cycle, conservation status, similar birds.
Males and females have similar plumage
Primary Color
Primary color (juvenile), secondary colors.
Black, Grey
Secondary Colors (female)
Secondary colors (juvenile).
White, Grey
Secondary Colors (seasonal)
Wing color (juvenile).
Large, Hooked
Beak Color (juvenile)
Leg color (juvenile), distinctive markings.
Black wings, white tail, large pink beak
Distinctive Markings (juvenile)
Darker than adults, brown beak
Tail Description
White with black edges
Tail Description (juvenile)
Brown with white edges
Size Metrics
107cm to 135cm
250cm to 350cm
6.72kg to 12kg
Click on an image below to see the full-size version
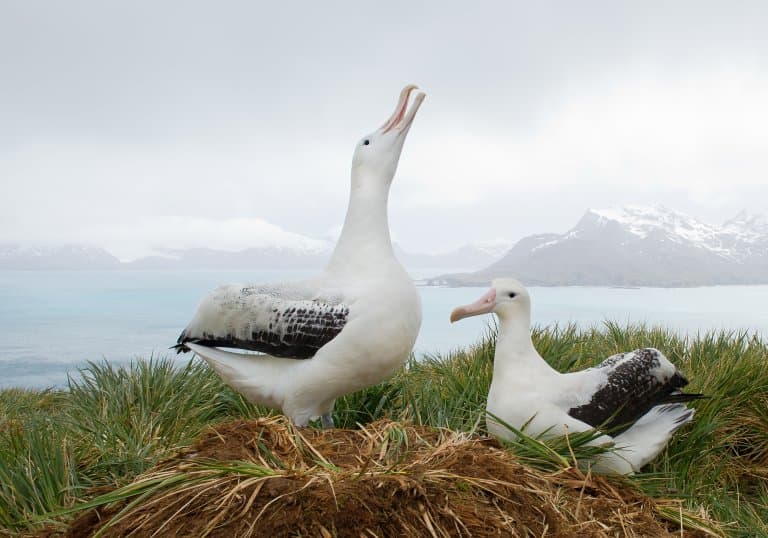
Pair of Wandering Albatrosses
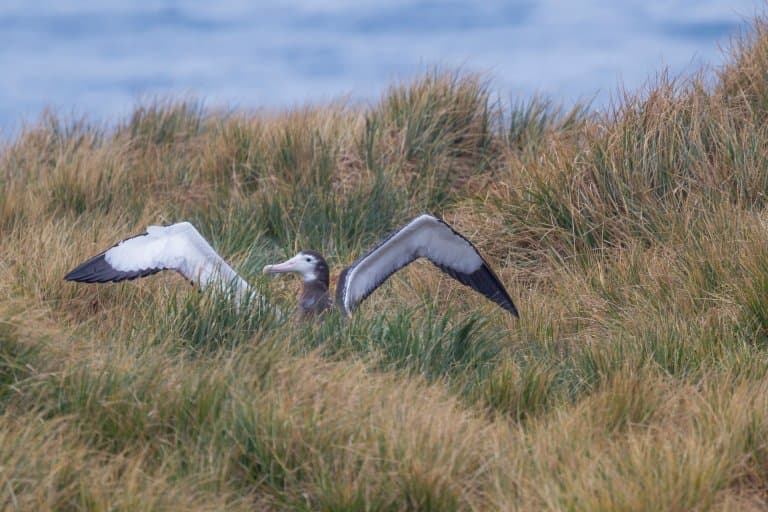
Juvenile Wandering Albatross
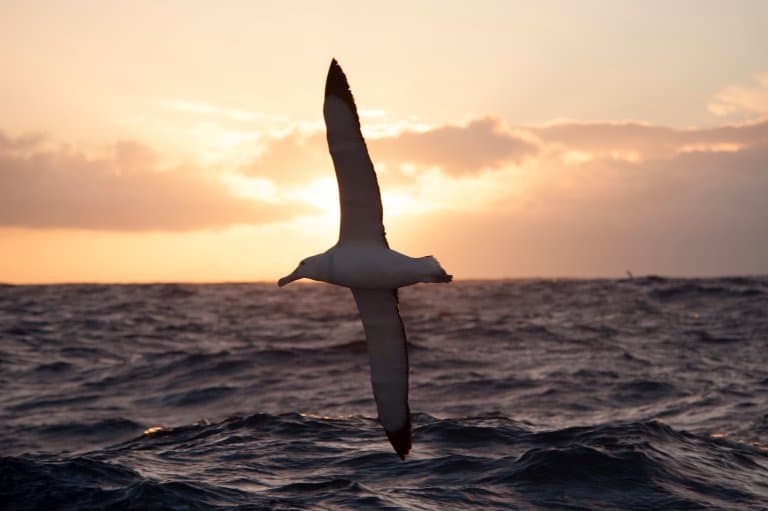
Wandering Albatross resting on the sea
Wandering Albatross in-flight over the ocean
Wandering Albatross at nest with downy chick
Primary Calls
Series of grunts and whistles
Call Description
Most vocal on breeding grounds, otherwise silent
Alarm Calls
Loud, harsh squawks
Daily Activities
Active during day, rests on water surface at night
Social Habits
Solitary at sea, social on breeding grounds
Territorial Behavior
Defends nest site during breeding season
Migratory Patterns
Non-migratory but wanders widely at sea
Interaction with Other Species
Occasionally forms loose flocks at sea
Primary Diet
Fish, Squid
Feeding Habits
Surface seizes and scavenges
Feeding Times
Day and night
Prey Capture Method
Plunge-diving, surface-seizing
Diet Variations
May eat carrion
Special Dietary Needs (if any)
Nesting location.
On ground on isolated islands
Nest Construction
Mound of mud and vegetation
Breeding Season
Every other year
Number of clutches (per breeding season)
Once every two years
Egg Appearance
White, oval
Clutch Characteristics
Incubation period.
Around 80 days
Fledgling Period
Approximately 9 months
Parental Care
Both parents incubate and feed chick
Geographic Range
Circumpolar in Southern Ocean
Habitat Description
Open ocean, breeds on remote islands
Elevation Range
Migration patterns, climate zones.
Polar, Temperate
Distribution Map
Please note, this range and distribution map is a high-level overview, and doesn't break down into specific regions and areas of the countries.
Non-breeding
Lifespan range (years)
Average lifespan, maturity age.
7-10 year(s)
Breeding Age
Reproductive behavior.
Monogamous, long-term pair bonds
Age-Related Changes
Younger birds are darker, gain white plumage with age
Current Status
Vulnerable (IUCN Red List)
Major Threats
Longline fishing, plastic ingestion, climate change
Conservation Efforts
Protected under international law, conservation programs on breeding islands
Population Trend
Slow but steady population decrease due to threats
Royal Albatross
Diomedea epomophora
Classification
Other names:
Snowy Albatross, White-winged Albatross
Population size:
Population trend:
Conservation status:
IUCN Red List
Get the best of Birdfact
Brighten up your inbox with our exclusive newsletter , enjoyed by thousands of people from around the world.
Your information will be used in accordance with Birdfact's privacy policy . You may opt out at any time.
© 2024 - Birdfact. All rights reserved. No part of this site may be reproduced without our written permission.

Wandering Albatross
Diomedea exulans.
The snowy albatross, also known as the white-winged albatross or goonie, is a majestic seabird belonging to the Diomedeidae family. It is recognized for its impressive wingspan, which is the largest of any living bird, and its predominantly white plumage that becomes whiter with age. The snowy albatross is distinguished by its large pink bill and feet, and the males exhibit whiter wings than females.
Identification Tips
Adult snowy albatrosses have white bodies contrasted with black and white wings. The wings of males are predominantly white, with only the tips and trailing edges presenting as black. This species is the whitest within its complex, with others showing more brown and black on the wings and body. A salt gland above their nasal passage helps them excrete excess salt due to their oceanic diet.
The snowy albatross boasts a wingspan that can exceed 3.5 meters (11 feet), with an average span of around 3.1 meters (10 feet 2 inches). Body length ranges from 107 to 135 cm (3 feet 6 inches to 4 feet 5 inches), with females being slightly smaller than males. Adults typically weigh between 5.9 to 12.7 kg (13 to 28 lb).
Distribution and Habitat
This bird has a circumpolar range in the Southern Ocean and breeds on islands such as South Georgia, Crozet, Kerguelen, Prince Edward, and Macquarie. It is also seen feeding year-round off the coast of New Zealand and is known for its extensive flights, sometimes circumnavigating the Southern Ocean three times in a year.
The snowy albatross is a far-ranging bird, spending most of its life in flight and landing only to breed and feed. It is capable of gliding for hours without flapping its wings, thanks to its large wingspan.
Song & Calls
During courtship, snowy albatrosses engage in a variety of displays, including spreading their wings, head-waving, bill-rapping, and producing a range of vocalizations from screams and whistles to grunts and bill clapping.
Snowy albatrosses are monogamous, often mating for life, and breed biennially. They lay a single white egg with a few spots in a large grassy nest. Incubation takes about 11 weeks, with both parents sharing the responsibility. The chicks are nurtured by both parents, who take turns foraging for food.
Similar Species
The snowy albatross is part of the wandering albatross species complex, which includes the Tristan albatross and the Antipodean albatross. It can be distinguished from its relatives by its whiter plumage and larger size.
Diet and Feeding
These birds feed on cephalopods, small fish, and crustaceans, often foraging further out in the open ocean than other albatross species. They are known to follow ships and can make shallow dives to capture their prey.
Conservation Status
The IUCN lists the snowy albatross as vulnerable. Threats include longline fishing and pollution. Conservation measures have been implemented in some regions to reduce bycatch and protect their breeding grounds.
.css-1cn5y0j{border-radius:0.25rem;font-size:0.875rem;line-height:1.25rem;font-weight:650;letter-spacing:0em;--tw-text-opacity:1;color:rgb(45 49 66 / var(--tw-text-opacity));font-style:normal;font-weight:650;margin-left:2rem;margin-right:2rem;margin-bottom:1.5rem;font-size:1.875rem;line-height:2.25rem;}@media (min-width: 768px){.css-1cn5y0j{margin-left:3rem;margin-right:3rem;}} Wandering Albatrosses on Birda
More albatrosses, amsterdam albatross, antipodean albatross, tristan albatross, southern royal albatross, northern royal albatross, short-tailed albatross, laysan albatross, waved albatross, black-footed albatross, sooty albatross, light-mantled albatross, buller's albatross, indian yellow-nosed albatross, shy albatross, atlantic yellow-nosed albatross, grey-headed albatross, chatham albatross, campbell albatross, black-browed albatross, salvin's albatross, your birdwatching journey like never before, connect with nature in minutes, discover the joy of birding, play your part in saving nature, what our birders say, great app for beginner twitchers, great app for learning birds, fantastic app - love it, app got me interested in birding, very wholesome app, sense of community, very knowledgeable group, friendly and helps to identify birds, fun way to add to your birdwatching experience.

- Skip to content
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology builds the eBird global platform for communities and partners around the world to advance data-driven science, education, and conservation.
- Procellariiformes
- Diomedeidae
Wandering Albatross Diomedea exulans
Sign in to see your badges
Identification
Huge albatross of the Southern Ocean; the southernmost breeder of the Wandering Albatross complex (including Snowy, Tristan, Antipodean, and Amsterdam albatrosses). Main colonies on South Georgia in the South Atlantic, and various islands in the southern Indian Ocean, but ranges extensively at sea. Plumage highly variable, starting chocolate-brown with a white face and gradually becoming whiter over many years. Younger birds separated from Southern Royal Albatross by darker tail, brown markings on head and back, and lack of black “lips” on cutting edge of bill. Older birds more difficult to separate; focus on more coarsely marked upperwings, often with conspicuous white patch in center of wing, and lack of black “lips”. Often shows orange stain on cheek, never shown by Southern Royal. Identification from other Wandering-type Albatross, especially “Gibson’s” Antipodean and Tristan, extremely difficult and often presumed by range. Adult male Snowy is the whitest of any Wandering, but intermediate ages often best left unidentified.
Exotic species
Exotic species flags differentiate locally introduced species from native species.
Naturalized : Exotic population is self-sustaining, breeding in the wild, persisting for many years, and not maintained through ongoing releases (including vagrants from Naturalized populations). These count in official eBird totals and, where applicable, have been accepted by regional bird records committee(s).
Provisional : Either: 1) member of exotic population that is breeding in the wild, self-propagating, and has persisted for multiple years, but not yet Naturalized; 2) rarity of uncertain provenance, with natural vagrancy or captive provenance both considered plausible. When applicable, eBird generally defers to bird records committees for records formally considered to be of "uncertain provenance". Provisional species count in official eBird totals.
Escapee : Exotic species known or suspected to be escaped or released, including those that have bred but don't yet fulfill the criteria for Provisional. Escapee exotics do not count in official eBird totals.

Wandering albatross

Scientific name: Diomedea exulans
Physical description
Wandering albatross have a white head, neck and body, a wedge-shaped tail, and a large pink beak.
Juveniles have mostly dark plumage, which gradually whitens with age.
Distribution and abundance
Wandering albatross are found across the Southern Ocean. This includes Antarctic, sub-Antarctic and subtropical waters.
Wandering albatross breed on sub-Antarctic and Antarctic islands between 46° and 56°S.
Breeding islands include Iles Kerguelen, South Georgia and Macquarie Island.
Young birds remain at sea for 5–10 years before returning to their natal island to breed.
Conservation status: vulnerable with population trends decreasing. Decreasing populations are due to the birds being caught in long-line fishing operations.
Wandering albatross breed once every two years. Both parents share the task of incubating the half-kilogram egg and rearing the chick.
Diet and feeding
Wandering albatross eat fish, cephalopods, jellyfish and sometimes crustaceans. They also eat penguin and seal carrion.
Chicks consume up to 100 kg of food during their rearing period. The rearing period lasts for approximately 300 days.
Foraging trips of wandering albatross can last for 50 days at a time. These trips tend to be much shorter during the breeding season.
Photo gallery

You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.

- Buy Tickets
- Join & Give
Wandering Albatross
- Updated 25/07/24
- Read time 2 minutes

- IUCN Conservation Status VULNERABLE (VU)
- Classification Genus Diomedea Species exulans Family Diomedeidae Order Procellariiformes Class Aves
- Size Range 80 cm to 135 cm
The Wandering Albatross is the largest of the albatrosses and is the living bird with the greatest wingspan, measuring almost 3.5 m.
What do Wandering Albatrosses look like?
Identification.
The adult Wandering Albatross appears entirely white from a distance. Close up, the fine black wavy lines on the breast, neck and upper back become visible. The bill can vary in colour, but is normally yellowish-pink. The white tail is occasionally tipped with black and the back of the wing changes from black to white with age. A series of plumage phases are passed through as young birds reach full adult plumage, which can take up to nine years. Females are slightly smaller than males.
Where do Wandering Albatrosses live?
Wandering Albatrosses spend most of their life in flight, landing only to breed and feed. Distances travelled each year are hard to measure, but one banded bird was recorded travelling 6000 km in twelve days.
Distribution
The Wandering Albatross visits Australian waters from Fremantle, Western Australia to northern New South Wales between June and September each year. At other times birds roam the southern oceans and commonly follow fishing boats for several days.
What do Wandering Albatrosses eat?
Feeding and diet.
Wandering Albatrosses are often seen scavenging scraps from fishing boats, but squid and fish are the preferred foods. Galley refuse and floating waste also form part of the diet. Feeding is one of the few times that birds land, and this is mostly undertaken at night.
What are Wandering Albatrosses breeding behaviours?
Breeding behaviour/s.
Pairs of Wandering Albatrosses mate for life and breed every two years. Breeding takes place on subantarctic islands and commences in early November. The nest is a mound of mud and vegetation, and is placed on an exposed ridge near the sea. During the early stages of the chick's development, the parents take turns to sit on the nest while the other searches for food. Later, both adults hunt for food and visit the chick at irregular intervals.
Breeding Season: November.

The Australian Museum respects and acknowledges the Gadigal people as the First Peoples and Traditional Custodians of the land and waterways on which the Museum stands.
Image credit: gadigal yilimung (shield) made by Uncle Charles Chicka Madden

- Text account
- Data table and detailed info
- Distribution map
- Reference and further resources
Taxonomic source(s) AERC TAC. 2003. AERC TAC Checklist of bird taxa occurring in Western Palearctic region, 15th Draft. Available at: #http://www.aerc.eu/DOCS/Bird_taxa_of _the_WP15.xls# . Brooke, M. de L. 2004. Albatrosses and Petrels Across the World . Oxford University Press, Oxford. Christidis, L. and Boles, W.E. 2008. Systematics and Taxonomy of Australian Birds . CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood, Australia. del Hoyo, J., Collar, N.J., Christie, D.A., Elliott, A. and Fishpool, L.D.C. 2014. HBW and BirdLife International Illustrated Checklist of the Birds of the World. Volume 1: Non-passerines . Lynx Edicions BirdLife International, Barcelona, Spain and Cambridge, UK. Robertson, C. J. R.; Nunn, G. B. 1998. Towards a new taxonomy for albatrosses. In: Robertson, G.; Gales, R. (ed.), Albatross biology and conservation , pp. 13-19. Surrey Beatty & Sons, Chipping Norton, Australia. SACC. 2005 and updates. A classification of the bird species of South America. Available at: #http://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm# .
In 1998, the total annual breeding population was estimated at 8,500 pairs, equivalent to c. 28,000 mature individuals (Gales 1998). However, current estimates are 1,553 pairs on South Georgia (Georgias del Sur) (Poncet et al. 2006), 1,800 pairs on Prince Edward Island (2008, Ryan et al. 2009), c. 1,900 pairs on Marion Island (2013, ACAP 2009), c. 340 pairs on Iles Crozet (CNRS Chinzè Monitoring Database 2010), c. 354 pairs in Iles Kerguelen (CNRS Chinzè Monitoring Database 2011), and 4 pairs on Macquarie Island (DPIWPE 2010, unpublished data), making a total of c. 6,000 annual breeding pairs. Using the same ratio as Gales (1998) for estimating the number of mature individuals, this would equate to approximately 20,100 mature individuals.
Recommended citation BirdLife International (2024) Species factsheet: Wandering Albatross Diomedea exulans . Downloaded from https://datazone.birdlife.org/species/factsheet/wandering-albatross-diomedea-exulans on 01/09/2024. Recommended citation for factsheets for more than one species: BirdLife International (2024) IUCN Red List for birds. Downloaded from https://datazone.birdlife.org/species/search on 01/09/2024.

Wandering Albatross
These remarkably efficient gliders, named after the Greek hero Diomedes, have the largest wingspan of any bird on the planet

Region: Antarctica
Destinations: Bouvet Island, Antarctic Peninsula, South Georgia
Name : Wandering Albatross, Snowy Albatross, White-winged Albatross ( Diomedea exulans )
Length: Up to 135 cm.
Weight : 6 to 12kg.
Location : All oceans except in the North Atlantic.
Conservation status : Vulnerable.
Diet : Cephalopods, small fish, crustaceans.
Appearance : White with grey-black wings, hooked bill.
How do Wandering Albatrosses feed?
Wandering Albatrosses make shallow dives when hunting. They’ll also attempt to eat almost anything they come across and will follow ships in the hopes of feeding on its garbage. They can gorge themselves so much that they become unable to fly and just have to float on the water.
How fast do Wandering Albatrosses fly?
Wandering Albatrosses can fly up to 40 km per hour.

What are Wandering Albatross mating rituals like?
Wandering Albatrosses mature sexually around 11 years of age. When courting, the male Wandering Albatross will spread his wings, wave his head around, and rap his bills against that of the female while making a braying noise. The pair will mate for life, breeding every 2 years. Mating season starts in early November with the Albatrosses creating nests of mud and grass on one of the Sub-Antarctic islands. The female will lay 1 egg about 10 cm long, sometime between the middle of December and early January. Incubation takes around 11 weeks, the parents taking turns. Once the chick is born the adults switch off between hunting and staying to care for the chick. The hunting parent returns to regurgitate stomach oil for the chick to feed on. Eventually both parents will start to hunt at the same time, visiting with the chick at widening intervals.

How long do Wandering Albatrosses live?
Wandering Albatrosses can live for over 50 years.
How many Wandering Albatrosses are there today?
There are about 25.200 adult Wandering Albatrosses in the world today.

Do Wandering Albatrosses have any natural predators?
Because they’re so big and spend almost all of their lives in flight, Wandering Albatrosses have almost no natural predators.
7 Wonderful Wandering Albatross Facts
- The Wandering Albatross is the largest member of its genus ( Diomedea ) and is one of the largest birds in the world.
- Wandering Albatrosses are also one of the best known and most studied species of birds.
- Diomedea refers to Diomedes, a hero in Greek mythology; of all the Acheaens he and Ajax were 2 nd only to Achilles in prowess. In mythology all of his companions turned into birds. Exulans is Latin for “exile” or “wanderer.”
- Wandering Albatrosses have the largest wingspan of any bird in the world today, stretching up to 3.5 metres across.
- Wandering Albatrosses are great gliders – they can soar through the sky without flapping their wings for several hours at a time. They’re so efficient at flying that they can actually use up less energy in the air than they would while sitting in a nest.
- Wandering Albatrosses have a special gland above their nasal passage that excretes a high saline solution. This helps keep salt level in their body, combating all the salt water they take in.
- Wandering Albatrosses get whiter the older they get.

Related cruises

Falkland Islands - South Georgia - Antarctica
Meet at least six penguin species!
PLA20-24 A cruise to the Falkland Islands, South Georgia & the Antarctic Peninsula. Visit some of the most beautiful arrays of wildlife on Earth. This journey will introduce you to at least 6 species of penguin and a whole lot of Antarctic fur seals!
m/v Plancius
Cruise date:
18 Oct - 7 Nov, 2024
Berths start from:

Antarctica - Basecamp - free camping, kayaking, snowshoe/hiking, photo workshop, mountaineering
The best activity voyage in Antarctica
HDS21a24 The Antarctic Peninsula Basecamp cruise offers you a myriad of ways to explore and enjoy the Antarctic Region. This expedition allows you to hike, snowshoe, kayak, go mountaineering, and even camp out under the Southern Polar skies.
m/v Hondius
1 Nov - 13 Nov, 2024

Weddell Sea – In search of the Emperor Penguin, incl. helicopters
Searching for the Elusive Emperor Penguins
OTL22-24 A true expedition, our Weddell Sea cruise sets out to explore the range of the Emperor Penguins near Snow Hill Island. We will visit the area via helicopter and see a variety of other birds and penguins including Adélies and Gentoos.
m/v Ortelius
10 Nov - 20 Nov, 2024

OTL23-24 A true expedition, our Weddell Sea cruise sets out to explore the range of the Emperor Penguins near Snow Hill Island. We will visit the area via helicopter and see a variety of other birds and penguins including Adélies and Gentoos.
20 Nov - 30 Nov, 2024

Antarctica - Basecamp - free camping, kayaking, snowshoe/hiking, mountaineering, photo workshop
HDS23-24 The Antarctic Peninsula Basecamp cruise offers you a myriad of ways to explore and enjoy the Antarctic Region. This expedition allows you to hike, snowshoe, kayak, go mountaineering, and even camp out under the Southern Polar skies.
23 Nov - 5 Dec, 2024
We have a total of 61 cruises

- Diomedeidae
- Diomedea exulans
- Procellariiformes
Wandering Albatross
The Wandering Albatross is a massive bird known by many names. In various regions, people call this bird a Snowy Albatross, Goonie, and White Winged Albatross.
Not only are they the largest of the 22 albatross species, but they also have the longest wingspan of any bird. Their wings commonly measure up to 10 ft. across, and the largest confirmed specimen had a wingspan over 12 ft. across! Read on to learn about the Wandering Albatross .
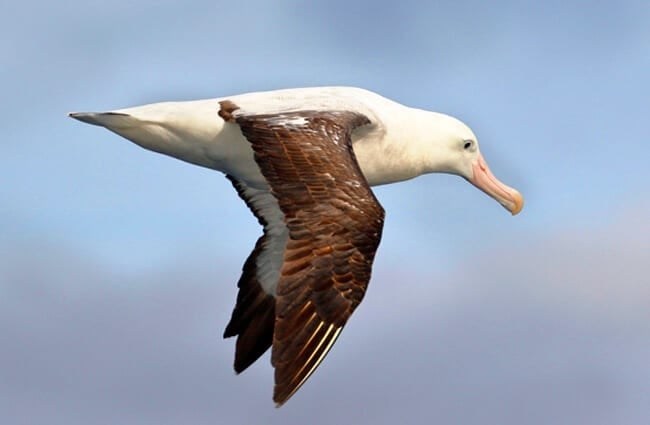

Description of the Wandering Albatross
This species of albatross has white plumage, or feathers, with darker wings. Their wing feathers are black, and speckled with varying degrees of white. Young birds have brown feathers, which become white as they age.
This bird’s wingspan is quite large, and averages 10 feet across, though some individuals are larger. Finally, their beaks are moderately long, with a hook at the end to help grasp fish.
Interesting Facts About the Wandering Albatross
This species has the longest wingspan of any living bird … Ever! However, that is not the only notable thing about the Wandering Albatross.
- Monogamous Mates – Once a Wandering Albatross has found a suitable mate, it continues to breed with that bird for the rest of its life. They are doting parents, and take great care in rearing their chicks. It sometimes takes up to 10 months for the chick to learn how to fly and become independent of its parents.
- Time Constraints – Obviously when it takes 10 months to raise a single chick, it can be difficult to jump right back into parenthood. For this reason, Wandering Albatrosses breed once every 2 years.
- Slow to Mature – Adult albatrosses don’t even begin reproducing until they are about 10 years old on average. They sometimes join the other birds at the breeding colonies and perform mating displays. However, most of the time they do not find a mate and begin to breed until they are around 10 years old.
- Slow Growth – Unfortunately, because these birds are so slow to mature, and they breed at a very slow rate, their populations do not increase quickly. Because of this, when their populations decline it takes a long time for them to make a comeback. Humans pose threats to these birds in a number of different ways, and the IUCN lists the species as Vulnerable .
Habitat of the Wandering Albatross
These birds spend the vast majority their life flying over, or floating on the surface of, the ocean. They inhabit the open ocean, primarily where the waters are deep, and fish are plentiful. The only time they come to land is for the mating season. During this time, colonies of birds land on plateaus, valleys, and plains.
Distribution of the Wandering Albatross
There are several different subspecies of Wandering Albatross, all of which live in the open oceans of the Southern Hemisphere. Outside of the breeding season, they roam the open oceans in between Antarctica and the southern coasts of Africa, South America, and Australia. Their primary breeding colonies are on various islands across the Southern Hemisphere, including South Georgia, Macquarie, Amsterdam Island, and more.
Diet of the Wandering Albatross
This seabird unsurprisingly feeds primarily on fish and other aquatic organisms. They eat fish, octopus, squid, shrimp, and krill.
They also scavenge on the remains of carcasses, as well as feeding on the scraps from commercial fishing operations and other predators. Though they can dive if they need to, they catch most of their food at the surface of the water.
Wandering Albatross and Human Interaction
Unfortunately, humans are extremely detrimental to these birds. Sailors have killed birds, both at sea and in nesting colonies, for decades. In fact, humans are the only known predator of adult albatrosses.
Nowadays it is illegal to harm these birds, though killing does still occur. Sadly, they frequently, and accidentally, become trapped in fishing nets or on fishing lines. Humans have also introduced many different feral animals to their breeding islands, and these animals eat the eggs and chicks.
Domestication
Humans have not domesticated this species of bird in any way.
Does the Wandering Albatross Make a Good Pet
No, the Wandering Albatross does not make a good pet. Their huge wings carry them across open ocean, which would make them a poor household pet. It most places, it is illegal to harm, harass, capture, or kill these birds.
Wandering Albatross Care
These birds do not often find themselves in zoos. The only time any albatross species lives in a zoo or aquarium is when something has severely injured them in some way.
During those times, zoos attempt to heal and rehabilitate the birds, and release them back into the wild if possible. Albatrosses that live in zoos because they cannot survive in the wild act as ambassadors to the plight of their species.
Behavior of the Wandering Albatross
This species is quite social, even outside of the breeding season. While in the open ocean, small groups of Wandering Albatrosses forage together. These groups frequently converge upon one another when feeding opportunities, like bait balls or fishing vessels, arise.
As the breeding season arrives, huge colonies of birds flock to their breeding grounds together. Birds searching for mates perform elaborate courtship displays, and mated pairs renew their bonds.
Reproduction of the Wandering Albatross
Every 2 years a pair breeds and produces a single egg, usually in December. Both the male and the female help incubate the egg, which hatches after 2.5 months. Once the chick hatches the parents alternate between keeping it warm and fishing for food.
After the chick is a month old, both parents leave it alone to hunt for food. It takes between 9 and 10 months for the chick to learn how to fly and gain independence.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
![Red Angus Closeup of a beautiful Red Angus cowPhoto by: U.S. Department of Agriculture [pubic domain]https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://animals.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Red-Angus-4-238x178.jpg)
Paint Horse

Expert Recommendations

Best Dog Car Seat

Best Dog Training Treats

Best Natural Dog Food

Best Wireless Dog Fences

Best Dog Vitamins

Best Dog Beds for Large Dogs

Best Smelling Dog Shampoo

Best Dog Nail Clippers

Best Dog Life Jacket

Best Dog Gifts
Even more news.
![Red Angus Closeup of a beautiful Red Angus cowPhoto by: U.S. Department of Agriculture [pubic domain]https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/](https://animals.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Red-Angus-4-100x75.jpg)
House Spider
Popular category.
- Chordata 694
- Mammalia 247
- Dog Breeds 184
- Actinopterygii 121
- Reptilia 87
- Carnivora 72
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Wandering Albatross - Diomedea exulans
Wandering albatross range map.
Click here to return to the species description page

SOUTH DAKOTA BIRDS AND BIRDING - LOCATIONS OF WEBSITE VISITORS
Please mail any comments/suggestions/additional links for this page to: DakotaBirder

Woods Hole, Mass. — Wandering albatrosses, which are an iconic sight in the Southern Ocean, are highly adapted to long-distance soaring flight. Their wingspan of up to 11 feet is the largest known of any living bird, and yet wandering albatrosses fly while hardly flapping their wings. Instead, they depend on dynamic soaring—which exploits wind shear near the ocean surface to gain energy—in addition to updrafts and turbulence.
Now researchers, including Philip Richardson , a senior scientist emeritus in Physical Oceanography Department at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), are unlocking more clues about exactly how wandering albatrosses are such amazing flyers.
In a new paper analyzing GPS tracks of wandering albatrosses, researchers have found that the birds’ airspeed increases with wind speed up to a maximum airspeed of 20 meters per second (m/s; 45 mph). Researchers developed a model of dynamic soaring, which predicts that the birds could fly much faster than 20 m/s. The paper concludes that the birds limit their airspeed by adjusting the turns in their trajectories to be around 60°, and that in low winds the birds exploit updrafts over waves to supplement dynamic soaring.
“We hypothesize that wandering albatrosses limit their maximum across-wind airspeeds to ~ 20 m/s in higher wind speeds (and greater wind turbulence), probably to keep the aerodynamic force on their wings during dynamic soaring well below the mechanically-tolerable limits of wing strength,” according to the paper, “Observations and Models of Across-wind Flight Speed of the Wandering Albatross,” published in the journal Royal Society Open Science .
The paper adds that, given the complex field of wind waves and swell waves often present in the Southern Ocean, “it is also possible that birds find it increasingly difficult to coordinate dynamic soaring maneuvers at faster speeds.”
Regarding low flight speeds by albatrosses, the paper notes that a theoretical model predicted that the minimum wind speed necessary to support dynamic soaring is greater than 3 m/s. “Despite this, tracked albatrosses were observed in flight at wind speeds as low as 2 m/s. We hypothesize at these very low wind speeds, wandering albatrosses fly by obtaining additional energy from updrafts over water waves,” according to the paper.
“We tried to figure out how these birds are using the winds to go long distances—without overstressing their wings—for foraging for food and returning to feed their chicks. To do that, we modeled dynamic soaring and what different turn angles would do to stress on the birds’ wings and speed over the water,” said journal paper co-author Richardson. A dynamic soaring trajectory is an s-shaped maneuver consisting of a series of connected turns, he noted.
“This research is a step in the direction of understanding how wandering albatrosses are able to do these foraging trips and maintain a fairly large population. These birds figured out an amazing way to use the wind to almost effortlessly soar for thousands of miles over the ocean. We wanted to find out exactly how they did it,” he said.
In addition to learning more about albatrosses, the study could have broader implications for helping researchers better understand how to use dynamic soaring to power potential albatross-type gliders to observe ocean conditions, Richardson added.
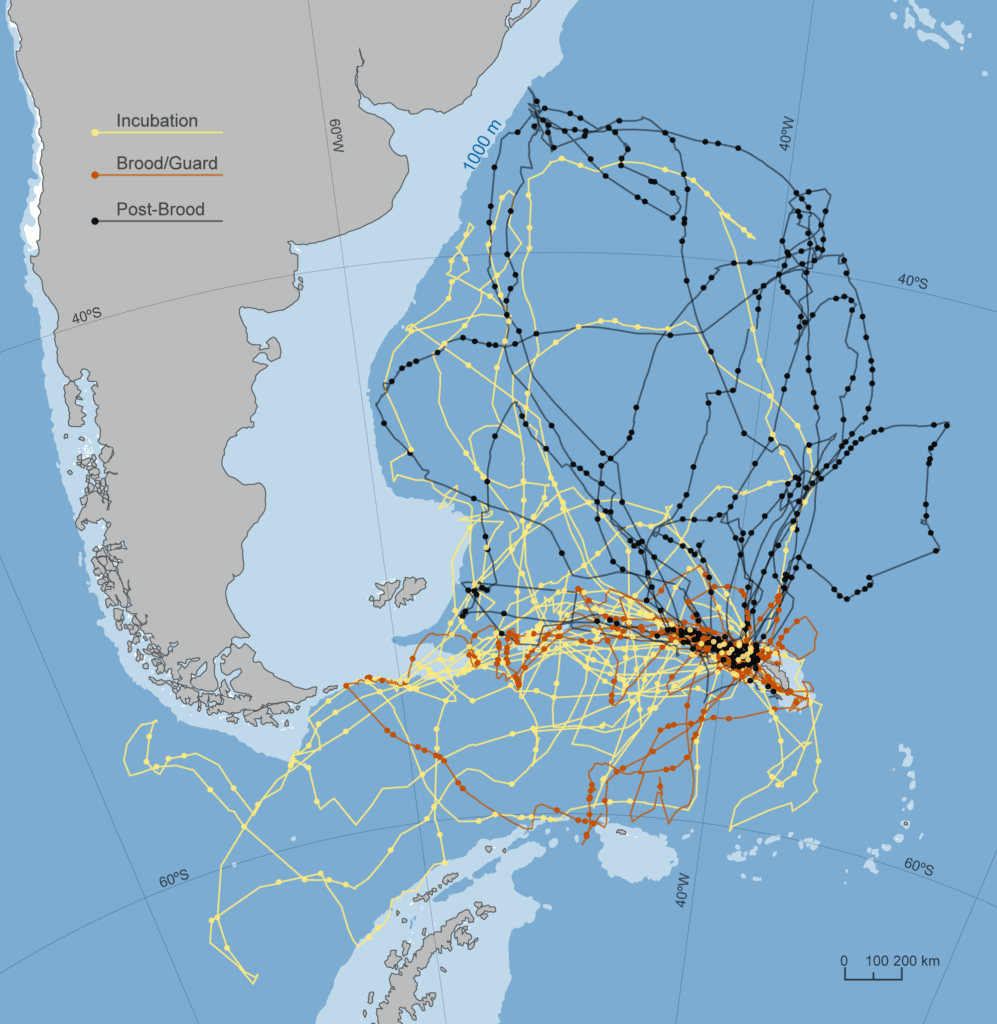
Trajectories of breeding wandering albatrosses nesting on South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic. These birds are highly adapted to long-distance soaring flight assisted by a wingspan of up to 11 feet--the largest known of any living bird. They use the winds to soar thousands of miles seeking food to bring back to nourish their chicks. (Map by Natalie Renier, ©Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution)
For the study, researchers used GPS to track 46 wandering albatrosses during foraging trips the birds made between February to September 2004. The birds were breeding on Bird Island, which is off the northwest tip of South Georgia in the Southern Atlantic Ocean. Wandering albatrosses lack sufficient musculature to sustain continuous flapping flight for long periods of time; however they have a shoulder lock that mechanically holds their wings outstretched so that little energy is expended while soaring, according to the paper.
Since the earliest days of scientific inquiry, the way that many birds are able soar—that is, fly without flapping their wings—has fascinated and perplexed observers, said paper co-author Ewan D. Wakefield , affiliate researcher at the University of Glasgow and postdoctoral research associate at the University of Durham, UK. Wandering albatrosses are particularly remarkable for their ability to soar over the surface of the sea for long periods, covering vast distances, Wakefield said. He added that the physical principles explaining dynamic soaring flight were established over a century ago: Basically, albatrosses swoop up and down between layers of fast and slow moving air near the surface of the sea, gaining airspeed each time they do so.
“However, as our study shows, real-world albatross flight differs considerably from the predictions of simple physical models,” Wakefield said. “On the one hand, our GPS-tracking data show that they can and do fly in lighter winds than dynamic soaring models say should be possible. We suspect that this is because they can also fly by surfing updrafts created by the large waves that constantly surge around their Southern Ocean home. On the other hand, the upper limit of albatrosses' airspeed that we measured is much slower than physics predicts. We think that this is because albatrosses need to keep the forces on their wings within tolerable limits. After all, they're made from bone and muscle, not aluminum and titanium. Our study therefore points to ways in which theoretical models need to be refined to capture more faithfully the amazing complexity and beauty of albatross flight.”
Richardson recalled being entranced by wandering albatrosses ever since he observed them during a 1997 oceanographic cruise in the South Atlantic Ocean. “We were steaming upwind at 15 knots, pounding into waves, and these albatrosses caught up to us from astern and were cruising around and having a grand old time,” Richardson said. “I sat there for hours watching these birds in amazement, and wondering how they could fly like that. Now we are learning more about how they do it.”
Funding for this research was provided by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution emeritus fund and the UK Natural Environment Research Council.
Authors: Philip L. Richardson 1 and Ewan D. Wakefield 2
Affiliations:
1 Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, USA
2 Institute of Biodiversity, Animal Health and Comparative Medicine, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK
About Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Massachusetts, dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate an understanding of the ocean’s role in the changing global environment. WHOI’s pioneering discoveries stem from an ideal combination of science and engineering—one that has made it one of the most trusted and technically advanced leaders in basic and applied ocean research and exploration anywhere. WHOI is known for its multidisciplinary approach, superior ship operations, and unparalleled deep-sea robotics capabilities. We play a leading role in ocean observation and operate the most extensive suite of data-gathering platforms in the world. Top scientists, engineers, and students collaborate on more than 800 concurrent projects worldwide—both above and below the waves—pushing the boundaries of knowledge and possibility. For more information, please visit www.whoi.edu
Key takeaways:
- By analyzing GPS tracks of wandering albatrosses, researchers have found that the birds’ airspeed increases with wind speed up to a maximum of 20 meters per second (45 miles per hour).
- Researchers developed a model of dynamic soaring, which predicts that the birds could fly much faster than 20 meters per second (m/s). However, researchers hypothesize that the birds limit their maximum across-wind airspeeds to about 20 m/s in higher wind speeds (and greater wind turbulence), probably to keep the aerodynamic force on their wings during dynamic soaring well below the mechanically-tolerable limits of wing strength.
- The paper concludes that the birds limit airspeed by adjusting the turns in their trajectories to be around 60° and that in low winds the birds exploit updrafts over waves to supplement dynamic soaring.
- Although a theoretical model predicted that the minimum wind speed necessary to support dynamic soaring is greater than 3 meters per second (m/s), GPS-tracked albatrosses were observed in flight at wind speeds as low as 2 m/s. Researchers hypothesize at these very low wind speeds, wandering albatrosses fly by obtaining additional energy from updrafts over water waves.
- The study points to ways in which theoretical models need to be refined to capture more faithfully the amazing complexity and beauty of albatross flight.

Fact Animal
Facts About Animals
Wandering Albatross Facts
Wandering albatross profile.
In 1961, Dion and the Del Satins had a song from the perspective of an albatross. It wasn’t accurate on many counts, but it did get one thing right: they get around.
The Diomedea exulans, more commonly known as the wandering albatross is perhaps the most accomplished wanderer of any animal, with routine voyages of hundreds of kilometres per day on record-breaking wings.
They are a large seabird with a circumpolar range in the Southern Ocean, and sometimes known as snowy albatross, white-winged albatross or goonie.

Wandering Albatross Facts Overview
The wandering albatross breeds on islands in the South Atlantic Ocean, such as South Georgia Island, Crozet Islands, Prince Edward Island and others.
They spend most of their life in flight , and land only to breed and feed.
These are phenomenal birds, capable of surviving some of the harshest weather conditions even at the most vulnerable stages of their development.
They are slow to reproduce, spending extra time to develop into one of the biggest and most specialised animals in the air.
Sadly, this is what makes them vulnerable to population declines, and longline fishing vessels are responsible for many adult deaths.
Interesting Wandering Albatross Facts
1. they can travel 120k km (75k) miles in a year.
The Wandering albatross might be the most wide-ranging of all foraging sea birds, and maybe of all animals. They’ve been tracked over 15,000 km in a single foraging trip, capable of speeds of up to 80 kmph and distances of over 900 km per day. 1

2. They’re monogamous (mostly)
This goes against the entire theme of the Del Satins song and is probably why it’s no longer used as a learning aid in the zoological curriculum.
Contrary to the promiscuous subject of the ‘60s hit, the Wandering Albatrosses mate for life and are (on average) monogamous.
When breeding, they take on incubation shifts, and it’s during these periods when the wanderer goes out on their epic voyages to return with food for their family.
Still, there’s an element of personal preference when it comes to breeding.
Most females will take a year or two off after the long and arduous task of reproduction. During this time the parents will go their separate ways, only to reunite when the time is right.
In these periods, some females will take on a temporary mate, so they can squeeze out one more chick before reuniting with their permanent nesting partner. 2
3. Wandering albatross are active in moonlight
When on these journeys, the albatross is almost constantly active. During the day they spend the entire time in the air, and while they don’t cover much distance at night, they were still recorded almost constantly moving – never stopping for more than 1.6h in the dark.
They appear to travel more on moonlit nights than on darker ones.
All of this data comes from satellite trackers attached to some birds, which are always going to skew the results.
Flying birds are optimised for weight, and trackers add to this weight, so there’s necessarily a negative effect on the individual’s fitness when lumbering them with a tracker.
Still, these subjects were able to outlast the trackers’ batteries on many occasions, and it’s safe to assume they’re capable of even more than we can realistically measure!

4. They have the largest wingspan of any bird in the world
One advantage that an albatross has over, say, a pigeon, when it comes to carrying a researcher’s hardware, is that it doesn’t need to flap much.
The albatross is the bird with the longest wingspan of any flying animal – growing up to 3.2 m (10.5 ft), and these wings are meticulously adapted for soaring.
The Guiness Book of Records claims the largest wingspan of any living species of bird was a wandering albatross with a wingspan of 3.63m (11 ft 11) caught in 1965 by scientists on the Antarctic research ship USNS Eltanin in the Tasman Sea.
Research has suggested that these wings function best against slight headwinds, and act like the sails of a boat, allowing the bird to cover more ground by “tacking”, like a sailboat: zig-zagging across the angle of the wind to make forward progress into it. 3
5. Fat chicks
As mentioned, these voyages are usually a result of foraging trips for their chicks.
The environment for a growing albatross is one of the least conducive for life. Freezing winter storms and exposed ledges make for a hilly upbringing for the baby birds.
Fed on a healthy diet of regurgitated squid, these albatross chicks grow to enormous sizes. On nesting sites, it’s not uncommon to find a fluffy baby albatross weighing up to 10kg.
These chicks are heavier than their parents, and they need the extra mass to protect them from the Winter season while they grow into fledglings. They’re also such big birds that they take longer than a season to reach maturity.
It takes around ten months of feeding, back and forth from the ocean every few days, for the parents to grow a healthy adult offspring.
6. Being a parent takes practice
When inexperienced parents were compared with those who’d brought up chicks before, it was found that their chicks are a little slower to fatten up, at least in the first few months.
Parents would feed less regularly, but with much larger amounts, and it seems to take a while to get the routine down.
By the end of the breeding season, these differences disappeared and the parents became fully qualified.
7. 25% of chicks die when they leave the colony
The huge chicks have one of the longest rearing periods of any bird, and this is after an 11-month incubation period! And if they survive all this, they still have a long way to go.
There’s a period of 3 to 7 years during which the young chick will leave the colony alone and spend the entire time at sea.
During the first two months of this learning phase, 25% of chicks die. This is a critical time for the young birds, but if they survive, they’ll return to the colony and find a mate. 4

8. They’re good sniffers
These birds feed primarily on smelly things like squid, and they’ve developed a very keen sense of smell to find them from downwind.
Wandering Albatrosses have one of the largest olfactory bulbs of any bird and they’re honed to fishy aromas.
They combine this sense with strong vision to identify productive areas of the ocean for hunting and foraging. 5
9. They are part of a ‘species complex’
When multiple species are so similar in appearance and other features, it makes their boundaries unclear and this group is known as a species complex.
The wandering albatross was long considered the same species as the Tristan albatross and the Antipodean albatross. Along with the Amsterdam albatross, they form a species complex.
Taxonomy of animals in general is tricky, and some researchers still describe them as the same species.

10. The wandering albatross is vulnerable
The ICUN has classified the wandering albatross as vulnerable, and the last study of their population size in 2007 indicated there were an estimated 25,000 birds.
The biggest threat to their survival is fishing, in particular longline fishing. This is where a long mainline is used with baited hooks, and they are prone to accidental catching of birds, as well as dolphins, sharks, turtles and other sea creatures. Pollution, mainly from plastics and fishing hooks is also a problem for birds such as the wandering albatross.
Convervation efforts are underway to reduce bycatch of albatrosses and some breeding islands are now classified as nature reserves.
Wandering Albatross Fact-File Summary
Scientific classification, fact sources & references.
- Jouventin, P., Weimerskirch, H (1990), “ Satellite tracking of Wandering albatrosses “, Nature.
- GrrlScientist (2022), “ Divorce Is More Common In Albatross Couples With Shy Males, Study Finds “, Forbes.
- Richardson, P. L., Wakefield, E. D., & Phillips, R. A. (2018), “ Flight speed and performance of the wandering albatross with respect to wind “, Movement Ecology.
- Weimerskirch, H., Cherel, Y., Delord, K., Jaeger, A., Patrick, S. C., & Riotte-Lambert, L. (2014), “ Lifetime foraging patterns of the wandering albatross: Life on the move! “, Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology.
- Nevitt, G. A., Losekoot, M., & Weimerskirch, H. (2008), “ Evidence for olfactory search in wandering albatross, Diomedea exulans “, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
January 12, 2024
How Does the World’s Largest Seabird Know Where to Fly?
Wandering albatrosses navigate thousands of miles using “the voice of the sea.”
By Joseph Polidoro
A pair of wandering albatrosses.
Getty Images/Imazins

Joseph Polidoro: Imagine for a moment that you’re a very hungry bird soaring over 30-foot ocean swells in high winds, with no land for thousands of miles.
How do you know where you’re going?
If you’re a wandering albatross, you listen .
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
[CLIP: Music]
According to a new finding in October’s Proceedings of the National Association of Sciences USA, this seabird navigates using sounds below our thresholds for hearing .
For Science, Quickly, I’m Joseph Polidoro.
The wandering albatross thrives in the circumpolar band of ocean north of Antarctica—a windswept region that the world’s best sailors say has the most inhospitable seas on the planet.
On the Southern Ocean’s islands where they nest and brood, one wandering albatross parent tends the nest while its partner takes to the sea, traveling as much as 10,000 kilometers as it forages for scattered prey. The bird must eat enough to fuel its turn on the nest, which can be a long time ...
Samantha Patrick: Birds might go for, perhaps, a minimum of four or five days, up to 30 days.
Polidoro: Samantha Patrick is a marine ecologist at the University of Liverpool in England and a co-author of the study.
Wandering albatrosses actually gain weight on these long trips because they’re extremely efficient flyers.
Sophie de Grissac: It almost never beats its wings. It’s quite fascinating to see them flying in the winds. When they’re flying, their heartbeat is the same as when they’re resting.
Polidoro: That’s Sophie de Grissac , an ornithologist and a researcher at the French National Museum of Natural History in Paris, who wasn’t involved in the study.
With their long wingspan—the longest of any bird, maxing out at nearly 12 feet—wandering albatrosses use wind, air pressure gradients, and gravity above the swells and waves to soar for thousands of miles, reaching top speeds of 45 miles an hour .
Basically, wandering albatrosses don’t fly. They soar.
De Grissac: The more distance you cover, the more you may find food.
Polidoro: The wandering albatross’s keen senses of sight and smell help it locate prey. But these senses are good for about 100 kilometers—a distance the bird can travel in as little as an hour and a half. So how does the albatross know where to soar toward?
Patrick: There does seem to be this large gap in information that they’re able to access.
Polidoro: A clue came in a chance encounter on the way to the Crozet Islands, part of the French Southern and Antarctic Territories, where Patrick was headed to study albatrosses.
Patrick: On the same vessel were some researchers from the [United Nations]. They were going to work with the hydrophone station that’s used to monitor nuclear tests. It also gathers infrasound data. And we came up with the question of whether seabirds could use infrasound. And it was clear that no one had really thought about this before, and that’s where the idea for the project came from.
Polidoro: Infrasound is any sound below 20 hertz, where human hearing starts to drop off. At the very low end of the infrasound spectrum are microbaroms—very low-frequency sounds between 0.1 and 0.6 Hz that are detectable across thousands of miles.
Natasha Gillies: Microbaroms are generated by the collision of ocean waves.
Polidoro: Natasha Gillies is a seabird ecologist at the University of Liverpool and a co-author of the study.
The constant hum of microbarom infrasound is called “the voice of the sea.” It’s present everywhere, all the time. But it’s unevenly distributed.
Gillies: Where you have more energy in the ocean system because you have wavier areas or windy areas, then you get louder microbarom regions.
Polidoro: Ideal soaring conditions for wandering albatrosses.
Patrick: But it also gives them information about standing ocean waves, and this is often caused by things like storms. So it would enable birds to try and gauge where storms are, potentially. So this might be be cause they want to move toward windier areas that could be optimal, or they might want to move away from windy areas if they’re too strong, and they want to try and avoid storms.
Polidoro: Directly testing this apex predator’s hearing is not an option. So Natasha and her colleagues arrived at a creative experimental solution: Get a large enough sample of wandering albatross flight paths. Then, using wind and infrasound data, create a sound map of the total flight area—a map of microbaroms across space and time. Send out another set of albatrosses equipped with sensors to field check the sound map. Finally, overlay the birds’ flight paths on the sound map.
Gillies: So essentially what we can get is: if you put an albatross at point X in space and on this day in time, what infrasound would it be likely to hear and experience?
Patrick: We didn’t have an expectation at the beginning that they would move toward louder or quieter areas.
Polidoro: What the team found is that wandering albatrosses aren’t exactly wandering. Instead they seem to use microbaroms to head toward ideal wind conditions.
Ventura: Looking at the soundscape and how the birds move, you know, almost following this wave of sound, I found that beautiful.
My name is Francesco Ventura , and I’m a postdoc at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution.
Polidoro: He wasn’t involved in the study either.
Ventura: It’s another world–that’s the thing. It’s something that we cannot fully understand, I think; we are humans and we just cannot even imagine how that would work for us. But it seems to be working fine for them because they have been doing it for a long time.
They seem to be [reading] what’s going on and kind of orienting toward that. You know that is something that is…it’s SciFi.
Gillies: We know that there is something about infrasound that they want to move toward, that they like, that is beneficial to them in some way.
Ventura: It was kind of a badly needed paper at this point because it sheds some new light into a fundamental question that is at the core of a lot of marine megafauna research in general but also at the core of seabird research, which is: “How do they manage to find food in such a vast area?”
Polidoro: This reliance on infrasound may actually extend to other species, too.
Gillies: Most seabirds are highly dependent on wind for movement. It seems to be involved in animal behavior in a lot of contexts, in a lot of different species.
Polidoro: They include whales, elephants, pigeons and peacocks.
Gillies: So I would be very surprised if this was in any way unique to wandering albatrosses.
De Grissac: So albatrosses have had a very long time to evolve ways of feeling the environment—lots of ways they can perceive what’s around them. And I think because they really need this condition, this stormy conditions, these winds, it makes perfect sense that it would have evolved more than one way of finding them.
Gillies: I think it’s a really nice reminder of the different sources of information animals might be using—especially in this sort of environment that is so featureless—and how animals can still extract so much information and context out of that despite there seemingly not being much there.
De Grissac: Evolution in animals is almost always very surprising. When you study the evolution of the animal closely, you find remarkable things, remarkable inventions.
Polidoro: Science, Quickly is produced by Tulika Bose and Jeff DelViscio. Our music is composed by Dominic Smith.
Subscribe to Science, Quickly wherever you get your podcasts. If you like the show, give us a rating or review.
Albatross: Lifetime at Sea
When hearing the word albatross , some might think of a really good round of golf (three under par). Like scoring an albatross in golf, sighting a long-lived master of flight in the Albatross family is a special treat. Chances are you haven’t seen one in person, but to put a name to this special type of seabird opens the door to their world.
Masters of Efficient Flight
There are 22 species of albatross that share the gift of efficient long-distance gliding flight. They are famously recognized by their lengthy wingspans with the Wandering Albatross holding the record at nearly 12 feet. These remarkable wingspans are vital for a lifetime at sea. With the help of air currents and temperature changes, these wings are able to provide enormous amounts of lift; albatross can spend hours in flight without rest or a single flap. Their flying abilities allow albatross to journey thousands of miles across open oceans.

Many people view their elders and put some thought into what those eyes have seen over a lifetime; what experiences that person has had, or wisdom and knowledge they’ve picked up through the years. These same thoughts could be applied when looking into the eyes of an albatross. Albatross can live decades and spend most of their long lives at sea. When an albatross encounters a fishing vessel or is counted on the breeding grounds, these birds may be decades older than the people studying these magnificent gliders. It could be safe to assume that an adult albatross knows their way around the seas better than the career fisherman or woman they are following.
Throughout history, humans have shared the seas with these seabirds. Many sailors recognize that albatross will follow their vessels, looking for an easy meal. Interactions, intentional or accidental, have resulted in the near-extinction of some species of albatross. Conservation efforts have been put in place by multi-nation partnerships, which have contributed to success in rising numbers of albatross seen in the Pacific Ocean.
Albatrosses in Alaska
Alaska is within the range of Short-tailed, Laysan and Black-footed Albatross which are commonly seen at-sea. These birds take to land to breed on ocean islands, including the world’s largest albatross colony on Midway Atoll National Wildlife Refuge .
Short-tailed Albatrosses
This endangered species breeds primarily on two remote islands in the western Pacific with the majority (~85%) breeding on Torishima, Japan (an active volcano in the Izu Island Group, northwest of Taiwan). From 2008 to 2012 the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and Japanese partners at the Yamashina Institute for Ornithology worked together to establish a third breeding colony by translocating chicks from Torishima to a historic breeding location on the island of Mukojima. Recently, short-tailed albatrosses have also successfully bred on Midway Atoll.
Short-tailed Albatrosses generally head toward their feeding grounds around April and May, but have been known to make the long journey into Alaskan waters just to feed and return to their nest. They have been seen feeding along shelf breaks in the Bering Sea and Gulf of Alaska, along the Aleutian Islands, and southeast Alaska. They also occur along the Pacific coasts of Canada and the United States including waters along Washington, Oregon, and California.
Short-tailed Albatross follow fishing vessels and are sometimes hooked or entangled in longline fishing gear and drowned. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has been working with the commercial fishing industry, Washington Sea Grant, and National Marine Fisheries Service to minimize take of this endangered seabird. Through this collaborative conservation effort, a type of seabird avoidance technology called “streamerlines” was developed to reduce the bycatch of albatrosses.
Streamerlines create a visual barrier that keeps seabirds away from the baited hooks. In Alaska, streamerlines deployed on fishing vessels has led to a major reduction in the bycatch of albatrosses. Fishermen who have used streamerlines to ward off seabirds say there is also a financial benefit: the streamer lines keep seabirds from swiping their bait, saving them money in the long run.
From near extinction at the turn of the 20th century, to being listed as endangered throughout its range in 2000, the population of short-tailed albatross continues to grow with a current estimate of 7,365 individuals and a population growth rate of 8.9%. This is something to celebrate.
Black-footed Albatross
Unlike the Short-Tailed Albatross, the Black-footed Albatross is not currently listed as threatened or endangered under the Endangered Species Act (ESA). Black-Footed Albatross are only found in the Pacific Ocean with breeding populations located on the Hawaiian and Japanese islands. Breeding occurs from late fall to mid-summer and involves a colorful display of head bobs, wing flaps, and foot stomps. If you have not witnessed a Black-Footed Albatross mating dance, that should be your next internet search as it is a sight to see. Black-footed Albatross, like other albatross species, are thought to mate for life but will find a new mate if their partner disappears or passes away.
After breeding these seabirds can be seen in the North Pacific where they feed on fish, squid, and crustaceans. Like other albatross species, these birds can also be seen tailing ships for easy meals and have sometimes become victims to accidental entanglement into fishing equipment at sea. They too have benefited from Short-tailed Albatross conservation efforts via reduced accidental bycatch.

Laysan Albatross
One of the easier identifiable albatross seen in the seas surrounding Alaska is the Layson Albatross. These seabirds are generally smaller in size when compared to other albatross sharing its range, but is most noticeably different by its white belly and head that is often referred to as “gull-like”. Add in a gray-brown wings with white undersides and a dark tail and you’ve got yourself a Laysan Albatross.

Laysan Albatross are more commonly seen out at sea away from North American shores. 97.7% of the population call the northwestern Hawaiian Islands home during the breeding season (late fall to mid-summer) before moving north through the Pacific eventually making their way to Alaskan fishing regions. For those of you traveling through the southwest, don’t be too surprised to see one of these seabirds overhead, they’ve been known to wander inland during their migration north.
These seabird’s have a diet consisting of squid, fish, crustaceans and flying fish eggs. They primarily feed at night. In regards to fishing bycatch, this could be beneficial or negative depending on fishing operation times and the effectiveness and use of mitigating equipment such as streamers at night. Like other albatross, Laysan Albatross sometimes fall victim to fishing equipment such as baited lines and driftnets. They have also benefited from conservation efforts to reduce seabird bycatch during fishing operations. Fishing bycatch, however, is not the only issue that Laysans and other sea life must face, plastics and debris scattered through the world’s oceans are also part of this seabird’s diet, which in many cases can prove to be fatal.
A note on plastic pollution: Be Part of the Solution
Like many birds, albatross can fall victim to plastic pollution that makes its way to sea. Because they feed along the surface on squid, krill, fish eggs and other items, albatrosses often accidentally swallow floating plastic. This becomes a problem when their stomach becomes impacted and full of plastic resulting in lack of nutrition from natural prey. On the breeding grounds, baby albatrosses suffer from a diet of this plastic trash brought in by their parents from the ocean. Parents feed their chicks by regurgitating what they’ve found out at sea. It’s estimated that adult albatrosses unwittingly bring back thousands of pounds of marine debris back to places like Midway atoll every year. Dead chicks that have starved due to plastic ingestion can be found on the breeding grounds and are testament to this global problem.One way you can make a small difference is picking up plastic trash before it makes its way into rivers and eventually to sea.

You can help albatross and all seabirds by recycling as much or your plastic as possible, saying ‘no’ to single use plastic, using a re-usable water bottle, bringing re-usable bags to the grocery store. We can all do our part to help make the oceans safe for all birds and ensure that the graceful flight of the albatross can be witnessed by generations to come.
In Alaska we are shared stewards of world renowned natural resources and our nation’s last true wild places. Our hope is that each generation has the opportunity to live with, live from, discover and enjoy the wildness of this awe-inspiring land and the people who love and depend on it. Compiled by Kristopher Pacheco, Alaska Digital Media Assistant for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, with Katrina Liebich and staff from Migratory Birds Management and Ecological Services. For this article and others, follow us on Medium .
Recreational Activities
Related stories.

Latest Stories

The Black-footed Albatross, Layson Albatross and the Short-tailed Albatross are some of the albatrosses you would expect to see along the Pacific coast of North America. The albatrosses are the largest pelagic seabirds in the world, with some having wingspans over 10', as is the case with the Wandering Albatross. They have the ability to stay aloft over long periods of time and travel great distances.

Return to Seabirds
Return to Birds of North America Home Page
References to Other Bird Sites:
Avibase - the world bird database This site provides the user with a complete list of bird species, broken down per country, or in the example of the US or Canada, per state and province. Here, bird species names are available in other languages, a great asset to be used as a translation of foreign bird names.
ABA - American Birding Association This site represents an organization that maintains official records of all birds species that have been proven to have been seen inside the perimeters of the North American Continent and the surrounding bodies of water. Regular revised versions are posted to keep the bird list current at all times. This is the list used by all serious birders over their lifetime. You may be aware of the movie called the "Big Year". It was with this list that all the competing birders used in an attempt to set a new record as to how many bird species that could be seen by an individual birder in one calendar year.
I hope you will take advantage of these suggested websites. I have used each of them, in one way or another, throughout the years in my quest to better identify and understand our fine feathered friends.
Classic Collection of North American Birds CCNAB
- Birds of North America
North American Birding Information
- Bird Songs and Calls
- Bird Range Maps
Different Types Of Bird Groups
- Black Birds
- Brown Birds
- Green Birds
- Orange Birds
- Yellow Birds
- Birds Of Prey
- Exotic Birds
- Field & Stream
- Forest Birds
- Hummingbirds
- Marsh Birds
- Wading Birds
Birds by Locations
- Birds of Canada
- Birds of USA
- Bird Terminology
Concerned Bird Groups
- Extinct Birds
- Endangered Birds
- Threatened Birds
Bird Topics
- Attracting Birds
- Birdfeeders
- Birder's Code of Ethics
Albatrosses are big, majestic birds that can be found soaring above most of the world’s oceans.
These frequent fliers are known for spending months in the air without touching down, as well as having some unique mating arrangements. However, thanks to harmful fishing techniques and predation by invasive species, albatrosses around the world are either under threat or endangered.
There are 23 species of albatrosses, though arguably the most famous is the wandering albatross ( Diomedea exulans ), which is the largest flying bird in the world. This bird has a 11-foot (3.4 meter) wingspan, according to the Encyclopedia Britannica — even bigger than the famous California condor — and it uses those massive flappers to travel thousands of miles in a single journey.
Related: Your dumb party balloons are killing all the seabirds
A life in the air
But rather than flapping its wings, wandering albatrosses (and many other large albatrosses) travel such far distances by holding their extended wings in place so that the air rushing around the wings generates lift, similar to an airplane's wings. An airplane forces air over its wings with an engine, whereas albatross take advantage of the extremely windy latitudes in the southern oceans.
This latitude range is "called the 'roaring 40s' and 'furious 50s' for a reason," said Andrea Angel, the Albatross Task Force manager with Birdlife South Africa, a nonprofit organization dedicated to bird conservation. With near constant wind in their environment, albatrosses are able to "lock their elbow joints and literally just fix their wings [in place] and just glide," Angel said. The birds also use something called "dynamic soaring," which involves changing the angle of their wings relative to the wind, to maximize the lift generated — a similar technique could help unmanned research aircraft stay aloft for months, the Independent reported .
Related: A hot blob in the Pacific Ocean caused 1 million seabirds to die
An albatross can go a year or more without setting foot on land, Angel said, although the birds do touch down in water in order to feed on the squid and fish that make up their diet. In fact, it's the tiny alpine swift, not the albatross, that holds the record for non-stop distance flying, as reported in a 2013 study published in the journal Nature Communications .
As for sleep, Angel said that it's very likely that albatrosses sleep on the wing. A 2016 study published in Nature Communications described how a distant cousin of the albatross, the frigatebird, has many, seconds-long periods of sleep while flying, suggesting that sleeping in the air is definitely possible for other long-distance traveling seabirds. And, based on microchip-tracked movements of albatrosses, "they can [fly] for hours on end, and so it is theorized that they do sleep on the wing," Angel said. "It's an accepted fact [that] because of their movements, they have to sleep."

All albatrosses are very long-lived. The oldest wild bird in the world is a Laysan albatross ( Phoebastria immutabilis ) named Wisdom, who was tagged in 1956 at the Laysan albatross colony at Midway Atoll in the North Pacific Ocean when she was already a mature adult. That makes her at least 66 years old, but she's likely older, and she's still going strong — as of 2018 she was still raising chicks, NPR reported . According to Breck Tyler, a lecturer at the University of California, Santa Cruz and retired research scientist who studied the Laysan albatross colony on Midway Atoll for decades, there are other Laysan albatrosses just a few years younger than Wisdom, so "she's probably not an outlier."
Related: World's oldest wild breeding bird is expecting her 41st chick
Although they're seabirds, albatrosses are generally poor divers, with few exceptions. The wandering albatross can only dive about 2 to 3 feet (0.6 to 1 m) into the ocean, yet based on an analysis of its diet, scientists are pretty sure the wandering albatross eats squid that live deeper in the water, and are too big for an albatross to convincingly take down. It's possible the large bird just waits until a squid swims up to the surface, but a more convincing hypothesis is that the birds are actually eating squid bits that have been vomited up by whales, as described in a 1994 study published in the journal Antarctic Science .
After a meal of whale upchuck, an albatross might wash that down with some refreshing seawater. All seabirds have a gland above their eyes that functions like a miniature kidney, allowing them to drink salt water and excrete it through the tip of their beak, according to the Travis Audubon Society .
Albatrosses mate for life, but aren't exclusive
Because albatrosses mate for life, picking the right partner is a major decision. All species of albatross have some sort of complicated mating dance. For the Laysan albatross, the dance has 24 separate, complex steps, and it takes years for males to learn them all, Tyler said. And until the young males can master the choreography, they won't find a mate, he said. The females can afford to be picky, so if a male's sequence of honks, whistles, wiggles and neck thrusts doesn't impress her, she'll just move on to the next suitor.

But once a pair does form, the "divorce rate" of albatrosses is among the lowest in the animal kingdom, and because albatrosses are so long-lived, these pairs can persist for decades. For this reason, it's been posited that albatrosses are the "most romantic" bird. But that human characterization ignores some key facts about albatrosses, Tyler said.
An albatross mating pair only sees each other a few days a year, when they meet at their breeding grounds. After a few days of catching up, the pair takes turns incubating the egg; one stays behind while the other forages for food. After about 90 days, and when the chick is big enough, the mating pair go their separate ways for the rest of the year, according to the Cornell Lab’s All About Birds .
Related: Adorable photos of baby shorebirds
Although they mate for life, albatross pairs aren't exclusive. Casual sex between non-paired birds, and even forced copulation, is not uncommon, the New York Times reported in 2010 . A 2006 study published in the journal IBIS found that out of 75 wandering albatross couples, about eight had chicks that weren't fathered by their mother's primary mate.
And in many albatross species, female-female pairs are quite common (so far, male-male pairs haven't been reported), as Live Science has previously reported . Those females rely on "cheating" paired males or unpaired males to fertilize their eggs, and then the two females raise a clutch of two eggs together, without a male's involvement, the Times reported. Laysan albatross males and females look virtually identical, so unless you were specifically looking for evidence of same-sex pairs, you'd likely miss them, the Times said — and it's likely that many other species of birds, especially if there aren't enough males to go around, form similar pair bonds, Tyler said.

Threats to albatrosses
All but one species of albatross are either threatened, endangered or likely to become so, according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature . The biggest threats are invasive species at the birds' nesting grounds, and fishing vessels, which unintentionally snare birds when they're pursuing tuna and other commercial fish, Angel said.
Many of the world's albatrosses nest on islands that were once used as whaling vessel stopovers, Angel explained. With the human ships came cats and rats and mice. Gough Island in the South Atlantic, for example, is one of the most important seabird colonies, home to 24 different species of birds and multiple types of albatross. But the colony is gruesomely preyed upon by invasive mice that have evolved to be a much larger than normal size without the presence of predators, Hakai magazine reported .
Perhaps because they have no other predators that would attack them this way, Albatross have not evolved a way to defend themselves against a mouse attack, and so some of the adults sit motionless, letting "the mice nibble on their flesh while they steadfastly incubate their egg." On a number of important bird islands, conservationists are launching aggressive mouse-eradication programs to attempt to save the remaining birds, National Geographic reported .
Related: In photos: Mice brutally attack and devour albatross on Gough Island
At sea, albatrosses face a different threat: fishing vessels. Albatrosses are pretty good at detecting fishing vessels — so good that researchers think the birds, outfitted with tiny radar detectors, could be used to find boats operating illegally, The New York Times reported.
Large fishing vessels have onboard processing facilities where fish heads and tails and guts are removed and dumped back into the sea, which attracts all sorts of seabirds. "It is a seabird spectacle," Angel said. But as the trawler is dumping fish guts, it's simultaneously dropping the giant fishing net back into the ocean for the next catch. Seabirds, including albatrosses, get entangled in the net cables and dragged under water, then drown. And longline fishing boats, in which a 30-mile-long (48 kilometer) floating fishing line is set with hundreds of baited hooks, also attract seabirds which see the enticing meal from the surface, but get caught on the hooks and drown.
BirdLife South Africa has reduced albatross deaths in the local trawl fishery by 99% by simply encouraging boats to use bird-scaring streamers and shifting the time that the boats dump out the fish waste to after the net is set. But worldwide there's still much more work to be done when it comes to encouraging commercial fishers to practice more seabird-friendly fishing techniques.
Additional resources:
- Learn more about the relationship between birds and humans on Midway Atoll with this feature from American Bird Conservancy
- Watch a Laysan albatross perform its complicated (and comical) mating dance .
- View not-quite-live-cam shots of albatrosses on Bird Island near the Antarctic Circle on BirdLife International’s Facebook page .
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Rachel is a writer and editor based in Washington, D.C., who covers a range of topics for Live Science, from animals and global warming to technology and human behavior. Rachel also contributes to National Geographic News, Smithsonian Magazine and Scientific American, and she is currently a senior editor at Next City, a national urban affairs magazine. She has an English degree with a journalism concentration from Adelphi University in New York.
Mice on remote island that eat albatrosses alive sentenced to death by 'bombing,' scientists decree
Meet 'small diver': One of the tiniest penguins ever discovered
Astronomers discover new 'odd radio circle' near the center of our galaxy
Most Popular
- 2 World War I British warship that sank in a surprise U-boat attack 110 years ago discovered in North Sea
- 3 Thorny devil: The spike-covered lizard that sucks water from sand through its skin
- 4 Why is everything in space always moving?
- 5 See a jaguar shattering a crocodilian's skull and a 'David Bowie' spider in this sneak peak of the 2024 Wildlife Photographer of the Year

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Length. 107-135. cm inch. Wingspan. 2.5-3.5. m ft. Described as "The bird which made the breeze to blow" the wingspan of a Wandering albatross ( Diomedea exulans) is the longest of any bird. It lives up to its name when it takes fishing trips that last 10-20 days and can cover 10,000 km while using hardly more energy than when sitting on its nest.
Diomedea exulans. Vulnerable. Known for its majestic wingspan and far-ranging travels, the Wandering Albatross is a captivating presence in the Southern Ocean's expanse. As the bird with the widest wingspan globally, this remarkable creature glides effortlessly across vast oceanic distances, its brilliant white plumage and solitary habits ...
The snowy albatross (Diomedea exulans), also known as the white-winged albatross, wandering albatross, or goonie, is a large seabird from the family Diomedeidae; they have a circumpolar range in the Southern Ocean.It is the most recently described species of albatross and was long considered to be the same species as the Tristan albatross and the Antipodean albatross.
Behaviour Diomedea exulans is a biennial breeding species, although about 30% of successful and 35% of failed breeders (on average) defer breeding beyond the expected year. Adults return to colonies in November, and eggs are laid over a period of 5 weeks during December and January. Most chicks hatch in March and fledge in December.
The snowy albatross boasts a wingspan that can exceed 3.5 meters (11 feet), with an average span of around 3.1 meters (10 feet 2 inches). Body length ranges from 107 to 135 cm (3 feet 6 inches to 4 feet 5 inches), with females being slightly smaller than males. Adults typically weigh between 5.9 to 12.7 kg (13 to 28 lb).
Longline fishing is likely to be the main cause of decline in this species, causing reductions in adult survival and juvenile recruitment, and this threat is on-going. Population size: 20100 mature individuals. Population trend: decreasing. Extent of occurrence (breeding/resident): 128,000,000 km 2. Country endemic: no.
Merlin. Take Merlin with you in the field! Free, global bird ID and field guide app powered by your sightings and media. Learn about Wandering Albatross: explore photos, sounds, and observations collected by birders around the world.
Wandering albatross are found across the Southern Ocean. This includes Antarctic, sub-Antarctic and subtropical waters. Wandering albatross breed on sub-Antarctic and Antarctic islands between 46° and 56°S. Breeding islands include Iles Kerguelen, South Georgia and Macquarie Island. Young birds remain at sea for 5-10 years before returning ...
The adult Wandering Albatross appears entirely white from a distance. Close up, the fine black wavy lines on the breast, neck and upper back become visible. The bill can vary in colour, but is normally yellowish-pink. The white tail is occasionally tipped with black and the back of the wing changes from black to white with age.
Description. The Wandering Albatrosses has the largest wingspan of any living bird, with a wingspan between 251-350 cm (8.2-11.5 ft). The longest-winged examples verified have been about 3.7 m (12 ft), but probably apocryphal reports of as much as 5.3 m (17 ft) are known. As a result of its wingspan, it is capable of remaining in the air ...
Trend justification: At South Georgia, this species has declined by 1.8% per annum over the past 20 years, and there has been an acceleration in the rate of decrease to over 4% per annum since 1997 (Poncet et al. 2006). Overall, the South Georgian population has declined by 30% between 1984-2004 (Poncet et al. 2006), and by 18% between 2004 and ...
These remarkably efficient gliders, named after the Greek hero Diomedes, have the largest wingspan of any bird on the planet. Name: Wandering Albatross, Snowy Albatross, White-winged Albatross ( Diomedea exulans) Length: Up to 135 cm. Weight: 6 to 12kg. Location: All oceans except in the North Atlantic.
This species of albatross has white plumage, or feathers, with darker wings. Their wing feathers are black, and speckled with varying degrees of white. Young birds have brown feathers, which become white as they age. This bird's wingspan is quite large, and averages 10 feet across, though some individuals are larger.
Other articles where wandering albatross is discussed: albatross: The wandering albatross (D. exulans) has the largest wingspread among living birds—to more than 340 cm (11 feet). The adult is essentially like the royal albatross. It nests on islands near the Antarctic Circle and on some islands in the South Atlantic, and in the nonbreeding…
Wandering Albatross Range Map. ALL SPECIES MAPS ON THIS PAGE ARE THE PROPERTY OF SOUTH DAKOTA BIRDS AND BIRDING, and may not be used, copied, or distributed on any other website, blog, or other distribution media without written approval by the site owner. EMAIL IF YOU WISH TO USE THIS RANGE MAP IN ANY WAY. Map created with ArcGIS.
Wandering albatrosses' wingspan of up to 11 feet and is the largest known of any living bird, and yet wandering albatrosses fly while hardly flapping their wings. Instead, they depend on dynamic soaring in addition to updrafts and turbulence. ... (Map by Natalie Renier, ©Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution) For the study, researchers used ...
Interesting Wandering Albatross Facts 1. They can travel 120k km (75k) miles in a year. The Wandering albatross might be the most wide-ranging of all foraging sea birds, and maybe of all animals. They've been tracked over 15,000 km in a single foraging trip, capable of speeds of up to 80 kmph and distances of over 900 km per day. 1. 2.
Polidoro: The wandering albatross's keen senses of sight and smell help it locate prey. But these senses are good for about 100 kilometers—a distance the bird can travel in as little as an ...
There are 22 species of albatross that share the gift of efficient long-distance gliding flight. They are famously recognized by their lengthy wingspans with the Wandering Albatross holding the record at nearly 12 feet. These remarkable wingspans are vital for a lifetime at sea. With the help of air currents and temperature changes, these wings ...
Information, images and range maps on over 1,000 birds of North America, including sub-species, vagrants, introduced birds and possibilities ... Layson Albatross, Light-mantled Albatross, Short-tailed Albatross, Shy Albatross, Wandering Albatross and the Yellow-nosed Albatross. The Black-footed Albatross, Layson Albatross and the Short-tailed ...
Find local businesses, view maps and get driving directions in Google Maps.
Support our work. Albatrosses are under threat and need your help. They simply can't breed fast enough to replace the numbers of individuals killed by fisheries out at sea and by mice at their breeding colonies. You can help prevent these needless deaths by supporting our work today. Become a Friend of the Albatross.
John's sketches of the wandering albatross. I sent out a message that read 'albatross sp past Seven Heads 5.55 pm' and called Dennis. Given the distance and time this was not Dennis's bird, which had a dark underwing and he identified as an immature Black-browed Albatross.
There are 23 species of albatrosses, though arguably the most famous is the wandering albatross ( Diomedea exulans ), which is the largest flying bird in the world. This bird has a 11-foot (3.4 ...