- Culture - Sports
- Environment
- Destinations
- Media Center Mega Story Infographics Photos Videos Podcast
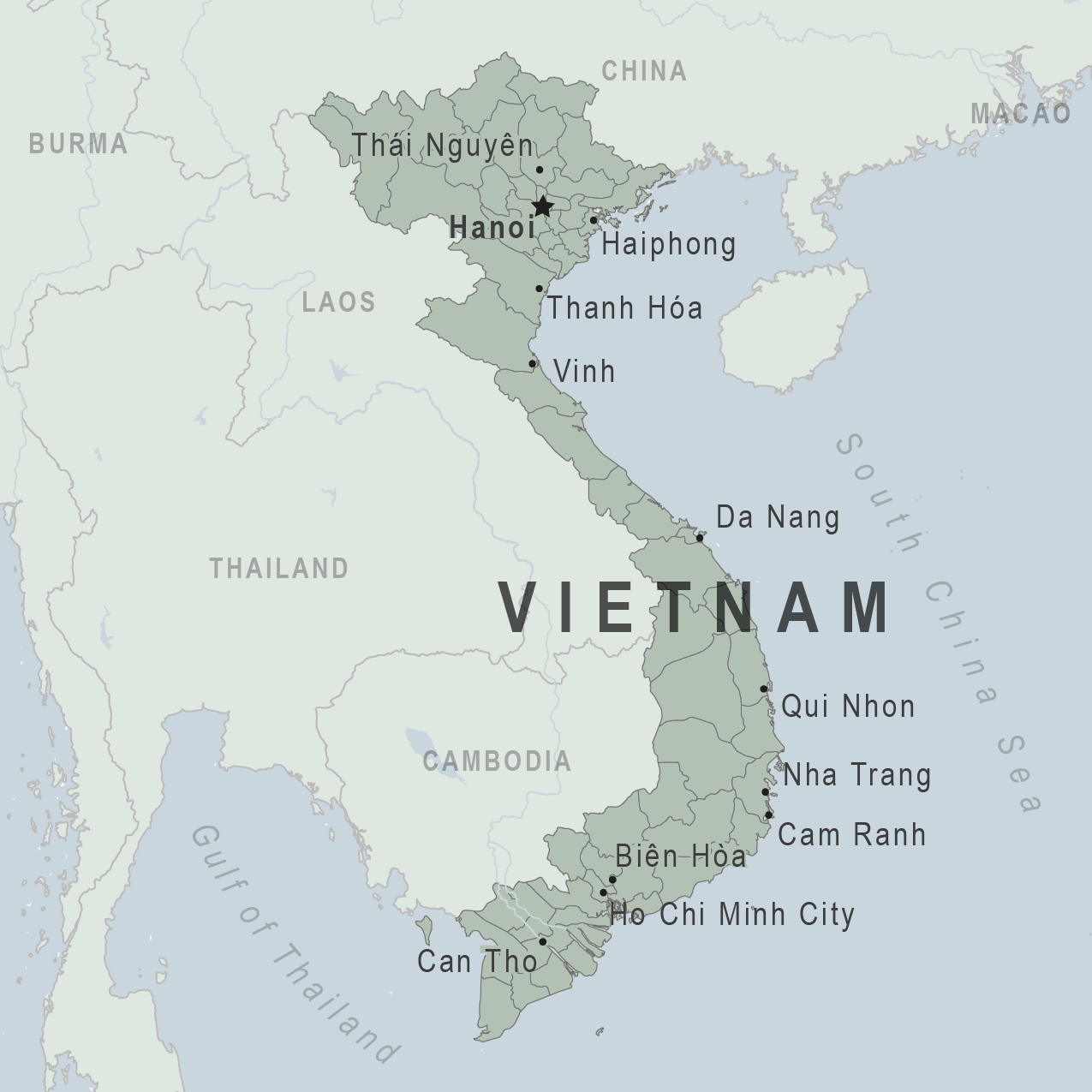
- Ho Chi Minh City

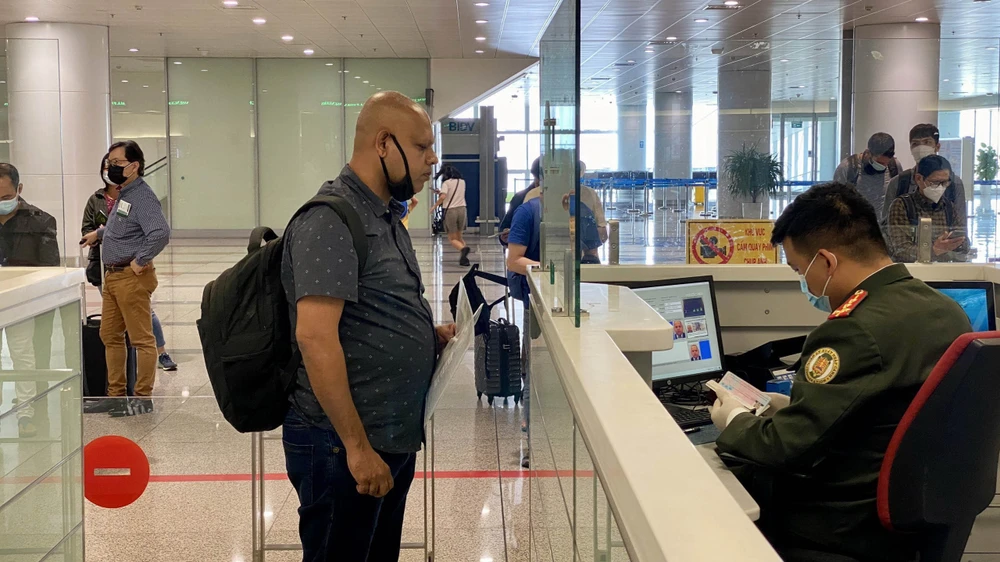
Detailed entry requirements for international visitors to Vietnam

Related News

Health ministry asked to quickly adjust entry regulations

Vietnam reinstates pre-pandemic entry and exit procedures

Spokeswoman gives more details on Vietnam’s plan to reopen to int’l visitors

Ministry issues detailed guidance on entry regulations

Vietnam now has easiest entry requirements in SEA: travel website

Con Dao during sea turtle breeding season

Vietnam gets various nominations at World Travel Awards 2024

Hanoi in seasonal transition

Dien Bien’s historical relic sites flooded with tourists

Sports tourism – potential awaits to be awakened

Foreign tourist arrivals up 68.3% in first 4 months

Lam Dong targets becoming “green paradise” by 2030

Hanoi works hard to lure more visitors

HCM City makes Agoda list of ideal Asian destinations for extended stays

Vietnam’s inbound tourism booms, surpassing pre-pandemic levels

Da Nang eyes top spot in Southeast Asia MICE tourism

Measures needed to promote Dien Bien's tourism potential

Vietnam among Koreans’ most favourite destinations in 2024 summer

Southwestern Tay Ninh province acts to lure visitors

Quang Ninh aims to become international tourism hub

Hanoi’s Tran Nhat Duat pedestrian bridge with contemporary art installations put into use

Ninh Thuan strengthening regional and national connections to develop tourism

Developing cultural tourism in Dien Bien province

Vietnam develops railway tourism associated with “awakening” heritage
Regulations for international visitors to Vietnam from 15th March 2022 - Viet Nam National Authority of Tourism
(TITC) – Vietnam officially reopens tourism from 15th March. On the same day, Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism promulgated the guidance including requirements for international visitors to Vietnam.

International tourists in Hoi An City, Quang Nam Provinve. Photo VOV
Accordingly, international visitors entering into Vietnam are not required for mandatory quarantine.
Requirements for international visitors to Vietnam
- Have a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result using RT-PCR/RT-LAMP method within 72 hours before entry into Vietnam or have a negative rapid test result within 24 hours before departure certified by the competent authority of the country where the test is performed.
- For international visitors entering via land, rail and sea border gates, undergo test for SARS-CoV-2 at border before entry in case of no proof of negative test result.
- Children under 2 years old are not required to be test for SARS-CoV-2.
- Have medical or travel insurance that covers COVID-19 treatment with a minimum liability of USD10,000.
- Complete a health declaration before entry. (at https://tokhaiyte.vn)
- Install and use PC-COVID application.
- Self-monitor health for 10 days after entry.
- Notify health authority if having signs and symptoms of COVID-19.
- Ensure conditions on exit and entry according to Vietnam's immigration laws and other relevant regulations when travelling in Vietnam.
Visa policy
Vietnam restored the policies on entry visas for foreigners as before the pandemic outbreak.
From 15th March 2022 to 14th March 2025, Vietnam applies visa exemption for citizens of 13 countries (Germany, French, Italy, Spain, UK and Northern Ireland, Russian, Japan, Republic of Korea, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland and Belarus) with maximum length of stay to 15 days.
In case of need support in acquiring the entry permit, please contact Vietnam Immigration as following:
Email: [email protected], and [email protected]
Tel: +84 (024) 3826114 / (024) 3826026 (Ha Noi) / (028) 3920 0365 (Ho Chi Minh City)
Website: https://xuatnhapcanh.gov.vn
Tourism Information Technology Center
Vietnam scraps quarantine, other travel restrictions for tourists as COVID cases climb

HANOI, Vietnam — Vietnam on Wednesday scrapped quarantine and other travel restrictions for foreign visitors in an effort to fully reopen its border after two years of pandemic-related closure, the government said.
Visitors entering the Southeast Asian country only need to show a negative COVID-19 test prior to arrival, according to the Health Ministry, which said the new measures were effective immediately.
Visitors must monitor their own health during the first 10 days of their stay and notify medical professionals in Vietnam if they experience any COVID-19-like symptoms .
Vietnam also reinstated visa exemptions and the issuance of visas on arrival similar to their pre-pandemic status.
'IT'S NOW SAFE TO OPEN UP': New Zealand moves up reopening for vaccinated US tourists to May
Learn more: Best travel insurance
QUARANTINE FREE: South Korea to allow fully vaccinated travelers to visit without quarantine period
Vietnam closed its border and stopped issuing tourist visas in March 2020 to contain the spread of the coronavirus. It partially reopened to international tourism last November for visitors traveling in strict bubbles.
In Hanoi’s Old Quarter, where streets were bustling before the pandemic, many shops have closed due to a lack of tourists. The few that remain open are struggling.
“It has been very hard. Business is so slow because there are no foreign tourists,” said Tuyet Lien, the owner of a shop selling silk and other souvenir products.
“I’m very excited the country is reopening completely. The tourists will come back soon and business will thrive again,” Lien added.
The tourism industry comprised nearly 10% of the country’s economy before the pandemic.
“We believe Vietnam is quickly changing to be better aligned with other global destinations that have reopened for tourism. We remain positive that inbound travel volume will gradually rise,” said Mathieu Le Besq, general manager of Accor hotels in Vung Tau, a beach resort city in southern Vietnam.
The reopening comes as Vietnam reports record numbers of new COVID-19 infections , with a daily average of nearly 200,000 cases over the past two weeks.
The CDC and State Department have advised Americans to " avoid travel to Vietnam " due it "very high" levels of COVID.
Despite the high infection rate, the Health Ministry says the majority of patients have mild symptoms from the omicron variant and do not require hospitalization.
Vietnam has administered over 200 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines, covering 80% of the country's 98 million people, according to the Health Ministry.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This information is for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK. It is based on the UK government’s understanding of the current rules for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Vietnam set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Vietnamese Embassy in the UK .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Vietnam.
Passport validity requirements
To enter Vietnam, your passport must have:
- an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive
- at least 2 blank pages
- no damage – British nationals have been denied entry and exit due to passport damage
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Make sure you get your passport stamped.
Check the visa expiry date written in your passport is correct before leaving border control. If it is wrong, you could be accused of overstaying.
Visa requirements
You can visit Vietnam without a visa for up to 45 days for tourism or business.
If you want to stay longer than 45 days, you can:
- book with a travel agent in Vietnam and ask them to apply for a visa pre-approval letter – your agent will tell you when to collect your visa from the embassy
- apply for other visa types from the Vietnamese Embassy in the UK
- apply for an e-visa that allows a 90-day stay and multiple entries
E-visas restrict you to the entry and exit points you select when you apply. If you get an e-visa while in Vietnam, you must exit the country and re-enter to start your e-visa.
The British Embassy will not assist with visa extensions.
Work or study
If you want to work or study, check which type of visa or work permit you need with the Vietnam Immigration Department .
Read about visas and work permits if you live in Vietnam .
If you overstay your visa or work illegally, the authorities can prevent you from leaving until you pay a fine. You could be deported and prevented from visiting Vietnam in the future.
Travelling through Vietnam
If you transfer from an international flight to a domestic flight in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City, you must go through immigration and enter Vietnam. You must do this even if your final destination is outside Vietnam.
Check with your airline before departing.
Vaccine requirements
For details about medical entry requirements and recommended vaccinations, see TravelHealthPro’s Vietnam guide
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of Vietnam . You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
If you’re taking prescription medication into Vietnam, carry it in your hand luggage with a copy of the prescription. If it has a total import value greater than 100 US dollars, you must declare it at customs. For information about restrictions on medication, see Health .
Taking money into or out of Vietnam
If you’re taking cash into or out of Vietnam, you must declare amounts over:
- 15 million Vietnamese dong
- 5,000 US dollars (or the same value in other currencies)
If you’re leaving the country with more than these amounts, declare the money at customs and show either:
- confirmation you’re carrying cash abroad, issued by an authorised credit institution
- written approval to carry cash, issued by the State Bank of Vietnam
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey .
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

- Guidance on COVID-19 prevention for travelers to Viet Nam
The Ministry of Health's most recent guidance on COVID-19 prevention and control allows travelers to enter Vietnam without being isolated, and exempts children under 2 years of age from arrival testing.
The Ministry of Health issued Dispatch No. 1265/BYT-DP on COVID-19 prevention and control measures for travelers to Viet Nam. The new Dispatch has been communicated to all other Ministries, government departments and agencies, and provincial People's Committees.
According to the Ministry of Health, although the daily number of confirmed COVID-19 cases remained high and new mutations of the Omicron variant were detected in the community, Vietnam maintained a high vaccination rate (in fact, Vietnam was among the countries having the highest vaccine rate) and the number of COVID-19 severe cases and deaths was still under control.
In accordance with the Government’s Resolution No. 128/NQ-CP on the temporal strategy of “Safe and flexible adaptation, and effective control of COVID-19 pandemic”, the Ministry of Health (Standing committee of the National task force for COVID-19 prevention and control) updated the requirements for international travels to Viet Nam.
Requirements for all travelers to enter Viet Nam
All travelers boarding a flight to Viet Nam are required to show a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result (except those aged 2 years and under) obtained within 72 hours before travel if using the RT-PCR/RT-LAMP test, or within 24 hours before travel if using the SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test. The test results must be approved by the authority in the country where the tests were performed.
Travelers arriving in Viet Nam via alternative modes of transportation (by land, sea and rail) are subject to the same requirements as air travelers
If travelers do not have a proof of negative SARS-CoV-2 test, they must take a SARS-CoV-2 test (RT-PCR/RT-LAMP test or SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test) within 24 hours of arrival in Viet Nam.
If the test results are negative, they are allowed to leave their places of accommodation and only need to adhere to applicable COVID prevention guidance.
If the test results are positive, they must immediately report the results to local health authorities for further guidance.
COVID testing is not required for children under the age of 2. All children aged 2 years and under are allowed to enter Viet Nam and participate in outside activities with their parents and relatives, regardless of whether they have received vaccination or are infected with COVID-19.
Health declaration prior to arrival in Viet Nam
All travelers must submit a health declaration before they enter Viet Nam and use the PC-COVID app throughout their stay.
If travelers develop COVID-19 symptoms (fever; cough; sore throat; congestion or runny nose; body aches, fatigue, chills; reduced or lost sense of taste; reduced or lost sense of smell; headache; diarrhea; shortness of breath; respiratory tract inflammation, etc.) at the point of entry, they must immediately contact health authorities for further guidance.
Post-arrival monitoring and implementation of COVID prevention measures
After arriving in Viet Nam, all travelers must monitor their health for the next 10 days. If any of the COVID-19 symptoms occur (fever; cough; sore throat; congestion or runny nose; body aches, tiredness, chills; decrease or loss of taste; decrease or loss of smell; headache; diarrhea; shortness of breath; respiratory tract inflammation, etc.), contact the nearest health institution for further guidance.
All travelers must comply with prevention measures: wear a mask frequently and wash their hands with an antiseptic solution.
Travelers who do not have negative test results prior to departure must limit their stopping or parking along the route from the point of entry to their place of accommodation, and maintain a safe distance from others.
The Ministry of Health emphasized that this Dispatch would supersede Dispatch No. 10688/BYT-MT by the Ministry of Health dated December 16, 2021 on COVID-19 prevention and control measures for travelers to Viet Nam; Dispatch No. 10943/BYT-MT by the Ministry of Health dated December 24, 2021 on medical guidance for travelers to Viet Nam on a short-term business trip of less than 14 days; Decision No. 2553/QĐ-BYT by the Ministry of Health dated June 18, 2020 on “Temporary guidance on medical inspection to prevent COVID-19 infection, required for vehicles and drivers at the points of entry by land, rail, sea and air”; Dispatch No. 429/BYT-MT dated January 26, 2022 on COVID-19 prevention and control measures for international flight crews.
The Ministry of Health (Standing committee of the National task force for COVID-19 prevention and control) requested that provincial People’s Committees, Ministries, and Agencies instruct relevant departments and units to implement the latest Dispatch as an approach to lower the risks of transmission.
For more details, please check here .
- You are here:
- Things to do
Create an account
Already have an account? Click here to sign in
By clicking submit, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use
Sign in with your social accounts
Sign in with your email
Forgot password? Click here to get it back
Don't have an account? Sign up here
Forgot Password
The entered email has subscribed for Vietnam Tourism monthly newsletter

Update May 10, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Vietnam Travel Advisory
Travel advisory july 24, 2023, vietnam - level 1: exercise normal precautions.
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed. Exercise normal precautions in Vietnam.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Vietnam.
If you decide to travel to Vietnam:
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook and Twitter .
- Review the Country Security Report for Vietnam.
- Visit the CDC page for the latest Travel Health Information related to your travel.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Travel Advisory Levels
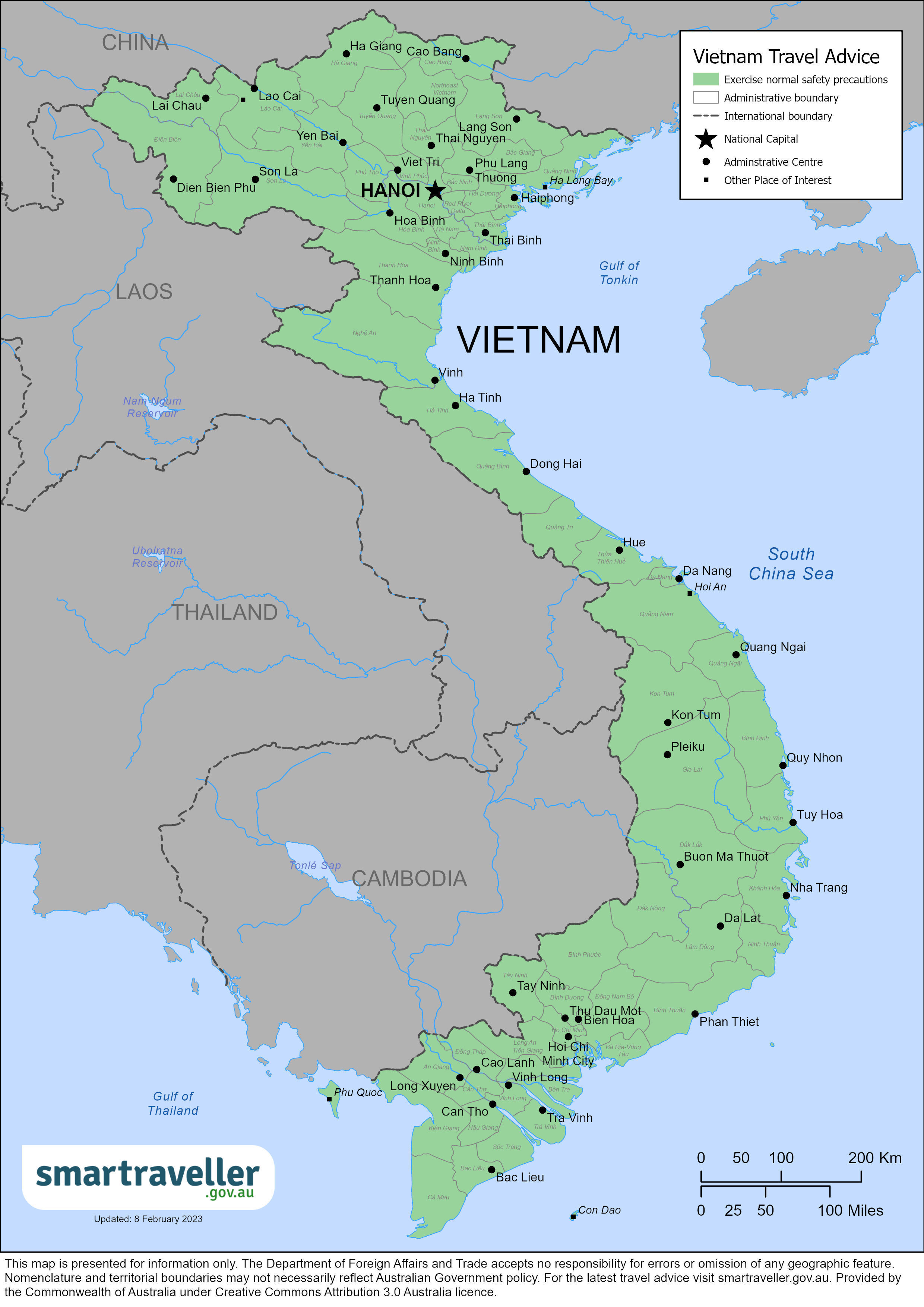
Assistance for u.s. citizens, vietnam map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Vietnam Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
There are no notices currently in effect for Vietnam.
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to Vietnam.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers of all ages traveling to Vietnam.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of Vietnam take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for Vietnam.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Rabid dogs are commonly found in Vietnam. However, if you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other mammal while in Vietnam, rabies treatment is often available.
Consider rabies vaccination before your trip if your activities mean you will be around dogs or wildlife.
Travelers more likely to encounter rabid animals include
- Campers, adventure travelers, or cave explorers (spelunkers)
- Veterinarians, animal handlers, field biologists, or laboratory workers handling animal specimens
- Visitors to rural areas
Since children are more likely to be bitten or scratched by a dog or other animals, consider rabies vaccination for children traveling to Vietnam.
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
- Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
Clinical Guidance
Schistosomiasis
- Wading, swimming, bathing, or washing in contaminated freshwater streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, or untreated pools.
Avoid bug bites
Chikungunya
- Mosquito bite
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in Vietnam, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene | Healthy Water
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in Vietnam. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in Vietnam—such as dengue, Zika, and filariasis—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in Vietnam include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Leptospirosis, a bacterial infection that can be spread in fresh water, is found in Vietnam. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call Vietnam’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Vietnam. If you are going to a risk area, fill your malaria prescription before you leave, and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.

Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of Vietnam may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in Vietnam, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in Vietnam, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for Vietnam .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in Vietnam, dial 115 for an ambulance, 114 for the fire department, and 113 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip.
Learn as much as you can about Vietnam before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Vietnam from the US Department of State
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Vietnam for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Conventus Law
More results...

New Rules For Tourist Visas In Vietnam Take Effect On 15 August 2023.
August 25, 2023 by Rohin Pujari
In Vietnam, since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has imposed stringent visa restrictions for foreign nationals. As a reminder, beginning March 22, 2020, Vietnam enacted a suspension of entry for all foreign nationals.
During COVID-19 pandemic, Vietnam undertook a comprehensive suspension of entry for all foreign nationals
During this period, visa issuance was halted, and entry was denied to all travelers, even those holding existing visas or visa exemptions. Exceptions were made for individuals engaged in diplomatic or official purposes , foreign guests attending important foreign affairs activities, experts, business managers, and high-skilled workers. While this decisive action safeguarded the nation, positioning it as one of the least impacted globally by the pandemic, it also had profound repercussions on the economy.
The pre-COVID-19 rules for tourists seeking to enter Vietnam were comparatively straightforward:
• The option to obtain a 3-month tourist visa (single or multi entry); • E-visa, accessible to citizens from 80 countries, offering a 30-day single-entry tourist visa; • Visa exemptions for citizens from 24 countries, allowing trips ranging from 14 to 90 days based on bilateral agreements.
On March 15, 2022, Vietnam officially reopened its borders to international visitors after a two-year closure.
Upon this reopening, alongside COVID-19-related regulations, the government aimed to restrict entry and ceased issuing 3-month tourist visas. Nonetheless, e-visas were reinstated for over 80 countries, and nationals from 13 countries, (Denmark, France, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Spain, and UK, etc…), regained the 15-day visa exemption, simplifying entry into Vietnam.
On June 24, 2023, the National Assembly approved new measures pertaining to tourist entry to Vietnam.
The e-visa program unfurls its welcome mat to citizens across the globe
Starting from August 15, 2023, foreign tourists will be subject to new regulations:
• Availability of 3-month multiple-entry visas from August 15, 2023. • The e-visa program now extends to citizens of all countries. • As of August 15, 2023, regular passport holders from the 13 aforementioned countries will enjoy an extended 45-day visa exemption, instead of the previous 15-day period.
Through these fresh regulations, the Vietnamese government aims to entice more international tourists, fostering the country’s development and aligning it with the sustainable tourism models observed in other Southeast Asian nations.
Hoteliers, restaurateurs, and all stakeholders in the tourism sector are anticipating a surge in activity, with the aspiration of rejuvenating an economy that has experienced minimal growth since the advent of COVID-19.
VCI LEGAL stands ready to offer insights into these matters, as it consistently supports tourism endeavors and collaborates with numerous hospitality and F&B entities.

For further information, please contact:
Kent Wong , Partner, VCI Legal
Register for your monthly Asia legal updates from Conventus Law
Error: Contact form not found.

Borrowing Offshore From Vietnam – Question & Answers.

Vietnam – Responsibilities Of Big 4 Auditing Companies And Auditors In The SCB Case.

Indonesia – Labor & Employment.

CONVENTUS LAW
CONVENTUS DOCS CONVENTUS PEOPLE
3/f, Chinachem Tower 34-37 Connaught Road Central, Central, Hong Kong
- Account Details
- Newsletters
- Group Subscription
Foreign tourism in Vietnam a shadow of pre-COVID boom
Visa policy, missing Chinese blamed for slow recovery; India offers hope
HANOI -- Tourism in Vietnam is struggling to recover from the COVID-19 slowdown, although the country has already lifted pandemic-related travel restrictions.
In the first 10 months of this year, 2.4 million foreign tourists visited Vietnam, around 15% of the number before who entered the country before the pandemic struck, according to Vietnam's General Statistics Office.
From Singapore to Japan, Asian airlines rush to ramp up routes
Thailand, singapore tourists jump in line as japan opens borders, airport projects in thailand, singapore resume after covid hiatus, thailand, vietnam, myanmar deepen russia ties to blunt economic woes, asean hotels roll out red carpet for 'revenge travel', latest on travel & leisure, japan sees less domestic golden week travelers amid inflation, tokyo disney aims to keep magic alive with new 'frozen,' 'peter pan' areas, tokyo disney unveils luxury hotel with rooms from $2,200 a night, sponsored content, about sponsored content this content was commissioned by nikkei's global business bureau..
Nikkei Asian Review, now known as Nikkei Asia, will be the voice of the Asian Century.
Celebrate our next chapter Free access for everyone - Sep. 30

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise normal safety precautions in Vietnam.
Vietnam (PDF 920.32 KB)
Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies, advice levels.
Exercise normal safety precautions in Vietnam.
- Road accidents are a major cause of injury. Be alert at all times on the roads.
- Petty theft, including bag slashing, is common in tourist areas and crowded places, especially during holiday times. Snatch-and-grab theft by thieves on motorcycles is also common. Hold bags and backpacks in front of you or on the opposite side to the traffic to make them harder to steal. Be aware of motorbikes approaching as you walk. Carry the minimum amount of valuables. Be prepared to surrender your valuables rather than risk being injured in a struggle.
- Aggravated theft, sexual assault and assault happen. Travellers have been assaulted after having their food or drinks spiked. Pay attention when your drinks are being mixed. Get urgent medical help if you suspect drink spiking.
- Personal or commercial disputes sometimes lead to threats of physical violence or death. Have a clear agreement on the expected level of service. Report any threats to police.
- Travellers have been robbed withdrawing money from ATMs. Credit and debit card fraud and card skimming happen across Vietnam. Taxi and gambling scams are also common. Only use ATMs in banks and shopping centres. Always keep your credit card in sight. Use metered or prearranged taxis, especially at airports. Report gambling scams to police.
- During the rainy season (June to November), floods, typhoons and severe weather can disrupt essential services. Follow the advice of local officials.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Air pollution levels can be high in Vietnam, particularly in large cities.
- Insect-borne diseases such as dengue, Japanese encephalitis, malaria and zika virus are a risk. If you’re pregnant, discuss your travel plans with your doctor. Use insect repellent. Get vaccinated before you travel. Consider taking anti-malarial medication.
- Rabies occurs in Vietnam, especially in the north. It’s fatal without treatment. If you’re bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help immediately.
- HIV/AIDS is a risk. Take precautions if you’re taking part in high-risk activities.
- Diphtheria is a risk. Ensure your vaccinations are up-to-date.
- Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is common. It mainly affects children and young adults. Foodborne, waterborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases include cholera, hepatitis and typhoid. Wash your hands well and often. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don’t use or carry illegal drugs, including marijuana. Penalties for drug offences include the death penalty and life imprisonment. Never carry parcels or luggage for others.
- Get professional legal advice before signing any contract. If you're in a business or civil dispute, officials could stop you leaving Vietnam until it’s resolved.
- It's illegal to gamble in a non-government licensed casino or possess pornography. Non-state sanctioned political or religious activity or material, or involvement with groups perceived by the Government of Vietnam to be associated with dissident groups, is also illegal.
- It’s illegal to export antiques without a permit. Get a permit from the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (Vietnamese) . It’s illegal to photograph border areas or military sites. Be careful when taking photos.
- Possessing or distributing images or objects linked to the former Republic of Vietnam, including commemorative or Vietnam War service-related items, is an offence that could attract harsh penalties.
- Vietnam recognises dual nationality in limited situations. If you're a dual national, travel on your Australian passport. You may need to do compulsory military service. Contact your nearest Vietnamese embassy or consulate for details.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You must have an appropriate visa before travelling to Vietnam. You can apply online for an eVisa for tourism or business purposes. If approved, the eVisa allows for a stay of up to 90 days and is valid for multiple entries. Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. You should contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for the latest details.
- You must check your details are correct when applying for a visa. The visa details must match exactly the information on your passport's biodata page, such as your full name and date of birth. Any errors or name omissions may result in you being refused entry. You may be charged a significant fee at check-in or on arrival to correct the visa error.
- If you're travelling with prescription medication, check the value and quantity restrictions on the import and export of prescription medication with the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam .
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can’t do to help you overseas.
- For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Hanoi , or the Australian Consulate-General in Ho Chi Minh City .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy’s social media accounts
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Petty crime.
Petty crime, street crime and harassment happen, especially in larger cities.
Bag slashing is common in tourist areas, at markets, on crowded trains and buses, and at supermarkets. It increases in the lead up to and during Vietnamese and Western holiday periods.
Thieves on motorcycles commit snatch-and-grab crimes against pedestrians. This happens often and sometimes results in injury.
Thieves steal valuables, such as jewellery, handbags, mobile phones and cameras.
To protect your belongings:
- take care crossing the street or walking along footpaths
- be aware of motorcycles approaching from behind as you walk on the footpath
- hold bags and backpacks in front of you or in ways that make them harder to snatch
- carry only what you need and leave other valuables in a secure location
- be prepared to surrender your valuables rather than risk being injured in a struggle
Violent crime
Aggravated theft, sexual assault and assault happen. Hot spots include:
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Sapa, especially on the train to and from Lao Cai
- Cat Ba Island, near Ha Long Bay
Reports of groping and other sexual assault are rising.
Drink spiking occurs. Foreigners have been robbed and sexually assaulted after having spiked food and drinks. This happens at late-night establishments in major cities.
To protect yourself from drink spiking:
- only drink alcohol at reputable places
- pay attention when your alcoholic drinks are being mixed
- stay with people you trust in bars and at nightclubs
If you think your drink or a friend's drink has been spiked, get urgent medical attention.
If you're a victim of a violent crime, especially sexual assault, get medical attention. There is a risk of contracting HIV/AIDS, hepatitis and other sexually transmitted diseases in Vietnam.
Although gun violence is uncommon in Vietnam, there have been isolated incidents in recent years.
Travellers have been robbed after withdrawing money from ATMs.
Break-ins to hotels and private homes are reported. This happens even while guests are in their rooms.
To protect yourself from robbery :
- only use ATMs in banks and shopping centres
- make sure your hotel room is locked at all times, including when you're inside
- pay close attention to your personal belongings, especially in crowded areas
- be alert on overnight trains and buses and on quiet stretches of road
Report thefts straight away to the local police and hotel management.
Personal or commercial arguments sometimes lead to threats of physical violence or death.
If you're threatened with violence, report it to local police.
To avoid commercial disputes, have a clear agreement on what the expected level of service is.
Many travellers have become victims of credit and debit card, taxi and gambling scams .
Credit and debit card skimming is where card data is taken for use in fraudulent transactions. This happens throughout Vietnam.
Some Australians have lost thousands of dollars after accepting invitations to private homes from friendly locals. Beware of rigged card games and other confidence tricks organised by criminals.
Gambling may break local laws, which also apply to travellers. See Laws .
To avoid credit and debit card scams:
- keep your credit card in sight at all times
- don't share or show your PIN to others, especially when using ATMs
- check your transaction statements
At airports, use airport taxis, prearranged hotel transfer services, taxis from clearly marked taxi ranks with staff, or one reserved through a car booking app.
Check that any person holding a placard with your name on it knows where you are going.
Be careful of people who are overly friendly and invite you to their home.
If you're a victim of a gambling scam, report it to local police.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Kidnapping can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at low risk.
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
More information:
Civil unrest and political tension
Although rare, protests sometimes happen.
Don't take photos of demonstrations, the military or the police. Authorities may not tolerate this.
Some localised violent clashes between protesters and police have resulted in casualties. The most recent incident occurred in Đắk Lắk Province in June 2023, when several police were killed in organised attacks on police stations.
Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can turn violent.
Demonstrations and civil unrest
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators' safety and maintenance standards may not meet your expectations. This can include adventure activities, such as mountain climbing and boat trips.
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Climate and natural disasters
Vietnam experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- flash floods
Severe weather events can disrupt air, sea, road and rail transport, electricity and communications.
If there's a natural disaster:
- always carry your passport in a waterproof bag
- keep in regular touch with family and friends
- check the media and other local sources for information
- follow the advice of local authorities
Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Flooding and typhoons
Floods , flash floods, typhoons and severe weather are common during the rainy season, from June to November.
Flooding can lead to landslides including in built up and residential areas of towns and villages.
Typhoons mostly affect the coastal areas of the north and central regions. Though less common, typhoons also happen in the south.
Monitor the media, and weather and flood level reports during the rainy season.
The Mekong River Commission gives information on flood levels for the Mekong River region.
If there's a flood, typhoon or severe weather:
- don't enter the affected areas without getting advice from local authorities
- check with tour operators before travelling to affected areas
- if in doubt about the safety of any location, change your travel plans.
Large, frequent earthquakes in the region make destructive tsunamis more likely.
Be alert to warnings. A tsunami can arrive within minutes of a nearby tremor or earthquake.
To receive tsunami alerts, register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System .
Move immediately to high ground if advised by local authorities or if you:
- feel a strong earthquake that makes it hard to stand up
- feel a weak, rolling earthquake that lasts a minute or more
- see a sudden rise or fall in sea level
- hear loud and unusual noises from the sea
Do not wait for official warnings. Once on high ground, monitor local media.
If there's a tsunami or if a tsunami warning is current, check the US Tsunami Warning System .
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won’t pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you’ll be away
Physical and mental health
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare, or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some addictive and psychotropic medications are controlled.
If you plan to take medication, check if it's legal in Vietnam. Take enough legal medicine for your trip and always carry it in its original packaging.
If you are travelling with prescription medication, check the value and quantity restrictions on the import and export of prescription medication with the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam .
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Localised outbreaks of diphtheria can occur in Vietnam.
Seek medical advice to en sure your vaccinations are up-to-date.
- Diphtheria (HealthDirect)
Insect-borne illnesses
Zika virus continues to be a risk. There's no vaccination for it.
If you're pregnant, the Australian Department of Health recommends you:
discuss any travel plans with your doctor
consider deferring non-essential travel to affected areas
Dengue is found, especially in the south. There's no vaccine or treatment.
Japanese encephalitis is also found. To protect yourself, consider getting vaccinated. A vaccine is available in Australia.
Malaria is a risk in some remote mountainous areas.
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
Discuss your travel plans and other vaccination needs with your doctor before you travel.
Infectious diseases
Rabies is potentially fatal if you don't get vaccinated or receive quick treatment.
Rabies is found in infected dogs, monkeys, bats and other mammals.
Most reported cases are in the mountain areas of northern Vietnam. It's most commonly passed on through dog bites.
To reduce your risk of rabies, don't go near dogs and other mammals.
If you're bitten or scratched, seek medical help immediately.
HIV/AIDS is a risk.
Take precautions if you engage in activities that expose you to risk of infection.
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is common. Sometimes more serious outbreaks happen.
Outbreaks usually peak from March to May and from September to December.
HFMD mostly affects children under the age of 10 years. Adult cases, especially young adults, are not unusual.
The illness appears as a fever, blisters and rashes on the hands, feet and buttocks.
HFMD is spread by direct contact with nose and throat discharges and faeces of infected people.
To reduce the risk of getting or passing on HFMD, pay close attention to hygiene. Wash your hands well and often.
Bird flu (avian influenza)
Human cases of avian influenza or 'bird flu' are reported in Vietnam.
Cholera and other health risks
Acute watery diarrhoea and cholera occur.
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases occur. These include:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid uncooked and undercooked food, such as salads
Get urgent medical attention if you have a fever or diarrhoea or you suspect food poisoning.
Air pollution
There can be high levels of air pollution, up to and including hazardous levels, in major cities, especially during January to March. Pollution can increase the risk of breathing problems. People with pre-existing medical conditions, particularly heart and lung conditions, may be affected.
If you're concerned about the levels of air pollution:
- seek medical advice
- follow advice from local authorities about methods to reduce exposure
- monitor an air quality index
- reduce your exposure
World Air Quality
Drug use has been reported to cause psychotic episodes and hospitalisation.
If you use drugs in Vietnam, you face possible health and legal risks. See Local laws
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities and care varies, is generally below Australian standards, and may lack medicine and supplies.
Foreign private medical clinics are available in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang. They may not meet Australian standards.
Medical facilities and care at most public hospitals are poor. This is especially true outside Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
You may need medical evacuation to a major centre, even for minor operations.
Doctors and hospitals expect payment before providing medical services, including for emergency care.
Some hospitals may talk with your travel insurance company to secure payment. Others may need up-front payment before they will start treating you.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you may need to be evacuated to Bangkok or Singapore. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
You may need to show a legalised birth certificate to be recognised as next of kin for medical consent purposes.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Vietnamese authorities have broad powers to implement various measures to contain COVID-19. These include movement restrictions and mandatory isolation for positive cases. These can vary from province to province. Follow the advice of local authorities.
There are strict security and investigative measures to stop drug trafficking.
Penalties for all types of drug offences, including those with small amounts of drugs, are severe. Many drug offences attract the death penalty or life in jail.
Marijuana in any form is illegal.
More than 20 Australians are serving sentences for drug offences in Vietnam. More have been arrested and are waiting for further investigation or trials.
Never carry parcels or luggage for others.
For information about carrying prescription medications into Vietnam, see Travel .
Carrying or using drugs
Marriage laws
Foreigners who want to marry a Vietnamese citizen in Vietnam must get formal approval from the Department of Justice. This must be done in the province where the Vietnamese citizen is registered.
You also need a Certificate of No Impediment to Marriage (CNI) if you plan to marry in Vietnam.
Apply for a CNI through the:
- Australian Embassy in Hanoi
- Australian Consulate-General in Ho Chi Minh City
You can also apply for the CNI from DFAT in Australia. Fees apply. The embassy or consulate of Vietnam in Australia needs to authenticate it. Only then will the Department of Justice in Vietnam recognise it.
Getting married
Business laws
Increased Australian business activity has resulted in a higher number of commercial disputes in recent years.
If you're thinking about entering into a contract, get professional legal advice.
If you're involved in a business or civil dispute, authorities could stop you from leaving Vietnam until you resolve the matter.
- Doing business
- Doing business in Vietnam
- Living or working overseas
Disputes over alleged misrepresentation of working and living conditions for Australians working in Vietnam often happen. This is especially the case for people teaching English.
Before signing an employment contract or travelling to Vietnam for work, verify the true nature of the work you're offered.
Check for unacceptable employment conditions. For example, conditions for early termination may state that you surrender your right to a return air ticket. Your potential employer may also withhold your pay.
To safeguard your stay, also:
- check the living arrangements your potential employer has offered
- make sure you have the correct visa before arriving — ask an embassy or consulate of Vietnam
- get professional legal advice before signing any contract
- get all the work permits you need
The Australian embassy or consulate-general can provide a limited range of notarial services for some documents needed for a work permit.
Never hand over your passport to your employer, even for safekeeping. Reputable businesses won't ask you to hand over your passport.
Make sure you keep a valid visa and work permit. If you don't, authorities will fine you and could detain you.
Going overseas to live or work
Penalties for serious crime, such as rape, espionage and hijacking, may include the death penalty.
It's illegal to:
- take photos at border crossings or military installations
- go too close to the border with China, Cambodia or Laos without prior written permission from the local authorities
- gamble, except in government-licensed casinos where foreign passport holders can gamble
- possess pornography
- possess non-state sanctioned political or religious material
These activities may result in arrest and imprisonment.
Taking part in unsanctioned religious activities, including online, is against the law. Any involvement with non-state sanctioned political organisations, or groups perceived by the Government of Vietnam to be associated with dissident groups is also illegal. If authorities suspect you of involvement in these activities, they could stop you from entering the country, detain or deport you. Authorities could also stop you from leaving, place you under surveillance or subject you to interrogation until an investigation has been completed.
It's illegal to export antiques without a permit. The Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (Vietnamese) offers advice and necessary permits.
Possessing or distributing images or objects linked to the former Republic of Vietnam, including commemorative or Vietnam War service-related items, is an offence that could attract harsh penalties.
Embassy or consulate of Vietnam
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you’re overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law
Local customs
Same-sex relationships are legal. However, social and cultural attitudes towards same-sex relationships can be conservative, especially in rural areas.
Avoid public displays of affection.
Same-sex partners aren't legally protected or recognised.
Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Dual citizenship
Vietnam recognises dual nationality in limited situations.
If you're a dual citizen and you enter Vietnam on a Vietnamese passport, this limits the consular services we can give if you're arrested or detained. Vietnamese authorities may not tell us of your situation.
Always travel on your Australian passport .
Australian citizens must re-enter Australia on an Australian passport.
If you're a dual national, you may need to do compulsory military service in Vietnam.
Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam in Australia before you travel.
Advice for dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
To enter Vietnam, you must have either a:
- visa exemption certificate
Australian passport holders are not able to obtain visas on arrival in Vietnam.
Learn more about visa requirements.
You can now apply for an eVisa for tourism or business purposes. It allows eligible travellers to stay up to 90 days in Vietnam if granted. The eVisa is valid for single or multiple entries.
You can complete the visa application form online. As there have been reports of difficulties in accessing eVisas during airport check-in, once granted, you should consider printing a hard copy of the visa approval document.
Make sure you enter your details correctly when applying for a visa. The visa details must match exactly the information on your passport's biodata page, such as your full name and date of birth details. When you're issued a visa to enter Vietnam, check that all your Vietnam visa details are correct, match the information in your passport, that your full name is listed, and that there are no spelling or other errors. Any errors or name omissions may result in you being refused entry, or you could be charged a significant fee at check-in or on arrival to correct the visa error.
For stays longer than 90 days, please contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam.
If your visa expires or is no longer valid, you may be detained and/or fined when leaving.
The Australian Government cannot sponsor your visa application or extension.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
You must register your place of residence with local police within 24 hours of arrival. Check that your hotel does this as part of the check-in process. Register at the local police station if you're staying in private accommodation.
Travellers have been scammed by private online visa services and travel agents.
Only apply for your visa through the Government of Vietnam’s official website or offices.
Vietnamese spouse or parent visas
If your spouse or parent is a Vietnamese national, you can apply for a visa exemption certificate.
Changes to visa status and visa extensions
You can't change the status of your entry visa to any other visa type in Vietnam. For example, you can't change a tourist or a spouse visa to a working visa.
Vietnam does not issue automatic visa extensions. If your visa has expired, contact the Vietnamese immigration authorities to make arrangements to exit Vietnam. Visa extensions are only possible before your visa expiry date.
To get a visa extension from the Vietnamese immigration authorities, your passport must have at least 6 months validity left at the time of application.
This requirement is subject to change.
Check with the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for details.
Border measures
Travel and entry requirements may change rapidly. Contact your nearest Vietnamese Embassy or Consulate for details on entry and exit requirements.
Other formalities
Import and export of prescription medication .
Medication and medical equipment
Register place of residence
All foreigners must register their place of residence with the local police within 24 hours of arrival.
The Australian embassy and consulate can't provide translation services to help with registration.
If you stay at a hotel, check that you'll be registered as part of the normal check-in process. They'll need your passport details.
Many hotels ask foreigners to leave their passport with hotel staff for registration purposes. It isn't a legal requirement for hotels to keep your passport for the time you stay there.
If you stay with family, friends or in another private residence, you need to register at the local police station. Use a translator if needed.
Local hosts need to pre-register foreign guests. If you stay in a private residence, make sure your host has followed this legal requirement.
Some countries won’t let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you’re just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport’s expiry date before you travel. If you’re not sure it’ll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost and stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
Keep a photocopy (or photograph) of your passport bio page and visa somewhere separately in case you lose your passport.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with 'X' gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The currency of Vietnam is the Vietnamese Dong (VND).
When you arrive or exit Vietnam, declare:
- foreign currency in excess of $US5,000, including cash and traveller's cheques
- more than 15 million Vietnamese dong
If you carry more currency or gold than you declared, authorities could confiscate it. They could arrest or fine you.
These requirements may be subject to change. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Vietnam for details.
Credit cards are widely accepted throughout major cities in Vietnam.
ATMs are widespread in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang.
Check with your bank to confirm if your ATM (eftpos) card will work in Vietnam.
Card skimming happens throughout Vietnam. See Safety .
You may have trouble getting replacement ATM cards.
Many Australian banks don't have local or regional branches with English-speaking staff.
The Vietnamese postal services are generally unreliable. If you need a new card, consider using an international courier service. The Australian embassy or consulate can't help you with money while you wait for a new card. It can't act as a personal mail-holding service.
Local travel
Travel is restricted:
- in some parts of the central Highlands
- around some border areas
- near military installations
Long Tan Cross site
The Vietnamese Government won't permit official Long Tan commemorations at the Long Tan Cross site in Ba Ria-Vung Tau Province.
Access to the site will remain open to small groups of people for private visits without media coverage. This may change at short notice.
Visitors to the site may not:
- wear medals or uniforms
- carry banners or flags
You must behave in a solemn manner, respecting the wishes of local communities.
Landmines and explosive remnants of war
Unexploded ordinance and landmines are a danger in former battlefields, especially in central Vietnam and along the Laos border.
Mine-free roads and paths are well-marked.
If you visit former battlefields, stay on marked pathways.
Driving permit
You must have a valid Vietnamese driver's licence to drive or ride in Vietnam. This includes for motorcycles of 50cc or more.
An International Driving Permit (IDP) issued in Australia is not recognised in Vietnam.
Authorities may fine you for driving without a valid licence.
Your travel insurer will likely deny any claims you make if:
- You're unlicensed and/or
- You don't hold the correct class of licence.
Australian embassy, Hanoi
Road travel
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Vietnam than in Australia.
Hazards include:
- crowded streets in major cities
- drivers ignoring road rules
- poor vehicle and road maintenance
Traffic accidents often happen and attract large crowds.
If you're involved in an accident, you could face criminal charges. This is regardless of who's at fault. You may need to pay a large sum to the injured person or their family.
If you're not familiar with local conditions, avoid driving or riding a motorcycle.
Whether driving, riding or walking, be very careful when crossing busy streets. Traffic can appear from any direction.
Road Safety
Motorcycles
The number of travellers involved in serious motorcycle accidents is increasing.
Check your travel insurance policy covers you when travelling by motorcycle.
Always wear a helmet that meets Australian safety standards.
Only ride motorcycles if you're:
- properly licensed (Australian driver licences or International Driver Licences issued in Australia are not accepted in Vietnam; you must hold a Vietnamese driving licence to ride a motorbike 50cc or above); and
- familiar with and comfortable in local driving conditions
Be careful using taxis hailed on the street.
Major metered taxis are generally reliable. Ensure the taxi driver knows how to get to where you're going before you get in.
Check the meter is used. Leave the taxi if the driver tries to pick other passengers up.
If you book a taxi online or through an app, make sure the details of the vehicle and driver match those the company gives you.
Unless using an Australian safety standard-approved helmet, we discourage using motorcycle taxis as they provide riders with helmets that offer little to no protection against injury in the case of an accident.
Be careful of taxi scams. See Safety
Public transport
Inter-city buses have a high accident rate.
Petty theft often happens on buses. See Safety .
When travelling by rail, keep the ticket stub as you need it when leaving the train station.
Getting around
Boats, hydrofoils and ferries may not meet Australian safety standards.
Accidents on waterways happen. Vessels have sunk and people have died. This includes in Ha Long Bay.
Whenever you plan to travel by boat :
- ask tour operators about the safety record and emergency procedures
- make sure there is enough safety equipment such as life jackets on board
- if proper equipment is not available, use another provider
Piracy happens in coastal areas of Vietnam.
- Reducing the risk of piracy
- International Maritime Bureau piracy reports
You may need to show your luggage tags when leaving a Vietnamese airport. Keep your luggage receipt from your airline on you at all times.
By law, children under 14 years travelling alone on domestic flights must:
- bring a birth certificate
- have an authorisation letter between the legal guardian of the child and the airline confirming the child can travel alone
Contact the airline in advance to check what is needed for unaccompanied minors.
DFAT doesn’t provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Vietnam's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Travelling by air
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Emergency numbers in Vietnam are operated in Vietnamese only and may be unreliable. You may have a long wait before emergency services arrive.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Take a translator with you to report a crime to the local police. Cases reported by foreigners may be accepted at the discretion of local police.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can’t do to help you overseas.
For consular assistance, contact the nearest embassy or consulate.
Australian Embassy, Hanoi
8 Dao Tan Street
Ba Dinh District, Hanoi, Vietnam
Phone: (+84 24) 3774 0100
Website: vietnam.embassy.gov.au
Facebook: Australia in Vietnam
X: @AusAmbVN
Australian Consulate-General, Ho Chi Minh City
20th Floor, Vincom Centre
47 Ly Tu Trong Street
Ben Nghe Ward, District 1
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Phone: (+84 28) 3521 8100
Website: hcmc.vietnam.embassy.gov.au
Check the relevant website for details about opening hours, and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Vietnam?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
- Vacation Rentals
- Restaurants
- Things to do
- Things to Do
- Travel Stories
- Rental Cars
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travelers' Choice
- Help Center
Can I reschedule my flight to an earlier date at the airport - Air Travel Forum
- Tripadvisor Forums
- Air Travel Forums
Can I reschedule my flight to an earlier date at the airport
- United States Forums
- Europe Forums
- Canada Forums
- Asia Forums
- Central America Forums
- Africa Forums
- Caribbean Forums
- Mexico Forums
- South Pacific Forums
- South America Forums
- Middle East Forums
- Honeymoons and Romance
- Business Travel
- Train Travel
- Traveling With Disabilities
- Tripadvisor Support
- Solo Travel
- Bargain Travel
- Timeshares / Vacation Rentals
- Air Travel forum
This post was determined to be inappropriate by the Tripadvisor community and has been removed.
This post has been removed at the author's request.

What do your fare conditions say about changes?
- Luggage from baggage claim & check back in. Security again? 2:38 pm
- Watching own content on flight 2:38 pm
- Customs 2:36 pm
- London Heathrow Terminal 5 to 3 2:31 pm
- EasyJet Row 1, D,E,F 2:24 pm
- Lufthansa vs United 2:20 pm
- Premium seats on Dreamliner 1:54 pm
- TUI UK flight changes affecting booked seats 1:20 pm
- India on F1 visa Los Angeles to Bangkok 1:02 pm
- Ryanair – Check In At The Airport 12:52 pm
- Cheapoair.ca, is it a scam ? 12:40 pm
- Zipair Review 12:35 pm
- Jet2 from ema 12:01 pm
- Can I reschedule my flight to an earlier date at the airport 11:25 am
- ++++ ESTA (USA) and eTA (Canada) requirements for visa-exempt foreign nationals ++++
- ++++ TIPS - PLANNING YOUR FLIGHTS +++++++
- Buy now or later? What's with these screwy ticket prices?
- Around-the-world (RTW) tickets
- All you need to know about OPEN JAW tickets
- Beware of cheap business class tickets (sold by 3rd parties)
- ++++ TIPS - PREPARING TO FLY +++++++++
- TIPS - How to prepare for Long Haul Flights
- TIPS - Being Prepared for Cancellations and Long Delays
- TIPS - How to survive being stuck at an airport
- Flights delays and cancellations resources
- How do I effectively communicate with an airline?
- Airline, Airport, and Travel Abbreviations
- Air Travel Queries: accessibility,wedding dresses,travelling with children.
- Connecting Flights at London Heathrow Airport
- TUI Airways (formerly Thomson) Dreamliner - Movies and Seating Information
- ++++ COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS INFORMATION ++++
- Covid-19 Coronavirus Information for Air Travel
- Sunday, 12 May, 2024
- Almaty 57 °F / 14 °C
- Astana 48 °F / 9 °C

- All Stories
- Kazakhstan Region Profiles: A Deep Dive Into the Heart of Central Asia
- State of the Nation
- Election 2022
- Election 2023
- Astana International Forum
- Kazakhstan’s Presidency in SCO
- Central Asia
- Kazakhstan, Vietnam Introduce Visa-Free Travel This Month
By Dana Omirgazy in International on 10 May 2024
ASTANA – The agreement on a visa-free regime between Kazakhstan and Vietnam will come into force on May 25, said Aibek Smadiyarov, the Kazakh Foreign Ministry’s Spokesperson, during his weekly briefing on May 6, reported the ministry’s press service.

Photo credit: Shutterstock
The relevant agreement was signed in August last year in Hanoi.
“Citizens of the two nations – holders of national passports – are exempt from the need for a visa under the agreement. Moreover, tourists are permitted to stay in the country for 30 calendar days from the date of entry, for a total of 90 calendar days every six months,” said Smadiyarov.
Get The Astana Times stories sent directly to you! Sign up via the website or subscribe to our Twitter , Facebook , Instagram , Telegram , YouTube and Tiktok !
Most Recent Stories
- Kazakh President Signs Decree on Measures to Liberalize Economy
- Shymkent to Host First Go Viral Central Asia Festival
- Transcontinental Corridor Forges Path to Europe’s Energy Future
- Nation Marks 120 Years of Kazakh Archaeologist Alkey Margulan
- Azerbaijan, Armenia Hold Peace Talks in Almaty
- News Digest: Foreign Media on Victory Day, AI in Railway Transportation and More
- Civil Aviation Academy’s Female Crew Makes its First Flight
- Kazakhstan, Netherlands Sign Eight Commercial Documents
- KazEnergy, US Companies Exchange Experience in Developing Clean Energy
- Dialogue of Civilisations
- Editor’s Picks
- International
- Constitutional Referendum
- National Overview
- © 2010-2024 The Astana Times
- Privacy Policy
- About Us
- Share full article

Opinion Nicholas Kristof
The Case for Hope
Credit... Cecilia Carlstedt
Supported by

By Nicholas Kristof
Opinion Columnist
- May 9, 2024
Mr. Kristof is the author of a new memoir, “Chasing Hope: A Reporter’s Life,” from which this essay is adapted.
More than three-quarters of Americans say the United States is headed in the wrong direction. This year, for the first time, America dropped out of the top 20 happiest countries in the World Happiness Report. Some couples are choosing not to have children because of climate threats. And this despair permeates not just the United States, but much of the world.
This moment is particularly dispiriting because of the toxic mood. Debates about the horrifying toll of the war in Gaza have made the atmosphere even more poisonous, as the turmoil on college campuses underscores. We are a bitterly divided nation, quick to point fingers and denounce one another, and the recriminations feed the gloom. Instead of a City on a Hill, we feel like a nation in despair — maybe even a planet in despair.
Yet that’s not how I feel at all.
What I’ve learned from four decades of covering misery is hope — both the reasons for hope and the need for hope. I emerge from years on the front lines awed by material and moral progress, for we have the good fortune to be part of what is probably the greatest improvement in life expectancy, nutrition and health that has ever unfolded in one lifetime.
Many genuine threats remain. We could end up in a nuclear war with Russia or China; we might destroy our planet with carbon emissions; the gap between the wealthy and the poor has widened greatly in the United States in recent decades (although global inequality has diminished ); we may be sliding toward authoritarianism at home; and 1,000 other things could go wrong.
Yet whenever I hear that America has never been such a mess or so divided, I think not just of the Civil War but of my own childhood: the assassinations of the 1960s; the riots; the murders of civil rights workers; the curses directed at returning Vietnam veterans; the families torn apart at generational seams; the shooting of students at Kent State; the leftists in America and abroad who quoted Mao and turned to violence because they thought society could never evolve.
If we got through that, we can get through this.
My message of hope rubs some Americans the wrong way. They see war, can’t afford to buy a house, struggle to pay back student debt and what’s the point anyway, when we’re boiling the planet? Fair enough: My job is writing columns about all these worries.
Yet all this malaise is distorting our politics and our personal behaviors, adding to the tensions and divisions in society. Today’s distress can nurture cynicism rather than idealism, can be paralyzing, can shape politics by fostering a Trumpian nostalgia for some grand mythical time in the past.
The danger is that together all of us in society collectively reinforce a melancholy that leaves us worse off. Despair doesn’t solve problems; it creates them. It is numbing and counterproductive, making it more difficult to rouse ourselves to tackle the challenges around us.
The truth is that if you had to pick a time to be alive in the past few hundred thousand years of human history, it would probably be now.
When I step back, what I see over the arc of my career is a backdrop of progress in America and abroad that is rarely acknowledged — and that should give us perspective and inspire us to take on the many challenges that still confront us.
I think of a woman named Delfina, whom I interviewed in 2015 in a village in Angola. She had never seen a doctor or dentist and had lost 10 of her 15 children. Delfina had rotten teeth and lived in constant, excruciating dental pain. She had never heard of family planning, and there was no school in the area, so she and all the other villagers were illiterate.
A young journalist following in my footsteps today may never encounter a person like Delfina — and that’s because of the revolution in health care, education and well-being that we are in the middle of, yet often seem oblivious to.

I have implored President Biden to do more for the children and babies dying in Gaza. I’ve been unwavering about the need to support the people suffering bombardment in Ukraine . And I regularly report on the conflicts and humanitarian disasters in Sudan, Myanmar, Yemen and elsewhere that garner less attention.
Some people see my career covering massacres and oppression and assume that I must be dour and infused with misery, a journalistic Eeyore. Not so! Journalism is an act of hope. Why else would reporters rush toward gunfire, visit Covid wards or wade into riots to interview arsonists? We do all this because we believe that better outcomes are possible if we just get people to understand more clearly what’s going on. So let me try with you.
Just 100 years ago, doctors could do nothing when President Calvin Coolidge’s 16-year-old son developed a blister on a toe while playing tennis on the White House court. It became infected, and without antibiotics the boy was dead within a week. Today the most impoverished child in the United States on Medicaid has access to better health care than the president’s son did a century ago.
Consider that a 2016 poll found that more than 90 percent of Americans think that global poverty stayed the same or got worse over the previous 20 years. This is flat wrong: Arguably the most important trend in the world in our lifetime has been the enormous reduction in global poverty.
About one million fewer children will die this year than in 2016, and 2024 will probably set yet another record for the smallest share of children dying before the age of 5. When I was a child, a majority of adults were illiterate, and it had been that way forever; now we’re close to 90 percent adult literacy. Extreme poverty has plunged to just 8 percent of the world’s population.
Those are statistics, but much of my career has been spent documenting the revolution in human conditions they represent. In the 1990s I saw human traffickers openly sell young girls in Cambodia for their virginity; it felt like 19th-century slavery, except most of these girls were going to be dead of AIDS by their 20s. Trafficking remains a huge problem, but the progress is manifest. In Kolkata, India, where I’ve covered this issue for decades, one study found an 80 percent reduction in the number of children in brothels since 2016.
Two decades ago, AIDS was ravaging poor countries, and it wasn’t clear we would ever control it. Then America under President George W. Bush started a program, Pepfar , that allowed the world to turn the corner on AIDS globally, saving 25 million lives so far. One reason you don’t hear much about AIDS today is that it’s among the great successes in the history of health care.
It’s not just that the world has in our lifetimes seen the greatest improvement in human wellness that we know of since the birth of our species. Despite some setbacks for democracy — and real risks here in the United States — I’ve learned to doubt despotism in the long run.
One of my searing experiences as a young journalist was covering that terrible night in June 1989 when Chinese Army troops turned their automatic weapons on unarmed protesters in Tiananmen Square, including the crowd that I was in. You never forget seeing soldiers use weapons of war to massacre unarmed citizens; I still have my notebook from that night, stained with the sweat of fear.
“Maybe we’ll fail today,” my scribbles record, as I quoted an art student nearly incoherent with grief. “Maybe we’ll fail tomorrow. But someday we’ll succeed.”
Yet I also remember a day five weeks earlier in the democracy movement, April 27, 1989, when Beijing students prepared for a protest march from the university district to Tiananmen.
Students knew that if they marched, they were risking expulsion, imprisonment or worse. The evening before, some students spent the night writing their wills in case they were killed.
I drove out to the university district that morning and saw roads lined with tens of thousands of People’s Armed Police. I slipped onto the Beijing University campus by pretending to be a foreign student and watched as a frightened band of 100 students emerged from a dormitory, parading with pro-democracy banners. Gradually other students joined in, and perhaps 1,000 marched, clearly terrified, toward the gate. Rows of armed police blocked their way, but the students jostled and pushed and finally forced their way onto the road. To everyone’s surprise, the police didn’t club the students or shoot them that day. Once the vanguard broke through, thousands more students materialized to join the march.
Word spread rapidly. As the marchers passed other universities, tens of thousands more joined the protest march, and so did ordinary citizens. Old people shouted encouragement from balconies and shopkeepers rushed out to give drinks and snacks to protesters. The police tried many times to block the students, but each time huge throngs of young people forced their way through.
By the time they reached Tiananmen Square, the protesters numbered perhaps half a million. Then they marched triumphantly back to their universities, hailed by the people of Beijing screaming support. That evening at the gate of Beijing University, the students were met not by phalanxes of armed police but by white-haired professors waiting for them, crying happy tears, cheering for them.
“You are heroes,” one professor shouted. “You are sacrificing for all of us. You are braver than we are.”
It was a privilege to witness the heroism of that day. There is much to learn from the commitment to democracy shown that spring by Chinese students.
The exhilaration of that march to Tiananmen Square didn’t last. But in my reporting career, I’ve learned first to be careful of betting on democracy in the short run, and second, to never bet against it in the long run.
Some day, I hope to see the arrival of democracy in China, as well as in Russia, Venezuela and Egypt.
Commentators are always predicting the end of American primacy. First it was the book “Japan as No. 1” in 1979 by Ezra F. Vogel, then Patrick Buchanan’s 2002 right-wing “The Death of the West” and Naomi Wolf’s 2007 leftist “The End of America.” It seemed for a time that Europe might surpass us, while in the longer run China appeared poised to overtake America and become the world’s largest economy.
Yet the United States maintains its vitality. World Bank figures suggest that the United States has actually increased its share of global G.D.P., measured by official exchange rates, by a hair since 1995. Europe today is leaderless and has anemic growth. Japan, China and South Korea are losing population and lagging economically. “Uncle Sam is putting the rest of the world to shame,” The Economist noted recently.
China’s struggles today are particularly important, for it was China that was the foremost challenger to American pre-eminence. Many people around the world thought that China had a more vibrant political and economic model. Yet today China is struggling and even with its population advantage it is no longer clear that China’s economy will ever eclipse America’s. The United States is the undisputed titan in the world today.
As I see it, the possibility of a Donald Trump election hangs as a shadow over America. Yet even if Trump were elected, there is a dynamism and inner strength in America — in technology, culture, medicine, business, education — that I think can survive four years of national misrule, chaos and subversion of democracy. Indeed, Trump might wreck Europe and Asia — by abandoning NATO and Taiwan — even more than he would damage America, in a way that would perversely cement U.S. primacy.
Note that one of the dominant issues in this year’s general election will be immigration. That’s partly because of the determination of people around the world to come to America, just as my dad risked his life to escape Eastern Europe and make his way here in 1952. Desperate foreigners sometimes see our nation’s resilience more clearly than we do.
I have seen that faith in America in surprising places, even when I periodically slipped into Darfur to cover the genocide there in the 2000s. I couldn’t obtain a government pass to get through checkpoints, but I realized that U.N. workers were showing English-language credentials that the soldiers surely couldn’t read. So I put my United Airlines Mileage Plus card on a lanyard, drove up to a checkpoint and showed it — and the soldiers waved me through.
Recklessness caught up with me, and eventually I was stopped at a checkpoint and kept in a detention hut decorated with a grisly mural of a prisoner being impaled by a stake through the stomach. It was a frightening wait as the soldiers summoned their commander. He eventually arrived and ordered me released — and then one of my captors who previously had seemed ready to execute me sidled up.
“Hi,” he said. “Can you get me a visa to America?”
I share the view that a Trump election would pose immense damage to American political and legal systems. But in the scientific world we would continue to move forward with new vaccines for breast cancer, new drugs to combat obesity and new CRISPR gene-editing techniques to treat sickle cell and other diseases.
How can we weigh democratic decline against lives saved through medical progress? Of course we can’t. As my intellectual hero, Isaiah Berlin , might say, they are incommensurate yardsticks — but that does not mean that they are irrelevant to our well-being.
And no one can accuse me of ignoring the problems that beset us at home and abroad, for they have been my career. They’ve left me a bit too scarred to be a classic optimist. Hans Rosling, a Swedish development expert, used to say that he wasn’t an optimist but a possibilist. In other words, he saw better outcomes as possible if we worked to achieve them. That makes sense to me, and it means replacing despair with guarded hope.
This isn’t hope as a naïve faith that things will somehow end up OK. No, it is a somewhat battered hope that improvements are possible if we push hard enough.
In 2004 I introduced Times readers to the story of an illiterate woman named Mukhtar Mai, whom I met in the remote village of Meerwala in Pakistan. She had been gang-raped on order of a village council, as punishment for a supposed offense by her brother, and she was then expected to disappear in shame or kill herself. Instead, she prosecuted her attackers, sent them to prison and then used her compensation money to start a school in her village.
Instead of giving in to despair, Mukhtar nursed a hope that education would chip away at the misogyny and abuse of women that had victimized her and so many others. Then she enrolled the children of her rapists in her school.
Mukhtar taught me that we humans are endowed with strength — and hope — that, if we recognize it and flex it, can achieve the impossible.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Nicholas Kristof became a columnist for The Times Opinion desk in 2001 and has won two Pulitzer Prizes. His new memoir is “ Chasing Hope: A Reporter's Life .” @ NickKristof
Advertisement
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Click this link or access https://immigration.gov.vn/ and go to 'E-visa Issuance' then click on the link for 'Outside Vietnam foreigners'. Step 3: Upload your .jpg images (passport data page and passport photo) and fill out the required fields on the form completely. Submit your form. Step 4: Pay the e-Visa fee of 25 USD.
If you are in Vietnam, please contact the nearest Vietnamese Immigration Office. For travelers entering Vietnam, the Ministry of Health requires either a negative PCR test taken within 72 hours of travel or rapid test taken with 24 hours. COVID-19 tests must be administered and certified by competent health authorities.
E-transaction applying for visa at oversea Vietnamese representative offices and Checkpoints; ... - All entrants must adhere to applicable Covid-19 prevention regulations by the Ministry of Health. ... Sports, Tourism's pilot inbound tourism program./. VIETNAM IMMIGRATION DEPARTMENT. Related news. NOTICE (25/04/2024) NOTICE (16/04/2024 ...
Vietnam accommodated more than 6.2 million international visitors in the first four months of this year, up 68.3% year on year and 3.9% compared to the same period in 2019 before the COVID-19 ...
Get ready for your Vietnam trip with this guide to tourist visas. Find all the information you need on Vietnam's e-visa, visa on arrival, and visa exemptions. Home; Live fully in Vietnam . ... Vietnam's new visa policy effective from 15th August 2023 extends stay duration for 13 countries enjoying unilateral visa exemption from 15 days to 45 ...
- A test is required if an international visitor shows COVID-19 symptoms. If the test result is positive, he/she must comply with the Ministry of Health's guidance. - The rule that international arrivals by air have to undergo another test when entering Vietnam, as well as quarantine requirements, is no longer in place.
(TITC) - Vietnam officially reopens tourism from 15th March. On the same day, Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism promulgated the guidance including requirements for international visitors to Vietnam.
In response to a spate of new cases of COVID-19, Vietnam is stepping up its measures to stop the virus from entering and spreading within the country. ... 2020 on visa exemptions, e-visas or tourism visas will be given automatic stay extensions at no charge until May 30, 2021.
0:03. 1:22. HANOI, Vietnam — Vietnam on Wednesday scrapped quarantine and other travel restrictions for foreign visitors in an effort to fully reopen its border after two years of pandemic ...
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed. Exercise normal precautions in Vietnam. Read the country ... On a receipt of a pre-approval letter, travelers may then travel to Vietnam and apply for a visa upon landing to Vietnam. Please be advised that you should not travel to Vietnam without having been issued a pre-approval letter as it ...
Health Alert - U.S. Embassy and U.S. Consulate General Ho Chi Minh City - COVID-19 Update (May 7, 2021) Locat. Due to heightened risk of COVID-19 in Vietnam, the Vietnamese Government is increasing restrictions on movement and calling for increased vigilance. Starting May 5, the Government of Vietnam instituted a 21-day quarantine period.
The Vietnam Immigration portal provides the following services: E-visa issuance. E-transaction applying for visa at oversea Vietnamese representative offices and Checkpoints. Declare temporary residence for foreigners. ABTC issuance. Passports issuance for Vietnamese nationals. Vietnam evisa, evisa Vietnam, Vietnam immigration, Vietnam visa ...
Question 1:I would like to inquire about the regulations on foreigners' entry into Vietnam to work for less than 14 days, do they need to undergo quarantine? Answer: At the moment, for Covid-19 prevention and control, the Government of Vietnam only allows entry of foreigners who are investors, experts, high-skilled workers, business managers.They must comply with quarantine measures.
FCDO travel advice for Vietnam. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences. ... COVID-19 rules. ... If you get an e-visa while in Vietnam, you must exit the ...
The Ministry of Health's most recent guidance on COVID-19 prevention and control allows travelers to enter Vietnam without being isolated, and exempts children under 2 years of age from arrival testing. The Ministry of Health issued Dispatch No. 1265/BYT-DP on COVID-19 prevention and control measures for travelers to Viet Nam. The new Dispatch has been communicated to all other Ministries ...
Reissued with obsolete COVID-19 page links removed. Exercise normal precautions in Vietnam. Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Vietnam. If you decide to travel to Vietnam: Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
To call for emergency services while in Vietnam, dial 115 for an ambulance, 114 for the fire department, and 113 for the police. Write these numbers down to carry with you on your trip. Learn as much as you can about Vietnam before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on Vietnam from the US Department of ...
In Vietnam, since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has imposed stringent visa restrictions for foreign nationals. As a reminder, beginning March 22, 2020, Vietnam enacted a suspension of entry for all foreign nationals. ... 2023, the National Assembly approved new measures pertaining to tourist entry to Vietnam. The e-visa ...
HANOI -- Tourism in Vietnam is struggling to recover from the COVID-19 slowdown, although the country has already lifted pandemic-related travel restrictions. In the first 10 months of this year ...
You can apply online for an eVisa for tourism or business. You must have a visa before travelling to Vietnam (See 'Travel'). We advise: Exercise normal safety precautions in Vietnam. ... COVID-19; Serious outbreaks sometimes occur. ... contact the Vietnamese immigration authorities to make arrangements to exit Vietnam. Visa extensions are only ...
Immigration Department in Hanoi. Address: 44-46 Tran Phu, Ba Dinh, Hanoi. Phone: (24) 3825-7941. Email: [email protected]. Immigration Office in Da Nang. (Handing Vietnamese visa and residence applications for foreigners residing in Central Vietnam) Address: 78 Le Loi, Hai Chau, Da Nang. Phone: 0694260192 - 0906091269.
Airline, Airport, and Travel Abbreviations; Air Travel Queries: accessibility,wedding dresses,travelling with children. Connecting Flights at London Heathrow Airport; TUI Airways (formerly Thomson) Dreamliner - Movies and Seating Information ++++ COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS INFORMATION ++++ Covid-19 Coronavirus Information for Air Travel
Kazakhstan, Vietnam Introduce Visa-Free Travel This Month By Dana Omirgazy in International on 10 May 2024 ASTANA - The agreement on a visa-free regime between Kazakhstan and Vietnam will come into force on May 25, said Aibek Smadiyarov, the Kazakh Foreign Ministry's Spokesperson, during his weekly briefing on May 6, reported the ministry ...
The U.S. still requires proof of a negative COVID-19 test or a letter of recovery from a doctor prior to entry. More information about travel into the U.S. can be found at the CDC website. Please see the U.S. Mission in Vietnam's COVID-19 Information Page for additional information regarding the COVID-19 situation in Vietnam.
The truth is that if you had to pick a time to be alive in the past few hundred thousand years of human history, it would probably be now. When I step back, what I see over the arc of my career is ...
This upgrade reflects the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's (CDC) Level 4 Health Travel Notice indicating that there is a very high level of COVID-19 in Vietnam. For more information, please refer to the advisory and CDC notice. The COVID-19 situation in Vietnam is constantly changing and varies from province to province.