Wood is a natural material and over time will rot if not preserved or treated correctly.
At Morris Minor Workshop we can repair and/or renew all woodwork on Morris Minor Travellers to make it as good as new.
Services include:
- Replacement of complete wood using good quality treated ash
- Replacement of rear doors, rear door pillars and middle waste rails depending on the condition of the rest of the woodwork
- Rub down and retreat of all exterior woodwork
- Fitting of new window channels and re sealing of inner capping, should you have soggy rear carpets.

1_Bowdens Trav 012.jpg
1_10 rear.jpg, 1_crundwell traveller 028.jpg, 1_crundwell traveller 031.jpg, 1_crundwell traveller 030.jpg.
Morris Minor Workshop Battenhurst Farm Battenhurst Road Stonegate East Sussex TN5 7DU
Tel/Fax : 01580 200062
email: [email protected]
Site Map
© 2015 Morris Minor Workshop
- Products & Prices

Welcome to Woodies
We are the world No.1 manufacturer and supplier of Morris Traveller woodwork. We have gained this status and reputation through using only the best materials and always ensuring the satisfaction of our customers.
At Woodies we specialise in the Morris Traveller and Mini Countryman but we can, and will, fabricate timber frames for all classic cars. We have completed in excess of 600 Morris Travellers over 30 years, as well as many other wood framed classic and vintage vehicles.
Our kits are exported around the world and include everything you need to replace a Traveller woodframe, along with instructions and a full back-up service.

Only the highest quality ash is selected from renewable sources allowing excellent colour and grain match. We take extra care to avoid knots and imperfections resulting in a product that is second to none.
Replacing the wood on a Traveller is a major undertaking so getting it right first time is essential. We're confident that our timber frames are the best available, which can be confirmed by organisations such as the Morris Minor Owners Club.
Web View Mobile View
- Restoration
- Cars For Sale
Morris Minor Traveller Restorers & Woodwork Specialists
Traveller Woodwork: Spares, DIY timber kits and fitting.
If you’re new to Travellers, you may not know that their iconic timber frames are structural, as well as beautiful, so it’s essential they’re properly constructed.
Staying true to the original, all our frame and door timbers are meticulously hand-crafted using carefully selected, fully seasoned English Ash for the highest quality.
Built in our own workshops, we have full quality control over the manufacturing process, giving you complete peace of mind that your car will be structurally sound.
We can supply and offer worldwide shipping of full timber kits or individual timbers as DIY spares, or provide a professional fitting service from our base in Yorkshire.
This service includes us taking care of any welding repairs or paintwork that may be needed as part of the re-fit.
All woodwork is fully treated and sealed before fitting. Also for DIY we can supply your accessories fitting kit. This includes sliding window runners, rear roof guttering, seals and screws.
Wood repairs
Individual wood parts replacement is our speciality, providing the surrounding woodwork is sound, we can remove and replace any existing part and blend it into the natural colour of your woodwork.
For existing rot-free wood, which doesn’t need to be replaced or repaired, we can also provide a full strip down service to clean, treat and re-seal , returning your woodwork to its former glory.
This enhances its beauty and protects the timber from future damage (caused by weather, climate or road salt for example), extending its life for many years to come.
- Morris Minor Owners
The Morris Minor International Message Board
Skip to content
Wood treatment.
Post by greendefender123 » Mon Aug 10, 2015 4:29 pm
Contribution Stars
MMO Annual Award
Re: Wood treatment.
Post by ruairidh » Mon Aug 10, 2015 9:20 pm
Post by greendefender123 » Tue Aug 11, 2015 7:28 am
Post by ruairidh » Tue Aug 11, 2015 6:43 pm
Post by greendefender123 » Tue Aug 11, 2015 7:09 pm
Post by ruairidh » Tue Aug 11, 2015 8:06 pm
Post by ruairidh » Tue Aug 11, 2015 8:08 pm
Post by bmcecosse » Tue Aug 11, 2015 8:17 pm
Post by greendefender123 » Tue Aug 11, 2015 9:08 pm
Post by jonathon H » Tue Aug 11, 2015 9:13 pm
Post by qwertyhenry » Tue Aug 11, 2015 10:22 pm
Post by greendefender123 » Thu Aug 13, 2015 1:29 pm
Post by cmea » Mon Aug 24, 2015 8:09 pm
Post by greendefender123 » Mon Aug 24, 2015 9:09 pm
Return to “Body, Paint, Glass & Wood Work”
- All times are UTC
Powered by phpBB ® Forum Software © phpBB Limited
Privacy | Terms
- Body inc. Panels & Trim
- Traveller Parts
Traveller Replacement External Wood Kit - Late Type **DOUBLE LAMP HOLE** (Wood Only) ***ASSEMBLED***
- £1,258.20 £1,048.50 (ex. VAT) (ex. VAT) (inc. VAT) (inc. VAT)
- Product Information
- Delivery & Returns
- Payment & Security
Please contact us for our Delivery & Returns Policy
- View All Traveller Parts

- Latest Topics Table
- Morris Minor
- Woodies Chat
- Modified Minors
- Morris Mini
- Morris Major
- Morris Isis
- Buy, Sell & Trade
- Vendor Market
- List Archives
- Random Topic
- Who's Online?
- Add Your Car
- Top Rated Cars
- Browse Registry
- Recently Added
- Search Registry
- Random Vehicle
- Cars For Sale
- Sell Your Car
- Parts For Sale
- Buyer Safety
- Buy & Sell Forum
- MinorForum Regalia Shop
- Parts & Accessories
- Tires & Wheels
- My Order Status
- Events Calendar
- Add an Event
- Featured Build Journals
- Latest Journal Posts
- Create a Journal
- Tech Library
- Featured Articles
- Submit an Article
- Buying a Used Vehicle
- Frequently Asked Questions
- General Maintenance
- Service & Repair
- Body Repair & Paint
- Restoration
- Video Library
- Scanned Publications
- Miscellaneous
- Link Directory
- Link to This Website
- Member Services
- Parts Suppliers
- Reference & Tech
- Clubs & Registers
- Personal Sites
- Specialist Services
- General Suppliers
- Other Links
Morris Minor Forum
Traveller wood treatment--usa.

To reply or ask your own question: Members Sign In or Create an Account Registration is FREE and takes less than a minute

Having trouble posting or changing forum settings? Read the Forum Help (FAQ) or contact the webmaster Phorum Open Source Software -->

Travel Itinerary For One Week in Moscow: The Best of Moscow!
I just got back from one week in Moscow. And, as you might have already guessed, it was a mind-boggling experience. It was not my first trip to the Russian capital. But I hardly ever got enough time to explore this sprawling city. Visiting places for business rarely leaves enough time for sightseeing. I think that if you’ve got one week in Russia, you can also consider splitting your time between its largest cities (i.e. Saint Petersburg ) to get the most out of your trip. Seven days will let you see the majority of the main sights and go beyond just scratching the surface. In this post, I’m going to share with you my idea of the perfect travel itinerary for one week in Moscow.
Moscow is perhaps both the business and cultural hub of Russia. There is a lot more to see here than just the Kremlin and Saint Basil’s Cathedral. Centuries-old churches with onion-shaped domes dotted around the city are in stark contrast with newly completed impressive skyscrapers of Moscow City dominating the skyline. I spent a lot of time thinking about my Moscow itinerary before I left. And this city lived up to all of my expectations.

Travel Itinerary For One Week in Moscow
Day 1 – red square and the kremlin.
Metro Station: Okhotny Ryad on Red Line.
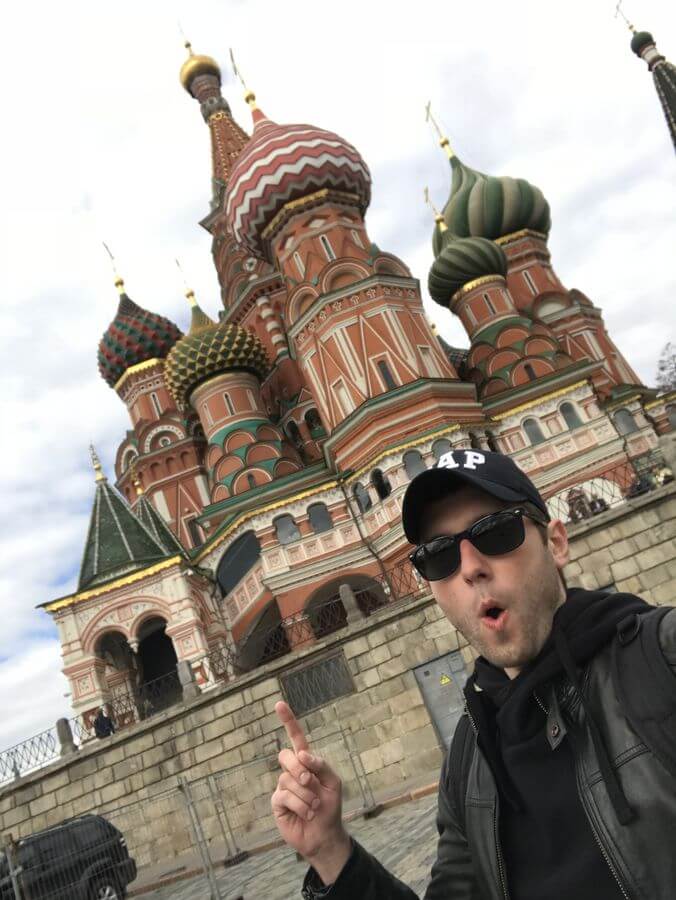
No trip to Moscow would be complete without seeing its main attraction. The Red Square is just a stone’s throw away from several metro stations. It is home to some of the most impressive architectural masterpieces in the city. The first thing you’ll probably notice after entering it and passing vendors selling weird fur hats is the fairytale-like looking Saint Basil’s Cathedral. It was built to commemorate one of the major victories of Ivan the Terrible. I once spent 20 minutes gazing at it, trying to find the perfect angle to snap it. It was easier said than done because of the hordes of locals and tourists.
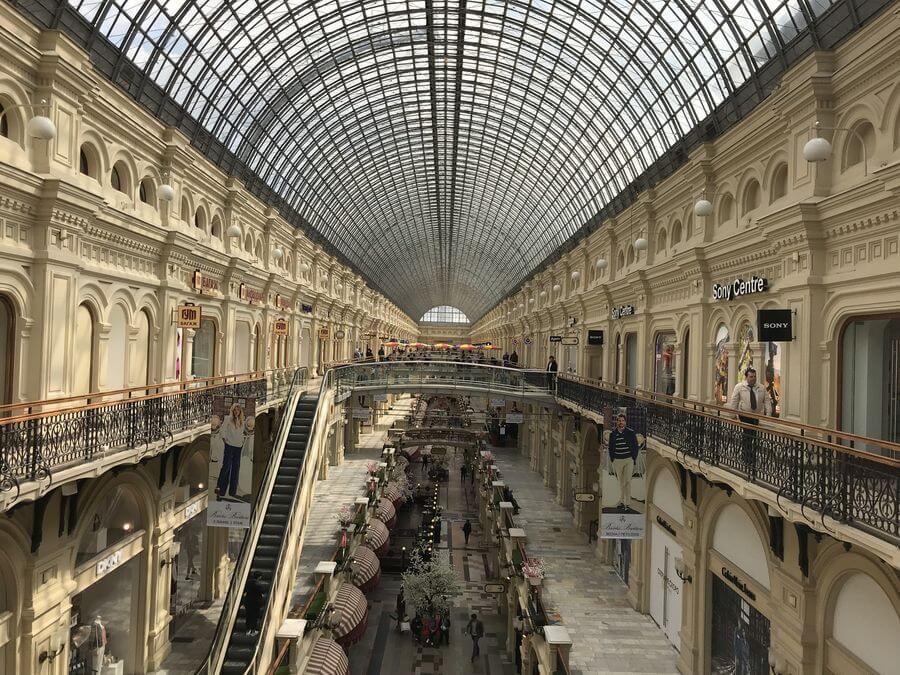
As you continue strolling around Red Square, there’s no way you can miss Gum. It was widely known as the main department store during the Soviet Era. Now this large (yet historic) shopping mall is filled with expensive boutiques, pricey eateries, etc. During my trip to Moscow, I was on a tight budget. So I only took a retro-style stroll in Gum to get a rare glimpse of a place where Soviet leaders used to grocery shop and buy their stuff. In case you want some modern shopping experience, head to the Okhotny Ryad Shopping Center with stores like New Yorker, Zara, and Adidas.

Read Next: Things To Do on Socotra
To continue this Moscow itinerary, next you may want to go inside the Kremlin walls. This is the center of Russian political power and the president’s official residence. If you’re planning to pay Kremlin a visit do your best to visit Ivan the Great Bell Tower as well. Go there as early as possible to avoid crowds and get an incredible bird’s-eye view. There are a couple of museums that are available during designated visiting hours. Make sure to book your ticket online and avoid lines.
Day 2 – Cathedral of Christ the Saviour, the Tretyakov Gallery, and the Arbat Street
Metro Station: Kropotkinskaya on Red Line
As soon as you start creating a Moscow itinerary for your second day, you’ll discover that there are plenty of metro stations that are much closer to certain sites. Depending on your route, take a closer look at the metro map to pick the closest.
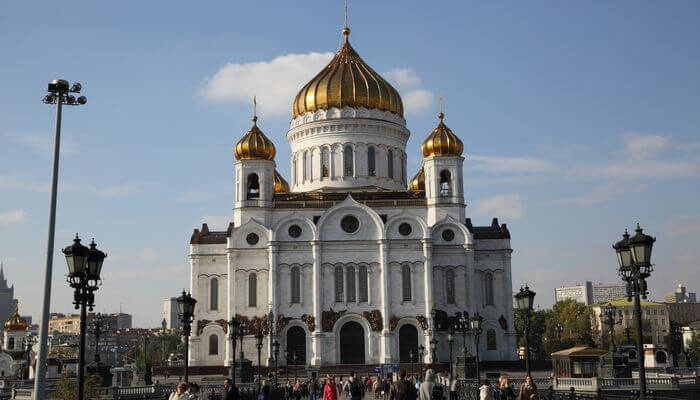
The white marble walls of Christ the Saviour Cathedral are awe-inspiring. As you approach this tallest Orthodox Christian church, you may notice the bronze sculptures, magnificent arches, and cupolas that were created to commemorate Russia’s victory against Napoleon.

How to Get a Decent Haircut in a Foreign Country
Unfortunately, the current Cathedral is a replica, since original was blown to bits in 1931 by the Soviet government. The new cathedral basically follows the original design, but they have added some new elements such as marble high reliefs.
Home to some precious collection of artworks, in Tretyakov Gallery you can find more than 150,000 of works spanning centuries of artistic endeavor. Originally a privately owned gallery, it now has become one of the largest museums in Russia. The Gallery is often considered essential to visit. But I have encountered a lot of locals who have never been there.
Famous for its souvenirs, musicians, and theaters, Arbat street is among the few in Moscow that were turned into pedestrian zones. Arbat street is usually very busy with tourists and locals alike. My local friend once called it the oldest street in Moscow dating back to 1493. It is a kilometer long walking street filled with fancy gift shops, small cozy restaurants, lots of cute cafes, and street artists. It is closed to any vehicular traffic, so you can easily stroll it with kids.
Day 3 – Moscow River Boat Ride, Poklonnaya Hill Victory Park, the Moscow City
Metro Station: Kievskaya and Park Pobedy on Dark Blue Line / Vystavochnaya on Light Blue Line
Voyaging along the Moscow River is definitely one of the best ways to catch a glimpse of the city and see the attractions from a bit different perspective. Depending on your Moscow itinerary, travel budget and the time of the year, there are various types of boats available. In the summer there is no shortage of boats, and you’ll be spoiled for choice.

Travel Itinerary for One Week in Beijing
If you find yourself in Moscow during the winter months, I’d recommend going with Radisson boat cruise. These are often more expensive (yet comfy). They offer refreshments like tea, coffee, hot chocolate, and, of course, alcoholic drinks. Prices may vary but mostly depend on your food and drink selection. Find their main pier near the opulent Ukraine hotel . The hotel is one of the “Seven Sisters”, so if you’re into the charm of Stalinist architecture don’t miss a chance to stay there.
The area near Poklonnaya Hill has the closest relation to the country’s recent past. The memorial complex was completed in the mid-1990s to commemorate the Victory and WW2 casualties. Also known as the Great Patriotic War Museum, activities here include indoor attractions while the grounds around host an open-air museum with old tanks and other vehicles used on the battlefield.
How I Planned My Trip to Vietnam
The hallmark of the memorial complex and the first thing you see as you exit metro is the statue of Nike mounted to its column. This is a very impressive Obelisk with a statue of Saint George slaying the dragon at its base.
Maybe not as impressive as Shanghai’s Oriental Pearl Tower , the skyscrapers of the Moscow City (otherwise known as Moscow International Business Center) are so drastically different from dull Soviet architecture. With 239 meters and 60 floors, the Empire Tower is the seventh highest building in the business district.
The observation deck occupies 56 floor from where you have some panoramic views of the city. I loved the view in the direction of Moscow State University and Luzhniki stadium as well to the other side with residential quarters. The entrance fee is pricey, but if you’re want to get a bird’s eye view, the skyscraper is one of the best places for doing just that.
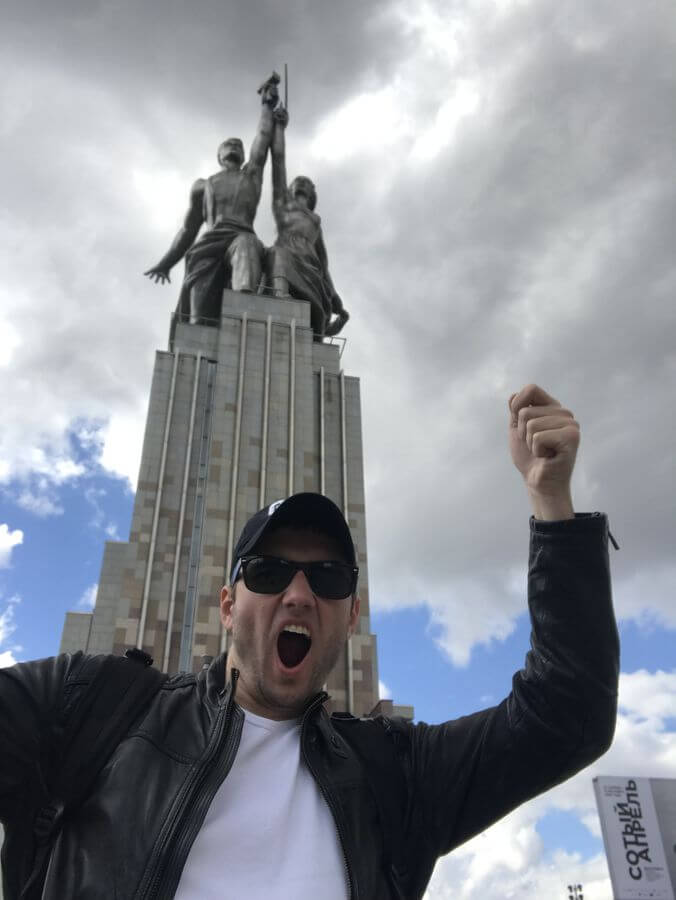
Day 4 – VDNKh, Worker and Collective Farm Woman Monument, The Ostankino TV Tower
Metro Station: VDNKh on Orange Line
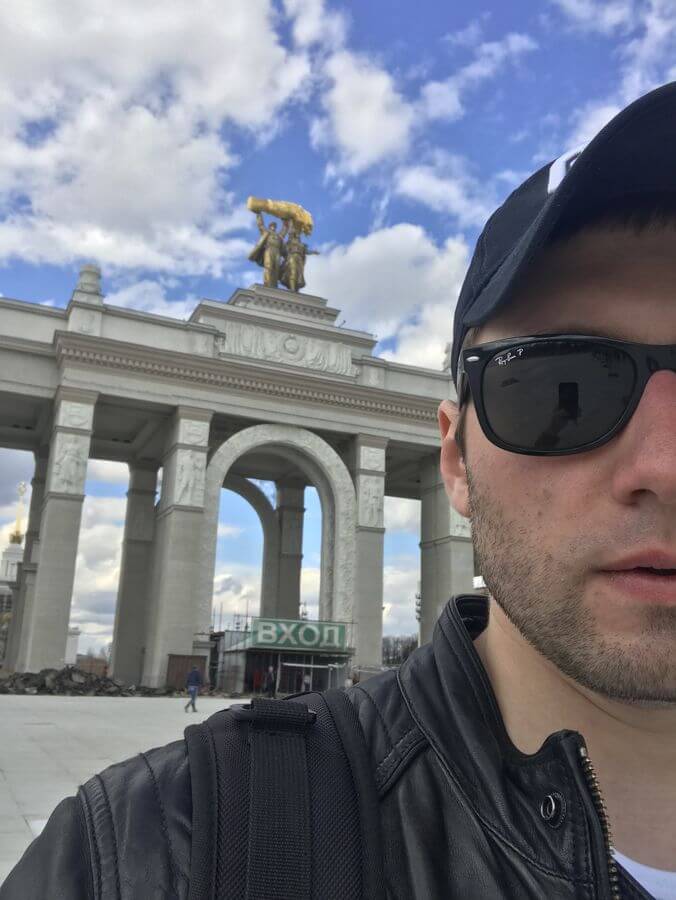
VDNKh is one of my favorite attractions in Moscow. The weird abbreviation actually stands for Russian vystavka dostizheniy narodnogo khozyaystva (Exhibition of Achievements of the National Economy). With more than 200 buildings and 30 pavilions on the grounds, VDNKh serves as an open-air museum. You can easily spend a full day here since the park occupies a very large area.

Places to Visit in Barcelona That Aren’t Beaches
First, there are pavilions that used to showcase different cultures the USSR was made of. Additionally, there is a number of shopping pavilions, as well as Moskvarium (an Oceanarium) that features a variety of marine species. VDNKh is a popular venue for events and fairs. There is always something going on, so I’d recommend checking their website if you want to see some particular exhibition.
A stone’s throw away from VDNKh there is a very distinctive 25-meters high monument. Originally built in 1937 for the world fair in Paris, the hulking figures of men and women holding a hammer and a sickle represent the Soviet idea of united workers and farmers. It doesn’t take much time to see the monument, but visiting it gives some idea of the Soviet Union’s grandiose aspirations.
I have a thing for tall buildings. So to continue my travel itinerary for one week in Moscow I decided to climb the fourth highest TV tower in the world. This iconic 540m tower is a fixture of the skyline. You can see it virtually from everywhere in Moscow, and this is where you can get the best panoramic views (yep, even better than Empire skyscraper).
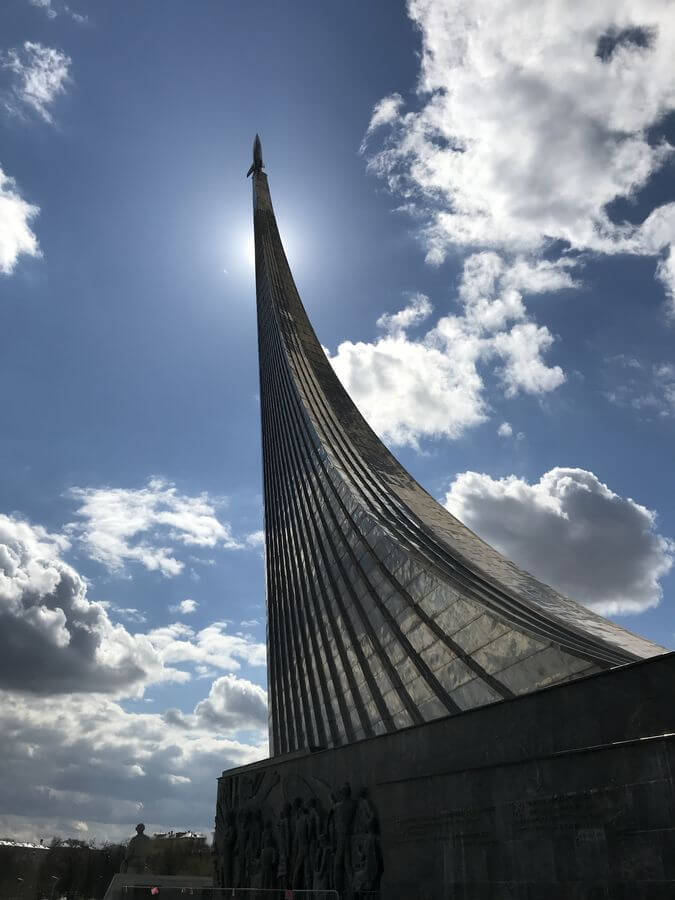

Parts of the floor are made of tempered glass, so it can be quite scary to exit the elevator. But trust me, as you start observing buildings and cars below, you won’t want to leave. There is only a limited number of tickets per day, so you may want to book online. Insider tip: the first tour is cheaper, you can save up to $10 if go there early.
Day 5 – A Tour To Moscow Manor Houses
Metro Station: Kolomenskoye, Tsaritsyno on Dark Green Line / Kuskovo on Purple Line
I love visiting the manor houses and palaces in Moscow. These opulent buildings were generally built to house Russian aristocratic families and monarchs. Houses tend to be rather grand affairs with impressive architecture. And, depending on the whims of the owners, some form of a landscaped garden.
During the early part of the 20th century though, many of Russia’s aristocratic families (including the family of the last emperor) ended up being killed or moving abroad . Their manor houses were nationalized. Some time later (after the fall of the USSR) these were open to the public. It means that today a great many of Moscow’s finest manor houses and palaces are open for touring.

20 Travel Tips I’ve Learned From Travelling The World
There are 20 manor houses scattered throughout the city and more than 25 in the area around. But not all of them easily accessible and exploring them often takes a lot of time. I’d recommend focusing on three most popular estates in Moscow that are some 30-minute metro ride away from Kremlin.
Sandwiched between the Moscow River and the Andropov Avenue, Kolomenskoye is a UNESCO site that became a public park in the 1920’s. Once a former royal estate, now it is one of the most tranquil parks in the city with gorgeous views. The Ascension Church, The White Column, and the grounds are a truly grand place to visit.
You could easily spend a full day here, exploring a traditional Russian village (that is, in fact, a market), picnicking by the river, enjoying the Eastern Orthodox church architecture, hiking the grounds as well as and wandering the park and gardens with wildflower meadows, apple orchards, and birch and maple groves. The estate museum showcases Russian nature at its finest year-round.
12 Stunning National Parks and Regional Parks In France
If my travel itinerary for one week in Moscow was a family tree, Tsaritsyno Park would probably be the crazy uncle that no-one talks about. It’s a large park in the south of the city of mind-boggling proportions, unbelievable in so many ways, and yet most travelers have never heard of it.
The palace was supposed to be a summer home for Empress Catherine the Great. But since the construction didn’t meet with her approval the palace was abandoned. Since the early 1990’s the palace, the pond, and the grounds have been undergoing renovations. The entire complex is now looking brighter and more elaborately decorated than at possibly any other time during its history. Like most parks in Moscow, you can visit Tsaritsyno free of charge, but there is a small fee if you want to visit the palace.

How To Stop Procrastinating When Trip Planning
Last, but by no means least on my Moscow itinerary is Kuskovo Park . This is definitely an off-the-beaten-path place. While it is not easily accessible, you will be rewarded with a lack of crowds. This 18th-century summer country house of the Sheremetev family was one of the first summer country estates of the Russian nobility. And when you visit you’ll quickly realize why locals love this park.
Like many other estates, Kuskovo has just been renovated. So there are lovely French formal garden, a grotto, and the Dutch house to explore. Make sure to plan your itinerary well because the estate is some way from a metro station.
Day 6 – Explore the Golden Ring
Creating the Moscow itinerary may keep you busy for days with the seemingly endless amount of things to do. Visiting the so-called Golden Ring is like stepping back in time. Golden Ring is a “theme route” devised by promotion-minded journalist and writer Yuri Bychkov.
Having started in Moscow the route will take you through a number of historical cities. It now includes Suzdal, Vladimir, Kostroma, Yaroslavl and Sergiev Posad. All these awe-inspiring towns have their own smaller kremlins and feature dramatic churches with onion-shaped domes, tranquil residential areas, and other architectural landmarks.
Two Weeks In Thailand: The Perfect 14-Day Itinerary
I only visited two out of eight cities included on the route. It is a no-brainer that Sergiev Posad is the nearest and the easiest city to see on a day trip from Moscow. That being said, you can explore its main attractions in just one day. Located some 70 km north-east of the Russian capital, this tiny and overlooked town is home to Trinity Lavra of St. Sergius, UNESCO Site.

You Will Also Like: 3-Day London Itinerary
Sergiev Posad is often described as being at the heart of Russian spiritual life. So it is uncommon to see the crowds of Russian pilgrims showing a deep reverence for their religion. If you’re traveling independently and using public transport, you can reach Sergiev Posad by bus (departs from VDNKh) or by suburban commuter train from Yaroslavskaya Railway Station (Bahnhof). It takes about one and a half hours to reach the town.
Trinity Lavra of St. Sergius is a great place to get a glimpse of filling and warming Russian lunch, specifically at the “ Gostevaya Izba ” restaurant. Try the duck breast, hearty potato and vegetables, and the awesome Napoleon cake.
Day 7 – Gorky Park, Izmailovo Kremlin, Patriarch’s Ponds
Metro Station: Park Kultury or Oktyabrskaya on Circle Line / Partizanskaya on Dark Blue Line / Pushkinskaya on Dark Green Line
Gorky Park is in the heart of Moscow. It offers many different types of outdoor activities, such as dancing, cycling, skateboarding, walking, jogging, and anything else you can do in a park. Named after Maxim Gorky, this sprawling and lovely park is where locals go on a picnic, relax and enjoy free yoga classes. It’s a popular place to bike around, and there is a Muzeon Art Park not far from here. A dynamic location with a younger vibe. There is also a pier, so you can take a cruise along the river too.

How to Save Money While Traveling in Europe
The Kremlin in Izmailovo is by no means like the one you can find near the Red Square. Originally built for decorative purposes, it now features the Vernissage flea market and a number of frequent fairs, exhibitions, and conferences. Every weekend, there’s a giant flea market in Izmailovo, where dozens of stalls sell Soviet propaganda crap, Russian nesting dolls, vinyl records, jewelry and just about any object you can imagine. Go early in the morning if you want to beat the crowds.
All the Bulgakov’s fans should pay a visit to Patriarch’s Ponds (yup, that is plural). With a lovely small city park and the only one (!) pond in the middle, the location is where the opening scene of Bulgakov’s novel Master and Margarita was set. The novel is centered around a visit by Devil to the atheistic Soviet Union is considered by many critics to be one of the best novels of the 20th century. I spent great two hours strolling the nearby streets and having lunch in the hipster cafe.
Conclusion and Recommendations
To conclude, Moscow is a safe city to visit. I have never had a problem with getting around and most locals are really friendly once they know you’re a foreigner. Moscow has undergone some serious reconstruction over the last few years. So you can expect some places to be completely different. I hope my one week Moscow itinerary was helpful! If you have less time, say 4 days or 5 days, I would cut out day 6 and day 7. You could save the Golden Ring for a separate trip entirely as there’s lots to see!
What are your thoughts on this one week Moscow itinerary? Are you excited about your first time in the city? Let me know in the comments below!
JOIN MY FREE WEEKLY NEWSLETTER!
Email Address *
YOU WILL ALSO LIKE

10 Dishes You Must Try When Going To Moscow

15 Fantastic and Easy Day Trips Close to Moscow

When Is the Best Time To Visit Russia
24 comments.
Ann Snook-Moreau
Moscow looks so beautiful and historic! Thanks for including public transit information for those of us who don’t like to rent cars.
MindTheTravel
Yup, that is me 🙂 Rarely rent + stick to the metro = Full wallet!

Mariella Blago
Looks like you had loads of fun! Well done. Also great value post for travel lovers.
Thanks, Mariella!
I have always wanted to go to Russia, especially Moscow. These sights look absolutely beautiful to see and there is so much history there!
Agree! Moscow is a thousand-year-old city and there is definitely something for everyone.
Tara Pittman
Those are amazing buildings. Looks like a place that would be amazing to visit.
Adriana Lopez
Never been to Moscow or Russia but my family has. Many great spots and a lot of culture. Your itinerary sounds fantastic and covers a lot despite it is only a short period of time.
What was their favourite thing about Russia?
Gladys Parker
I know very little about Moscow or Russia for the\at matter. I do know I would have to see the Red Square and all of its exquisite architectural masterpieces. Also the CATHEDRAL OF CHRIST THE SAVIOUR. Thanks for shedding some light on visiting Moscow.
Thanks for swinging by! The Red Square is a great starting point, but there way too many places and things to discover aside from it!
Ruthy @ Percolate Kitchen
You are making me so jealous!! I’ve always wanted to see Russia.
Moscow is in my bucket list, I don’t know when I can visit there, your post is really useful. As a culture rich place we need to spend at least week.
DANA GUTKOWSKI
Looks like you had a great trip! Thanks for all the great info! I’ve never been in to Russia, but this post makes me wanna go now!
Wow this is amazing! Moscow is on my bucket list – such an amazing place to visit I can imagine! I can’t wait to go there one day!
The building on the second picture looks familiar. I keep seeing that on TV.
Reesa Lewandowski
What beautiful moments! I always wish I had the personality to travel more like this!
Perfect itinerary for spending a week in Moscow! So many places to visit and it looks like you had a wonderful time. I would love to climb that tower. The views I am sure must have been amazing!
I was lucky enough to see the skyline of Moscow from this TV Tower and it is definitely mind-blowing.
Chelsea Pearl
Moscow is definitely up there on my travel bucket list. So much history and iconic architecture!
Thumbs up! 🙂
Blair Villanueva
OMG I dream to visit Moscow someday! Hope the visa processing would be okay (and become more affordable) so I could pursue my dream trip!
Yup, visa processing is the major downside! Agree! Time and the money consuming process…
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
My website uses cookies so that I can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to my website and helping me to understand which sections of Mind The Travel you find most interesting and useful.
You can adjust all of your cookie settings by navigating the tabs on the left hand side.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that I can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, I will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit my website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 15 March 2024
Metagenomic insights into the wastewater resistome before and after purification at large‑scale wastewater treatment plants in the Moscow city
- Shahjahon Begmatov 1 ,
- Alexey V. Beletsky 1 ,
- Alexander G. Dorofeev 2 ,
- Nikolai V. Pimenov 2 ,
- Andrey V. Mardanov 1 &
- Nikolai V. Ravin 1
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 6349 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
805 Accesses
Metrics details
- Antimicrobials
- Microbial communities
- Industrial microbiology
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are considered to be hotspots for the spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). We performed a metagenomic analysis of the raw wastewater, activated sludge and treated wastewater from two large WWTPs responsible for the treatment of urban wastewater in Moscow, Russia. In untreated wastewater, several hundred ARGs that could confer resistance to most commonly used classes of antibiotics were found. WWTPs employed a nitrification/denitrification or an anaerobic/anoxic/oxic process and enabled efficient removal of organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as fecal microbiota. The resistome constituted about 0.05% of the whole metagenome, and after water treatment its share decreased by 3–4 times. The resistomes were dominated by ARGs encoding resistance to beta-lactams, macrolides, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, quaternary ammonium compounds, and sulfonamides. ARGs for macrolides and tetracyclines were removed more efficiently than beta-lactamases, especially ampC , the most abundant ARG in the treated effluent. The removal efficiency of particular ARGs was impacted by the treatment technology. Metagenome-assembled genomes of multidrug-resistant strains were assembled both for the influent and the treated effluent. Ccomparison of resistomes from WWTPs in Moscow and around the world suggested that the abundance and content of ARGs depend on social, economic, medical, and environmental factors.
Similar content being viewed by others

Metagenomic analysis of an urban resistome before and after wastewater treatment
Mobile resistome of microbial communities and antimicrobial residues from drinking water supply systems in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Differential effects of wastewater treatment plant effluents on the antibiotic resistomes of diverse river habitats
Introduction.
The spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the environmental microbiome has become one of the frequently noted problems in recent years, along with global climate change, food security and other technological challenges. Numerous studies show that from year to year, in addition to increasing the cost of hospitalization and treatment of patients infected with multidrug-resistant bacteria, the number of deaths of such patients is growing 1 , 2 . Understanding the mechanisms underlying the emergence, selection and dissemination of AMR, and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), is required for the development of sustainable strategies to control and minimize this threat. The dissemination of antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) and ARGs occurs differently and this process is more active in urban territories rather than in rural ones. The rate of spread of ARGs and ARB in urban areas is obviously determined by the high population density and, as a rule, wastewater which flows from these areas contains both ARG and ARB. Most antibiotics used in medicine, agriculture and the food industry, as well as resistant bacteria, end up in wastewater. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) therefore could provide a comprehensive overview of ARG abundance, diversity and genomic backgrounds in particular region 3 . Moreover, wastewater and WWTPs are places where ARGs and ARB are particularly abundant and are often considered “hotspots” for the formation of strains with multiple resistance and one of the main sources of the spread of AMR in the environment 4 .
Despite numerous studies on the role of WWTPs in resistome diversity and dissemination, each new study is, in terms of time and geography, unique, as many urban areas and countries have not yet been studied. In addition, some studies are dedicated to explore only one component of the wastewater treatment system, such as wastewater, activated sludge or treated effluent, and there is a lack of research that would give a comprehensive view of the diversity and change in the composition of the resistome at different stages of water cleaning, from wastewater to treated effluent, released into the environment.
Usually, wastewater treatment in large facilities takes place in three stages. The first stage includes physical methods of water cleaning, the second stage is microbiological treatment in bioreactors with activated sludge (AS), and the third stage is the final treatment of water and its disinfection. At the second stage, than could be performed using several technologies, microorganisms of AS are used to remove organic matter, ammonium, and (in more complex processes) phosphorus 5 . At this stage, the removal of microorganisms present in the wastewater, including ARB, occurs due to their adsorption on AS particles, which are removed along with excess AS. The efficiency of this process differs for various bacteria and depends on the purification technology used. Therefore, purification technologies directly affect the removal of particular ARGs and ARB, however, this issue was poorly studied 6 .
ARGs representing all known resistance mechanisms have been found in WWTP environments 7 . ARGs for beta-lactams, macrolides, quinolones, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and multidrug efflux pump genes have been found in the incoming wastewater, AS, and treated effluent in various countries 7 , 8 . Recently, Munk and coauthors (2022) using metagenomics methods characterized resistomes of 757 urban wastewater samples from 243 cities in 101 countries covering 7 major geographical regions. They reported regional patterns in wastewater resistomes that differed between subsets corresponding to drug classes and were partly driven by taxonomic variation 3 . Although this study did not analyzes the composition of the wastewater resistome after treatment, there are numerous evidences that the prevalence of ARB and ARG in rivers may increase downstream from the point of discharge of treated wastewater into them 9 , 10 . In a study of WWTPs in Germany, 123 types of clinically significant antibiotic resistance genes were found in treated wastewater discharged into water bodies 11 . An analysis of the presence of 30 ARGs at different stages of wastewater treatment at WWTPs in Northern China showed that the content of most ARGs in the treated effluent was lower compared to the influent entering the treatment, although an increase in the abundance of some ARGs and their release into the environment was also observed 12 . A metagenomic analysis of WWTP in Hong Kong revealed seasonal changes in the content of several types of ARG and its decrease in the treated effluent 13 , 14 . Most ARGs were reduced by more than 98% in the treated effluent compared to the wastewater entering the treatment 14 . Some other studies have also reported a decrease in ARGs after wastewater treatment 15 , 16 , 17 . However, in other studies, no changes in the ARG content or even an increase were observed 17 , 18 , 19 . Although there are numerous studies of resistomes in WWTP-related environments the distribution of samples was geographically biased and covered mostly North America, Western Europe, Eastern Asia (mostly China), Australasia, and few places in South America/Caribbean and Sub-Saharan Africa 3 .
In order to expand the geographical coverage and our knowledge about global resistome abundance and diversity, we analyzed resistomes of wastewater before and after treatment at large-scale WWTPs in the city of Moscow (Russia). Although Moscow WWTPs are among the largest in the world and may play an important role in the spread of antibiotic resistance, the resistomes of municipal wastewaters in Moscow have not previously been studied by modern molecular genetic methods. Previously we performed 16S rRNA gene profiling of AS microbial communities at large-scale WWTPs responsible for the treatment of municipal wastewater ion Moscow 5 . Comparison of microbial communities of AS samples from WWTPs in Moscow and worldwide revealed that Moscow samples clustered together indicating the importance of influent characteristics, related to local social and environmental factors, for wastewater microbiomes 5 . For example, due to the relatively low cost of water for household consumption, wastewater in Moscow has a relatively low content of organic matter. Apparently the presence of ARB and ARGs in communal wastewater depends on the frequency of antibiotic use and the range of drugs used. These factors differ in different countries and cities. Therefore, the characterization of the resistome and the role of Moscow WWTPs in the dispersion of ARGs is an important goal. Of particular interest is also the assessment of the impact of wastewater treatment technology on the composition of the resistome and the degree of ARG removal.
Here we present the first metagenomic overview of the composition of resistome of influent wastewater, AS and treated effluent released into the environment at two Moscow WWTPs employing different treatment technologies.
Characteristics of WWTPs and water chemistry
The Lyuberetskiy WWTP complex of JSC “Mosvodokanal” carry out the treatment of wastewater in the city of Moscow with a capacity of about 2 million m 3 per day. This complex consists of several wastewater treatment units (hereafter referred to as WWTPs). They purify the same inflow wastewater but otherwise are independent installations between which there is no transfer and mixing of AS. Two WWTPs implementing different technologies for wastewater treatment were chosen as the objects of study. The first one (LOS) is operated using anaerobic/anoxic/oxic process, also known as the University of Cape Town (UCT) technology. There the sludge mixture first enters the anaerobic zone, where phosphate-accumulating microorganisms (PAO) consume easily degradable organics, then to the anoxic zone, where denitrification and accumulation of phosphates by denitrifying PAO occur, and finally to the aerobic zone, where organic matter and ammonium are oxidized while PAO accumulate large quantities of polyphosphate. The second WWTP (NLOS2) uses a simpler nitrification–denitrification technology (N-DN). In the aerobic zones organics and ammonium are oxidized, while in the anoxic zone nitrate is reduced to gaseous nitrogen. This treatment technology removes organic matter and nitrogen, but was not specially aimed to remove phosphates. The production capacity of LOS is approximately 2 times more than that of NLOS2; there are no other important differences between these WWTPs besides treatment technology.
Sampling and chemical analysis
Wastewater and AS samples were collected in September 2022 and kindly provided by “Mosvodokanal” JSC. The temperature of water samples was about 24 °C. Samples of AS from bioreactors of two WWTPs were taken in 50 ml Falcon tubes (BD Biosciences). Wastewater samples (influent and effluents from two WWTPs) were taken in 5 L plastic bottles. The cells were collected by centrifugation at 3000 g for 20 min at 4 °C.
Wastewater quality values, namely, biochemical oxygen demand (five days incubation) (BOD 5 ), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), sludge volume index (SVI), ammonium nitrogen (N-NH 4 ), nitrate nitrogen (N-NO 3 ), nitrite nitrogen (N-NO 2 ) and phosphorus (P-PO 4 ) in the influent and effluents of two WWTPs were measured by the specialized laboratory “MSULab” according to the Federal inspection of environmental management’s protocols for chemical analyses of water.
DNA isolation, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and analysis
Total genomic DNA was isolated using a Power Soil DNA isolation kit (Qiagen, Germany). DNA for each sample was isolated in four parallel replicates, which were then pooled. PCR amplification of 16S rRNA gene fragments comprising the V3–V4 variable regions was performed using the universal primers 341F (5′-CCTAYG GGDBGCWSCAG) and 806R (5′-GGA CTA CNVGGG THTCTAAT) 20 . The obtained PCR fragments were bar-coded and sequenced on Illumina MiSeq (2 × 300 nt reads). Pairwise overlapping reads were merged using FLASH v.1.2.11 21 . All sequences were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at 97% identity using the USEARCH v.11 program 22 . Low quality reads were removed prior to clustering, chimeric sequences and singletons were removed during clustering by the USEARCH algorithms. To calculate OTU abundances, all reads obtained for a given sample were mapped to OTU sequences at a 97% global identity threshold by USEARCH. The taxonomic assignment of OTUs was performed by searching against the SILVA v.138 rRNA sequence database using the VSEARCH v. 2.14.1 algorithm 23 .
The diversity indices at a 97% OTU cut-off level were calculated using USEARCH v.11 22 . To avoid sequencing depth bias, the numbers of reads for each sample were randomly sub-sampled to the size of the smallest set.
Sequencing of metagenomic DNA, contigs assembly and binning of MAGs
Metagenomic DNA was sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq2500 platform according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The sequencing of a paired-end (2 × 150 bp) NEBNext Ultra II DNA Library prep kit (NEB) generated from 145 to 257 million read pairs per sample. Adapter removal and trimming of low-quality sequences (Q < 30) were performed using Cutadapt v.3.4 24 and Sickle v.1.33 ( https://github.com/najoshi/sickle ), respectively. The resulting Illumina reads were de novo assembled into contigs using SPAdes v.3.15.4 in metagenomic mode 25 .
The obtained contigs were binned into metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs) using 3 different programs: MetaBAT v.2.2.15 26 , MaxBin v.2.2.7 27 and CONCOCT v.1.1.0 28 . The results of the three binning programs were merged into an optimized set of MAGs using DAS Tool v.1.1.4 29 . The completeness of the MAGs and their possible contamination (redundancy) were estimated using CheckM v.1.1.3 30 with lineage-specific marker genes. The assembled MAGs were taxonomically classified using the Genome Taxonomy Database Toolkit (GTDB-Tk) v.2.0.0 31 and Genome Taxonomy database (GTDB) 32 .
ARG identification
Open reading frames (ORFs) were predicted in assembled contigs using Prodigal v.2.6.3 33 . ARGs were predicted using the NCBI AMRFinderPlus v.3.11.4 ( https://github.com/ncbi/amr/wiki ) command line tool and its associated database 34 . The predicted protein sequences of all ORFs were analyzed in this tool with parameter “-p”.
Efficiency of wastewater treatment
Two wastewater treatment technologies were used in the investigated WWTPs,—nitrification/denitrification at NLOS2 and more advanced anaerobic/anoxic/oxic UCT process at LOS. LOS removed more than 99.5% of organic matter (according to the BOD5 data) and more than 99.9% of ammonium while the performance of NLOS2 was poorer (Table 1 ). Particularly noticeable differences were observed in nitrate and nitrite concentrations in the effluents suggesting the lower efficiency of denitrification in the NLOS2. Interestingly, although the NLOS2 unit was not designed to remove phosphorus, the concentration of phosphates in the treated effluent at this WWTP is only slightly higher than at LOS. The treated influent at LOS contains fewer solids consistently with lower SVI. Overall, the technology used at LOS plant is more efficient.
Microbiomes of the influent wastewater, activated sludge and treated effluent
The 16S rRNA gene profiling of microbial communities revealed 1013 species-level OTUs (97% identity) in the influent and 1.2–1.7 times more OTUs in the AS and treated effluent samples (Supplemental Table S1 ). The Shannon diversity indices correlated with the number of detected OTUs and increased in the series “influent” – “activated sludge” – “effluent” at each WWTP (Supplemental Table S2 ).
Analysis of the microbiome of wastewater supplied for biological treatment showed that that the most numerous phyla in the microbial community were Firmicutes (28.4% of all 16S rRNA gene sequences), Campylobacterota (28.0%), Proteobacteria (20.9%), and Bacteroidota (10.5%) (Fig. 1 ). These were mainly representatives of the fecal microbiota, which are often found in wastewater. The phylum Firmicutes was dominated by Streptococcaceae (9.7%, mostly S treptococcus sp.), Lachnospiraceae (5.9%), Ruminococcaceae (3.0%), Carnobacteriaceae (1.7%), Peptostreptococcaceae (1.6%) and Veillonellaceae (1.4%). Most of Campylobacterota belonged to the family Arcobacteraceae (26.8%) of the genera Arcobacter (19.9%), Pseudarcobacter (2.5%) and uncultured lineage (4.3%), as well as by sulfur-oxidizing Sulfurospirillum (1.0%). Among the Proteobacteria the most abundant genera were Acinetobacter (7.8%) , Aeromonas (1.8%) and Pseudomonas (1.1%). Most of the identified Bacteroidota were typical fecal contaminants such as members of the genera Bacteroides (2.6%), Macellibacteroides (1.5%), Prevotella (1.4%), and Cloacibacterium (1.2%).
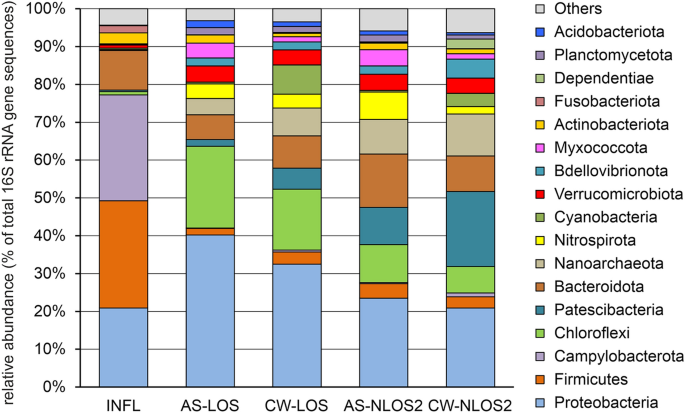
Microbial community composition in the influent, AS and treated effluent samples according to 16S rRNA gene profiling. The composition is displayed at the phylum level. INFL, influent wastewater; AS-LOS, AS at LOS plant; CW-LOS, treated effluent at LOS plant; AS-NLOS2, AS at NLOS2 plant; CW-NLOS2, treated effluent at NLOS2 plant.
Activated sludge of WWTP bioreactors is a complex microbial community consisting of physiologically and phylogenetically heterogeneous groups of microorganisms involved in the removal of major contaminants from wastewater. The composition of AS microbiomes was very different from the microbiome of incoming wastewater (Fig. 1 ). The phyla Campylobacterota (less than 0.5%) and Firmicutes (2–4%) were much less abundant in AS microbiomes. Proteobacteria was the dominant group in the microbiomes of AS (23–40%), but its composition differed from the microbiome of influent wastewater: instead of the fecal microflora (Enterobacterales and others) the AS community harbored lineages involved in the purification processes ( Competibacteraceae , Rhodocyclaceae , Nitrosomonadaceae , etc.). Likewise, Bacteroidota were among the most numerous phyla in AS microbiomes at both LOS (6.5%) and NLOS2 (14.1%), but instead of Bacteroidales mostly comprised Chitinophagales and Sphingobacteriales typical for AS communities. The numerous groups of AS community also included Chloroflexi (22% and 10% in LOS and NLOS2, respectively), Patescibacteria (1.8% and 9.9%), Nanoarchaeota (4.3% and 9.1%), Nitrospirota (3.9% and 7.3%), Verrucomicrobiota and Myxococcota (about 4% in both WWTPs). Bacteria that play an important role in the removal of nitrogen ( Nitrospira and Nitrosomonas ) and phosphorus ( Dechloromonas ), as well as glycogen-accumulating Ca . Competibacter, have been found in large numbers. The abundance of these functional groups is consistent with the high efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
The main source of microorganisms in treated effluent is the AS, from which they are washed out; bacteria from the influent water may also be present in minor amounts. Therefore, as expected, the microbiome composition of treated wastewater was similar to that of activated sludge. Consistently, compositions of microbiomes of treated effluent were similar to that of AS samples. However, some differences were observed, in particular, the microbiomes of the treated effluent contained many Cyanobacteria (7.74% and 3.49% for LOS and NLOS2, respectively) which were found in minor amounts both in the influent water and in the ASs (< 0.5%). Probably, these light-dependent bacteria proliferate in the final clarifier and then can be easily washed out with the effluent.
Diversity of resistomes
The results of metagenomic analysis of incoming wastewater revealed 544 ARGs in the assembled contigs, classified into 33 AMR gene families (Table 2 and Supplemental Table S3 ). Among the most numerous were classes A, C, D and metallo- beta-lactamases, rifampin ADP-ribosyltransferase, Erm 23S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase, aminoglycoside nucleotidyl-, acetyl- and phospho-transferases, the ABC-F type ribosomal protection proteins, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, trimethoprim-resistant dihydrofolate reductase, quaternary ammonium compound efflux SMR transporters, lincosamide nucleotidyltransferases, tetracycline efflux MFS transporters and tetracycline resistance ribosomal protection proteins (Table 2 ). These genes may enable antibiotic inactivation (373 genes), target protection (85 genes), efflux (44 genes) and target replacement (25 genes).
The abovementioned genes confer resistance to most of commonly used drugs: beta-lactams (198 genes), macrolides (74 genes), rifamycin (60 genes), aminoglycosides (51 genes), tetracycline (27 genes), phenicols (27 genes), diaminopyrimidines (19 genes), quaternary ammonium compounds (16 genes), glycopeptides (15 genes), lincosamide (13 genes), fosfomycine (12 genes) and drugs of 11 others classes (Fig. 2 ).
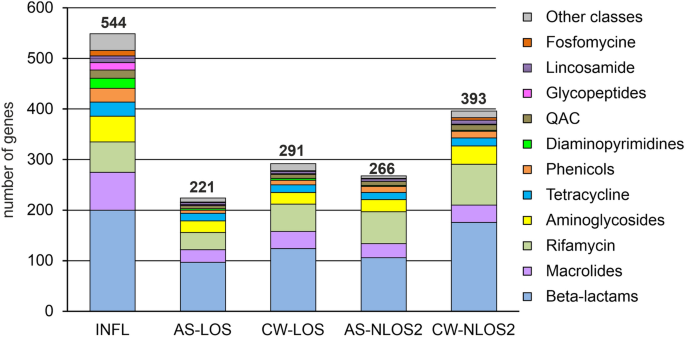
ARGs identified in wastewater and AS samples categorized by drug classes.
About twice less ARGs were identified in AS samples from both WWTPs. Like in the influent, beta-lactamases of classes A, D, and metallo-beta-lactamases were the most numerous, while only a few genes for class C enzymes were found (Table 2 ). Other families of ARGs, numerous in the influent, were also numerous in AS microbiomes. A notable difference between the resistomes of the AS samples is the greater number of rifampin-ADP-ribosyltransferase genes ( arr ) in NLOS2 compared to LOS (63 vs 33). The largest number of arr genes was assigned to Bacteroidota, and the lower relative abundance of this phylum in AS at LOS likely explains these differences. Like in the wastewater, resistance to beta-lactams, macrolides, rifamycin, aminoglycosides, and tetracyclines was the most common (Fig. 2 ). On the contrary, genes for some drug classes were underrepresented in AS resistomes, especially for diaminopyrimidines (3 and 2 genes for LOS and NLOS2, respectively) and glycopeptide antibiotics (2 and 0 genes).
The results of metagenomic analysis of treated effluent showed that the diversity of these resistomes was only slightly higher than that of the corresponding AS samples. This result was expected since the main source of microorganisms in the effluent is activated sludge, from which they are partially washed. However, resistomes of treated effluent at both WWTPs contains about twice more class A beta-lactamase genes than AS samples suggesting less efficient absorption of their host bacteria at AS particles (Table 2 ).
Quantitative analysis of antibiotic resistance genes of WWTP
The results described above provide information on the diversity of resistance genes, but not on their abundance in the metagenomes, which depends on the abundance of corresponding bacterial hosts. To quantify the shares of individual ARGs in the metagenome and resistome, the amounts of metagenomic reads mapped to the corresponding ARGs in contigs were determined. In total, the resistome accounted for about 0.05% of the metagenome of wastewater supplied for treatment, while the shares of resistomes in the metagenomes of AS and treated effluent samples were 0.02% and 0.014% at the LOS and NLOS2 WWTPs, respectively.
Quantitative analysis of the content of individual ARGs in metagenomes showed that the structure of the influent resistome was very different from that of AS and treated effluent. The relative content of ARGs accounting for more than 1% in at least one analyzed resistome is shown in Fig. 3 . The LOS and NLOS2 WWTPs differed significantly from each other, and the differences between the AS and effluent resistomes at each WWTP were much less pronounced.
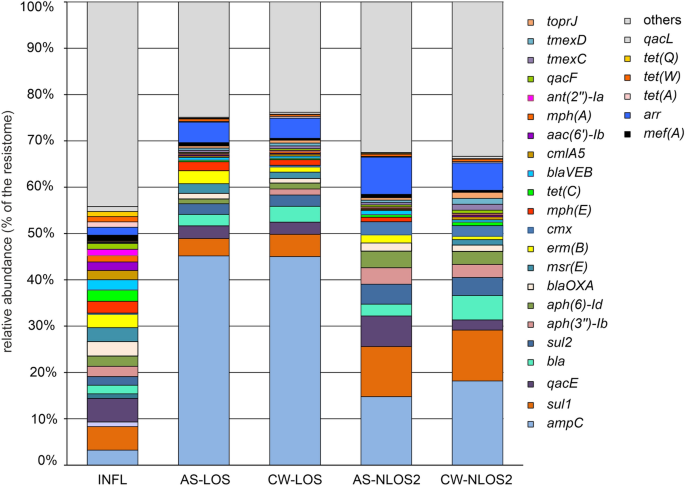
The relative abundancies of particular ARGs in the resistomes. Only ARGs with shares greater than 1% in at least one sample are shown, all other ARGs are shown as “others”.
The resistome of the influent was not only the most diverse, but also the most even in composition. The shares of none of the ARGs exceeded 5% of the resistome, and the 23 most common ARGs accounted for a half of the resistome. The most abundant ten ARGs were qacE, sul1, ampC, blaOXA, msr(E), erm(B), mph(E), tet(C), aph(3'')-Ib and aph(6)-Id, conferring resistance to antiseptics, sulfonamides, beta-lactams, macrolides, aminoglycosides (streptomycin), and tetracyclines.
AS and treated effluent at LOS plant was strongly dominated by a single AGR type, class C beta-lactamase ampC , accounting for about 45% of their resistomes. This gene was also the most abundant one in the resistomes of AS and effluent at NLOS2 (14.8% and 18.2%, respectively). Apparently it originates from the influent wastewater supplied for treatment where its share in the resistome was 3.2%. AmpC β-lactamases are considered clinically important cephalosporinases encoded on the chromosomes and plasmids of various bacteria (especially Enterobacteriaceae ), where they mediate resistance to cephalothin, cefazolin, cefoxitin and most penicillins 35 . Close homologues of this gene, with a nucleotide sequence identity of 99.8–100%, have been found in plasmids and chromosomes of various Proteobacteria ( Thauera, Sphingobium, Aeromonas etc.). Since in all samples ampC was found in short contigs with very high coverage, it is likely widespread in the genomes of various bacteria in different genetic contexts.
The second most abundant ARG in the resistomes of AS samples was sulfonamide-resistant dihydropteroate synthase ( sul1 ). It accounted for 4–5% of AS and treated effluent resistomes in LOS and for about 11% in NLOS2, while its share in the influent water resistome was about 5%. The sul1 gene is usually found in class 1 integrons being linked to other resistance genes, including qacE 36 . Consistently, sul1 and qacE were found in one contig assembled for the influent water samples and assigned to Gammaproteobacteria. Another sulfonamide-resistance gene, sul2 , was also numerous, accounting for about 2% of the resistomes in the influent and LOS samples, and for about 4% in the AS and water treated at NLOS2.
Since ARGs entering the activated sludge and then into the treated effluent originate mostly from wastewater supplied for treatment, the absolute majority of ARGs present in the influent in significant amounts (more than 0.2% resistome) in were also found in AS and effluent samples. The only exception macrolide 2′-phosphotransferase gene mph(B) accounting for 0.51% in the influent resistome. Likewise, all ARGs accounting for more than 0.2% of resistomes in the treated effluent were present also in the influent.
Potential multidrug resistant strains
One of the most important public health problems is the spread of multidrug resistant pathogens (MDR), which refers to resistance to at least one agent in three or more chemical classes of antibiotic (e.g. a beta-lactam, an aminoglycoside, a macrolide) 37 . Such strains can arrive with wastewater entering the treatment, and also form in AS communities. AS are dense and highly competitive microbial communities, which, along with the presence of sublethal concentrations of antibiotics and other toxicants in wastewater, creates ideal conditions not only for the selection of resistant strains, but also for the formation of multiple resistance through horizontal gene transfer 4 . To identify MDR bacteria, we binned metagenomic contigs into metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs) and looked for MAGs comprising several ARGs. Only MAGs with more than 70% completeness and less than 15% contamination were selected for analysis: 117, 56, 72, 94 and 121 for influent, AS of LOS, effluent of LOS, AS of NLOS2 and effluent of NLOS2, respectively. Five MAGs of MDR bacteria were identified in the metagenome of the influent, one—in AS of LOS, two—in the LOS effluent and one in the NLOS2 effluent (Table 3 ). These MAGs were assigned to unclassified genus-level lineages of Ruminococcaceae and Cyclobacteriaceae, Phocaeicola vulgatus, Streptococcus parasuis, Ancrocorticia sp., Enterococcus sp., Bacillus cereus and Undibacterium sp.
Disscussion
We characterized the composition of microbial communities and the resistomes of influent wastewater, activated sludge and treated effluent from two WWTPs in city of Moscow, where various biological water treatment technologies are used. Among the predominant bacteria in the influent wastewater we found mainly fecal contaminants of the genera Collinsella , Bacteroides , Prevotella , Arcobacter , Arcobacteraceae , Blautia , Faecalibacterium, Streptococcus , Acinetobacter , Aeromonas and Veillonella 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 . Previously, we performed 16S rRNA gene profiling of wastewater before and after treatment at one WWTP (LOS) and revealed that all abovementioned potential pathogens were efficiently removed and their relative abundance in the water microbiome decreased by 50‒100 times 44 . Similar pattern of removal of potential pathogenic bacteria was observed here for NLOS2 where another water treatment technology is used.
An important indicator of the dissemination of ARG is the proportion of the resistome in the entire metagenome before and after wastewater treatment. In the influent, the resistome accounted for about 0.05% of the metagenome, which corresponds to approximately two ARGs per bacterial genome. Approximately the same values are typical for most countries 3 . After treatment, the fraction of the resistome in the wastewater metagenomes decreases, but, surprisingly, only by 2–4 times. However, since the total concentration of microorganisms in treated effluent is approximately two orders of magnitude lower than in raw wastewater, it is likely that the total abundance of ARGs in the treated effluent is significantly reduced.
Apparently, fecal contaminants effectively removed during treatment are not the only carriers of ARG in wastewater, which are also found in bacteria characteristic of activated sludge and thus appearing in the effluents. Unfortunately, due to the high diversity of microbiomes and the tendency of ARG to be present in multiple copies in different genomic environments, most of the contigs containing ARG turned out to be short, which did not allow to define their taxonomic affiliation.
The resistome of influent water includes 26 ARGs, the share of which is more than 1%. Among of them the prevalence of ampC, aadA, qacE, bla, qacF and qacL is specific for Moscow WWTPs, since these genes were not among the 50 most common ARGs according to the results of a worldwide analysis of wastewater resistomes in large cities 3 . Different ARGs were most “evenly” represented in the influent wastewater while in the AS and treated effluent, a clear selection of particular types of ARGs was observed, which obviously reflects a change in the composition of microbiomes. A vivid example is the increase in the proportion of ampC in the resistomes, especially at LOS.
The discovered ARGs can confer resistance to most classes of antibiotics and among the resistomes of the studied WWTPs in the city of Moscow, genes conferring resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics were the most common, they accounted for about 26% of the resistome in the water supplied for treatment (Fig. 4 ). Similar values have been observed for wastewater in some other countries, particularly in Eastern Europe and Brazil, where 20 to 25% of reads were assigned to ARGs conferring resistance to beta-lactams 3 . According to data for 2021, beta lactams accounted for about 40% of the total antibiotic consumption in Russia in the medical sector 45 .
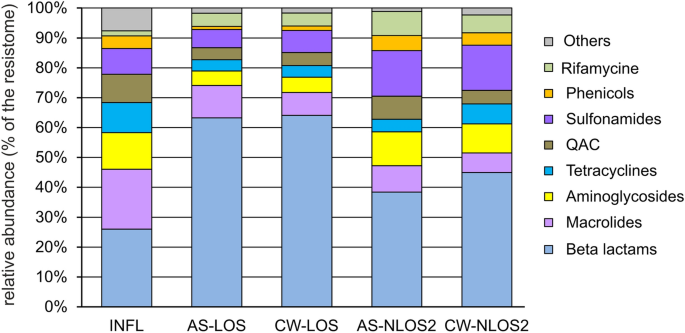
The relative abundancies of ARGs in the resistomes categorized by drug classes.
Like in most wastewater resistomes in different countries, ARGs conferring resistance to macrolides, aminoglycosides and tetracycline were also among the most abundant in wastewater from Moscow (Fig. 4 ). Resistance to macrolides, rather than beta-lactams, was most common in wastewater from most countries in Europe and North America, while in Moscow ARGs to macrolide were the second most common. Macrolides and tetracyclines are also widely used in medicine in Russia (20% and 5% of total antibiotic consumption in 2021, respectively). On the contrary, medical consumption of aminoglycosides in Russia is rather low (< 1% of the total), therefore, the high abundance of relevant ARGs was unexpected. The opposite pattern was observed for quinolones, which make up about 22% of the antibiotics used in medicine, but their ARGs accounted for only about 1% of the resistome. However the main mechanisms of resistance to quinolones, mutations in the target enzymes, DNA gyrase and DNA topoisomerase IV, and increased drug efflux 46 , were not addressed in our study.
A peculiar feature of Moscow wastewater resistome was the high content of resistance genes to sulfonamides (about 9%), which were not among the major genes in wastewater resistomes worldwide 3 . Sulfonamides are synthetic antimicrobial agents that currently have limited use in the human medicine, alone or mainly in combination with trimethoprim (a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor), in the treatment of uncomplicated respiratory, urinary tract and chlamydia infections 7 , 47 . Different sulfonamide ARGs ( sul1, sul2 and sul3 ) were detected in the wastewater in the some countries, including Denmark, Canada, Spain and China, applying culture dependent, independent and qPCR methods 7 . The opposite picture was observed for streptogramin resistance genes, which were among the ARGs in the majority of resistomes worldwide, but in Moscow wastewater they accounted for less than 1%. This is probably due to the limited use of this drug in Russia.
Another distinguishing feature of the resistome of wastewater in Moscow is the high content of ARGs conferring resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds (QAC), about 9%. It can be explained by the frequent use of these antiseptics in medicine. QACs are active ingredients in more than 200 disinfectants currently recommended for inactivation the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) virus 48 . A recent study showed that the number of QACs used to inactivate the virus in public facilities, hospitals and households increased during the COVID-19 pandemic 49 . Indeed, the results of a study dedicated to the study of wastewater resistome worldwide 3 did not reveal the presence of QAC ARGs in the wastewater, since the samples for this study were collected before the pandemic.
An important issue is the extent to which different water treatment technologies remove ARGs. The effective removal of ARG was primary due to a decrease in the concentration of microorganisms in treated effluent, since the share of resistome in the metagenome after treatment decreased by only 2.6 –3.7 times and the NLOS2 plant appeared to be more effective in this respect. However, compared to LOS, treated effluent at NLOS2 contains approximately twice as much suspended solids, probably due to poorer settling characteristics of the sludge indicated by the higher SVI. Therefore, the overall efficiency of removing ARGs from wastewater at two WWTPs may be similar.
Considering the relative abundances of ARGs in the resistomes, genes conferring resistance to macrolides and tetracyclines were removed more efficiently than beta lactamases, especially ampC , and rifampin ADP-ribosyltransferase genes. The low efficiency of removal of the ampC gene and the increase in its abundance in the resistome after wastewater treatment were previously reported for WWTPs in Germany 50 . Efficient removal of ARGs to macrolides ( ermB, ermF, mph(A), mef(A) ) and tetracyclines ( tet(A), tet(C), tet(Q), tet(W) ) has been reported in a number of studies worldwide 51 . ARGs enabling resistance to sulfonamides, tetracyclines and chloramphenicol were more efficiently removed at LOS than at NLOS2, while the opposite was observed for beta lactamases (Fig. 4 ). The later became the most abundant class of ARGs in the treated effluent.
Metagenomic analysis not only identified resistance genes, but also revealed probable MDR strains based on the analysis of assembled MAGs. We identified 9 such strains in both influent, AS and treated effluent. The real number of MDR strains is probably higher, since only a small fraction of all metagenomic contigs was included in the assembled high quality MAGs.
Phocaeicola vulgatus , (formerly Bacteroides vulgatus ), is a mutualistic anaerobic bacteria commonly found in the human gut microbiome and frequently involved in human infections. The results of whole genome analysis showed presence of blaTEM-1 and blaCMY-2 ARGs, which confers resistant to beta-lactams 52 , 53 . P. vulgatus was also identified as potential host for the transmission of tetracycline ARGs 54 . Streptococcus parasuis is an important zoonotic pathogen that causes primarily meningitis, sepsis, endocarditis, arthritis, and pneumonia in both pigs and humans 55 . A variety of MDR strains of this bacterium have been described. For instance, S. parasuis strain H35 was isolated from a lung sample of a pig in China; several ARGs, including optrA , catQ , erm(B), lsa(E), msr(D), mef(A), mdt(A), tet(M), lnu(B), aadE and two copies of aacA-aphD , were found in the chromosome and cfr(D) was detected on plasmid pH35-cfrD 56 . MDR strain of Bacillus cereus was identified in the effluent water microbiome. This bacterium is known as human pathogen and a common cause of food poisoning with toxin-producing property 57 . Bacillus cereus was isolated from drinking water treatment plant in China and antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed that it was resistant to cefoxitin, penicillin tetracycline 58 , macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin (MLSB), aminoglycoside and tetracycline antibiotics 59 . Assembled MAG B.cereus from effluent water contained ARGs conferring to macrolides, beta-lactams, fosfomycin and streptogramin and may be considered as MDR strain. Genomes of members of the genera Streptococcus (AS of LOS) and Enterococcus (influent), not identified at the species level, were found to contain multiple ARGs. Most of species of these genera are opportunistic and true pathogens known for their drug resistance 60 , 61 . One MAG from the influent water metagenome was assigned to uncultured lineage of the family Ruminococcaceae. Members of this family are typical non-pathogenic gut inhabitants, although genomes of some strains could harbor ARGs 62 .
Three MAGs retrieved from influent wastewater microbiome ( Ancrocorticia ) and treated effluent water ( Cyclobacteriaceae and Undibacterium ) were found to contain several ARGs. However, we found no evidences about pathogenic and MDR strains in these taxa. It is possible that these environmental bacteria acquired ARGs via horizontal gene from outside their lineages. WWTPs are an ideal environment for horizontal gene transfer (HGT), since when bacteria are exposed to strong selective pressures, such as the presence of antimicrobials, the horizontal acquisition of ARGs enables genetic diversification and create the potential for rapid gains in fitness 63 .
Conclusions
Metagenome sequencing of the raw wastewater, activated sludge and treated wastewater at two large WWTPs of the Moscow city revealed several hundreds of ARGs that could confer resistance to most commonly used classes of antibiotics.
Resistome accounted for about 0.05% of the wastewater metagenome and after wastewater treatment its share decreased by 3–4 times.
The resistomes were dominated by ARGs encoding resistance to beta-lactams, macrolides, aminoglycosides, tetracycline, QAC, and sulfonamides. A peculiar feature of Moscow wastewater resistome was the high content of ARGs to sulfonamides and limited occurrence of resistance to streptogramins.
ARGs for macrolides and tetracyclines were removed more efficiently than ARGs for beta-lactamases.
A comparison of wastewater resistomes from Moscow and around the world suggested that the abundance and content of ARG in wastewater depend on social, medical, and environmental factors.
Data availability
The raw data generated from 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metagenome sequencing have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) and are available via the BioProject PRJNA945245.
Cassini, A. et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19 , 56–66 (2019).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Thorpe, K. E., Joski, P. & Johnston, K. J. Antibiotic-resistant infection treatment costs. antibiotic-resistant infection treatment costs have doubled since 2002, now exceeding $2 billion annually. Health Aff. 37 , 662–669 (2018).
Article Google Scholar
Munk, P. et al. Genomic analysis of sewage from 101 countries reveals global landscape of antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Commun. 13 , 7251 (2022).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rizzo, L. et al. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 447 , 345–360 (2013).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Begmatov, S. et al. The structure of microbial communities of activated sludge of large-scale wastewater treatment plants in the city of Moscow. Sci. Rep. 12 , 3458 (2022).
Mosaka, T. B. M., Unuofin, J. O., Daramola, M. O., Tizaoui, C. & Iwarere, S. A. Inactivation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic-resistance genes in wastewater streams: Current challenges and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 13 , 1100102 (2022).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pazda, M., Kumirska, J., Stepnowski, P. & Mulkiewicz, E. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 697 , 134023 (2019).
Karkman, A., Do, T. T., Walsh, F. & Virta, M. P. J. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 26 , 220–228 (2018).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Amos, G. C., Hawkey, P. M., Gaze, W. H. & Wellington, E. M. Waste water effluent contributes to the dissemination of CTX-M-15 in the natural environment. J. Antimicrob Chemother. 69 , 1785–1791 (2014).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Marti, E., Jofre, J. & Balcazar, J. L. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in a river influenced by a wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 8 , e78906 (2013).
Szczepanowski, R. et al. Detection of 140 clinically relevant antibiotic-resistance genes in the plasmid metagenome of wastewater treatment plant bacteria showing reduced susceptibility to selected antibiotics. Microbiology 155 , 2306–2319 (2009).
Mao, D. et al. Prevalence and proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes in two municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 85 , 458–466 (2015).
Yang, Y., Li, B., Ju, F. & Zhang, T. Exploring variation of antibiotic resistance genes in activated sludge over a four-year period through a metagenomic approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 , 10197–10205 (2013).
Yang, Y., Li, B., Zou, S., Fang, H. H. & Zhang, T. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes in sewage treatment plant revealed by metagenomic approach. Water Res. 62 , 97–106 (2014).
Bengtsson-Palme, J. et al. Elucidating selection processes for antibiotic resistance in sewage treatment plants using metagenomics. Sci. Total Environ. 572 , 697–712 (2016).
Karkman, A. et al. High-throughput quantification of antibiotic resistance genes from an urban wastewater treatment plant. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 92 , fiw014 (2016).
Laht, M. et al. Abundances of tetracycline, sulphonamide and beta-lactam antibiotic resistance genes in conventional wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) with different waste load. PLoS ONE 9 , e103705. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103705 (2014).
Auerbach, E. A., Seyfried, E. E. & McMahon, K. D. Tetracycline resistance genes in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 41 , 1143–1151 (2007).
Harris, S. J., Cormican, M. & Cummins, E. Antimicrobial residues and antimicrobial-resistant bacteria: Impact on the microbial environment and risk to human health—a review. Human Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 18 , 767–809 (2012).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Frey, B. et al. Microbial diversity in European alpine permafrost and active layers. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 3 , fiw018 (2016).
Magoc, T. & Salzberg, S. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27 , 2957–2963 (2011).
Edgar, R. C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26 , 2460–2461 (2010).
Rognes, T., Flouri, T., Nichols, B., Quince, C. & Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4 , e2584 (2016).
Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.journal 17 , 10–12 (2011).
Nurk, S., Meleshko, D., Korobeynikov, A. & Pevzner, P. A. metaSPAdes: A new versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Res. 27 , 824–834 (2017).
Kang, D. D. et al. MetaBAT 2: an adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ. 7 , e7359 (2019).
Wu, Y. W., Simmons, B. A. & Singer, S. W. MaxBin 2.0: An automated binning algorithm to recover genomes from multiple metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics. 32 , 605–607 (2016).
Alneberg, J. et al. Binning metagenomic contigs by coverage and composition. Nat. Methods 11 , 1144–1146 (2014).
Sieber, C. M. K. et al. Recovery of genomes from metagenomes via a dereplication, aggregation and scoring strategy. Nat. Microbiol. 3 , 836–843 (2018).
Parks, D. H., Imelfort, M., Skennerton, C. T., Hugenholtz, P. & Tyson, G. W. CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2 , 1043–1055 (2015).
Chaumeil, P. A., Hugenholtz, P. & Parks, D. H. GTDB-Tk v2: memory friendly classification with the genome taxonomy database. Bioinformatics 38 , 5315–5316 (2022).
Parks, D. H. et al. A standardized bacterial taxonomy based on genome phylogeny substantially revises the tree of life. Nat. Biotechnol. 36 , 996–1004 (2018).
Hyatt, D. et al. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 11 , 119 (2010).
Feldgarden, M. et al. AMRFinderPlus and the reference gene catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence. Sci. Rep. 11 , 12728 (2021).
Jacoby, G. A. AmpC beta-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 22 , 161–182 (2009).
Antunes, P., Machado, J., Sousa, J. C. & Peixe, L. Dissemination of sulfonamide resistance genes (sul1, sul2, and sul3) in Portuguese Salmonella enterica strains and relation with integrons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49 , 836–839 (2005).
Magiorakos, A. P. et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18 , 268–281 (2012).
Azcarate-Peril, M. A. et al. Impact of short-chain galactooligosaccharides on the gut microbiome of lactose-intolerant individuals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114 , E367–E375 (2017).
Koskey, A. M. et al. Blautia and Prevotella sequences distinguish human and animal fecal pollution in Brazil surface waters. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 6 , 696–704 (2014).
Altwegg, M. & Geiss, H. K. Aeromonas as a human pathogen. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 16 , 253–286 (1989).
Wexler, A. G. & Goodman, A. L. An insider’s perspective: Bacteroides as a window into the microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2 , 17026 (2017).
Collado, L. & Figueras, M. J. Taxonomy, epidemiology, and clinical relevance of the genus Arcobacter . Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 24 , 174–192 (2011).
Antunes, L. C., Visca, P. & Towner, K. J. Acinetobacter baumannii : evolution of a global pathogen. Pathog. Dis. 71 , 292–301 (2014).
Begmatov, S. A., Dorofeev, A. G., Pimenov, N. V., Mardanov, A. V. & Ravin, N. V. High efficiency of removal of pathogenic microorganisms at wastewater treatment plants in the city of Moscow. Microbiology 92 , 734–738. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261723601124 (2023).
Zakharenkov, I. A., Rachina, S. A., Kozlov, R. S. & Belkova, Yu. A. Consumption of systemic antibiotics in the Russian Federation in 2017–2021. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. Chemother. 24 , 220–225. https://doi.org/10.36488/cmac.2022.3.220-225 (2022).
Hooper, D. C. & Jacoby, G. A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: quinolone resistance. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1354 , 12–31 (2015).
Littlefield, B. A., Gurpide, E., Markiewicz, L., McKinley, B. & Hochberg, R. B. A simple and sensitive microtiter plate estrogen bioassay based on stimulation of alkaline phosphatase in Ishikawa cells: estrogenic action of Δ5 adrenal steroids. Endocrinology 127 , 2757–2762 (1990).
Hora, P. I., Pati, S. G., McNamara, P. J. & Arnold, W. A. Increased use of quaternary ammonium compounds during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and beyond: consideration of environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 7 , 622–631 (2020).
Liu, C. et al. Low concentration quaternary ammonium compounds promoted antibiotic resistance gene transfer via plasmid conjugation. Sci. Total. Environ. 887 , 163781 (2023).
Alexander, J., Bollmann, A., Seitz, W. & Schwartz, T. Microbiological characterization of aquatic microbiomes targeting taxonomical marker genes and antibiotic resistance genes of opportunistic bacteria. Sci. Total. Environ. 512–513 , 316–325 (2015).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Uluseker, C. et al. A Review on Occurrence and spread of antibiotic resistance in wastewaters and in wastewater treatment plants: mechanisms and perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 12 , 717809 (2021).
Vázquez-López, R. et al. The beta-lactam resistome expressed by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria isolated from human feces of healthy donors. Pharmaceuticals 14 , 533 (2021).
Vishwanath, S., Shenoy, P. A. & Chawla, K. Antimicrobial resistance profile and nim gene detection among Bacteroides fragilis group isolates in a university hospital in South India. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 11 , 59–62 (2019).
Qin, R., Yu, Q. G., Liu, Z. Y. & Wang, H. Co-occurrence of tetracycline antibiotic resistance genes and microbial communities in plateau wetlands under the influence of human activities. Huan Jing Ke Xue 44 , 169–179 (2023).
PubMed Google Scholar
Wang, J. et al. Investigation of the genomic and pathogenic features of the potentially zoonotic Streptococcus parasuis . Pathogens 10 , 834 (2021).
Zhu, Y. et al. Identification of a Streptococcus parasuis isolate co-harbouring the oxazolidinone resistance genes cfr(D) and optrA . J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 76 , 3059–3061 (2021).
Enosi, T. D., Mathur, A., Ngo, C. & Man, S. M. Bacillus cereus : Epidemiology, virulence factors, and host-pathogen interactions. Trends Microbiol. 29 , 458–471 (2021).
Gu, Q. et al. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in full-scale drinking water treatment system using metagenomics and culturing. Front. Microbiol. 12 , 798442 (2022).
Han, Z. et al. Antibiotic resistomes in drinking water sources across a large geographical scale: Multiple drivers and co-occurrence with opportunistic bacterial pathogens. Water Res. 183 , 116088 (2020).
Fiore, E., Van, T. D. & Gilmore, M. S. Pathogenicity of Enterococci . Microbiol. Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0053-2018 (2019).
Patterson, M. J. Streptococcus. In Medical Microbiology 4th edn (ed. Baron, S.) (University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, 1996).
Google Scholar
Abdugheni, R. et al. Comparative genomics reveals extensive intra-species genetic divergence of the prevalent gut commensal Ruminococcus gnavus . Microb. Genom. 9 , mgen001071 (2023).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lerminiaux, N. A. & Cameron, A. D. S. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 65 , 34–44 (2019).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Project 22-74-00022 to S.B.).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Bioengineering, Research Center of Biotechnology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninsky Prosp, bld. 33‑2, Moscow, Russia, 119071
Shahjahon Begmatov, Alexey V. Beletsky, Andrey V. Mardanov & Nikolai V. Ravin
Winogradsky Institute of Microbiology, Research Center of Biotechnology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninsky Prosp, bld. 33‑2, Moscow, Russia, 119071
Alexander G. Dorofeev & Nikolai V. Pimenov
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.B. and N.V.R. designed and supervised the research project; A.G.D. collected the samples and analysed chemical composition of wastewater; A.V.M. performed 16S rRNA gene profiling and metagenome sequencing; S.B., A.V.B., N.V.P., and N.V.R. analysed the sequencing data; S.B. and N.V.R. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Shahjahon Begmatov or Nikolai V. Ravin .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary tables., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Begmatov, S., Beletsky, A.V., Dorofeev, A.G. et al. Metagenomic insights into the wastewater resistome before and after purification at large‑scale wastewater treatment plants in the Moscow city. Sci Rep 14 , 6349 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56870-0
Download citation
Received : 26 October 2023
Accepted : 12 March 2024
Published : 15 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56870-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Translational Research newsletter — top stories in biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma.
2018 Primetime Emmy & James Beard Award Winner
R&K Insider
Join our newsletter to get exclusives on where our correspondents travel, what they eat, where they stay. Free to sign up.
A History of Moscow in 13 Dishes
Featured city guides.

COMMENTS
There is no right answer. If you put 10 Traveller owners in a room, you'll get at least 12 different views. For original good looks and lovely light wood, then varnish is the best, BUT if you want to use the car and let it out in anything other than mild sunshine, then other treatments rule. I like Burgess wood sealer.
Woodies of West Sussex have been in the business of maintaining and restoring traveller wood since the eighties. They are the recognized UK expert in the field. They recommend a mix of 90% Blackfriar's Exterior Gloss varnish with 10% Owatrol oil. Sand first then apply three or four coats with 24 hours between coats.
Morris Minor Workshop repair and/or renew all woodwork on Morris Minor Travellers to make it as good as new. Services include: Replacement of complete wood using good quality treated ash, Replacement of rear doors, rear door pillars and middle waste rails depending on the condition of the rest of the woodwork, Rub down and retreat of all exterior woodwork, Fitting of new window channels and re ...
At Woodies we specialise in the Morris Traveller and Mini Countryman but we can, and will, fabricate timber frames for all classic cars. We have completed in excess of 600 Morris Travellers over 30 years, as well as many other wood framed classic and vintage vehicles. Our kits are exported around the world and include everything you need to ...
Traveller Wood treatment--USA. Long story short, I am replacing the RH Timber on my '59 Traveller. Should have left it alone but I had to start poking and then--uggh. Anyway, what seems to be the highly preferred method of preserving the timber, 90% Cuprinol+ 10% Sikkens, the Cuprinol part has not be available in the USA for quite some time.
The rear wood section of the Traveller is structural and must be maintained or the entire thing could collapse. Several good articles have been written on the process of repair and/or replacement of the wood; one of these articles can be found on the Mini Mania web site under "Technical Articles". This is the full kit that includes all of the wood.
The episode of Salvage Hunters, Classic cars with Traveller Timbers restoring the woodwork on a classic Moris Minor traveller (woodie)
We've joined forces with Cambrian Classics Ltd to show how the woodwork is replaced on a 1967 Morris Minor Traveller - the factory woodie built from 1953 unt...
The rear wood section of the Traveller is structural and must be maintained or the entire thing could collapse. Several good articles have been written on the process of repair and/or replacement of the wood; one of these articles can be found on the Mini Mania web site under "Technical Articles". This is a basic or standard kit .
5 The Close, Little Weighton, East Yorkshire, HU20 3XA - 01482 84 67 87 | 07949 438 075 - [email protected]
Of all the models to be produced, the Morris Traveller is perhaps the most striking in terms of appearance. With an ash wood frame and two side-hinged rear doo. Call us now on 0333 005 3355. Existing customers. Get a bike quote. Trustpilot ... With an ash wood frame and two side-hinged rear doors, the Traveller was billed as an estate model. ...
The grain, finish. and colour of the wood on the traveller is beautiful. I have no knowledge of the other Company, but I can thoroughly recommend Woodies through personal experience. Ray Newell's book 'The Complete Traveller' has a whole section on wood replacement, and the car featured having the wood replaced, is the traveller I now own.
Re: Wood treatment. by jonathon H » Tue Aug 11, 2015 9:13 pm. IMO I'd sand back the varnish, use fresh lemon juice to gradually bleach out the staining, then Cuprinol 5 star, Burgess wood sealer diluted to choice of tone, then 5-8 coats of a good quality exterior varnish.
Good Day, Long story short, I am replacing the RH Timber on my '59 Traveller. Should have left it alone but I had to start poking and then--uggh. Anyway, what seems to be the highly preferred method of preserving the timber, 90% Cuprinol+ 10% Sikkens, the Cuprinol part has not be av
This is an external wood replacement set comprising of: 1x Pair pre-assembled side frames, 1x Pair pre-assembled door frames, 1x Rear base rail, 1x Rear roof rail. Made with top quality ash from the original Morris Minor Centre Bath supplier since 1982 (as also previously supplied by Bull Motif Spares). Both this supply & Woodies are of high ...
Stock 1961 Morris Minor Traveller body. Reproduction wood from Traveller Timbers in the U.K. Custom frame and suspension from Art Morrison Enterprises. Four-wheel disc brakes. Rack and pinion ...
The backwashed water is returned back to the wastewater influent for continued treatment and the clean water flows into the re-aeration basin. Re-Aeration Basin. To help support life in the receiving water, an amount of dissolved oxygen is added to the wastewater. The re-aeration tank contains a floating mechanical aerator that cascades the ...
Good Day, Long story short, I am replacing the RH Timber on my '59 Traveller. Should have left it alone but I had to start poking and then--uggh. Anyway, what seems to be the highly preferred method of preserving the timber, 90% Cuprinol+ 10% Sikkens, the Cuprinol part has not be av ... Apr 28 Morris Minor Rear Axle Filler ...
Day 6 - Explore the Golden Ring. Creating the Moscow itinerary may keep you busy for days with the seemingly endless amount of things to do. Visiting the so-called Golden Ring is like stepping back in time. Golden Ring is a "theme route" devised by promotion-minded journalist and writer Yuri Bychkov.
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are considered to be hotspots for the spread of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). We performed a metagenomic analysis of the raw wastewater, activated sludge ...
This tour of Moscow's center takes you from one of Moscow's oldest streets to its newest park through both real and fictional history, hitting the Kremlin, some illustrious shopping centers, architectural curiosities, and some of the city's finest snacks. Start on the Arbat, Moscow's mile-long pedestrianized shopping and eating artery ...