
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- For Travelers

Visit the United States
The Secretary of Homeland Security and the Secretary of State work together to create and maintain an effective, efficient visa process that secures America’s borders from external threats and ensures that our country remains open to legitimate travel.
DHS provides a full range of online resources to help you plan your trip, manage your arrival and if needed extend your stay.
Plan Your Trip
- Obtain a Visitor VISA - (U.S. State Department) Generally, a citizen of a foreign country who wishes to enter the United States must first obtain a visa, either a nonimmigrant visa for temporary stay, or an immigrant visa for permanent residence. The visa allows a foreign citizen, to travel to the United States port-of entry and request permission of the U.S. immigration inspector to enter the U.S.
- Determine the correct VISA category - (USCIS) There are more than 20 nonimmigrant visa types for people traveling to the United States temporarily. There are many more types of immigrant visas for those coming to live permanently in the United States. The type of visa you need is determined by the purpose of your intended travel. Get help determining the right VISA category at the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services homepage.
- Office of Biometric Identity Management (OBIM) - Provides biometric identification services to federal, state and local government decision makers to help them accurately identify the people they encounter and determine whether those people pose a risk to the United States. OBIM currently applies to all international visitors (with limited exemptions) entering the United States, but not to U.S. citizens.
- Visa Waiver Program: Passport Requirements Timeline - As of October 26, 2006, any passport issued on or after this date by a Visa Waiver Program (VWP) country must be an e-Passport for VWP travelers to be eligible to enter the United States without a visa. If your passport is older, see requirements here
- Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA) - A fully automated, electronic system for screening passengers before they begin travel to the United States under the Visa Waiver Program. Voluntary ESTA applications may be submitted at any time prior to travel to the United States, and Visa Waiver Program travelers are encouraged to apply for authorization as soon as they begin to plan a trip to the U.S.
Your Arrival
- Locate a Port Of Entry - Air, Land, or Sea (CBP) - At a port of entry, CBP enforces the import and export laws and regulations of the U.S. federal government and conducts immigration policy and programs. Ports also perform agriculture inspections to protect the USA from potential carriers of animal and plant pests or diseases that could cause serious damage to America's crops, livestock, pets, and the environment.
- Global Entry Program (CBP) - Expedited screening and processing for pre-screened international travelers entering the United States.
- CBP Traveler Entry Forms (CBP) - Whether you are a visitor to the United States or U.S. citizen, each individual arriving into the United States must complete one or more of U.S. Customs and Border Protection's (CBP) entry forms.
- DHS Traveler Redress Inquiry Program (DHS TRIP) - If you have difficulties experienced during their travel screening at transportation hubs--like airports and train stations--or crossing U.S. borders, use this system to make inquiries or seek resolution.
Extend Your Stay
- Apply to Extend Your Stay - (USCIS) If you want to extend your stay in the United States, you must file a request with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) on the Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status before your authorized stay expires. If you remain in the United States longer than authorized, you may be barred from returning and/or you may be removed (deported) from the United States.
- Change Your Non-Immigrant Status - (USCIS) If you want to change the purpose of your visit while in the United States, you (or in some cases your employer) must file a request with USCIS on the appropriate form before your authorized stay expires.
Tips During Your Trip to the United States
Beware of Scams - (Federal Trade Commission) The Department of State, Office of Visa Services, advises the public of a notable increase in fraudulent emails and letters sent to Diversity Visa (DV) program (Visa Lottery) applicants. The scammers behind these fraudulent emails and letters are posing as the U.S. government in an attempt to extract payment from DV applicants.
- Border Security
- Citizenship and Immigration Services
- How Do I - For Travelers
- International Travel
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Most popular
- Learn about nonimmigrant visas to visit the U.S.
- Find out how to apply for or renew your U.S. passport
- Learn how to get an international driver’s license
Find information on passports. Learn about traveling to, from, and within the U.S.
U.S. passports
Find out how to apply for or renew a passport and what to do if your passport is lost or stolen.
U.S. citizens traveling abroad
Find out about visas, the Trusted Traveler programs, what to do in an emergency, and more.
International travel documents for children
See what documents a child needs to travel to or from the U.S. alone or with a parent or relative.
Travel to or within the U.S.
As a visitor, find out which documents you will need to travel to and drive in the U.S.
How to get a REAL ID and use it for travel
The REAL ID Act sets higher security standards for state-issued driver's licenses and ID cards.
Travel documents for foreign citizens returning to the U.S.
As a non-citizen U.S. resident, learn what documents you need to return to the U.S. if you leave.
Looking for something else? Explore all topics and services
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know

Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- For International Visitors
Applying for Admission into United States
Emergency Visa to the US – Who Qualifies and How to Get It
If you need to travel to the United States for an emergency, you might qualify for an emergency appointment for a visa. However, few situations are considered dire enough to access this service.
US consulates only release this visa for funerals, medical, or work-related emergencies. You also need to prove the circumstances with certified documents to get an appointment. So, if you want to know if you qualify for an emergency visa to the US, read this post, we will go over all the details you need.
USA emergency visa appointment
Medical emergency visa to the us, emergency visa for a funeral in the us, who does not need a visa.
For an emergency visa appointment at a US consulate, the first step is to pay the fees (usually around $160). Then complete the DS-160 form and make your emergency appointment request using the Emergency Request Form. These documents are available on the website of any US consulate.
After sending your online request, you will receive an email letting you know if they accepted your request. Then, you’ll be able to go on and schedule your appointment online. If you don’t receive a reply, check your spam folder. The email is automated and might end up with your junk mail.
Going abroad and need a visa? Check out our other articles for more guidance:
- Which Countries Can Green Card Holders Travel to Without a Visa?
- Can a Permanent Resident Get a US Passport?
If you or a relative needs emergency medical treatment in the US, you might qualify for an emergency visa appointment. This also counts for visits to see immediate family members who are sick.
For these circumstances, the consulate will require:
- a letter from a doctor that describes the medical condition and explains why you seek treatment in the US
- a letter from the hospital in the US confirming that they are ready to treat the patient and an estimate of the cost.
- evidence of sufficient funds to pay for the treatment.
You can also request emergency appointments to attend the funeral of an immediate family member . The US Department of State only classifies parents, siblings, children, grandparents, and grandchildren as immediate family members.
To get a visa under these circumstances, you have to provide:
- proof of family relationship with the deceased
- a letter from the funeral director containing their contact information, the date of the ceremony, and details about the deceased.
In addition to these documents you will have to provide 2 (two) 2 x 2 inches photos, according to standard US requirements. Only the appointment will be moved up, the processing times will still be around 5 (five) weeks.
Depending on your country of origin, you may not need to apply for a US visa. As of 2022, 40 countries are part of the Visa Waiver Program. This allows citizens to enter the US for visits (regular or emergency) or business without a visa if the visit lasts less than 90 (ninety) days.
So, if you are a citizen of one of these countries, you might only need a valid passport to cross the border. For any other reason or to stay for over 90 (ninety) days, you have to apply for an emergency visa.
Passport Photo Online
To get your visa application underway, you need 2 (two) 2 x 2 inches photos, taken following the strict parameters set by the US Government. Did you know you can snap pictures for your official documents at home?
With Passport Photo Online , you only need a smartphone or a digital camera to turn any room into a photo studio! Our artificial intelligence will analyze your shots and make sure that they follow the official guidelines. In 3 seconds, you will have perfect US visa pictures , ready to go for your application.
Thanks to Passport Photo Online, you have a 100% guarantee of acceptance by the authorities. You also save up to 40% on your visa photos.
Emergency US visa – conclusions
In some cases, you might qualify for expedited appointments for a visa interview. However, the US Government only recognizes a handful of circumstances as emergencies. You also have to provide proof of urgency. The documents required to make the request change depending on the emergency. Get them on time, before sending in your forms.
Use Passport Photo Online to get your visa photos ready at home.
Emergency US visa: FAQ
To end this article, we will answer some of the most commonly asked questions about getting an emergency visa to the US.
What is an emergency visa for the US?
An emergency visa is a document that allows you to travel to the US. While the appointment will be the first available, the processing times are still 5 (five) weeks.
How do I get an emergency visa for the US?
You need to request an emergency appointment at the local US consulate, providing form DS-160 and the Emergency Request Form. The documents you need as proof of urgency change depending on the circumstances. The consulate will email you, letting you know if they accepted your request.
Can I get an emergency visa to the US for a sick relative ?
If you need to visit a sick family member in the United States, you might get an emergency visa appointment. However, you need to prove the urgency with a letter from the receiving hospital or physician in the US.
Can I get an emergency visa to the US for a death in the family?
You can qualify for an emergency US visa appointment to attend the funeral of an immediate family member in the United States. The Department of State only recognizes parents, siblings, children, grandparents, and grandchildren as immediate family members. Provide proof of family relations and a letter from the funeral director.
- [1] https://tr.usembassy.gov/visas/nonimmigrant-visas/emergency-requests/
Rate my article:
Average rating 4.6 / 5. Vote count: 24
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Riccardo Ollmert is a multilingual writer and travel expert. He studied Languages, Literature and Publishing Industry at La Sapienza University of Rome. His passions include traveling and learning new skills.
Share with friends
You may also like.

Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Create Account
Visit the U.S.
Generally, if you want to visit ( and not live in ) the United States you must first obtain a visitor visa . Travelers from certain countries may be exempt from this requirement. For more information, please see the U.S. Department of State website .
If you want to travel to the United States for reasons other than business or pleasure, you must apply for a visa in the appropriate category. This includes if you want to study, work as a crew member or journalist, etc. You can get help determining which visa you need by using the Explore My Options page.
Extending Your Visit
If Customs and Border Protection (CBP) authorizes your admission to the United States at the designated port of entry, you will receive a stamped Form I-94, Record of Arrival-Departure . If you wish to stay beyond the time indicated on the Form I-94, you may apply for an extension by filing Form I-539, Application to Extend/Change Nonimmigrant Status , with USCIS.
If You Lose Form I-94
You may apply for a replacement Form I-94 by filing a Form I-102, Application for Replacement/Initial Nonimmigrant Arrival/Departure Record .
Baguhin ang Wika: Change to Tagalog
Apply for a U.S. Visa
In the philippines.
Important Notice! Insert Message Here
- Bank and Payment Options/Pay My Visa Fee
- DS-160 Information
- Appointment Wait Times
- Photos and Fingerprints
- Visa Waiver Program
- Security Regulations
- Apply for a Visa
- Ages below 14 and over 79
- Renew My Visa
- Complete My DS-160
- Schedule My Appointment
- Change Document Delivery Address
- Retrieve My Passport/Visa
- Apply for an Expedited Appointment
- Application Refused Under INA 221(g)
- Visa Information
- Check My Petition Status
- Visa Wait Times
- Select Document Delivery Address
- Travel Coordinator
- Priority Interview Program
- Crew and Manning Program
- Group Appointments
- Diplomatic and Government Officials
- Visas for Children
- U.S. Embassy, Manila
- Passport/Visa Collection Locations
- Document Drop-Off Locations
- Bank Locations
- Holidays and Closures
- Helpful Links
You are here: Home / Apply for an Emergency Appointment
Apply for an Emergency Appointment
Qualifications, how to apply, more actions.
If you have an unforeseen emergency travel need as per one of the criteria listed below, you may qualify for an expedited emergency appointment depending on availability at the U.S. Embassy/Consulate.
Before you apply for an emergency appointment, you must ensure that you have documentary evidence to prove the urgency. If it appears during your visa interview that you misrepresented the reasons for emergency travel, such facts will be noted on your case file and may adversely influence the outcome of your visa application. All applicants requesting an emergency appointment are required to first pay visa fees for a regular visa appointment. Applicants who are granted an emergency appointment but subsequently refused a visa or who or missed their interview at the U.S. Embassy/Consulate will not be allowed to utilize this option to obtain another emergency appointment.
Note: Travel for the purpose of attending weddings and graduation ceremonies, assisting pregnant relatives, participating in an annual business/academic/professional conference, or enjoying last-minute tourism does not qualify for emergency appointments. For such travel, please schedule a regular visa appointment well in advance.
Purpose of travel is to obtain emergency medical care, or to accompany a relative or employer for emergency medical care, or to visit a relative suffering from an immediate, life-threatening medical condition.
- A letter from your doctor in the Philippines describing the medical condition and why you are seeking medical care in the United States.
- A letter from the physician or hospital in the United States indicating that they are prepared to treat the case and providing the approximate cost of the treatment.
- Evidence of how you will pay for the cost of the treatment.
- A letter from the funeral director stating the contact information, the details of the deceased and the date of the funeral.
- You must also present evidence that the deceased is an immediate relative.
Purpose of travel is to attend to an urgent business matter where the travel requirement could not be predicted in advance.
- A letter of invitation from the corresponding company in the United States attesting to the urgency of the planned visit, describing the nature of the business and that either the U.S. or Philippine company will suffer a significant loss of opportunity if an emergency appointment is not available.
- Evidence of a necessary training program in the United States of three months duration or less, to include letters from both the Philippine employer and the U.S. company providing the training. Both letters should include a detailed explanation of the training and explain why either the U.S. or Philippine company will suffer a significant loss of opportunity if an emergency appointment is not available.
The purpose of travel is to return to the U.S. to attend classes or resume working in a timely manner. We expect students and temporary workers to make every effort to schedule regular appointments during their planned stays in the Philippines. However, in limited cases, the Embassy will consider emergency appointments for these types of travel. A list of documentary requirements for students and temporary workers can be found on the U.S. Embassy Manila website .
- Original Form I-20 or DS-2019 indicating start date of program within 60 days.
- Evidence that you have paid the SEVIS fee (when applicable).
Pay the visa application fee .
Complete the Nonimmigrant Visa Electronic Application (DS-160) form .
Schedule an appointment online for the earliest available date. Please note that you must schedule an appointment before you can request an expedited date. At the time you schedule your appointment, you will see an onscreen message showing the earliest available appointment date, which includes emergency appointments. Accordingly, you may find that it is not necessary to request an emergency appointment because there are regular dates available. If you wish to proceed with requesting an emergency appointment, then complete the Emergency Request Form or contact the call center to request assistance. Please be sure to note the type of emergency you believe qualifies you for an emergency appointment. Once you have submitted your request, please wait for a response from the U.S. Embassy/Consulate, which will come via email.
If the U.S. Embassy/Consulate approves your request then you will receive an email alerting you to schedule your emergency appointment online . Please understand that the call center cannot schedule your emergency appointment for you, but agents are able to assist you if questions arise. Should the U.S. Embassy/Consulate deny your request for an emergency appointment, you will be notified of the denial by email and you should keep your existing appointment.
Note: The email confirming or denying your request will come from [email protected] . Some email applications have rules which filter unknown senders into a spam or junk mail folder. If you have not received your email notification, please look for the message in your junk and spam email folders.
Visit the U. S. Embassy/Consulate on the date and time of your visa interview. You will need to bring a printed copy of your appointment letter, your DS-160 confirmation page, one recent photograph, your current passport and all old passports. Applications without all of these items will not be accepted.
- Schedule an Emergency Appointment
- Modify your visa application
- Download your visa application
- Cancel your appointment
© CGI Federal Inc.
- NIV Information
- Bank and Payment Options
- NIV Application
- Pay My Visa Fee
- Immigrant Visas
- Local Visa Programs
- General Information
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2006 Feb-.

Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet].
Statistical brief #268 costs of emergency department visits in the united states, 2017.
Brian J. Moore , Ph.D. and Lan Liang , Ph.D.
Published: December 8, 2020 .
- Introduction
Emergency department (ED) visits have grown in the United States, with the rate of increase from 1996 to 2013 exceeding that for hospital inpatient care. 1 In 2017, 13.3 percent of the U.S. population incurred at least one expense for an ED visit. 2 Furthermore, more than 50 percent of hospital inpatient stays in 2017 included evidence of ED services prior to admission. 3 Trends in ED volume vary significantly by patient and hospital characteristics, but an examination of nationwide costs by these characteristics has not yet been explored in the literature. 4
This Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Brief presents statistics on the cost of ED visits in the United States using the 2017 Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS). Total ED charges were converted to costs using HCUP Cost-to-Charge Ratios based on hospital accounting reports from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). ED visits include patients treated and released from the ED, as well as those admitted to the same hospital through the ED. Aggregate costs, average costs, and number of ED visits are presented by patient and hospital characteristics. Because of the large sample size of the NEDS data, small differences can be statistically significant. Thus, only percentage differences greater than or equal to 10 percent are discussed in the text.
- There were 144.8 million total emergency department (ED) visits in 2017 with aggregate ED costs totaling $76.3 billion (B).
- Aggregate ED costs were higher for females ($42.6B, 56 percent) than males ($33.7B, 44 percent); 55 percent of total ED visits were for females.
- Average cost per ED visit increased with age, from $290 for patients aged 17 years and younger to $690 for patients aged 65 years and older.
- As community-level income increased, shares of aggregate ED costs decreased and average cost per visit increased.
- In rural areas, one half of ED visit costs were for patients from the lowest income communities.
- The expected payer with the largest share of aggregate costs was private insurance in large metropolitan areas (31.4 percent of $39.5B) and Medicare in micropolitan (34.0 percent of $7.6B) and rural (37.3 percent of $5.5B) areas.
- Patients aged 18–44 years represented the largest share of aggregate ED costs in large metropolitan, small metropolitan, and micropolitan areas (36.4, 34.2, 32.5 percent, respectively). Patients aged 65 years and older represented the largest share of aggregate ED costs in rural areas (32.5 percent).
Aggregate costs for emergency department (ED) visits by patient sex and age group, 2017
Figure 1 presents aggregate ED visit costs by patient sex and age group in 2017 as well as number of ED visits. Estimates of aggregate cost use the product of the number of cases and the average estimated cost per visit to account for records with missing ED charge information. Aggregate cost decompositions among different descriptive statistics or using multiple levels of aggregation in a single computation could lead to slightly different total cost estimates due to the use of slightly different and more specific estimates of the missing information.
Aggregate ED visit costs by patient sex and age, 2017. Abbreviation: ED, emergency department Notes: Statistics for ED visits with missing or invalid patient characteristics are not presented. Patient age and sex were each missing for <0.1% of (more...)
- Aggregate ED visit costs in 2017 were higher overall for females than for males. Of the $76.3 billion in aggregate ED visit costs in 2017, females accounted for $42.6 billion (55.9 percent) and males accounted for $33.7 billion (44.1 percent). This cost differential was largely driven by a difference in ED visit volume, with females having a larger number of ED visits than males (80.2 vs. 64.6 million visits, or 55.4 vs. 44.6 percent of visits). Females had higher aggregate ED visit costs and more ED visits for all age groups except children. The discrepancy was highest for patients aged 18–44 years, with aggregate ED visit costs for females approximately 50 percent higher than costs for males ($15.9 vs. $10.7 billion), followed by patients aged 65 years and older, for which aggregate ED visit costs were approximately one-third higher for females than for males ($11.5 vs. $8.6 billion).
Costs of ED visits by patient characteristics, 2017
Table 1 presents the aggregate and average costs for ED visits, the number of ED visits, and the distributions of costs and visits, by select patient characteristics in 2017.
Aggregate costs, average costs, and number of ED visits by patient characteristics, 2017.
- In 2017, aggregate ED visit costs totaled $76.3 billion across 144.8 million ED visits, with an average cost per visit of $530. Aggregate ED visit costs totaled $76.3 billion in the United States in 2017, encompassing 144.8 million ED visits with an average cost per visit of $530. Routine discharge was the most frequent disposition from the ED, representing 80.8 percent of aggregate ED costs and a similar share of ED visits. Transfers represented 6.2 percent of aggregate ED costs but just 3.0 percent of ED visit volume because they had the highest average cost of any discharge disposition at $1,100 per ED visit. In contrast, ED visits resulting in an inpatient admission to the same hospital had the lowest average cost of any discharge disposition at $360 per ED visit and represented 9.4 percent of aggregate ED costs and 14.0 percent of ED visits.
- The share of aggregate ED visit costs attributed to patients aged 65 years and older was higher than the share of ED visits for this group, and the average cost per visit was highest among patients aged 65 years and older. Aggregate ED visit costs among patients aged 65 years and older totaled $20.2 billion (26.4 percent of the $76.3 billion total for the entire United States in 2017) despite just 29.2 million ED visits from patients in this age group (20.2 percent of the 144.8 million total). Conversely, the share of aggregate ED costs attributed to patients aged 17 years and younger was substantially lower than this group’s corresponding share of ED visits (10.3 percent of ED costs vs.18.5 percent of ED visits). This differential is due in part to the difference in average cost per visit, which increased with age. The average cost per visit among patients aged 65 years and older was more than twice as high as average costs among patients aged 17 years and younger ($690 vs. $290 per visit).
- Medicaid as the primary expected payer had the lowest average cost per ED visit, more than 50 percent lower than average costs for Medicare and one-third lower than for private insurance. Medicaid as the primary expected payer had an average cost per ED visit that was more than 50 percent lower than average costs per visit for Medicare ($420 vs. $660 per visit) and one-third lower than average costs for private insurance ($420 vs. $560 per visit). Due in part to these differences in average costs by expected payer, Medicare represented 30.1 percent of aggregate ED visit costs but 24.1 percent of total ED visits. In contrast, Medicaid represented 25.0 percent of ED costs but 31.5 percent of ED visits.
- As community-level income increased, the share of aggregate ED visit costs decreased and average cost per ED visit increased. The share of ED visit costs and ED visits decreased as community-level income increased. Patients residing in communities with the lowest income (quartile 1) represented roughly one-third of aggregate ED visit costs and ED visits (31.4 and 34.3 percent, respectively). Patients residing in quartiles 2 and 3 represented approximately one-fourth and one-fifth of aggregate ED visit costs and ED visits, respectively. Patients residing in communities with the highest income (quartile 4) represented less than one-fifth of aggregate ED costs and ED visits (18.1 and 16.0 percent, respectively). In contrast, average cost per ED visit increased as community-level income increased, ranging from $480 in communities with the lowest income (quartile 1) to $600 in communities with the highest income (quartile 4).
- The share of aggregate ED visit costs was highest among patients residing in large metropolitan areas. Aggregate ED visit costs for large metropolitan areas totaled $39.5 billion in 2017, more than half of the $76.3 billion in ED costs for the entire United States. The share of aggregate ED costs in large metropolitan areas was analogous to the overall distribution of ED visits in these areas: 51.8 percent of aggregate ED costs and 50.4 percent of ED visits.
Distribution of aggregate ED visit costs for location of patient residence by patient characteristics, 2017
Figures 2 – 4 present the distribution of aggregate costs for ED visits based on the location of the patient’s residence by age ( Figure 2 ), community-level income ( Figure 3 ), and primary expected payer ( Figure 4 ).
Aggregate ED visit costs by age and patient location, 2017. Abbreviations: B, billion; ED, emergency department; M, million Notes: Statistics for ED visits with missing or invalid patient characteristics are not presented. Patient age and patient location (more...)
Aggregate ED visit costs by primary expected payer and patient location, 2017. Abbreviations: B, billion; ED, emergency department; M, million Notes: Statistics for ED visits with missing or invalid patient characteristics are not presented. Expected (more...)
Aggregate ED visit costs by community-level income and location of patient’s residence, 2017. Abbreviations: B, billion; ED, emergency department; M, million Notes: Statistics for ED visits with missing or invalid patient characteristics are not (more...)
Figure 2 presents the distribution of aggregate costs for ED visits by patient age based on the location of the patient’s residence in 2017.
- Patients aged 18–44 years represented the largest share of aggregate ED visit costs in all locations except rural areas where patients aged 65 years and older represented the largest share. Compared with other age groups, patients aged 18–44 years represented the largest share of aggregate ED visit costs in large metropolitan areas in 2017 (36.4 percent). The share of ED costs attributed to patients aged 18–44 years also was larger than for other age groups in small metropolitan and micropolitan areas (34.2 and 32.5 percent, respectively). Overall, the share of ED costs attributed to patients aged 18–44 years decreased as urbanization decreased, from 36.4 percent in large metropolitan areas to 29.8 percent in rural areas. In rural areas, patients aged 65 years and older accounted for the largest share of aggregate ED visit costs (32.5 percent) compared with other age groups. The share of ED costs attributed to patients aged 65 years and older increased as urbanization decreased, from 24.7 percent in large metropolitan areas to 32.5 percent in rural areas. The share of aggregate ED visit costs attributed to patients aged 45–64 years and those aged 17 years and younger were similar across all patient locations (approximately 28 and 10 percent, respectively).
Figure 3 presents the distribution of aggregate costs for ED visits by quartile of community-level household income in the patient’s ZIP Code based on the location of the patient’s residence in 2017.
- In large metropolitan areas, patients residing in communities with the highest and lowest incomes represented the largest shares of aggregate ED visit costs. For other locations, patients in communities with lower incomes represented the largest share of ED costs. Patients residing in communities with the highest and lowest incomes (quartiles 4 and 1) accounted for 28.1 and 26.6 percent, respectively, of the $39.5 billion in aggregate ED visit costs in large metropolitan areas in 2017. In contrast, patients residing in communities with the two lowest income quartiles represented the largest share of ED costs for other patient locations (small metropolitan, micropolitan, and rural).
- As urbanization decreased, the share of aggregate ED visit costs for patients in the lowest income quartile increased and the share for those in the highest income quartile decreased. The share of aggregate ED visit costs attributed to patients residing in communities in the lowest income quartile (quartile 1) increased as urbanization decreased, from 26.6 percent in large metropolitan areas to 48.8 percent in rural areas. In contrast, the share of ED visit costs attributed to patients residing in communities in the highest income quartile (quartile 4) decreased as urbanization decreased, from 28.1 percent in large metropolitan areas to 1.2 percent in rural areas.
Figure 4 presents the distribution of aggregate costs for ED visits by primary expected payer based on the location of the patient’s residence in 2017.
- Private insurance as the primary expected payer accounted for the largest share of aggregate ED visit costs among patients living in large metropolitan areas. Medicare represented the largest share of ED costs in micropolitan and rural areas. Compared with other primary expected payers, private insurance represented the largest share of aggregate ED visit costs among those living in large metropolitan areas in 2017 (31.4 percent). The share of ED costs attributed to private insurance decreased as urbanization decreased, from 31.4 percent in large metropolitan areas to 27.9 percent in rural areas. More than one-third of ED visit costs were attributed to Medicare as the primary expected payer in micropolitan and rural areas. The share of ED costs attributed to Medicare increased as urbanization decreased, from 28.0 percent in large metropolitan areas to 37.3 percent in rural areas.

Costs of ED visits by hospital characteristics, 2017
Table 2 presents the aggregate and average costs for ED visits, the number of ED visits, and the distributions of costs and visits, by select hospital characteristics in 2017.
Aggregate costs, average costs, and number of ED visits by hospital characteristics, 2017.
- Aggregate ED visit costs were highest for hospitals located in the South in 2017. Aggregate ED visit costs in the South were $27.5 billion in 2017 (36.1 percent of the total $76.3 billion for the United States). The share of ED visit volume for the South was even larger (40.0 percent of the 144.8 million total visits). The distribution of aggregate ED visit costs across other hospital characteristics largely followed the pattern of the number of ED visits. Aggregate ED costs were highest in private, nonprofit hospitals; teaching hospitals; and hospitals not designated as a trauma center (72.0, 64.1, and 52.5 percent of ED costs, respectively). ED visits at private, for-profit hospitals had lower average costs per visit than did visits at either private, nonprofit or public hospitals ($420 vs. $540 and $550 per visit).
- About Statistical Briefs
Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs provide basic descriptive statistics on a variety of topics using HCUP administrative healthcare data. Topics include hospital inpatient, ambulatory surgery, and emergency department use and costs, quality of care, access to care, medical conditions, procedures, and patient populations, among other topics. The reports are intended to generate hypotheses that can be further explored in other research; the reports are not designed to answer in-depth research questions using multivariate methods.
- Data Source
The estimates in this Statistical Brief are based upon data from the HCUP 2017 Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS).
- Definitions
Types of hospitals included in the HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample
The Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) is based on emergency department (ED) data from community acute care hospitals, which are defined as short-term, non-Federal, general, and other specialty hospitals available to the public. Included among community hospitals are pediatric institutions and hospitals that are part of academic medical centers. Excluded are long-term care facilities such as rehabilitation, psychiatric, and alcoholism and chemical dependency hospitals. Hospitals included in the NEDS have EDs, and no more than 90 percent of their ED visits result in admission.
Unit of analysis
The unit of analysis is the ED visit, not a person or patient. This means that a person who is seen in the ED multiple times in 1 year will be counted each time as a separate visit in the ED.
Costs and charges
Total ED charges were converted to costs using HCUP Cost-to-Charge Ratios based on hospital accounting reports from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). a Costs reflect the actual expenses incurred in the production of hospital services, such as wages, supplies, and utility costs; charges represent the amount a hospital billed for the case. For each hospital, a cost-to-charge ratio constructed specifically for the hospital ED is used. Hospital charges reflect the amount the hospital billed for the entire ED visit and do not include professional (physician) fees.
Total charges were not available on all NEDS records. About 13 percent of all ED visits (weighted) in the 2017 NEDS were missing information about ED charges, and therefore, ED cost could not be estimated. For ED visits that resulted in admission, 24 percent of records were missing ED charges. For ED visits that did not result in admission, 11 percent of records were missing ED charges. The missing information was concentrated in the West (59 percent of records missing ED charges). For this Statistical Brief, the methodology used for aggregate cost estimation was analogous to what is recommended for the estimation of aggregate charges in the Introduction to the HCUP NEDS documentation. b Aggregate costs were estimated as the product of number of visits and average cost per visit in each reporting category. If a stay was missing total charges, average cost was imputed using the average cost for other stays with the same combination of payer characteristics. Therefore, a comparison of aggregate cost estimates across different tables, figures, or characteristics may result in slight discrepancies.
How HCUP estimates of costs differ from National Health Expenditure Accounts
There are a number of differences between the costs cited in this Statistical Brief and spending as measured in the National Health Expenditure Accounts (NHEA), which are produced annually by CMS. c The largest source of difference comes from the HCUP coverage of ED treatment only in contrast to the NHEA inclusion of inpatient and other outpatient costs associated with other hospital-based outpatient clinics and departments as well. The outpatient portion of hospitals’ activities has been growing steadily and may exceed half of all hospital revenue in recent years. On the basis of the American Hospital Association Annual Survey, 2017 outpatient gross revenues (or charges) were about 49 percent of total hospital gross revenues. d
Smaller sources of differences come from the inclusion in the NHEA of hospitals that are excluded from HCUP. These include Federal hospitals (Department of Defense, Veterans Administration, Indian Health Services, and Department of Justice [prison] hospitals) as well as psychiatric, substance abuse, and long-term care hospitals. A third source of difference lies in the HCUP reliance on billed charges from hospitals to payers, adjusted to provide estimates of costs using hospital-wide cost-to-charge ratios, in contrast to the NHEA measurement of spending or revenue. HCUP costs estimate the amount of money required to produce hospital services, including expenses for wages, salaries, and benefits paid to staff as well as utilities, maintenance, and other similar expenses required to run a hospital. NHEA spending or revenue measures the amount of income received by the hospital for treatment and other services provided, including payments by insurers, patients, or government programs. The difference between revenues and costs includes profit for for-profit hospitals or surpluses for nonprofit hospitals.
Location of patients’ residence
Place of residence is based on the urban-rural classification scheme for U.S. counties developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) and based on the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) definition of a metropolitan service area as including a city and a population of at least 50,000 residents. For this Statistical Brief, we collapsed the NCHS categories into four groups according to the following:
Large Metropolitan
- Large Central Metropolitan: Counties in a metropolitan area with 1 million or more residents that satisfy at least one of the following criteria: (1) containing the entire population of the largest principal city of the metropolitan statistical area (MSA), (2) having their entire population contained within the largest principal city of the MSA, or (3) containing at least 250,000 residents of any principal city in the MSA
- Large Fringe Metropolitan: Counties in a metropolitan area with 1 million or more residents that do not qualify as large central metropolitan counties
Small Metropolitan
- Medium Metropolitan: Counties in a metropolitan area of 250,000–999,999 residents
- Small Metropolitan: Counties in a metropolitan area of 50,000–249,999 residents
Micropolitan:
- Micropolitan: Counties in a nonmetropolitan area of 10,000–49,999 residents
- Noncore: Counties in a nonmetropolitan and nonmicropolitan area
Community-level income
Community-level income is based on the median household income of the patient’s ZIP Code of residence. Quartiles are defined so that the total U.S. population is evenly distributed. Cut-offs for the quartiles are determined annually using ZIP Code demographic data obtained from Claritas, a vendor that produces population estimates and projections based on data from the U.S. Census Bureau. e The value ranges for the income quartiles vary by year. The income quartile is missing for patients who are homeless or foreign.
Expected payer
- Medicare: includes fee-for-service and managed care Medicare
- Medicaid: includes fee-for-service and managed care Medicaid
- Private insurance: includes commercial nongovernmental payers, regardless of the type of plan (e.g., private health maintenance organizations [HMOs], preferred provider organizations [PPOs])
- Self-pay/No charge: includes self-pay, no charge, charity, and no expected payment
- Other payers: includes other Federal and local government programs (e.g., TRICARE, CHAMPVA, Indian Health Service, Black Lung, Title V) and Workers’ Compensation
ED visits that were expected to be billed to the State Children’s Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) are included under Medicaid.
- Northeast: Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania
- Midwest: Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, and Kansas
- South: Delaware, Maryland, District of Columbia, Virginia, West Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas
- West: Montana, Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, Nevada, Washington, Oregon, California, Alaska, and Hawaii
Discharge status
Discharge status reflects the disposition of the patient at discharge from the ED and includes the following categories reported in this Statistical Brief: routine (to home); admitted as an inpatient to the same hospital; transfers (transfer to another short-term hospital; other transfers including skilled nursing facility, intermediate care, and another type of facility such as a nursing home); and all other dispositions (home healthcare; against medical advice [AMA]; died in the ED; or destination unknown).
Hospital characteristics
Data on hospital ownership and status as a teaching hospital was obtained from the American Hospital Association (AHA) Annual Survey of Hospitals. Hospital ownership/control includes categories for government nonfederal (public), private not-for-profit (voluntary), and private investor-owned (proprietary). Teaching hospital is defined as having a residency program approved by the American Medical Association, being a member of the Council of Teaching Hospitals, or having a ratio of full-time equivalent interns and residents to beds of 0.25 or higher.
Hospital trauma level
- Level I centers have comprehensive resources, are able to care for the most severely injured, and provide leadership in education and research.
- Level II centers have comprehensive resources and are able to care for the most severely injured, but do not provide leadership in education and research.
- Level III centers provide prompt assessment and resuscitation, emergency surgery, and, if needed, transfer to a level I or II center.
- Level IV/V centers provide trauma support in remote areas in which no higher level of care is available. These centers resuscitate and stabilize patients and arrange transfer to an appropriate trauma facility.
For this Statistical Brief, trauma hospitals were defined as those classified by the ASC/COT as a level I, II, or III trauma center. This is consistent with the classification of trauma centers used in the NEDS. The ACS/COT has a program that verifies hospitals as trauma level I, II, or III. h It is important to note that although all level I, II, and III trauma centers offer a high level of trauma care, there may be differences in the specific services and resources offered by hospitals of different levels. Trauma levels IV and V are designated at the State level (and not by ACS/COT) with varying criteria applied across States.
The Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP, pronounced "H-Cup") is a family of healthcare databases and related software tools and products developed through a Federal-State-Industry partnership and sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). HCUP databases bring together the data collection efforts of State data organizations, hospital associations, and private data organizations (HCUP Partners) and the Federal government to create a national information resource of encounter-level healthcare data. HCUP includes the largest collection of longitudinal hospital care data in the United States, with all-payer, encounter-level information beginning in 1988. These databases enable research on a broad range of health policy issues, including cost and quality of health services, medical practice patterns, access to healthcare programs, and outcomes of treatments at the national, State, and local market levels.
- Alaska Department of Health and Social Services
- Alaska State Hospital and Nursing Home Services Association
- Arizona Department of Health Services
- Arkansas Department of Health
- California Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development
- Colorado Hospital Association
- Connecticut Hospital Association
- Delaware Division of Public Health
- District of Columbia Hospital Association
- Florida Agency for Health Care Administration
- Georgia Hospital Association
- Hawaii Laulima Data Alliance
- Hawaii University of Hawai’i at Hilo
- Illinois Department of Public Health
- Indiana Hospital Association
- Iowa Hospital Association
- Kansas Hospital Association
- Kentucky Cabinet for Health and Family Services
- Louisiana Department of Health
- Maine Health Data Organization
- Maryland Health Services Cost Review Commission
- Massachusetts Center for Health Information and Analysis
- Michigan Health & Hospital Association
- Minnesota Hospital Association
- Mississippi State Department of Health
- Missouri Hospital Industry Data Institute
- Montana Hospital Association
- Nebraska Hospital Association Services
- Nevada Department of Health and Human
- New Hampshire Department of Health & Human
- New Jersey Department of Health
- New Mexico Department of Health
- New York State Department of Health
- North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services
- North Dakota (data provided by the Minnesota Hospital Association)
- Ohio Hospital Association
- Oklahoma State Department of Health
- Oregon Association of Hospitals and Health Systems
- Oregon Office of Health Analytics
- Pennsylvania Health Care Cost Containment Council
- Rhode Island Department of Health
- South Carolina Revenue and Fiscal Affairs Office
- South Dakota Association of Healthcare Organizations
- Tennessee Hospital Association
- Texas Department of State Health Services
- Utah Department of Health
- Vermont Association of Hospitals and Health Systems
- Virginia Health Information
- Washington State Department of Health
- West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources, West Virginia Health Care Authority
- Wisconsin Department of Health Services
- Wyoming Hospital Association
- About the NEDS
The HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) is a unique and powerful database that yields national estimates of emergency department (ED) visits. The NEDS was constructed using records from both the HCUP State Emergency Department Databases (SEDD) and the State Inpatient Databases (SID). The SEDD capture information on ED visits that do not result in an admission (i.e., patients who were treated in the ED and then released from the ED, or patients who were transferred to another hospital); the SID contain information on patients initially seen in the ED and then admitted to the same hospital. The NEDS was created to enable analyses of ED utilization patterns and support public health professionals, administrators, policymakers, and clinicians in their decision making regarding this critical source of care. The NEDS is produced annually beginning in 2006. Over time, the sampling frame for the NEDS has changed; thus, the number of States contributing to the NEDS varies from year to year. The NEDS is intended for national estimates only; no State-level estimates can be produced. The unweighted sample size for the 2017 NEDS is 33,506,645 (weighted, this represents 144,814,803 ED visits).
- For More Information
For other information on emergency department visits, refer to the HCUP Statistical Briefs located at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb_ed.jsp .
- HCUP Fast Stats at www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/faststats/landing.jsp for easy access to the latest HCUP-based statistics for healthcare information topics
- HCUPnet, HCUP’s interactive query system, at www.hcupnet.ahrq.gov/
For more information about HCUP, visit www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/ .
For a detailed description of HCUP and more information on the design of the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS), please refer to the following database documentation:
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Overview of the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS). Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Updated December 2019. www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/nedsoverview.jsp . Accessed February 3, 2020.
- Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of Nils Nordstrand of IBM Watson Health.
The HCUP Cost-to-Charge Ratios (CCRs) for NEDS Files were not publicly available at the time of publication, so an internal version was used in this Statistical Brief.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUP Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS) Database Documentation. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Updated April 27, 2020. www .hcup-us.ahrq.gov /db/nation/neds/nedsdbdocumentation.jsp . Accessed October 27, 2020.
For additional information about the NHEA, see Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). National Health Expenditure Data. CMS website. Updated December 17, 2019. www .cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems /Statistics-Trends-and-Reports /NationalHealthExpendData/index .html?redirect= /NationalHealthExpendData/ . Accessed February 3, 2020.
American Hospital Association. TrendWatch Chartbook, 2019. Table 4.2. Distribution of Inpatient vs. Outpatient Revenues, 1995–2017. www .aha.org/system/files /media/file/2019 /11/TrendwatchChartbook-2019-Appendices .pdf . Accessed March 19, 2020.
Claritas. Claritas Demographic Profile by ZIP Code. https://claritas360.claritas.com/mybestsegments/. Accessed February 3, 2020.
American Trauma Society. Trauma Information Exchange Program (TIEP). www .amtrauma.org/page/TIEP . Accessed June 11, 2020.
MacKenzie EJ, Hoyt DB, Sacra JC, Jurkovich GJ, Carlini AR, Teitelbaum SD, et al. National inventory of hospital trauma centers. JAMA. 2003;289(12):1515–22. [ PubMed : 12672768 ]
American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma, Verification, Review, and Consultation Program for Hospitals. Additional details are available at www .facs.org/quality-programs/trauma/vrc . Accessed July 17, 2020.
Moore BJ (IBM Watson Health), Liang L (AHRQ). Costs of Emergency Department Visits in the United States, 2017. HCUP Statistical Brief #268. December 2020. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb268-ED-Costs-2017.pdf .
- Cite this Page Moore BJ, Liang L. Costs of Emergency Department Visits in the United States, 2017. 2020 Dec 8. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2006 Feb-. Statistical Brief #268.
- PDF version of this page (326K)
In this Page
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP)
- Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS)
- Kids' Inpatient Database (KID)
- Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS)
- State Inpatient Databases (SID)
- State Ambulatory Surgery Databases (SASD)
- State Emergency Department Databases (SEDD)
- HCUP Overview
- HCUP Fact Sheet
- HCUP Partners
- HCUP User Support
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Review Costs of Emergency Department Visits for Mental and Substance Use Disorders in the United States, 2017. [Healthcare Cost and Utilizatio...] Review Costs of Emergency Department Visits for Mental and Substance Use Disorders in the United States, 2017. Karaca Z, Moore BJ. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. 2006 Feb
- Review Expected Payers and Patient Characteristics of Maternal Emergency Department Care, 2019. [Healthcare Cost and Utilizatio...] Review Expected Payers and Patient Characteristics of Maternal Emergency Department Care, 2019. McDermott KW, Reid LD, Owens PL. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. 2006 Feb
- Review Emergency Department Visits Involving Dental Conditions, 2018. [Healthcare Cost and Utilizatio...] Review Emergency Department Visits Involving Dental Conditions, 2018. Owens PL, Manski RJ, Weiss AJ. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. 2006 Feb
- Review Overview of Emergency Department Visits Related to Injuries, by Cause of Injury, 2017. [Healthcare Cost and Utilizatio...] Review Overview of Emergency Department Visits Related to Injuries, by Cause of Injury, 2017. Weiss AJ, Reid LD, Barrett ML. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. 2006 Feb
- Review Racial and Ethnic Differences in Emergency Department Visits Related to Substance Use Disorders, 2019. [Healthcare Cost and Utilizatio...] Review Racial and Ethnic Differences in Emergency Department Visits Related to Substance Use Disorders, 2019. Owens PL, Moore BJ. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs. 2006 Feb
Recent Activity
- Costs of Emergency Department Visits in the United States, 2017 - Healthcare Cos... Costs of Emergency Department Visits in the United States, 2017 - Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Heat-Related E.R. Visits Rose in 2023, C.D.C. Study Finds

By Noah Weiland
Reporting from Washington
The rate of emergency room visits caused by heat illness increased significantly last year in large swaths of the country compared with the previous five years, according to a study published on Thursday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The research, which analyzed visits during the warmer months of the year, offers new insight into the medical consequences of the record-breaking heat recorded across the country in 2023 as sweltering temperatures stretched late into the year.

What the Numbers Say: People in the South were especially affected by serious heat illness.
The researchers used data on emergency room visits from an electronic surveillance program used by states and the federal government to detect the spread of diseases. They compiled the number of heat-related emergency room visits in different regions of the country and compared them to data from the previous five years.
Nearly 120,000 heat-related emergency room visits were recorded in the surveillance program last year, with more than 90 percent of them occurring between May and September, the researchers found.
The highest rate of visits occurred in a region encompassing Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas. Overall, the study also found that men and people between the ages of 18 and 64 had higher rates of visits.
How It Happens: Heat can be a silent killer, experts and health providers say.
Last year was the warmest on Earth in a century and a half, with the hottest summer on record . Climate scientists have attributed the trend in part to greenhouse gas emissions and their effects on global warming, and they have warned that the timing of a shift in tropical weather patterns last year could foreshadow an even hotter 2024.
Heat illness often occurs gradually over the course of hours, and it can cause major damage to the body’s organs . Early symptoms of heat illness can include fatigue, dehydration, nausea, headache, increased heart rate and muscle spasms.
People do not typically think of themselves as at high risk of succumbing to heat or at greater risk than they once were, causing them to underestimate how a heat wave could lead them to the emergency room, said Kristie L. Ebi, a professor at the University of Washington who is an expert on the health risks of extreme heat.
“The heat you were asked to manage 10 years ago is not the heat you’re being asked to manage today,” she said. One of the first symptoms of heat illness can be confusion, she added, making it harder for someone to respond without help from others.
What Happens Next: States and hospitals are gearing up for another summer of extreme heat.
Dr. Srikanth Paladugu, an epidemiologist at the New Mexico Department of Health, said the state had nearly 450 heat-related emergency room visits in July last year alone and over 900 between April and September, more than double the number recorded during that stretch in 2019.
In preparation for this year’s warmer months, state officials are working to coordinate cooling shelters and areas where people can be splashed by water, Dr. Paladugu said.
Dr. Aneesh Narang, an emergency medicine physician at Banner-University Medical Center in Phoenix, said he often saw roughly half a dozen heat stroke cases a day last summer, including patients with body temperatures of 106 or 107 degrees. Heat illness patients require enormous resources, he added, including ice packs, fans, misters and cooling blankets.
“There’s so much that has to happen in the first few minutes to give that patient a chance for survival,” he said.
Dr. Narang said hospital employees had already begun evaluating protocols and working to ensure that there are enough supplies to contend with the expected number of heat illness patients this year.
“Every year now we’re doing this earlier and earlier,” he said. “We know that the chances are it’s going to be the same or worse.”
Noah Weiland writes about health care for The Times. More about Noah Weiland
Explore Our Weather Coverage
Extreme Weather Maps: Track the possibility of extreme weather in the places that are important to you .
Tornado Alerts: A tornado warning demands instant action. Here’s what to do if one comes your way .
Climate Change: What’s causing global warming? How can we fix it? Our F.A.Q. tackles your climate questions big and small .
Evacuating Pets: When disaster strikes, household pets’ lives are among the most vulnerable. You can avoid the worst by planning ahead .
Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Travel.State.Gov Newsroom
U.S. Passports News
International Travel News
U.S. Visas News
Intercountry Adoption News and Notices
Share this page:
Update on Change to U.S. Travel Policy Requiring COVID-19 Vaccination for nonimmigrant travel
Worldwide Visa Operations: Update
Employment-Based Fourth Preference (EB-4) Announcement
Suspension of Visa Services in Sudan
Diversity Visa 2024 Update
Nonimmigrant Visa Fee Increases to Take Effect June 17, 2023
India EB-3 Retrogression
Expiration of Covid-Era Visa Application Fee Receipts
Digital Visa Authorization (DVA) Proof of Concept
Final Rule Governing Public Charge Grounds of Visa Ineligibility
Visa Waiver Travel for Israeli Citizens
Important Update on Waivers of the Interview Requirement for Certain Nonimmigrant Visa Applicants
Department of State to Process Domestic Visa Renewals in Limited Pilot Program
Visa Information for Nationals of Haiti
Department of State/AILA Liaison Committee Meeting March 20, 2024
The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with an accepted COVID-19 vaccine to board a flight to the United States. CDC’s Amended Order Implementing Presidential Proclamation on Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic will no longer be in effect when the Presidential Proclamation Advancing the Safe Resumption of Global Travel During the COVID-19 Pandemic is revoked .
Please see: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/05/01/the-biden-administration-will-end-covid-19-vaccination-requirements-for-federal-employees-contractors-international-travelers-head-start-educators-and-cms-certified-facilities/
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Morning Rundown: Columbia classes go virtual over Gaza protest tensions, U.S. ally blasts Biden's cannibal comments, and the Spice Girls have an impromptu reunion
Gaza war protesters shut down Golden Gate Bridge, block traffic in other cities
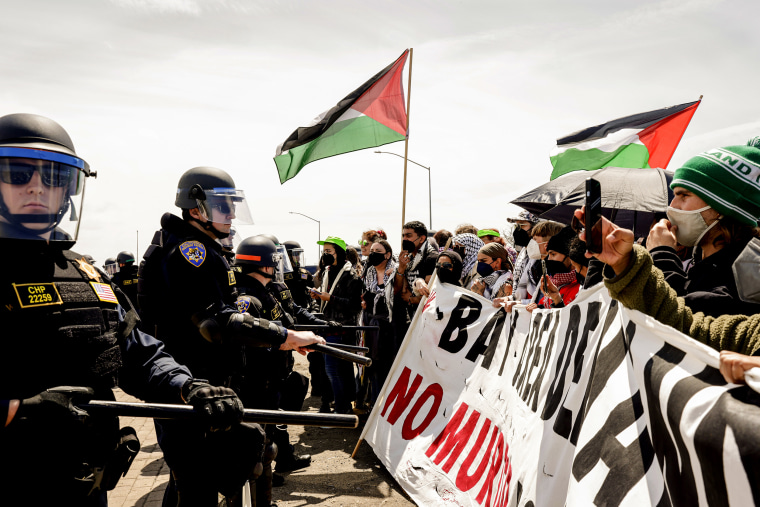

Demonstrators protesting the war in Gaza shut down San Francisco’s Golden Gate Bridge for around five hours Monday, as protests were also held in other cities in the U.S.
Demonstrators on the famous bridge held a sign that read “stop the world for Gaza” in capital letters. They used vehicles and chained themselves together to block travel lanes on the bridge, the California Highway Patrol said, adding that around 20 people were arrested.
NBC Bay Area reported that the bridge was closed for around five hours and that the traffic there was blocked beginning at around 7:30 a.m. The bridge reopened at around 12:15 p.m., the highway patrol said.
It’s not the first time pro-Palestinian protesters had blocked traffic on the Golden Gate Bridge to draw attention to the war and their cause. A group blocked traffic on the bridge in February, calling for a cease-fire and demanding the U.S. stop supplying weapons to Israel.
On Interstate 880 in Oakland, protesters chained themselves to 55-gallon drums filled with cement, according to the highway patrol.
“They are actively working to remove these individuals and lanes will be reopened,” the highway patrol said in a statement. “These individuals will be arrested.”
In Chicago, around 40 people were arrested at O’Hare International Airport after a group of protesters obstructed traffic, police said.
“Stop sending bombs,” read the stop sign-like badges on the chests of protesters who blocked the expressway leading to O’Hare by connecting themselves to one another with pipes over their arms.
The group Chicago Dissenters said the protest date was picked to coincide with the April 15 tax filing deadline.
“O’Hare International Airport is one of the largest in the country, and there will be NO business as usual while Palestinians suffer at the hands of American funded bombing by Israel,” the group wrote on social media.
New York City police said they were making arrests after protesters blocked traffic on the Brooklyn Bridge.
In Seattle, an expressway leading to Seattle-Tacoma International Airport was also blocked, airport authorities there said.
The Hamas attack on Israel on Oct. 7 and Israel's subsequent war against the group in Gaza have inflamed passions in the U.S. and in other parts of the world.
More than 30,000 people have been killed in Gaza, including thousands of civilians, according to health officials there. More than 1,200 people in Israel were killed in the Hamas attacks, and hostages were also taken.
Phil Helsel is a reporter for NBC News.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Statement from President Joe Biden on Iran’s Attacks against the State of Israel
Earlier today, Iran—and its proxies operating out of Yemen, Syria and Iraq—launched an unprecedented air attack against military facilities in Israel. I condemn these attacks in the strongest possible terms.
At my direction, to support the defense of Israel, the U.S. military moved aircraft and ballistic missile defense destroyers to the region over the course of the past week. Thanks to these deployments and the extraordinary skill of our servicemembers, we helped Israel take down nearly all of the incoming drones and missiles.
I’ve just spoken with Prime Minister Netanyahu to reaffirm America’s ironclad commitment to the security of Israel. I told him that Israel demonstrated a remarkable capacity to defend against and defeat even unprecedented attacks – sending a clear message to its foes that they cannot effectively threaten the security of Israel.
Tomorrow, I will convene my fellow G7 leaders to coordinate a united diplomatic response to Iran’s brazen attack. My team will engage with their counterparts across the region. And we will stay in close touch with Israel’s leaders. And while we have not seen attacks on our forces or facilities today, we will remain vigilant to all threats and will not hesitate to take all necessary action to protect our people.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Applying for a US visa is a lengthy process. Sometimes, the embassies may be overloaded and understaffed, making the visa application process even more difficult. That is why you have the option to apply for a US emergency visa in cases of emergency. The emergency visa refers only to the visa appointment. For example, getting […]
Applying for an Emergency Appointment. Step 1. Pay the visa application fee. Step 2. Complete the Nonimmigrant Visa Electronic Application (DS-160) form. Step 3. Request an emergency appointment by completing the online Emergency Request Form. If you require assistance with this form, call the call center. Please be sure to note the type of ...
Updated Date: April 21, 2022 Since January 22, 2022, DHS has required non-U.S. individuals seeking to enter the United States via land ports of entry and ferry terminals at the U.S.-Mexico and U.S.-Canada borders to be fully vaccinated for COVID-19 and provide proof of vaccination upon request.
To ask about emergency processing of a travel document, call the Contact Center at 800-375-5283 (TTY 800-767-1833) or request an appointment through My Appointment. If your situation qualifies for emergency processing, we will schedule an appointment for you with a local field office. Required Documents.
Visit the United States. The Secretary of Homeland Security and the Secretary of State work together to create and maintain an effective, efficient visa process that secures America's borders from external threats and ensures that our country remains open to legitimate travel. DHS provides a full range of online resources to help you plan ...
A citizen of a foreign country who seeks to enter the United States generally must first obtain a U.S. visa, which is placed in the traveler's passport, a travel document issued by the traveler's country of citizenship. Certain international travelers may be eligible to travel to the United States without a visa if they meet the ...
Emergencies. Getting Help in an Emergency. If you are overseas and in need of emergency assistance contact the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate . If you are concerned about a loved one overseas, please call: From the U.S. & Canada - 1-888-407-4747. From Overseas - +1 202-501-4444.
Learn about nonimmigrant visas to visit the U.S. ... the Trusted Traveler programs, what to do in an emergency, and more. International travel documents for children. ... Ask USA.gov a question at 1-844-USAGOV1 (1-844-872-4681) Find us on social media Facebook. Twitter. YouTube ...
Electronic System for Travel Authorization. ESTA is an automated system that determines the eligibility of visitors to travel to the United States under the Visa Waiver Program (VWP). Authorization via ESTA does not determine whether a traveler is admissible to the United States. U.S. Customs and Border Protection officers determine ...
Aliens seeking to lawfully enter into the United States must establish their admissibility to the satisfaction of the CBP officer. This is done as part of the inspection process. The reasons that a traveler who is applying for admission into the United States could be inadmissible are found in INA § 212(a).
This visualization depicts both counts and rates of emergency department visits from 2016-2021 for the 10 leading primary diagnoses and reasons for visit, stratified by selected patient and hospital characteristics. Rankings for the 10 leading categories were identified using weighted data from 2021 and were then assessed in prior years ...
November 17, 2022. The Department of State is committed to facilitating legitimate travel to the United States while safeguarding national security. Many applicants for U.S. visas are required by U.S. law to appear in person. However, local pandemic-era restrictions on public places like our overseas consular sections curbed our ability to see ...
Life-or-Death Emergencies. You may qualify for an appointment if you need to travel to a foreign country in the next two weeks because your immediate family member outside of the United States: Has died, or. Is dying (hospice care), or. Has a life-threatening illness or injury.
USA emergency visa appointment. For an emergency visa appointment at a US consulate, the first step is to pay the fees (usually around $160). Then complete the DS-160 form and make your emergency appointment request using the Emergency Request Form. These documents are available on the website of any US consulate.
Nonimmigrant visas allow people to visit the United States for short periods and for specific purposes. If you want to move here permanently, please see the information below on immigrant visas. A foreign national traveling to the United States for tourism needs a visitor visa (B-2) unless qualifying for entry under the Visa Waiver Program.
Key findings. Data from the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, 2018. The overall emergency department (ED) visit rate (39 visits per 100 persons) and visit rates by metropolitan statistical areas did not change between 2007 and 2018. The ED visit rate was highest for infants under age 1 year (101 visits per 100 infants) followed ...
Generally, if you want to visit (and not live in) the United States you must first obtain a visitor visa.Travelers from certain countries may be exempt from this requirement. For more information, please see the U.S. Department of State website.. If you want to travel to the United States for reasons other than business or pleasure, you must apply for a visa in the appropriate category.
How to Apply. Step 1. Pay the visa application fee. Step 2. Complete the Nonimmigrant Visa Electronic Application (DS-160) form. Step 3. Schedule an appointment online for the earliest available date. Please note that you must schedule an appointment before you can request an expedited date.
In 2020, an estimated 131 million emergency department (ED) visits occurred in the United States, with 19.0% of adults reporting a visit and 4.7% of children reporting two or more visits in the past 12 months ().In that time, over 20 million cases of COVID-19 caused a disruption in access to and use of care ().This report presents characteristics of ED visits, including those with mentions of ...
Introduction. Emergency department (ED) visits have grown in the United States, with the rate of increase from 1996 to 2013 exceeding that for hospital inpatient care. 1 In 2017, 13.3 percent of the U.S. population incurred at least one expense for an ED visit. 2 Furthermore, more than 50 percent of hospital inpatient stays in 2017 included evidence of ED services prior to admission. 3 Trends ...
Around 137 million people in the United States visit a hospital emergency room every year, according to a 2021 study published in the journal Health Services Research.The authors estimate that as ...
Nearly 120,000 heat-related emergency room visits were recorded in the surveillance program last year, with more than 90 percent of them occurring between May and September, the researchers found ...
The ED visit rates for patients with Medicare (46), patients with other primary expected sources of payment (43), and patients with no insurance (33) were not significantly different. Figure 3. Emergency department visit rates, by primary expected source of payment: United States, 2021 1Significantly different from all other sources of payment.
(ATLANTA) - Businesses and residents affected by the severe storms, straight-line winds, and flooding on April 2, 2024, in Dekalb, Gwinnett, Henry, Newton, Rockdale, and Walton Counties can now apply for low-interest disaster loans from the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA). SBA will open a Disaster Loan Outreach Center (DLOC) to assist Georgians in the declared counties applying for ...
Last Updated: May 4, 2023. The Administration will end the COVID-19 vaccine requirements for international air travelers at the end of the day on May 11, the same day that the COVID-19 public health emergency ends. This means starting May 12, noncitizen nonimmigrant air passengers will no longer need to show proof of being fully vaccinated with ...
Demonstrators protesting the war in Gaza shut down San Francisco's Golden Gate Bridge for around five hours Monday, as protests were also held in other cities in the U.S. Demonstrators on the ...
Statements and Releases. Earlier today, Iran—and its proxies operating out of Yemen, Syria and Iraq—launched an unprecedented air attack against military facilities in Israel. I condemn these ...
SMYRNA, Del. — The Delaware Emergency Management Agency (DEMA) and Delaware State Police, along with Public Service Enterprise Group Inc. (PSEG), will conduct a quarterly test of the Salem/Hope Creek Nuclear Generating Stations Alert and Notification system on Tuesday, April 2, 2024 at 7:20 p.m. There are 37 sirens in Delaware located within a 10-mile radius of the Salem-Hope Creek ...