- About Us 👨👩👧

Positive Impacts of Tourism on the Environment
If you asked random people from different countries whether tourism has negative or positive impacts on the environment, none of the answers would most likely prevail since their opinion will be based on their personal experience from travels. Tourism and environment have important, yet controversial relationship, that needs to be in a perfect balance to benefit each other.
Beautiful natural landscapes or unique flora and fauna are the main drivers of tourism into an area. But when too many tourists visit natural sites, environment and its inhabitants rather suffer from the negative impacts, which easily outweigh all the benefits due to exceeding the natural carrying capacity of a place .
On the other hand, when the number of visitors is balanced with respect for the natural environment, tourism has great potential in supporting or even starting out new conservation projects that protect unique areas and benefit local residents.
Sustainable tourism helps protect the environment
Many countries around the world depend on tourism as their main industry in providing jobs in rural areas and bringing in funds that would be otherwise out of their reach. Financial resources and employment are critical for local livelihoods and security. But as more and more countries focus on expanding their tourism sites, they often encounter problems with overconsumption of their finite natural resources, pollution, and degradation. This easily spirals into undesirable situations of negative impacts on the local environment and society.
Tourism as a fast-growing industry must follow the principles of sustainability in order to last long term while maintaining positive impacts for an area. In terms of environment, this means consumption of natural resources within acceptable limits, protecting biodiversity and making sure that essential ecological processes can take place, while providing a pleasant experience to visiting tourists [1] .
A part of striving towards sustainability is also raising awareness about the unique natural features of an area and educating visitors about their sustainable management. This helps them to understand the rules set in place and respect differences.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in relation to tourism
Tourism represents 10 percent of world GDP. The industry increasingly affects the environment, culture, and socio-economic development of a country. Due to such a great reach, it is a powerful tool in facilitating change.
According to the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism contributes directly or indirectly to all the 17 goals of sustainable development (SDGs) that were defined together with additional 169 SDG targets to ensure safer future for life on Earth by 2030.
Since 2018, UNWTO operates even an online platform dedicated to achievement of SDGs through tourism. You can visit it here: https://tourism4sdgs.org/ . On the platform is detailed description of each sustainable development goal in relation to tourism. SDGs address areas ranging from the importance of biodiversity, protection of marine ecosystems to urgent call for sustainable production and consumption.
Following the guidelines, UNWTO has, for example, partnered with the United Nations Environment Programme and the Ellen MacArthur Foundation and launched a Global Tourism Plastics Initiative to mitigate the problem of plastic pollution in the industry.
What are the positive impacts of tourism on the environment?
Sustainable tourism is the only way to go forward if the industry wants to grow. But throughout the last couple decades, tourism has been already growing and has introduced many new places to foreign visitors. In some regions, having the option of welcoming paying guests, tourism has brought many positive impacts on the environment. Let’s see their examples.
#1 Awareness raising and first-hand experience
Beautiful landscapes, animals in their natural environment, exotic ecosystems attract visitors from around the world. They are the primary reason why people travel. To get rest from their daily blues and experience ultimate relaxation from the connection with natural world. Tourism is the best tool to raise awareness of environmental values.
You learn the best when you do get to experience something directly, when you see it, touch it, and when you witness what threatens to destroy it. Personal visit of natural areas introduces you to the values they have for life. It makes you care about them, since you get to enjoy their special feeling. And memories you will have will encourage you to be environmentally-conscious in travel and personal life.
In January 2021, alarming pictures of the most touristy beaches in Bali buried in plastic waste that washed up on the shore due to the monsoon weather, appeared on social media of travelers and in the news [2] . The images have drawn global attention and created a bad rep for single-use plastic items, making us (consumers) more aware of the true impact.
#2 Tourism for skills learning and education
This is a special side of tourism but plays also an important role in positive impacts of tourism on the environment. Visitors do not have to be drawn to places just for entertainment or relaxation, they may come with the primary mission of learning a new skill or gaining certain knowledge. Tourists come to see a special feature in an area and often pay for their stay, for food, or training, which is a nice way to support the work they came to admire. Additionally, they may also put the new knowledge to use for their own projects.
One nice example of this form of tourism could be visiting a permaculture farm with the purpose to learn about the practices applied on the farm and exchange ideas on what might work at home. Another example, that could inspire many, is spending time on edible forest farms, learning about planting diversity of low maintenance plants on your piece of land. Or visiting villages excelling in agroforestry farming practices which have allowed them to harvest variety of products from their lands, while protecting sensitive mountainous environments, where intensive farming would not be an option.
#3 Support of conservation and biodiversity protection activities
Africa is a prime example of a country where tourism has had a positive effect on wildlife protection. Wildlife tourism in Africa makes around 36 percent of the tourism industry, contributing over $29 billion to the continent’s economy and provides jobs to 3.6 million people [3] .
The opportunity of seeing wild animals in their natural environment is what Africa is the most known for. This form of tourism reduces poverty and helps to empower women directly by giving them jobs, but even indirectly by allocating funds to build infrastructure – schools, hospitals.
Africa, Asia, South America, and the South Pacific focus more and more on the value of their wild natural areas. With the growth of tourism appear even new national and wildlife parks that connect sustainable tourism with biodiversity preservation.
For example, iSimangaliso Wetland Park in South Africa offers amazing experience for tourists who can choose between diving, snorkeling, kayaking or horseback riding in a landscape of 25,000 years old coastal dunes and swamp forests, while protecting the area’s sensitive ecosystems and unique species. The coastline is Africa’s only remaining nesting place of Loggerhead and Leatherback turtles [4] .
#4 Protection of endangered species
Countries begin to realize that their rare and endemic species are their symbol in the eyes of foreign visitors who are often attracted to the place because of them. Wild animals, virgin forests and a colorful palette of exotic plants are becoming an unusual sight in an economically developed world. The remaining spots that are still a home to this disappearing world are often turn to nature reserves and protected areas. This ensures better safety for endangered species that inhabit them.
Virunga National Park in East Africa has a story of conservation success to tell, even despite years of civil unrest and war in the surrounding areas, it has been declared an ecological pillar for the entire East and Central African biodiversity, having the largest concentration of birds and reptiles over other protected areas [5] .
Thanks to the initiative of the World Wildlife Fund and United Nations, the park has endured hard years and granted protection to endangered mountain gorillas, who were almost driven to extinction by human encroachment into their already limited habitat. Thanks to these extraordinary efforts and persistence, gorillas from the Virunga recovered and their number rose from 480 to over 600 [6] . The park is one of the most attractive tourist destinations, where you can see gorillas, chimpanzees, and many other iconic animals.
#5 Prevention of illegal trade and exploitation
Tourism brings new opportunities even to most remote places. The growing interest of tourists in visiting places where people live in connection with nature and animals gives chance to locals to sustain their families far from urban areas. In many cases, local communities quickly realize the need to protect what they have in order to attract tourists, as the stream of income from tourism is long-term and more advantageous than one-time sales of finite resources or poached animals.
A glimmer of hope sparked by the vision of attracting tourists takes place in two villages in Nepal that are known for being a transit points for illegal trade in pangolin meat and scales to Tibet and India.
The villages have joined a community-based pangolin conservation and education project . The goal of the project is to discourage local poachers from selling scales of pangolins to illegal traders, and thus interrupt the illegal trade pathway while protecting endangered pangolins . Participants of the project are also trained to help with long-term monitoring of pangolin population (species ecology, identification of threats and distribution).
#6 Finance and job opportunities
One in ten jobs worldwide are directly or indirectly in the tourism industry. Tourism creates decent work opportunities and economic growth even in rural or remote areas. Tourism employs women and is often the first job experience of young people. Money from the tourism then often goes into improving local infrastructure, and sustainable management and protection of natural wonders that attract visitors.
Better infrastructure and services have a positive impact on the environment. They revolve around consumption of resources and their management. Modern infrastructure for wastewater cleaning saves water and promotes more efficient use of it. Waste management facilities focus on recycling materials rather than just dumping waste into sea or to landfills.
Tourism also directly helps to fund conservation activities of national parks, or other nature and wildlife preservation projects. Visitors are usually asked to pay entrance fees or a small tax that is meant to support the project.
Costa Rica has one of the most successful rainforest conservation strategies, which enables the country to protect and care for its incredibly biodiversity rich rainforests, while at the same time generating income from tourism. A part of this income goes back to the rainforest conservation maintenance, research, and professional training of park guards. The rest sustains regional economy and creates balanced life opportunities for locals.
#7 Adoption of sustainable practices and new legislation
We have partially tapped into this aspect already in the previous point. It is closely linked. More funds available to a region mean better possibilities to improve infrastructure and services. Modernization of infrastructure goes hand in hand with a transition to sustainable technologies and seeking of long-term solutions that will benefit people and the local environment.
Many travelers care about their impact on the environment. They are willing to pay for environmentally friendly services and accommodation when visiting a new place. Many destinations already follow the suit and are changing their approach to tourism by considering their environmental impact in their management.
Additionally, governments also respond to this pressure and often enforce regulations to further protect local natural resources by adopting sustainable practices in the industry.
You can see this trend in increasing numbers of eco-tourism lodges around the world; or recycling bins placed in public areas to collect different materials for more efficient waste management; in water saving measures and recommendations adopted by accommodation providers; or even large-scale renewable energy projects that power whole regions.
Several studies highlighted the benefits of renewable energy for maintaining healthy environment during the seasonal influx of tourists to island destinations. For example, a study of Mediterranean islands sees renewable energy projects as a tool to provide sufficient energy to residents and tourists during the periods of increased demand, while protecting already fragile and limited resources islands have.
Tourism and the environment could go well together
The success of tourism relies on good infrastructure and decent quality of services. The industry therefore helps the community development and brings new sources of inspiration and motivation for protection of biodiversity rich natural areas, wildlife, or whole ecosystems.
Many new conservation projects raise hope of local people in being able to sustain their families, while taking care of their home, of their legacy, of a place shaped by the nurturing hands of their ancestors. They hope that their effort will be appreciated and rewarded by respectful visitors.
Was this article helpful?
About greentumble.
Greentumble was founded in the summer of 2015 by us, Sara and Ovi . We are a couple of environmentalists who seek inspiration for life in simple values based on our love for nature. Our goal is to inspire people to change their attitudes and behaviors toward a more sustainable life. Read more about us .
- Agriculture
- Biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Endangered Species
- Green Living
- Solar Energy
Sliding Sidebar
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Agriculture and the Environment
- Case Studies
- Chemistry and Toxicology
- Environment and Human Health
- Environmental Biology
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Ethics and Philosophy
- Environmental History
- Environmental Issues and Problems
- Environmental Processes and Systems
- Environmental Sociology and Psychology
- Environments
- Framing Concepts in Environmental Science
- Management and Planning
- Policy, Governance, and Law
- Quantitative Analysis and Tools
- Sustainability and Solutions
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
The role of tourism in sustainable development.
- Robert B. Richardson Robert B. Richardson Community Sustainability, Michigan State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.387
- Published online: 25 March 2021
Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world. In developing countries, tourism development has been used as an important strategy for increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, creating jobs, and improving food security. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage sites that attract international tourists whose local purchases generate income and support employment and economic development. Tourism has been associated with the principles of sustainable development because of its potential to support environmental protection and livelihoods. However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is multifaceted, as some types of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, many of which are borne by host communities.
The concept of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which involves the participation of large numbers of people, often in structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has been associated with economic leakage and dependence, along with negative environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to these economic, environmental, and social impacts. Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms. Tourism has played an important role in sustainable development in some countries through the development of alternative tourism models, including ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others that aim to enhance livelihoods, increase local economic growth, and provide for environmental protection. Although these models have been given significant attention among researchers, the extent of their implementation in tourism planning initiatives has been limited, superficial, or incomplete in many contexts.
The sustainability of tourism as a global system is disputed among scholars. Tourism is dependent on travel, and nearly all forms of transportation require the use of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for energy. The burning of fossil fuels for transportation generates emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to global climate change, which is fundamentally unsustainable. Tourism is also vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include the impacts of natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and civil unrest. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to global shocks include the impacts of climate change, economic crisis, global public health pandemics, oil price shocks, and acts of terrorism. It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, debatable, and potentially contradictory.
- conservation
- economic development
- environmental impacts
- sustainable development
- sustainable tourism
- tourism development
Introduction
Sustainable development is the guiding principle for advancing human and economic development while maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and social systems on which the economy depends. It is also the foundation of the leading global framework for international cooperation—the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015 ). The concept of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future (World Commission on Environment and Development [WCED], 1987 , p. 29), which defined it as “paths of human progress that meet the needs and aspirations of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.” Concerns about the environmental implications of economic development in lower income countries had been central to debates about development studies since the 1970s (Adams, 2009 ). The principles of sustainable development have come to dominate the development discourse, and the concept has become the primary development paradigm since the 1990s.
Tourism has played an increasingly important role in sustainable development since the 1990s, both globally and in particular countries and regions. For decades, tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, non-extractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ). Many developing countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development is increasingly viewed as an important tool in increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, and improving food security. Tourism enables communities that are poor in material wealth, but rich in history and cultural heritage, to leverage their unique assets for economic development (Honey & Gilpin, 2009 ). More importantly, tourism offers an alternative to large-scale development projects, such as construction of dams, and to extractive industries such as mining and forestry, all of which contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and the cultural values of Indigenous Peoples.
Environmental quality in destination areas is inextricably linked with tourism, as visiting natural areas and sightseeing are often the primary purpose of many leisure travels. Some forms of tourism, such as ecotourism, can contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of ecosystem functions in destination areas (Fennell, 2020 ; Gössling, 1999 ). Butler ( 1991 ) suggests that there is a kind of mutual dependence between tourism and the environment that should generate mutual benefits. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of species diversity, natural resources, and protected areas. Such ideas imply that tourism may be well aligned with the tenets of sustainable development.
However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is complex, as some forms of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, freshwater use, land use, and food consumption (Butler, 1991 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ; Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Assessments of the sustainability of tourism have highlighted several themes, including (a) parks, biodiversity, and conservation; (b) pollution and climate change; (c) prosperity, economic growth, and poverty alleviation; (d) peace, security, and safety; and (e) population stabilization and reduction (Buckley, 2012 ). From a global perspective, tourism contributes to (a) changes in land cover and land use; (b) energy use, (c) biotic exchange and extinction of wild species; (d) exchange and dispersion of diseases; and (e) changes in the perception and understanding of the environment (Gössling, 2002 ).
Research on tourism and the environment spans a wide range of social and natural science disciplines, and key contributions have been disseminated across many interdisciplinary fields, including biodiversity conservation, climate science, economics, and environmental science, among others (Buckley, 2011 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Given the global significance of the tourism sector and its environmental impacts, the role of tourism in sustainable development is an important topic of research in environmental science generally and in environmental economics and management specifically. Reviews of tourism research have highlighted future research priorities for sustainable development, including the role of tourism in the designation and expansion of protected areas; improvement in environmental accounting techniques that quantify environmental impacts; and the effects of individual perceptions of responsibility in addressing climate change (Buckley, 2012 ).
Tourism is one of the world’s largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020 ). As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national economies, and it represents a large and growing share of world trade (Hunter, 1995 ). Global tourism has had an average annual increase of 6.6% over the past half century, with international tourist arrivals rising sharply from 25.2 million in 1950 to more than 950 million in 2010 . In 2019 , the number of international tourists reached 1.5 billion, up 4% from 2018 (Fennell, 2020 ; United Nations World Tourism Organization [UNWTO], 2020 ). European countries are host to more than half of international tourists, but since 1990 , growth in international arrivals has risen faster than the global average, in both the Middle East and the Asia and Pacific region (UNWTO, 2020 ).
The growth in global tourism has been accompanied by an expansion of travel markets and a diversification of tourism destinations. In 1950 , the top five travel destinations were all countries in Europe and the Americas, and these destinations held 71% of the global travel market (Fennell, 2020 ). By 2002 , these countries represented only 35%, which underscores the emergence of newly accessible travel destinations in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the Pacific Rim, including numerous developing countries. Over the past 70 years, global tourism has grown significantly as an economic sector, and it has contributed to the economic development of dozens of nations.
Given the growth of international tourism and its emergence as one of the world’s largest export sectors, the question of its impact on economic growth for the host countries has been a topic of great interest in the tourism literature. Two hypotheses have emerged regarding the role of tourism in the economic growth process (Apergis & Payne, 2012 ). First, tourism-led growth hypothesis relies on the assumption that tourism is an engine of growth that generates spillovers and positive externalities through economic linkages that will impact the overall economy. Second, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis emphasizes policies oriented toward well-defined and enforceable property rights, stable political institutions, and adequate investment in both physical and human capital to facilitate the development of the tourism sector. Studies have concluded with support for both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Durbarry, 2004 ; Katircioglu, 2010 ) and the economic-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Katircioglu, 2009 ; Oh, 2005 ), whereas other studies have found support for a bidirectional causality for tourism and economic growth (e.g., Apergis & Payne, 2012 ; Lee & Chang, 2008 ).
The growth of tourism has been marked by an increase in the competition for tourist expenditures, making it difficult for destinations to maintain their share of the international tourism market (Butler, 1991 ). Tourism development is cyclical and subject to short-term cycles and overconsumption of resources. Butler ( 1980 ) developed a tourist-area cycle of evolution that depicts the number of tourists rising sharply over time through periods of exploration, involvement, and development, before eventual consolidation and stagnation. When tourism growth exceeds the carrying capacity of the area, resource degradation can lead to the decline of tourism unless specific steps are taken to promote rejuvenation (Butler, 1980 , 1991 ).
The potential of tourism development as a tool to contribute to environmental conservation, economic growth, and poverty reduction is derived from several unique characteristics of the tourism system (UNWTO, 2002 ). First, tourism represents an opportunity for economic diversification, particularly in marginal areas with few other export options. Tourists are attracted to remote areas with high values of cultural, wildlife, and landscape assets. The cultural and natural heritage of developing countries is frequently based on such assets, and tourism represents an opportunity for income generation through the preservation of heritage values. Tourism is the only export sector where the consumer travels to the exporting country, which provides opportunities for lower-income households to become exporters through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists. Tourism is also labor intensive; it provides small-scale employment opportunities, which also helps to promote gender equity. Finally, there are numerous indirect benefits of tourism for people living in poverty, including increased market access for remote areas through the development of roads, infrastructure, and communication networks. Nevertheless, travel is highly income elastic and carbon intensive, which has significant implications for the sustainability of the tourism sector (Lenzen et al., 2018 ).
Concerns about environmental issues appeared in tourism research just as global awareness of the environmental impacts of human activities was expanding. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm in 1972 , the same year as the publication of The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972 ), which highlighted the concerns about the implications of exponential economic and population growth in a world of finite resources. This was the same year that the famous Blue Marble photograph of Earth was taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft (Höhler, 2015 , p. 10), and the image captured the planet cloaked in the darkness of space and became a symbol of Earth’s fragility and vulnerability. As noted by Buckley ( 2012 ), tourism researchers turned their attention to social and environmental issues around the same time (Cohen, 1978 ; Farrell & McLellan, 1987 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Young, 1973 ).
The notion of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future , the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (WCED, 1987 ). The report characterized sustainable development in terms of meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987 , p. 43). Four basic principles are fundamental to the concept of sustainability: (a) the idea of holistic planning and strategy making; (b) the importance of preserving essential ecological processes; (c) the need to protect both human heritage and biodiversity; and (d) the need to develop in such a way that productivity can be sustained over the long term for future generations (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ). In addition to achieving balance between economic growth and the conservation of natural resources, there should be a balance of fairness and opportunity between the nations of the world.
Although the modern concept of sustainable development emerged with the publication of Our Common Future , sustainable development has its roots in ideas about sustainable forest management that were developed in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries (Blewitt, 2015 ; Grober, 2007 ). Sustainable forest management is concerned with the stewardship and use of forests in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and regeneration capacity as well as their potential to fulfill society’s demands for forest products and benefits. Building on these ideas, Daly ( 1990 ) offered two operational principles of sustainable development. First, sustainable development implies that harvest rates should be no greater than rates of regeneration; this concept is known as maximum sustainable yield. Second, waste emission rates should not exceed the natural assimilative capacities of the ecosystems into which the wastes are emitted. Regenerative and assimilative capacities are characterized as natural capital, and a failure to maintain these capacities is not sustainable.
Shortly after the emergence of the concept of sustainable development in academic and policy discourse, tourism researchers began referring to the notion of sustainable tourism (May, 1991 ; Nash & Butler, 1990 ), which soon became the dominant paradigm of tourism development. The concept of sustainable tourism, as with the role of tourism in sustainable development, has been interpreted in different ways, and there is a lack of consensus concerning its meaning, objectives, and indicators (Sharpley, 2000 ). Growing interest in the subject inspired the creation of a new academic journal, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , which was launched in 1993 and has become a leading tourism journal. It is described as “an international journal that publishes research on tourism and sustainable development, including economic, social, cultural and political aspects.”
The notion of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which is characterized by the participation of large numbers of people, often provided as structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has risen sharply in the last half century. International arrivals alone have increased by an average annual rate of more than 25% since 1950 , and many of those trips involved mass tourism activities (Fennell, 2020 ; UNWTO, 2020 ). Some examples of mass tourism include beach resorts, cruise ship tourism, gaming casinos, golf resorts, group tours, ski resorts, theme parks, and wildlife safari tourism, among others. Little data exist regarding the volume of domestic mass tourism, but nevertheless mass tourism activities dominate the global tourism sector. Mass tourism has been shown to generate benefits to host countries, such as income and employment generation, although it has also been associated with economic leakage (where revenue generated by tourism is lost to other countries’ economies) and economic dependency (where developing countries are dependent on wealthier countries for tourists, imports, and foreign investment) (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Khan, 1997 ; Peeters, 2012 ). Mass tourism has been associated with numerous negative environmental impacts and social impacts (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Ghimire, 2013 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ). Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to many of these economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Much of the early research on sustainable tourism focused on defining the concept, which has been the subject of vigorous debate (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Inskeep, 1991 ; Liu, 2003 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). Early definitions of sustainable tourism development seemed to fall in one of two categories (Sharpley, 2000 ). First, the “tourism-centric” paradigm of sustainable tourism development focuses on sustaining tourism as an economic activity (Hunter, 1995 ). Second, alternative paradigms have situated sustainable tourism in the context of wider sustainable development policies (Butler, 1991 ). One of the most comprehensive definitions of sustainable tourism echoes some of the language of the Brundtland Commission’s definition of sustainable development (WCED, 1987 ), emphasizing opportunities for the future while also integrating social and environmental concerns:
Sustainable tourism can be thought of as meeting the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunity for the future. Sustainable tourism development is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that we can fulfill economic, social and aesthetic needs while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity and life support systems. (Inskeep, 1991 , p. 461)
Hunter argued that over the short and long terms, sustainable tourism development should
“meet the needs and wants of the local host community in terms of improved living standards and quality of life;
satisfy the demands of tourists and the tourism industry, and continue to attract them in order to meet the first aim; and
safeguard the environmental resource base for tourism, encompassing natural, built and cultural components, in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.” (Hunter, 1995 , p. 156)
Numerous other definitions have been documented, and the term itself has been subject to widespread critique (Buckley, 2012 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, there have been numerous calls to move beyond debate about a definition and to consider how it may best be implemented in practice (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Liu, 2003 ). Cater ( 1993 ) identified three key criteria for sustainable tourism: (a) meeting the needs of the host population in terms of improved living standards both in the short and long terms; (b) satisfying the demands of a growing number of tourists; and (c) safeguarding the natural environment in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.
Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ). Similar criticisms have been leveled at the concept of sustainable development, which has been described as an oxymoron with a wide range of meanings (Adams, 2009 ; Daly, 1990 ) and “defined in such a way as to be either morally repugnant or logically redundant” (Beckerman, 1994 , p. 192). Sharpley ( 2000 ) suggests that in the tourism literature, there has been “a consistent and fundamental failure to build a theoretical link between sustainable tourism and its parental paradigm,” sustainable development (p. 2). Hunter ( 1995 ) suggests that practical measures designed to operationalize sustainable tourism fail to address many of the critical issues that are central to the concept of sustainable development generally and may even actually counteract the fundamental requirements of sustainable development. He suggests that mainstream sustainable tourism development is concerned with protecting the immediate resource base that will sustain tourism development while ignoring concerns for the status of the wider tourism resource base, such as potential problems associated with air pollution, congestion, introduction of invasive species, and declining oil reserves. The dominant paradigm of sustainable tourism development has been described as introverted, tourism-centric, and in competition with other sectors for scarce resources (McKercher, 1993a ). Hunter ( 1995 , p. 156) proposes an alternative, “extraparochial” paradigm where sustainable tourism development is reconceptualized in terms of its contribution to overall sustainable development. Such a paradigm would reconsider the scope, scale, and sectoral context of tourism-related resource utilization issues.
“Sustainability,” “sustainable tourism,” and “sustainable development” are all well-established terms that have often been used loosely and interchangeably in the tourism literature (Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, the subject of sustainable tourism has been given considerable attention and has been the focus of numerous academic compilations and textbooks (Coccossis & Nijkamp, 1995 ; Hall & Lew, 1998 ; Stabler, 1997 ; Swarbrooke, 1999 ), and it calls for new approaches to sustainable tourism development (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). The notion of sustainable tourism has been reconceptualized in the literature by several authors who provided alternative frameworks for tourism development (Buckley, 2012 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ; Sharpley, 2000 ).
Early research in sustainable tourism focused on the local environmental impacts of tourism, including energy use, water use, food consumption, and change in land use (Buckley, 2012 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ). Subsequent research has emphasized the global environmental impacts of tourism, such as greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity losses (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Additional research has emphasized the impacts of environmental change on tourism itself, including the impacts of climate change on tourist behavior (Gössling et al., 2012 ; Richardson & Loomis, 2004 ; Scott et al., 2012 ; Viner, 2006 ). Countries that are dependent on tourism for economic growth may be particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Richardson & Witkoswki, 2010 ).
The early focus on environmental issues in sustainable tourism has been broadened to include economic, social, and cultural issues as well as questions of power and equity in society (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Sharpley, 2014 ), and some of these frameworks have integrated notions of social equity, prosperity, and cultural heritage values. Sustainable tourism is dependent on critical long-term considerations of the impacts; notions of equity; an appreciation of the importance of linkages (i.e., economic, social, and environmental); and the facilitation of cooperation and collaboration between different stakeholders (Elliott & Neirotti, 2008 ).
McKercher ( 1993b ) notes that tourism resources are typically part of the public domain or are intrinsically linked to the social fabric of the host community. As a result, many commonplace tourist activities such as sightseeing may be perceived as invasive by members of the host community. Many social impacts of tourism can be linked to the overuse of the resource base, increases in traffic congestion, rising land prices, urban sprawl, and changes in the social structure of host communities. Given the importance of tourist–resident interaction, sustainable tourism development depends in part on the support of the host community (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ).
Tourism planning involves the dual objectives of optimizing the well-being of local residents in host communities and minimizing the costs of tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Tourism researchers have paid significant attention to examining the social impacts of tourism in general and to understanding host communities’ perceptions of tourism in particular. Studies of the social impacts of tourism development have examined the perceptions of local residents and the effects of tourism on social cohesion, traditional lifestyles, and the erosion of cultural heritage, particularly among Indigenous Peoples (Butler & Hinch, 2007 ; Deery et al., 2012 ; Mathieson & Wall, 1982 ; Sharpley, 2014 ; Whitford & Ruhanen, 2016 ).
Alternative Tourism and Sustainable Development
A wide body of published research is related to the role of tourism in sustainable development, and much of the literature involves case studies of particular types of tourism. Many such studies contrast types of alternative tourism with those of mass tourism, which has received sustained criticism for decades and is widely considered to be unsustainable (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ). Still, some tourism researchers have taken issue with the conclusion that mass tourism is inherently unsustainable (Sharpley, 2000 ; Weaver, 2007 ), and some have argued for developing pathways to “sustainable mass tourism” as “the desired and impending outcome for most destinations” (Weaver, 2012 , p. 1030). In integrating an ethical component to mass tourism development, Weaver ( 2014 , p. 131) suggests that the desirable outcome is “enlightened mass tourism.” Such suggestions have been contested in the literature and criticized for dubious assumptions about emergent norms of sustainability and support for growth, which are widely seen as contradictory (Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ).
Models of responsible or alternative tourism development include ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others. Most models of alternative tourism development emphasize themes that aim to counteract the perceived negative impacts of conventional or mass tourism. As such, the objectives of these models of tourism development tend to focus on minimizing environmental impacts, supporting biodiversity conservation, empowering local communities, alleviating poverty, and engendering pleasant relationships between tourists and residents.
Approaches to alternative tourism development tend to overlap with themes of responsible tourism, and the two terms are frequently used interchangeably. Responsible tourism has been characterized in terms of numerous elements, including
ensuring that communities are involved in and benefit from tourism;
respecting local, natural, and cultural environments;
involving the local community in planning and decision-making;
using local resources sustainably;
behaving in ways that are sensitive to the host culture;
maintaining and encouraging natural, economic, and cultural diversity; and
assessing environmental, social, and economic impacts as a prerequisite to tourism development (Spenceley, 2012 ).
Hetzer ( 1965 ) identified four fundamental principles or perquisites for a more responsible form of tourism: (a) minimum environmental impact; (b) minimum impact on and maximum respect for host cultures; (c) maximum economic benefits to the host country; and (d) maximum leisure satisfaction to participating tourists.
The history of ecotourism is closely connected with the emergence of sustainable development, as it was born out of a concern for the conservation of biodiversity. Ecotourism is a form of tourism that aims to minimize local environmental impacts while bringing benefits to protected areas and the people living around those lands (Honey, 2008 ). Ecotourism represents a small segment of nature-based tourism, which is understood as tourism based on the natural attractions of an area, such as scenic areas and wildlife (Gössling, 1999 ). The ecotourism movement gained momentum in the 1990s, primarily in developing countries in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and nearly all countries are now engaged in some form of ecotourism. In some communities, ecotourism is the primary economic activity and source of income and economic development.
The term “ecotourism” was coined by Hector Ceballos-Lascuráin and defined by him as “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 13). In discussing ecotourism resources, he also made reference to “any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 14). The basic precepts of ecotourism had been discussed long before the actual use of the term. Twenty years earlier, Hetzer ( 1965 ) referred to a form of tourism “based principally upon natural and archaeological resources such as caves, fossil sites (and) archaeological sites.” Thus, both natural resources and cultural resources were integrated into ecotourism frameworks from the earliest manifestations.
Costa Rica is well known for having successfully integrated ecotourism in its overall strategy for sustainable development, and numerous case studies of ecotourism in Costa Rica appear in the literature (Chase et al., 1998 ; Fennell & Eagles, 1990 ; Gray & Campbell, 2007 ; Hearne & Salinas, 2002 ). Ecotourism in Costa Rica has been seen as having supported the economic development of the country while promoting biodiversity conservation in its extensive network of protected areas. Chase et al. ( 1998 ) estimated the demand for ecotourism in a study of differential pricing of entrance fees at national parks in Costa Rica. The authors estimated elasticities associated with the own-price, cross-price, and income variables and found that the elasticities of demand were significantly different between three different national park sites. The results reveal the heterogeneity characterizing tourist behavior and park attractions and amenities. Hearne and Salinas ( 2002 ) used choice experiments to examine the preferences of domestic and foreign tourists in Costa Rica in an ecotourism site. Both sets of tourists demonstrated a preference for improved infrastructure, more information, and lower entrance fees. Foreign tourists demonstrated relatively stronger preferences for the inclusion of restrictions in the access to some trails.
Ecotourism has also been studied extensively in Kenya (Southgate, 2006 ), Malaysia (Lian Chan & Baum, 2007 ), Nepal (Baral et al., 2008 ), Peru (Stronza, 2007 ), and Taiwan (Lai & Nepal, 2006 ), among many other countries. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential for ecotourism to contribute to sustainable development by providing support for biodiversity conservation, local livelihoods, and regional development.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism (CBT) is a model of tourism development that emphasizes the development of local communities and allows for local residents to have substantial control over its development and management, and a major proportion of the benefits remain within the community. CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993 ; Hall & Lew, 2009 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ).
Community-based tourism has been examined for its potential to contribute to poverty reduction. In a study of the viability of the CBT model to support socioeconomic development and poverty alleviation in Nicaragua, tourism was perceived by participants in the study to have an impact on employment creation in their communities (Zapata et al., 2011 ). Tourism was seen to have had positive impacts on strengthening local knowledge and skills, particularly on the integration of women to new roles in the labor market. One of the main perceived gains regarding the environment was the process of raising awareness regarding the conservation of natural resources. The small scale of CBT operations and low capacity to accommodate visitors was seen as a limitation of the model.
Spenceley ( 2012 ) compiled case studies of community-based tourism in countries in southern Africa, including Botswana, Madagascar, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. In this volume, authors characterize community-based and nature-based tourism development projects in the region and demonstrate how community participation in planning and decision-making has generated benefits for local residents and supported conservation initiatives. They contend that responsible tourism practices are of particular importance in the region because of the rich biological diversity, abundant charismatic wildlife, and the critical need for local economic development and livelihood strategies.
In Kenya, CBT enterprises were not perceived to have made a significant impact on poverty reduction at an individual household level, in part because the model relied heavily on donor funding, reinforcing dependency and poverty (Manyara & Jones, 2007 ). The study identified several critical success factors for CBT enterprises, namely, awareness and sensitization, community empowerment, effective leadership, and community capacity building, which can inform appropriate tourism policy formulation in Kenya. The impacts of CBT on economic development and poverty reduction would be greatly enhanced if tourism initiatives were able to emphasize independence, address local community priorities, enhance community empowerment and transparency, discourage elitism, promote effective community leadership, and develop community capacity to operate their own enterprises more efficiently.
Pro-Poor Tourism
Pro-poor tourism is a model of tourism development that brings net benefits to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ; Harrison, 2008 ). Although its theoretical foundations and development objectives overlap to some degree with those of community-based tourism and other models of AT, the key distinctive feature of pro-poor tourism is that it places poor people and poverty at the top of the agenda. By focusing on a very simple and incontrovertibly moral idea, namely, the net benefits of tourism to impoverished people, the concept has broad appeal to donors and international aid agencies. Harnessing the economic benefits of tourism for pro-poor growth means capitalizing on the advantages while reducing negative impacts to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ). Pro-poor approaches to tourism development include increasing access of impoverished people to economic benefits; addressing negative social and environmental impacts associated with tourism; and focusing on policies, processes, and partnerships that seek to remove barriers to participation by people living in poverty. At the local level, pro-poor tourism can play a very significant role in livelihood security and poverty reduction (Ashley & Roe, 2002 ).
Rogerson ( 2011 ) argues that the growth of pro-poor tourism initiatives in South Africa suggests that the country has become a laboratory for the testing and evolution of new approaches toward sustainable development planning that potentially will have relevance for other countries in the developing world. A study of pro-poor tourism development initiatives in Laos identified a number of favorable conditions for pro-poor tourism development, including the fact that local people are open to tourism and motivated to participate (Suntikul et al., 2009 ). The authors also noted a lack of development in the linkages that could optimize the fulfilment of the pro-poor agenda, such as training or facilitation of local people’s participation in pro-poor tourism development at the grassroots level.
Critics of the model have argued that pro-poor tourism is based on an acceptance of the status quo of existing capitalism, that it is morally indiscriminate and theoretically imprecise, and that its practitioners are academically and commercially marginal (Harrison, 2008 ). As Chok et al. ( 2007 ) indicate, the focus “on poor people in the South reflects a strong anthropocentric view . . . and . . . environmental benefits are secondary to poor peoples’” benefits (p. 153).
Harrison ( 2008 ) argues that pro-poor tourism is not a distinctive approach to tourism as a development tool and that it may be easier to discuss what pro-poor tourism is not than what it is. He concludes that it is neither anticapitalist nor inconsistent with mainstream tourism on which it relies; it is neither a theory nor a model and is not a niche form of tourism. Further, he argues that it has no distinctive method and is not only about people living in poverty.
Slow Tourism
The concept of slow tourism has emerged as a model of sustainable tourism development, and as such, it lacks an exact definition. The concept of slow tourism traces its origin back to some institutionalized social movements such as “slow food” and “slow cities” that began in Italy in the 1990s and spread rapidly around the world (Fullagar et al., 2012 ; Oh et al., 2016 , p. 205). Advocates of slow tourism tend to emphasize slowness in terms of speed, mobility, and modes of transportation that generate less environmental pollution. They propose niche marketing for alternative forms of tourism that focus on quality upgrading rather than merely increasing the quantity of visitors via the established mass-tourism infrastructure (Conway & Timms, 2010 ).
In the context of the Caribbean region, slow tourism has been promoted as more culturally sensitive and authentic, as compared to the dominant mass tourism development model that is based on all-inclusive beach resorts dependent on foreign investment (Conway & Timms, 2010 ). Recognizing its value as an alternative marketing strategy, Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) make the case for rebranding alternative tourism in the Caribbean as a means of revitalizing the sector for the changing demands of tourists in the 21st century . They suggest that slow tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism, which “relies on increasing the quantity of tourists who move through the system with little regard to either the quality of the tourists’ experience or the benefits that accrue to the localities the tourist visits” (Conway & Timms, 2010 , p. 332). The authors draw on cases from Barbados, the Grenadines, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago to characterize models of slow tourism development in remote fishing villages and communities near nature preserves and sea turtle nesting sites.
Although there is a growing interest in the concept of slow tourism in the literature, there seems to be little agreement about the exact nature of slow tourism and whether it is a niche form of special interest tourism or whether it represents a more fundamental potential shift across the industry. Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) focus on the destination, advocating for slow tourism in terms of a promotional identity for an industry in need of rebranding. Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 77) discusses the implementation of slow tourism in terms of “encouraging visitors to make slower choices when planning and enjoying their holidays.” It is not clear whether slow tourism is a marketing strategy, a mindset, or a social movement, but the literature on slow tourism nearly always equates the term with sustainable tourism (Caffyn, 2012 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Oh et al., 2016 ). Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 80) suggests that slow tourism could offer a “win–win,” which she describes as “a more sustainable form of tourism; keeping more of the economic benefits within the local community and destination; and delivering a more meaningful and satisfying experience.” Research on slow tourism is nascent, and thus the contribution of slow tourism to sustainable development is not well understood.
Impacts of Tourism Development
The role of tourism in sustainable development can be examined through an understanding of the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism. Tourism is a global phenomenon that involves travel, recreation, the consumption of food, overnight accommodations, entertainment, sightseeing, and other activities that simultaneously intersect the lives of local residents, businesses, and communities. The impacts of tourism involve benefits and costs to all groups, and some of these impacts cannot easily be measured. Nevertheless, they have been studied extensively in the literature, which provides some context for how these benefits and costs are distributed.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The travel and tourism sector is one of the largest components of the global economy, and global tourism has increased exponentially since the end of the Second World War (UNWTO, 2020 ). The direct, indirect, and induced economic impact of global travel accounted for 8.9 trillion U.S. dollars in contribution to the global gross domestic product (GDP), or 10.3% of global GDP. The global travel and tourism sector supports approximately 330 million jobs, or 1 in 10 jobs around the world. From an economic perspective, tourism plays a significant role in sustainable development. In many developing countries, tourism has the potential to play a unique role in income generation and distribution relative to many other industries, in part because of its high multiplier effect and consumption of local goods and services. However, research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been fully realized (Liu, 2003 ).
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tourism expenditure on GDP, income, employment, and public sector revenue. Narayan ( 2004 ) used a computable general equilibrium model to estimate the economic impact of tourism growth on the economy of Fiji. Tourism is Fiji’s largest industry, with average annual growth of 10–12%; and as a middle-income country, tourism is critical to Fiji’s economic development. The findings indicate that an increase in tourism expenditures was associated with an increase in GDP, an improvement in the country’s balance of payments, and an increase in real consumption and national welfare. Evidence suggests that the benefits of tourism expansion outweigh any export effects caused by an appreciation of the exchange rate and an increase in domestic prices and wages.
Seetanah ( 2011 ) examined the potential contribution of tourism to economic growth and development using panel data of 19 island economies around the world from 1990 to 2007 and revealed that tourism development is an important factor in explaining economic performance in the selected island economies. The results have policy implications for improving economic growth by harnessing the contribution of the tourism sector. Pratt ( 2015 ) modeled the economic impact of tourism for seven small island developing states in the Pacific, the Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. In most states, the transportation sector was found to have above-average linkages to other sectors of the economy. The results revealed some advantages of economies of scale for maximizing the economic contribution of tourism.
Apergis and Payne ( 2012 ) examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic growth for a panel of nine Caribbean countries. The panel of Caribbean countries includes Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago. The authors use a panel error correction model to reveal bidirectional causality between tourism and economic growth in both the short run and the long run. The presence of bidirectional causality reiterates the importance of the tourism sector in the generation of foreign exchange income and in financing the production of goods and services within these countries. Likewise, stable political institutions and adequate government policies to ensure the appropriate investment in physical and human capital will enhance economic growth. In turn, stable economic growth will provide the resources needed to develop the tourism infrastructure for the success of the countries’ tourism sector. Thus, policy makers should be cognizant of the interdependent relationship between tourism and economic growth in the design and implementation of economic policy. The mixed nature of these results suggest that the relationship between tourism and economic growth depends largely on the social and economic context as well as the role of tourism in the economy.
The economic benefits and costs of tourism are frequently distributed unevenly. An analysis of the impact of wildlife conservation policies in Zambia on household welfare found that households located near national parks earn higher levels of income from wage employment and self-employment than other rural households in the country, but they were also more likely to suffer crop losses related to wildlife conflicts (Richardson et al., 2012 ). The findings suggest that tourism development and wildlife conservation can contribute to pro-poor development, but they may be sustainable only if human–wildlife conflicts are minimized or compensated.
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ranging from local effects to contributions to global environmental change (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Tourism is both dependent on water resources and a factor in global and local freshwater use. Tourists consume water for drinking, when showering and using the toilet, when participating in activities such as winter ski tourism (i.e., snowmaking), and when using swimming pools and spas. Fresh water is also needed to maintain hotel gardens and golf courses, and water use is embedded in tourism infrastructure development (e.g., accommodations, laundry, dining) and in food and fuel production. Direct water consumption in tourism is estimated to be approximately 350 liters (L) per guest night for accommodation; when indirect water use from food, energy, and transport are considered, total water use in tourism is estimated to be approximately 6,575 L per guest night, or 27,800 L per person per trip (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). In addition, tourism contributes to the pollution of oceans as well as lakes, rivers, and other freshwater systems (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling et al., 2011 ).
The clearing and conversion of land is central for tourism development, and in many cases, the land used for tourism includes roads, airports, railways, accommodations, trails, pedestrian walks, shopping areas, parking areas, campgrounds, vacation homes, golf courses, marinas, ski resorts, and indirect land use for food production, disposal of solid wastes, and the treatment of wastewater (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Global land use for accommodation is estimated to be approximately 42 m 2 per bed. Total global land use for tourism is estimated to be nearly 62,000 km 2 , or 11.7 m 2 per tourist; more than half of this estimate is represented by land use for traffic infrastructure.
Tourism and hospitality have direct and indirect links to nearly all aspects of food production, preparation, and consumption because of the quantities of food consumed in tourism contexts (Gössling et al., 2011 ). Food production has significant implications for sustainable development, given the growing global demand for food. The implications include land conversion, losses to biodiversity, changes in nutrient cycling, and contributions to greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change (Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Global food use for tourism is estimated to be approximately 39.4 megatons 1 (Mt), about 38% than the amount of food consumed at home. This equates to approximately 1,800 grams (g) of food consumed per tourist per day.
Although tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, (Gössling, 2000 ), assessments reveal that such pursuits have a significant carbon footprint, as tourism is significantly more carbon intensive than other potential areas of economic development (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Tourism is dependent on energy, and virtually all energy use in the tourism sector is derived from fossil fuels, which contribute to global greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change. Energy use for tourism has been estimated to be approximately 3,575 megajoules 2 (MJ) per trip, including energy for travel and accommodations (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). A previous estimate of global carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions from tourism provided values of 1.12 gigatons 3 (Gt) of CO 2 , amounting to about 3% of global CO 2 -equivalent (CO 2 e) emissions (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). However, these analyses do not cover the supply chains underpinning tourism and do not therefore represent true carbon footprints. A more complete analysis of the emissions from energy consumption necessary to sustain the tourism sector would include food and beverages, infrastructure construction and maintenance, retail, and financial services. Between 2009 and 2013 , tourism’s global carbon footprint is estimated to have increased from 3.9 to 4.5 GtCO 2 e, four times more than previously estimated, accounting for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). The majority of this footprint is exerted by and within high-income countries. The rising global demand for tourism is outstripping efforts at decarbonization of tourism operations and as a result is accelerating global carbon emissions.
Social Impacts of Tourism
The social impacts of tourism have been widely studied, with an emphasis on residents’ perceptions in the host community (Sharpley, 2014 ). Case studies include research conducted in Australia (Faulkner & Tideswell, 1997 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Tovar & Lockwood, 2008 ), Belize (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ), China (Gu & Ryan, 2008 ), Fiji (King et al., 1993 ), Greece (Haralambopoulos & Pizam, 1996 ; Tsartas, 1992 ), Hungary (Rátz, 2000 ), Thailand (Huttasin, 2008 ), Turkey (Kuvan & Akan, 2005 ), the United Kingdom (Brunt & Courtney, 1999 ; Haley et al., 2005 ), and the United States (Andereck et al., 2005 ; Milman & Pizam, 1988 ), among others. The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves.
Studies of residents’ perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys. In most cases, residents recognize the economic dependence on tourism for income, and there is substantial evidence to suggest that working in or owning a business in tourism or a related industry is associated with more positive perceptions of tourism (Andereck et al., 2007 ). The perceived nature of negative effects is complex and often conveys a dislike of crowding, traffic congestion, and higher prices for basic needs (Deery et al., 2012 ). When the number of tourists far exceeds that of the resident population, negative attitudes toward tourism may manifest (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ). However, residents who recognize negative impacts may not necessarily oppose tourism development (King et al., 1993 ).
In some regions, little is known about the social and cultural impacts of tourism despite its dominance as an economic sector. Tourism is a rapidly growing sector in Cuba, and it is projected to grow at rates that exceed the average projected growth rates for the Caribbean and the world overall (Salinas et al., 2018 ). Still, even though there has been rapid tourism development in Cuba, there has been little research related to the environmental and sociocultural impacts of this tourism growth (Rutty & Richardson, 2019 ).
In some international tourism contexts, studies have found that residents are generally resentful toward tourism because it fuels inequality and exacerbates racist attitudes and discrimination (Cabezas, 2004 ; Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Mbaiwa, 2005 ). Other studies revealed similar narratives and recorded statements of exclusion and socioeconomic stratification (Sanchez & Adams, 2008 ). Local residents often must navigate the gaps in the racialized, gendered, and sexualized structures imposed by the global tourism industry and host-country governments (Cabezas, 2004 ).
However, during times of economic crisis, residents may develop a more permissive view as their perceptions of the costs of tourism development decrease (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a decrease in the perception of the negative impacts.
There is a growing body of research on Indigenous and Aboriginal tourism that emphasizes justice issues such as human rights and self-empowerment, control, and participation of traditional owners in comanagement of destinations (Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Ryan & Huyton, 2000 ; Whyte, 2010 ).
Sustainability of Tourism
A process or system is said to be sustainable to the extent that it is robust, resilient, and adaptive (Anderies et al., 2013 ). By most measures, the global tourism system does not meet these criteria for sustainability. Tourism is not robust in that it cannot resist threats and perturbations, such as economic shocks, public health pandemics, war, and other disruptions. Tourism is not resilient in that it does not easily recover from failures, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. Furthermore, tourism is not adaptive in that it is often unable to change in response to external conditions. One example that underscores the failure to meet all three criteria is the dependence of tourism on fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which are key inputs for tourism development. This dependence itself is not sustainable (Wheeller, 2007 ), and thus the sustainability of tourism is questionable.
Liu ( 2003 ) notes that research related to the role of tourism in sustainable development has emphasized supply-side concepts such as sustaining tourism resources and ignored the demand side, which is particularly vulnerable to social and economic shocks. Tourism is vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include disaster vulnerability in coastal Thailand (Calgaro & Lloyd, 2008 ), bushfires in northeast Victoria in Australia (Cioccio & Michael, 2007 ), forest fires in British Columbia, Canada (Hystad & Keller, 2008 ); and outbreak of foot and mouth disease in the United Kingdom (Miller & Ritchie, 2003 ).
Like most other economic sectors, tourism is vulnerable to the impacts of earthquakes, particularly in areas where tourism infrastructure may not be resilient to such shocks. Numerous studies have examined the impacts of earthquake events on tourism, including studies of the aftermath of the 1997 earthquake in central Italy (Mazzocchi & Montini, 2001 ), the 1999 earthquake in Taiwan (Huan et al., 2004 ; Huang & Min, 2002 ), and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in western Sichuan, China (Yang et al., 2011 ), among others.
Tourism is vulnerable to extreme weather events. Regional economic strength has been found to be associated with lower vulnerability to natural disasters. Kim and Marcoullier ( 2015 ) examined the vulnerability and resilience of 10 tourism-based regional economies that included U.S. national parks or protected seashores situated on the Gulf of Mexico or Atlantic Ocean coastline that were affected by several hurricanes over a 26-year period. Regions with stronger economic characteristics prior to natural disasters were found to have lower disaster losses than regions with weaker economies.
Tourism is extremely sensitive to oil spills, whatever their origin, and the volume of oil released need not be large to generate significant economic losses (Cirer-Costa, 2015 ). Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to the localized shock of an oil spill include research on the impacts of oil spills in Alaska (Coddington, 2015 ), Brazil (Ribeiro et al., 2020 ), Spain (Castanedo et al., 2009 ), affected regions in the United States along the Gulf of Mexico (Pennington-Gray et al., 2011 ; Ritchie et al., 2013 ), and the Republic of Korea (Cheong, 2012 ), among others. Future research on the vulnerability of tourist destinations to oil spills should also incorporate freshwater environments, such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where the rupture of oil pipelines is more frequent.
Significant attention has been paid to assessing the vulnerability of tourist destinations to acts of terrorism and the impacts of terrorist attacks on regional tourist economies (Liu & Pratt, 2017 ). Such studies include analyses of the impacts of terrorist attacks on three European countries, Greece, Italy, and Austria (Enders et al., 1992 ); the impact of the 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States (Goodrich, 2002 ); terrorism and tourism in Nepal (Bhattarai et al., 2005 ); vulnerability of tourism livelihoods in Bali (Baker & Coulter, 2007 ); the impact of terrorism on tourist preferences for destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands (Arana & León, 2008 ); the 2011 massacres in Olso and Utøya, Norway (Wolff & Larsen, 2014 ); terrorism and political violence in Tunisia (Lanouar & Goaied, 2019 ); and the impact of terrorism on European tourism (Corbet et al., 2019 ), among others. Pizam and Fleischer ( 2002 ) studied the impact of acts of terrorism on tourism demand in Israel between May 1991 and May 2001 , and they confirmed that the frequency of acts of terrorism had caused a larger decline in international tourist arrivals than the severity of these acts. Most of these are ex post studies, and future assessments of the underlying conditions of destinations could reveal a deeper understanding of the vulnerability of tourism to terrorism.
Tourism is vulnerable to economic crisis, both local economic shocks (Okumus & Karamustafa, 2005 ; Stylidis & Terzidou, 2014 ) and global economic crisis (Papatheodorou et al., 2010 ; Smeral, 2010 ). Okumus and Karamustafa ( 2005 ) evaluated the impact of the February 2001 economic crisis in Turkey on tourism, and they found that the tourism industry was poorly prepared for the economic crisis despite having suffered previous impacts related to the Gulf War in the early 1990s, terrorism in Turkey in the 1990s, the civil war in former Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, an internal economic crisis in 1994 , and two earthquakes in the northwest region of Turkey in 1999 . In a study of the attitudes and perceptions of citizens of Greece, Stylidis and Terzidou ( 2014 ) found that economic crisis is associated with increased support for tourism development, particularly out of self-interest. Economic crisis diminishes residents’ concern for environmental issues. In a study of the behavior of European tourists amid an economic crisis, Eugenio-Martin and Campos-Soria ( 2014 ) found that the probability of households cutting back on travel expenditures depends largely on the climate and economic conditions of tourists’ home countries, and households that do reduce travel spending engage in tourism closer to home.
Becken and Lennox ( 2012 ) studied the implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism in New Zealand, and they estimate that a doubling of oil prices is associated with a 1.7% decrease in real gross national disposable income and a 9% reduction in the real value of tourism exports. Chatziantoniou et al. ( 2013 ) investigated the relationship among oil price shocks, tourism variables, and economic indicators in four European Mediterranean countries and found that aggregate demand oil price shocks generated a lagged effect on tourism-generated income and economic growth. Kisswani et al. ( 2020 ) examined the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts and the sensitive susceptibility of tourism to oil price changes using nonlinear analysis. The findings document a long-run asymmetrical effect for most countries, after incorporating the structural breaks, suggesting that governments and tourism businesses and organizations should interpret oil price fluctuations cautiously.
Finally, the sustainability of tourism has been shown to be vulnerable to the outbreak of infectious diseases, including the impact of the Ebola virus on tourism in sub-Saharan Africa (Maphanga & Henama, 2019 ; Novelli et al., 2018 ) and in the United States (Cahyanto et al., 2016 ). The literature also includes studies of the impact of swine flu on tourism demand in Brunei (Haque & Haque, 2018 ), Mexico (Monterrubio, 2010 ), and the United Kingdom (Page et al., 2012 ), among others. In addition, rapid assessments of the impacts of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 have documented severe disruptions and cessations of tourism because of unprecedented global travel restrictions and widespread restrictions on public gatherings (Gössling et al., 2020 ; Qiu et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Hotels, airlines, cruise lines, and car rentals have all experienced a significant decrease globally because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the shock to the industry is significant enough to warrant concerns about the long-term outlook (Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Qiu et al. ( 2020 ) estimated the social costs of the pandemic to tourism in three cities in China (Hong Kong, Guangzhou, and Wuhan), and they found that most respondents were willing to pay for risk reduction and action in responding to the pandemic crisis; there was no significant difference between residents’ willingness to pay in the three cities. Some research has emphasized how lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic can prepare global tourism for an economic transformation that is needed to mitigate the impacts of climate change (Brouder, 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, contested, and potentially paradoxical. This is due, in part, to the contested nature of sustainable development itself. Tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ), and many countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development has been viewed as an important sector for investment to enhance economic growth, poverty alleviation, and food security, and the sector provides an alternative opportunity to large-scale development projects and extractive industries that contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and cultural values. However, global evidence from research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been realized (Liu, 2003 ).
The role of tourism in sustainable development has been studied extensively and with a variety of perspectives, including the conceptualization of alternative or responsible forms of tourism and the examination of economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism development. The research has generally concluded that tourism development has contributed to sustainable development in some cases where it is demonstrated to have provided support for biodiversity conservation initiatives and livelihood development strategies. As an economic sector, tourism is considered to be labor intensive, providing opportunities for poor households to enhance their livelihood through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists.
Nature-based tourism approaches such as ecotourism and community-based tourism have been successful at attracting tourists to parks and protected areas, and their spending provides financial support for biodiversity conservation, livelihoods, and economic growth in developing countries. Nevertheless, studies of the impacts of tourism development have documented negative environmental impacts locally in terms of land use, food and water consumption, and congestion, and globally in terms of the contribution of tourism to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases related to transportation and other tourist activities. Studies of the social impacts of tourism have documented experiences of discrimination based on ethnicity, gender, race, sex, and national identity.
The sustainability of tourism as an economic sector has been examined in terms of its vulnerability to civil conflict, economic shocks, natural disasters, and public health pandemics. Most studies conclude that tourism may have positive impacts for regional development and environmental conservation, but there is evidence that tourism inherently generates negative environmental impacts, primarily through pollutions stemming from transportation. The regional benefits of tourism development must be considered alongside the global impacts of increased transportation and tourism participation. Global tourism has also been shown to be vulnerable to economic crises, oil price shocks, and global outbreaks of infectious diseases. Given that tourism is dependent on energy, the movement of people, and the consumption of resources, virtually all tourism activities have significant economic, environmental, and sustainable impacts. As such, the role of tourism in sustainable development is highly questionable. Future research on the role of tourism in sustainable development should focus on reducing the negative impacts of tourism development, both regionally and globally.
Further Reading
- Bramwell, B. , & Lane, B. (1993). Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 1–5.
- Buckley, R. (2012). Sustainable tourism: Research and reality. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (2), 528–546.
- Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation , 18 (3), 201–209.
- Butler, R. W. (1999). Sustainable tourism: A state‐of‐the‐art review. Tourism Geographies , 1 (1), 7–25.
- Clarke, J. (1997). A framework of approaches to sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (3), 224–233.
- Fennell, D. A. (2020). Ecotourism (5th ed.). Routledge.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 (4), 283–302.
- Honey, M. (2008). Ecotourism and sustainable development: Who owns paradise? (2nd ed.). Island Press.
- Inskeep, E. (1991). Tourism planning: An integrated and sustainable development approach . Routledge.
- Jamal, T. , & Camargo, B. A. (2014). Sustainable tourism, justice and an ethic of care: Toward the just destination. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 22 (1), 11–30.
- Liburd, J. J. , & Edwards, D. (Eds.). (2010). Understanding the sustainable development of tourism . Oxford.
- Liu, Z. (2003). Sustainable tourism development: A critique. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 11 (6), 459–475.
- Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28 (11), 1932–1946.
- Adams, W. M. (2009). Green development: Environment and sustainability in a developing world (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Andereck, K. L. , Valentine, K. M. , Knopf, R. A. , & Vogt, C. A. (2005). Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 1056–1076.
- Andereck, K. , Valentine, K. , Vogt, C. , & Knopf, R. (2007). A cross-cultural analysis of tourism and quality of life perceptions. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 483–502.
- Anderies, J. M. , Folke, C. , Walker, B. , & Ostrom, E. (2013). Aligning key concepts for global change policy: Robustness, resilience, and sustainability . Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 8.
- Apergis, N. , & Payne, J. E. (2012). Tourism and growth in the Caribbean–evidence from a panel error correction model. Tourism Economics , 18 (2), 449–456.
- Arana, J. E. , & León, C. J. (2008). The impact of terrorism on tourism demand. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 (2), 299–315.
- Ashley, C. , & Roe, D. (2002). Making tourism work for the poor: Strategies and challenges in southern Africa. Development Southern Africa , 19 (1), 61–82.
- Ashley, C. , Roe, D. , & Goodwin, H. (2001). Pro-poor tourism strategies: Making tourism work for the poor: A review of experience (No. 1). Overseas Development Institute.
- Baker, K. , & Coulter, A. (2007). Terrorism and tourism: The vulnerability of beach vendors’ livelihoods in Bali. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (3), 249–266.
- Baral, N. , Stern, M. J. , & Bhattarai, R. (2008). Contingent valuation of ecotourism in Annapurna conservation area, Nepal: Implications for sustainable park finance and local development. Ecological Economics , 66 (2–3), 218–227.
- Becken, S. , & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 133–142.
- Beckerman, W. (1994). “Sustainable development”: Is it a useful concept? Environmental Values , 3 (3), 191–209.
- Bhattarai, K. , Conway, D. , & Shrestha, N. (2005). Tourism, terrorism and turmoil in Nepal. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 669–688.
- Blewitt, J. (2015). Understanding sustainable development (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Brouder, P. (2020). Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 484–490.
- Brunt, P. , & Courtney, P. (1999). Host perceptions of sociocultural impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 26 (3), 493–515.
- Buckley, R. (2011). Tourism and environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources , 36 , 397–416.
- Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographe canadien , 24 (1), 5–12.
- Butler, R. , & Hinch, T. (Eds.). (2007). Tourism and indigenous peoples: Issues and implications . Routledge.
- Cabezas, A. L. (2004). Between love and money: Sex, tourism, and citizenship in Cuba and the Dominican Republic. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 29 (4), 987–1015.
- Caffyn, A. (2012). Advocating and implementing slow tourism. Tourism Recreation Research , 37 (1), 77–80.
- Cahyanto, I. , Wiblishauser, M. , Pennington-Gray, L. , & Schroeder, A. (2016). The dynamics of travel avoidance: The case of Ebola in the US. Tourism Management Perspectives , 20 , 195–203.
- Calgaro, E. , & Lloyd, K. (2008). Sun, sea, sand and tsunami: Examining disaster vulnerability in the tourism community of Khao Lak, Thailand. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography , 29 (3), 288–306.
- Castanedo, S. , Juanes, J. A. , Medina, R. , Puente, A. , Fernandez, F. , Olabarrieta, M. , & Pombo, C. (2009). Oil spill vulnerability assessment integrating physical, biological and socio-economical aspects: Application to the Cantabrian coast (Bay of Biscay, Spain). Journal of Environmental Management , 91 (1), 149–159.
- Cater, E. (1993). Ecotourism in the Third World: Problems for sustainable tourism development. Tourism Management , 14 (2), 85–90.
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. (1987, January). The future of “ecotourism.” Mexico Journal , 17 , 13–14.
- Chase, L. C. , Lee, D. R. , Schulze, W. D. , & Anderson, D. J. (1998). Ecotourism demand and differential pricing of national park access in Costa Rica. Land Economics , 74 (4), 466–482.
- Chatziantoniou, I. , Filis, G. , Eeckels, B. , & Apostolakis, A. (2013). Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: A structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Management , 36 (C), 331–341.
- Cheong, S. M. (2012). Fishing and tourism impacts in the aftermath of the Hebei-Spirit oil spill. Journal of Coastal Research , 28 (6), 1648–1653.
- Chok, S. , Macbeth, J. , & Warren, C. (2007). Tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation: A critical analysis of “pro-poor tourism” and implications for sustainability. Current Issues in Tourism , 10 (2–3), 144–165.
- Cioccio, L. , & Michael, E. J. (2007). Hazard or disaster: Tourism management for the inevitable in Northeast Victoria. Tourism Management , 28 (1), 1–11.
- Cirer-Costa, J. C. (2015). Tourism and its hypersensitivity to oil spills. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 91 (1), 65–72.
- Coccossis, H. , & Nijkamp, P. (1995). Sustainable tourism development . Ashgate.
- Coddington, K. (2015). The “entrepreneurial spirit”: Exxon Valdez and nature tourism development in Seward, Alaska. Tourism Geographies , 17 (3), 482–497.
- Cohen, E. (1978). The impact of tourism on the physical environment. Annals of Tourism Research , 5 (2), 215–237.
- Conway, D. , & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for “slow tourism.” Tourism and Hospitality Research , 10 (4), 329–344.
- Corbet, S. , O’Connell, J. F. , Efthymiou, M. , Guiomard, C. , & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 75 , 1–17.
- Daly, H. E. (1990). Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecological Economics , 2 (1), 1–6.
- Deery, M. , Jago, L. , & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 64–73.
- Diedrich, A. , & Garcia-Buades, E. (2008). Local perceptions of tourism as indicators of destination decline. Tourism Management , 41 , 623–632.
- Durbarry, R. (2004). Tourism and economic growth: The case of Mauritius. Tourism Economics , 10 , 389–401.
- Elliott, S. M. , & Neirotti, L. D. (2008). Challenges of tourism in a dynamic island destination: The case of Cuba. Tourism Geographies , 10 (4), 375–402.
- Enders, W. , Sandler, T. , & Parise, G. F. (1992). An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism. Kyklos , 45 (4), 531–554.
- Eugenio-Martin, J. L. , & Campos-Soria, J. A. (2014). Economic crisis and tourism expenditure cutback decision. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 53–73.
- Farrell, B. , & McLellan, R. (1987). Tourism and physical environment research. Annals of Tourism Research , 14 (1), 1–16.
- Faulkner, B. , & Tideswell, C. (1997). A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (1), 3–28.
- Fennell, D. A. , & Eagles, P. F. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration , 8 (1), 23–34.
- Fullagar, S. , Markwell, K. , & Wilson, E. (Eds.). (2012). Slow tourism: Experiences and mobilities . Channel View.
- Garau-Vadell, J. B. , Gutierrez-Taño, D. , & Diaz-Armas, R. (2018). Economic crisis and residents’ perception of the impacts of tourism in mass tourism destinations. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management , 7 , 68–75.
- Garrod, B. , & Fyall, A. (1998). Beyond the rhetoric of sustainable tourism? Tourism Management , 19 (3), 199–212.
- Ghimire, K. B. (Ed.). (2013). The native tourist: Mass tourism within developing countries . Routledge.
- Goodrich, J. N. (2002). September 11, 2001 attack on America: A record of the immediate impacts and reactions in the USA travel and tourism industry. Tourism Management , 23 (6), 573–580.
- Gössling, S. (1999). Ecotourism: A means to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem functions? Ecological Economics , 29 , 303–320.
- Gössling, S. (2000). Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation , 27 (3), 223–224.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 , 283–302.
- Gössling, S. , & Peeters, P. (2015). Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 23 (5), 639–659.
- Gössling, S. , Peeters, P. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J.‑P. , Dubois, G. , Lehman, L. V. , & Scott, D. (2011). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand and security, and international review. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 16–28.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , & Hall, C. M. (2020). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (1), 1–20.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J. P. , & Dubois, G. (2012). Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (1), 36–58.
- Gray, N. J. , & Campbell, L. M. (2007). A decommodified experience? Exploring aesthetic, economic and ethical values for volunteer ecotourism in Costa Rica. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 463–482.
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots—a conceptual history of “sustainable development” (Nachhaltigkeit) . Wissenschaftszentrum Berlin für Sozialforschung.
- Gu, H. , & Ryan, C. (2008). Place attachment, identity and community impacts of tourism—the case of a Beijing hutong. Tourism Management , 29 (4), 637–647.
- Gursoy, D. , Chi, C. G. , & Dyer, P. (2010). Locals’ attitudes toward mass and alternative tourism: The case of Sunshine Coast, Australia. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (3), 381–394.
- Haley, A. J. , Snaith, T. , & Miller, G. (2005). The social impacts of tourism a case study of Bath, UK. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 647–668.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (2009). Understanding and managing tourism impacts: An integrated approach . Routledge.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (Eds.). (1998). Sustainable tourism: A geographical perspective . Longman.
- Haque, T. H. , & Haque, M. O. (2018). The swine flu and its impacts on tourism in Brunei. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36 , 92–101.
- Haralambopoulos, N. , & Pizam, A. (1996). Perceived impacts of tourism: The case of Samos. Annals of Tourism Research , 23 (3), 503–526.
- Harrison, D. (2008). Pro-poor tourism: A critique. Third World Quarterly , 29 (5), 851–868.
- Hearne, R. R. , & Salinas, Z. M. (2002). The use of choice experiments in the analysis of tourist preferences for ecotourism development in Costa Rica. Journal of Environmental Management , 65 (2), 153–163.
- Hetzer, N. D. (1965). Environment, tourism, culture. Links , 1 (2), 1–3.
- Höhler, S. (2015). Spaceship earth in the environmental age, 1960–1990 . Routledge.
- Honey, M. , & Gilpin, R. (2009). Tourism in the developing world: Promoting peace and reducing poverty . United States Institute for Peace.
- Huan, T. C. , Beaman, J. , & Shelby, L. (2004). No-escape natural disaster: Mitigating impacts on tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 31 (2), 255–273.
- Huang, J. H. , & Min, J. C. (2002). Earthquake devastation and recovery in tourism: The Taiwan case. Tourism Management , 23 (2), 145–154.
- Hunter, C. (1995). On the need to re-conceptualise sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 3 (3), 155–165.
- Hunter, C. , & Green, H. (1995). Tourism and the environment. A sustainable relationship? Routledge.
- Huttasin, N. (2008). Perceived social impacts of tourism by residents in the OTOP tourism village, Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 13 (2), 175–191.
- Hystad, P. W. , & Keller, P. C. (2008). Towards a destination tourism disaster management framework: Long-term lessons from a forest fire disaster. Tourism Management , 29 (1), 151–162.
- Katircioglu, S. (2009). Tourism, trade and growth: The case of Cyprus. Applied Economics , 41 (21), 2741–2750.
- Katircioglu, S. (2010). Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Singapore: An empirical investigation from bounds test to cointegration and Granger causality tests. Tourism Economics , 16 (4), 1095–1101.
- Khan, M. M. (1997). Tourism development and dependency theory: Mass tourism vs. ecotourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 24 (4), 988–991.
- Kim, H. , & Marcouiller, D. W. (2015). Considering disaster vulnerability and resiliency: The case of hurricane effects on tourism-based economies. The Annals of Regional Science , 54 (3), 945–971.
- King, B. , Pizam, A. , & Milman, A. (1993). Social impacts of tourism: Host perceptions. Annals of Tourism Research , 20 (4), 650–665.
- Kisswani, K. M. , Zaitouni, M. , & Moufakkir, O. (2020). An examination of the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts. Current Issues in Tourism , 23 (4), 500–522.
- Kuvan, Y. , & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management , 26 (5), 691–706.
- Lai, P. H. , & Nepal, S. K. (2006). Local perspectives of ecotourism development in Tawushan Nature Reserve, Taiwan. Tourism Management , 27 (6), 1117–1129.
- Lanouar, C. , & Goaied, M. (2019). Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tourism Management , 70 , 404–418.
- Lee, C. C. , & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management , 29 , 180–192.
- Lenzen, M. , Sun, Y. Y. , Faturay, F. , Ting, Y. P. , Geschke, A. , & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change , 8 (6), 522–528.
- Lian Chan, J. K. , & Baum, T. (2007). Ecotourists’ perception of ecotourism experience in lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 574–590.
- Liu, A. , & Pratt, S. (2017). Tourism’s vulnerability and resilience to terrorism. Tourism Management , 60 , 404–417.
- Manyara, G. , & Jones, E. (2007). Community-based tourism enterprises development in Kenya: An exploration of their potential as avenues of poverty reduction. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (6), 628–644.
- Maphanga, P. M. , & Henama, U. S. (2019). The tourism impact of Ebola in Africa: Lessons on crisis management. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), 1–13.
- Mathieson, A. , & Wall, G. (1982). Tourism, economic, physical and social impacts . Longman.
- May, V. (1991). Tourism, environment and development—values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management , 12 (2), 112–124.
- Mazzocchi, M. , & Montini, A. (2001). Earthquake effects on tourism in central Italy. Annals of Tourism Research , 28 (4), 1031–1046.
- Mbaiwa, J. E. (2005). The socio-cultural impacts of tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change , 2 (3), 163–185.
- McKercher, B. (1993a). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 6–16.
- McKercher, B. (1993b). The unrecognized threat to tourism: Can tourism survive “sustainability”? Tourism Management , 14 (2), 131–136.
- Meadows, D. H. , Meadows, D. L. , Randers, J. , & Behrens, W. W. (1972). The limits to growth . Universe Books.
- Miller, G. A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2003). A farming crisis or a tourism disaster? An analysis of the foot and mouth disease in the UK. Current Issues in Tourism , 6 (2), 150–171.
- Milman, A. , & Pizam, A. (1988). Social impacts of tourism on central Florida. Annals of Tourism Research , 15 (2), 191–204.
- Monterrubio, J. C. (2010). Short-term economic impacts of influenza A (H1N1) and government reaction on the Mexican tourism industry: An analysis of the media. International Journal of Tourism Policy , 3 (1), 1–15.
- Narayan, P. K. (2004). Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics , 10 (4), 419–433.
- Nash, D. , & Butler, R. (1990). Towards sustainable tourism. Tourism Management , 11 (3), 263–264.
- Novelli, M. , Burgess, L. G. , Jones, A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2018). “No Ebola . . . still doomed”—the Ebola-induced tourism crisis. Annals of Tourism Research , 70 , 76–87.
- Oh, C. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management , 26 , 39–44.
- Oh, H. , Assaf, A. G. , & Baloglu, S. (2016). Motivations and goals of slow tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 55 (2), 205–219.
- Okumus, F. , & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 942–961.
- Page, S. , Song, H. , & Wu, D. C. (2012). Assessing the impacts of the global economic crisis and swine flu on inbound tourism demand in the United Kingdom. Journal of Travel Research , 51 (2), 142–153.
- Papatheodorou, A. , Rosselló, J. , & Xiao, H. (2010). Global economic crisis and tourism: Consequences and perspectives. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 39–45.
- Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David B. Weaver. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1038–1041.
- Pennington-Gray, L. , London, B. , Cahyanto, I. , & Klages, W. (2011). Expanding the tourism crisis management planning framework to include social media: Lessons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill 2010. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology , 1 (3–4), 239–253.
- Pizam, A. , & Fleischer, A. (2002). Severity versus frequency of acts of terrorism: Which has a larger impact on tourism demand? Journal of Travel Research , 40 (3), 337–339.
- Pratt, S. (2015). The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Annals of Tourism Research , 52 , 148–160.
- Prideaux, B. , Thompson, M. , & Pabel, A. (2020). Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 667–678.
- Qiu, R. T. , Park, J. , Li, S. , & Song, H. (2020). Social costs of tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic . Annals of Tourism Research , 84 , 102994.
- Rátz, T. (2000). Residents’ perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary. Tourism and Sustainable Community Development , 7 , 36.
- Ribeiro, L. C. D. S. , Souza, K. B. D. , Domingues, E. P. , & Magalhães, A. S. (2020). Blue water turns black: Economic impact of oil spill on tourism and fishing in Brazilian Northeast . Current Issues in Tourism , 1–6.
- Richardson, R. B. , Fernandez, A. , Tschirley, D. , & Tembo, G. (2012). Wildlife conservation in Zambia: Impacts on rural household welfare. World Development , 40 (5), 1068–1081.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Loomis, J. B. (2004). Adaptive recreation planning and climate change: A contingent visitation approach. Ecological Economics , 50 (1), 83–99.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Witkowski, K. (2010). Economic vulnerability to climate change for tourism-dependent nations. Tourism Analysis , 15 (3), 315–330.
- Ritchie, B. W. , Crotts, J. C. , Zehrer, A. , & Volsky, G. T. (2013). Understanding the effects of a tourism crisis: The impact of the BP oil spill on regional lodging demand. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (1), 12–25.
- Rogerson, C. M. (2011). Urban tourism and regional tourists: Shopping in Johannesburg, South Africa. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie , 102 (3), 316–330.
- Rutty, M. , & Richardson, R. (2019). Tourism research in Cuba: Gaps in knowledge and challenges for sustainable tourism. Sustainability , 11 (12), 3340–3346.
- Ryan, C. , & Huyton, J. (2000). Who is interested in Aboriginal tourism in the Northern Territory, Australia? A cluster analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 53–88.
- Salinas, E. , Mundet, L. , & Salinas, E. (2018). Historical evolution and spatial development of tourism in Cuba, 1919–2017: What is next? Tourism Planning & Development , 15 (3), 216–238.
- Sanchez, P. M. , & Adams, K. M. (2008). The Janus-faced character of tourism in Cuba. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 , 27–46.
- Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . Routledge.
- Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research , 38 (1), 291–308.
- Sharma, A. , & Nicolau, J. L. (2020). An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry . Annals of Tourism Research , 83 , 102990.
- Sharpley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 1–19.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management , 42 , 37–49.
- Smeral, E. (2010). Impacts of the world recession and economic crisis on tourism: Forecasts and potential risks. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 31–38.
- Southgate, C. R. (2006). Ecotourism in Kenya: The vulnerability of communities. Journal of Ecotourism , 5 (1–2), 80–96.
- Spenceley, A. (Ed.). (2012). Responsible tourism: Critical issues for conservation and development . Routledge.
- Stabler, M. (Ed.). (1997). Tourism and sustainability: Principles to practice . Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International.
- Stronza, A. (2007). The economic promise of ecotourism for conservation. Journal of Ecotourism , 6 (3), 210–230.
- Stylidis, D. , & Terzidou, M. (2014). Tourism and the economic crisis in Kavala, Greece. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 210–226.
- Suntikul, W. , Bauer, T. , & Song, H. (2009). Pro-poor tourism development in Viengxay, Laos: Current state and future prospects. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 14 (2), 153–168.
- Swarbrooke, J. (1999). Sustainable tourism management . CABI.
- Tovar, C. , & Lockwood, M. (2008). Social impacts of tourism: An Australian regional case study. International Journal of Tourism Research , 10 (4), 365–378.
- Tsartas, P. (1992). Socioeconomic impacts of tourism on two Greek isles. Annals of Tourism Research , 19 (3), 516–533.
- Turner, L. , & Ash, J. (1975). The golden hordes: International tourism and the pleasure periphery . Constable.
- United Nations . (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2002). Tourism and poverty alleviation . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2020). UNWTO world tourism barometer . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- Viner, D. (2006). Tourism and its interactions with climate change. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14 (4), 317–322.
- Vitousek, P. M. , Mooney, H. A. , Lubchenco, J. , & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science , 277 (5325), 494–499.
- World Commission on Environment and Development . (1987). Our common future . Oxford University Press.
- Weaver, D. (2007). Towards sustainable mass tourism: Paradigm shift or paradigm nudge? Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 65–69.
- Weaver, D. B. (2012). Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1030–1037.
- Weaver, D. B. (2014). Asymmetrical dialectics of sustainable tourism: Toward enlightened mass tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (2), 131–140.
- Wheeller, B. (2007). Sustainable mass tourism: More smudge than nudge the canard continues. Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 73–75.
- Whitford, M. , & Ruhanen, L. (2016). Indigenous tourism research, past and present: Where to from here? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 24 (8–9), 1080–1099.
- Whyte, K. P. (2010). An environmental justice framework for indigenous tourism. Environmental Philosophy , 7 (2), 75–92.
- Wolff, K. , & Larsen, S. (2014). Can terrorism make us feel safer? Risk perceptions and worries before and after the July 22nd attacks. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 200–209.
- Yang, W. , Wang, D. , & Chen, G. (2011). Reconstruction strategies after the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan, China. Tourism Management , 32 (4), 949–956.
- Young, G. (1973). Tourism—blessing or blight? Penguin.
- Zapata, M. J. , Hall, C. M. , Lindo, P. , & Vanderschaeghe, M. (2011). Can community-based tourism contribute to development and poverty alleviation? Lessons from Nicaragua. Current Issues in Tourism , 14 (8), 725–749.
1. One megatonne (Mt) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) metric tons.
2. One megajoule (MJ) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a 1-megagram (tonne) vehicle moving at 161 km/h.
3. One gigatonne (Gt) is equal to 1 billion (10 9 ) metric tons.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Environmental Science. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 09 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.80.151.9]
- 185.80.151.9
Character limit 500 /500
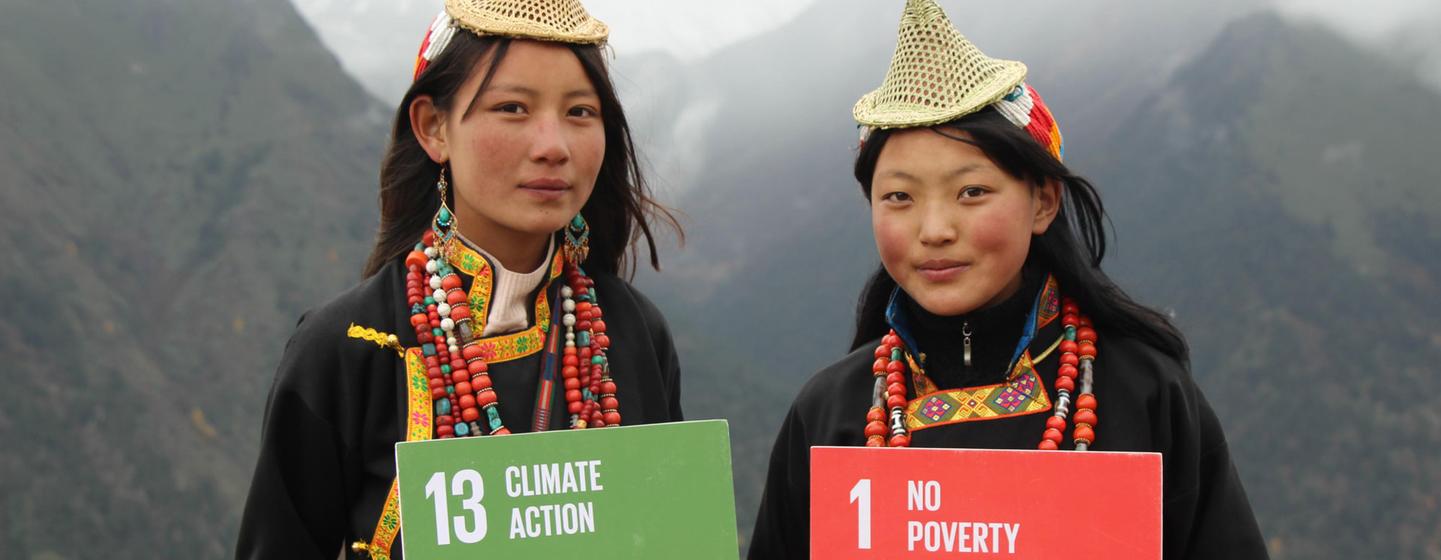

Is it possible to be a ‘sustainable tourist’? 12 ways to make a positive impact on your travels
Facebook Twitter Print Email
After a period of plummeting tourism numbers during the pandemic, tourism is having a resurgence. This is good news for many workers and businesses, but it could be bad for the planet. Here is a selection of ways tourists can ensure that their holidays don’t harm the environment.
There are many positive aspects to tourism. Around two billion people travel each year for tourism purposes. Travel and tourism connect people and bring the world closer through shared experiences, cultural awareness and community building. It provides jobs, spurs regional development, and is a key driver for socio-economic progress.
However, there is often a downside; Many popular destinations are threatened by increasing pollution, environmental hazards, damage to heritage sites and overuse of resources. And that’s without factoring the pollution caused by travel to and from these destinations.
So, with that in mind here are some tips that will help you to enjoy your trip, and leave with the confidence that your favoured tourist destination will not be damaged by your presence, once you return home.
1. Ditch single-use plastics
Often used for less than 15 minutes, single-use plastic items can take more than 1,000 years to degrade. Many of us are switching to sustainable options in our daily lives, and we can take the same attitude when we’re on the road. By choosing reusable bottles and bags wherever you go, you can help ensure there is less plastic waste in the ocean and other habitats.
2. Be ‘water wise’
On the whole, tourists use far more water than local residents. With a growing number of places experiencing water scarcity, the choices you make can help ensure people have adequate access to water in the future. By foregoing a daily change of sheets and towels during hotel stays, we can save millions of litres of water each year.
3. Buy local
When you buy local, you help boost the local economy, benefit local communities, and help to reduce the destination’s carbon footprint from transporting the goods. This is also true at mealtimes, so enjoy fresh, locally grown produce every chance you get.
4. Use an ethical operator
Tour operations involve people, logistics, vendors, transportation and much more. Each link in the chain can impact the environment - positively or negatively. If you prefer to leave the planning to someone else, be sure to pick an operator that prioritizes the environment, uses resources efficiently and respects local culture.

5. ‘Please don’t feed the animals’
Sharing food with wildlife or getting close enough to do so increases the chances of spreading diseases like cold, flu and pneumonia from humans to animals. Also, when animals get used to receiving food from humans, their natural behaviours are altered, and they become dependent on people for survival. In some cases, it can also lead to human-animal conflict.
6. And don’t eat them either!
By creating the demand, consuming endangered or exotic animals leads to an increase in poaching, trafficking and exploitation of animals. Besides the harm done to the individual animal on your plate, irresponsible dining can contribute to the extinction of species already threatened by climate change and habitat loss. Keep this in mind when shopping for souvenirs as well, and steer clear of products made from endangered wildlife.
7. Share a ride
Transportation is a major contributor to the carbon footprint from tourism. Instead of private taxis, explore using public transportation like trains, buses and shared cabs. You can also ride a bicycle, which offers a convenient and cheaper way to explore and learn about a place.
8. Consider a homestay
Staying with a local resident or family is a nature-friendly option that allows you to get up close and personal with local culture and customs. Staying at local homestays can uplift communities by providing income while giving you a peek into different ways of life.

9. Do your homework
Before your travel, educate yourself about your destination. Doing so will allow you to better immerse yourself in local traditions and practices and appreciate things that might have gone unnoticed otherwise. With the right information, you can explore a destination in a more sensitive manner and surprise yourself with new adventures and discoveries.
10. Visit national parks and sanctuaries
Exploring nature and wildlife through national parks is an intimate way to learn about the animals and their ecosystems first hand. In some cases, your entrance fee supports conservation efforts that protect species and landscapes and preserve these natural spaces for future visitors to enjoy.
11. Don’t leave a trace
You can make a mark by not leaving a mark on your vacation destination. Put garbage in its place to avoid litter, and don’t remove or alter anything without permission. Let’s make sure we leave only soft footprints, and not the environmental kind.
12. Tell your friends
Now that you’re ready to travel in eco-friendly style, it’s time spread the word! Inform fellow travellers, friends and family about how sustainable tourism benefits local people by enhancing their livelihoods and well-being, and helps all of us by safeguarding our beautiful environment.
The Environmental Impact Of Mass Tourism And How To Help Manage It
Mass tourism is a somewhat recent social phenomenon, with its numbers rising dramatically in current years. This negative side of tourism saw its first growth boost in the 1930s, and nowadays, people making over a billion international trips a year, so this phenomenon still affects certain destinations, making them unsustainable.
The rise of mobile apps such as Airbnb and budget-friendly package tours, artificially low flights fares, all-inclusive resorts, cruises; have made it way easier and financially friendly for a wide variety of social groups to go to famous international locations. As affordable group travel tours are on the rise, over-tourism now affects different destinations worldwide.
How it generates
In older times, touring used to be a trip for a privileged few, however, tourism has now grown to be available to a larger component of the population, which really isnât bad, however, thereâs a downside to this. Even if the industry has added massive revenues to increasingly visited countries, the consistent affluence of hundreds of thousands of tourists has mostly turned unsustainable.
Mass tourism allows vast numbers of travelers to descend on a given destination in a relatively short time, usually during peak season. The positive side of this phenomenon is that the extreme influx of tourists can help to generate jobs, therefore, stimulating the economy and developing much-needed infrastructure.
The bad side of this very popular form of tourism is that many of the jobs generated arenât precisely given to locals, the majority of these earnings are kept by international investors. The surprisingly high number of traveler crowds often keep the local community from enjoying such infrastructure benefits.
There are many contributing elements to over-tourism, and of course, these will differ according to each different area. As I mentioned earlier, Airbnb could be a significant contributor (but, not necessarily the leading player) as its made hundreds of beds available and accessible in towns and cities globally, this process is made even easier by them because thereâs no need of advanced planning or â in many cases â paying taxes.
Additionally, cheap flights have saturated different places, and particularly in recent years, Europe. Lastly, cruise ships not only burn a particularly cheap and polluting type of fuel (which keeps costs low) but also transport thousands of tourists into port cities. Wait⦠this could sound beneficial, right? Well, not exactly, passengers often spend very little in these ports, however, local historic spots, monuments, shops, and cafes are saturated with people.
For a long time, more has been better to local and national governments, as well as travel boards. A âprosperousâ reporting year in the travel industry is normally considered to be one in which numbers have improved substantially. The number is all that matters, thereâs no importance whether these numbers are of cruise ship passengers, duty-free shoppers, hotel or resorts guests, backpackers or visitors with luxurious preferences.
The negative impact of mass tourism
Responsible travel experts consider it a shallow, exploitative, and, most importantly, unsustainable form of travel. The main reason for this is that it consumes huge amounts of resources while the local people get very little benefits, this is inarguably hard to deal with and plagues destinations.
Itâs important to point out that over-tourism can take many forms; on one side, it could be a million additional vacationers arriving in a capital city, on the other, it could be seen as 20 extra tourists in a small, rural community. In present times, this isnât simply a large city issue, it has been documented in great wilderness destinations, natural parks, and more.
The travel industry, like many others, focuses almost solely on growth, with little to no space for concern about the consequences. After a long time of uncontrolled expansion, it has crossed a threshold: In numerous destinations all over the globe, tourism now demonstrably creates more troubles than benefits.
This isnât a new problem, but with visitor numbers steadily rising, local people from popular tourist areas have started attesting. Destinations around the world are taking action to limit the harmful impacts of over-tourism, making it possible to travel responsibly to popular places struggling with over-tourism and contributing positively to the local environment, people, animals, and historical monuments.
What tourism operators can do to avoid it
There are a handful of very easy adjustments you can make and values you can promote to decrease the influence of your customers on the local communities and the vacation spots that they visit, ensuring that itâs available for future travelers too:
- Respectful tourism: The number one rule for any traveler is to be respectful and staying within boundaries while abroad. Avoiding littering, and even going the extra mile by picking up any pieces of trash along the way could help make a difference. Making customers understand the local customs to adhere to.
- Off-season tours: If a place is crowded, the easy suggestion would be visiting somewhere else, the same thing would apply here. However, I understand that it isnât as easy as it sounds, as some destinations are simply unique and offer once-in-a-lifetime experiences. The solution to this? Visiting when there is less demand, customers will save a few bucks and have a move enjoyable experiences thanks to less crowding.
- Not-so-popular places: Itâs as simple as it sounds, while certain areas are saturated with travelers, there are many other places around the planet that need, and want, more tourists. This, combined with positive behaviour from visitors could help the travel industry to have a positive effect on these places, making local communities grow financially because of it.
- Ensure money gets spent locally: Make sure that any of the tours that you partner with ensuring that as much of the cash spent by tourists stay as local as possible. This way, travellers can influence locals positively, and even benefit habitats and animals by supporting well-managed wildlife-based tourism .
- Offer authenticity: Groups with a smaller number of people can significantly avoid over-tourism. It will also give your customers a stronger connection with local communities, their culture, and day-to-day routine. You can easily offer unique ethical adventures to the right audience on the worldâs largest travel marketplaces with the right tour operator software .
Tackling this challenge
Over-tourism is negatively affecting many of the most popular countries, cities and regions around the world. Luckily, several websites are imposing rules and limiting the range of tourists to combat overcrowding.
As tour operators, we can lessen these harmful consequences by choosing the right businesses to partner with, promoting off-peak seasons and, in a few words, standing by responsible and respectful tourism to any areas and the local people that reside in it.
Back to you, how does your business help tackle this phenomenon?

Tourism is dead, long live Tourism! Insights from the Travalyst Global Summit, July 30, 2020.
3 surefire ways to improve your tour operator business.

Personalization
Customer service, sustainability, getting started, selling online, reseller guides, get started with tashi today.
Try Tashi Free for 14 days. No credit card needed.
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
Transforming tourism for climate action, sustainable development.
- Biodiversity
Climate Action
- Global Tourism Plastics Initiative
- Hotel Energy Solutions (HES)
- Resource Efficiency in Tourism
- Small Islands Developing States (SIDS)
- Travel facilitation
- UNGA Sustainable Tourism Resolutions
share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Find out about the Glasgow Declaration
The tourism sector is highly vulnerable to climate change and at the same time contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG), which cause global warming. Accelerating climate action in tourism is therefore of utmost importance for the resilience of the sector. Climate action is understood as the efforts to measure and reduce GHG emissions and strengthen adaptive capacity to climate induced impacts. 1
There is a growing consensus among tourism stakeholders as to how the future resilience of tourism will depend on the sector’s ability to embrace a low carbon pathway and cut emissions by 50% by 2030
According to UN Tourism/ITF latest research , released in December 2019 at UNFCCC COP25, CO 2 emissions from tourism are forecasted to increase by 25% by 2030 from 2016 levels, against the current ambition scenario. The report provides insights into the evolution of tourism demand across the different global regions from 2016 to 2030 and presents transport-related CO2 emissions for the period. In 2016, transport-related emissions from tourism contributed to 5% of all man-made emissions and were set to increase to 5,3% by 2030 against a current ambition scenario.
Find Transport-related CO 2 Emissions of the Tourism Sector - Modelling
Therefore, the need to scale up climate action in tourism is of utmost importance, especially even more now that the sector has recovered from the COVID-19 pandemic, with 2023 reaching 88% levels of the international tourist arrivals in 2019. The cost of inaction with regards to climate will be in the long run larger than the cost of any other crisis.
UN Tourism is committed to accelerate progress towards low carbon tourism development and the contribution of the sector to international climate goals by:
- Strengthening the measurement and disclosure of CO 2 emissions in tourism
- Accelerating the decarbonization of tourism operations
- Engaging the tourism sector in adaptation and carbon removal
In order to support the tourism stakeholders to advance on measuring their GHG emissions, in March 2023, UN Tourism published the report on CLIMATE ACTION IN TOURISM SECTOR: AN OVERVIEW OF METHODOLOGIES AND TOOLS TO MEASURE GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS . The report was developed with support from the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection of Germany (BMU) and released in collaboration with UN Climate Change (UNFCCC). Read the full report here .

In order to support National Tourism Administrations, in March 2024 UN Tourism launched the Policy Guidance with support from the UN Climate Change (UNFCCC) and technical support from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The Policy Guidance has been developed to assist governmental agencies dedicated to tourism in the development of tourism climate action policies and initiatives to support the low-carbon transition for tourism. This policy guidance provides examples of good practice from around the world to illustrate how NTAs can implement climate-enabling policy and other initiatives as well as benefit from climate initiatives in other sectors. The policy guidance is complemented by a Glasgow Declaration signatory Pack for NTAs which provides practical recommendations on how to get started with climate action.

RELATED ACTIVITIES
The glasgow declaration: a commitment to a decade of climate action in tourism.
The Glasgow Declaration aims to act as a catalyst for increased urgency about the need to accelerate climate action in tourism and to secure strong actions and commitment.
The signatories of the Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action in Tourism are committing to act now and accelerate climate action to support the global goals of cutting emissions by at least a half over the next decade and reach Net Zero emissions as soon as possible before 2050. Signatories of the Glasgow Declaration are developing climate plans aligned with 5 pathways : measure, decarbonize, regenerate, collaborate, finance, and reporting progress on an annual basis.
UN Tourism outlined the collective progress with the first Glasgow Declaration Implementation Report (2023) .The Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action in Tourism Implementation Report 2023 presents the results of a systematic review of all progress updates received from signatories during the first reporting exercise conducted between January and June 2023 (over 400 updates), which in many cases include the submission of a Climate Action Plan. The report represents a first-of-its-kind picture of the rapidly developing engagement of the tourism sector with the challenges of climate action.

Please visit the One Planet network website to learn more about:
Participation at UN Climate Change Conferences of the Parties (COP)
Since 2019, COP25, UN Tourism has been participating on an annual basis to the Conference of the Parties of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change to position the important role that the tourism sector can play to support international climate goals.

Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action in Tourism
Related links
- Access UN Tourism/ITF research on transport-related CO2 emissions from tourism
- Access additional information on the official side-event at COP25
- Watch the Climate Panel from the 23rd UN Tourism General Assembly
- Download the report “Climate Change and Tourism – Responding to Global Challenges"
- Global Survey of Climate Action in Tourism
Tourism Stakeholders Invited to Share Progress on Climate Action
- The Road to Climate Neutrality: Experiences, Challenges and Support for the Caribbean tourism sector

Glasgow Declaration - Global Roundtable for Tourism Climate Action
Glasgow declaration - regenerative tourism for resilience: policy, practice and finance, tourism at cop28 – delivering on the climate action commitments of the glasgow declaration.

UN Tourism Welcomes Mexican States to Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action in Tourism

New Report to Support Climate Action in the Tourism Sector

UN Tourism at COP27: Uniting Tourism Around Tangible Climate Action Plans

Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action in Tourism Surpasses 500 Signatories

Tourism unites behind the Glasgow Declaration on Climate Action at COP26

Launch of the Glasgow Declaration: A commitment to a decade of climate action in tourism

The Glasgow Declaration: An urgent global call for commitment to a decade of climate action in tourism

Tourism’s Carbon Emissions Measured in Landmark Report Launched At COP25
1. View Goal 13 Targets 2 Carbon Brief 3. Cut Global Emissions by 7.6 Percent Every Year for Next Decade to Meet 1.5°C Paris Target - UN Report
Number of eco-tourist arrivals
Somewhere on Earth this year
The World Counts • Impact through Awareness
The world counts impact through awareness.
Eco tourism is a growing niche market but it’s difficult to measure the exact size of the industry. According to the OECD, a very rough estimate of the world’s international ecotourism arrivals is 7% of the total number of global tourist arrivals. This implies that there were 101 million eco tourist arrivals in 2018.
Eco-tourism offers a more sustainable alternative to travelling
Ecotourism can be defined as:
“Responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment and improves the well-being of local people.”
Tourism and the environment can be mutually supportive
In a number of destinations, tourism helps to ensure higher water quality and better protection of nature and local natural resources. It can generate additional resources to invest in environmental infrastructures and services.
A social dimension
Eco-tourism also has an active social dimension. It seeks to benefit local communities by giving them control over how tourism develops, and by helping locals to use their lands and resources in more sustainable ways.
A growing industry
Ecotourism has become one of the fastest growing sectors in the tourism industry, growing annually by 10-15 percent worldwide.
But be careful...
“Greenwashing” is a key problem in the industry, meaning that some agencies use the term “eco travel” much too loosely.
8,105,510,632
World population
All of us, right now
21,541,059,921
Tons of resources mined from Earth
Globally, this year
15.0246103056
World average temperature (°C)
- World Population
- The Consumer Economy
- Our Global Challenges
- The Project
- Keep the optimism
- Support green companies

14 important environmental impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
The environmental impacts of tourism have gained increasing attention in recent years.
With the rise in sustainable tourism and an increased number of initiatives for being environmentally friendly, tourists and stakeholders alike are now recognising the importance of environmental management in the tourism industry.
In this post, I will explain why the environmental impacts of tourism are an important consideration and what the commonly noted positive and negative environmental impacts of tourism are.
Why the environment is so important to tourism
Positive environmental impacts of tourism, water resources, land degradation , local resources , air pollution and noise , solid waste and littering , aesthetic pollution, construction activities and infrastructure development, deforestation and intensified or unsustainable use of land , marina development, coral reefs, anchoring and other marine activities , alteration of ecosystems by tourist activities , environmental impacts of tourism: conclusion, environmental impacts of tourism reading list.

The quality of the environment, both natural and man-made, is essential to tourism. However, tourism’s relationship with the environment is complex and many activities can have adverse environmental effects if careful tourism planning and management is not undertaken.
It is ironic really, that tourism often destroys the very things that it relies on!
Many of the negative environmental impacts that result from tourism are linked with the construction of general infrastructure such as roads and airports, and of tourism facilities, including resorts, hotels, restaurants, shops, golf courses and marinas. The negative impacts of tourism development can gradually destroy the environmental resources on which it depends.
It’s not ALL negative, however!
Tourism has the potential to create beneficial effects on the environment by contributing to environmental protection and conservation. It is a way to raise awareness of environmental values and it can serve as a tool to finance protection of natural areas and increase their economic importance.
In this article I have outlined exactly how we can both protect and destroy the environment through tourism. I have also created a new YouTube video on the environmental impacts of tourism, you can see this below. (by the way- you can help me to be able to keep content like this free for everyone to access by subscribing to my YouTube channel! And don’t forget to leave me a comment to say hi too!).
Although there are not as many (far from it!) positive environmental impacts of tourism as there are negative, it is important to note that tourism CAN help preserve the environment!
The most commonly noted positive environmental impact of tourism is raised awareness. Many destinations promote ecotourism and sustainable tourism and this can help to educate people about the environmental impacts of tourism. Destinations such as Costa Rica and The Gambia have fantastic ecotourism initiatives that promote environmentally-friendly activities and resources. There are also many national parks, game reserves and conservation areas around the world that help to promote positive environmental impacts of tourism.
Positive environmental impacts can also be induced through the NEED for the environment. Tourism can often not succeed without the environment due the fact that it relies on it (after all we can’t go on a beach holiday without a beach or go skiing without a mountain, can we?).
In many destinations they have organised operations for tasks such as cleaning the beach in order to keep the destination aesthetically pleasant and thus keep the tourists happy. Some destinations have taken this further and put restrictions in place for the number of tourists that can visit at one time.
Not too long ago the island of Borocay in the Philippines was closed to tourists to allow time for it to recover from the negative environmental impacts that had resulted from large-scale tourism in recent years. Whilst inconvenient for tourists who had planned to travel here, this is a positive example of tourism environmental management and we are beginning to see more examples such as this around the world.
Negative environmental impacts of tourism

Negative environmental impacts of tourism occur when the level of visitor use is greater than the environment’s ability to cope with this use.
Uncontrolled conventional tourism poses potential threats to many natural areas around the world. It can put enormous pressure on an area and lead to impacts such as: soil erosion , increased pollution, discharges into the sea, natural habitat loss, increased pressure on endangered species and heightened vulnerability to forest fires. It often puts a strain on water resources, and it can force local populations to compete for the use of critical resources.
I will explain each of these negative environmental impacts of tourism below.

Depletion of natural resources

Tourism development can put pressure on natural resources when it increases consumption in areas where resources are already scarce. Some of the most common noted examples include using up water resources, land degradation and the depletion of other local resources.
The tourism industry generally overuses water resources for hotels, swimming pools, golf courses and personal use of water by tourists. This can result in water shortages and degradation of water supplies, as well as generating a greater volume of waste water.
In drier regions, like the Mediterranean, the issue of water scarcity is of particular concern. Because of the hot climate and the tendency for tourists to consume more water when on holiday than they do at home, the amount used can run up to 440 litres a day. This is almost double what the inhabitants of an average Spanish city use.

Golf course maintenance can also deplete fresh water resources.
In recent years golf tourism has increased in popularity and the number of golf courses has grown rapidly.
Golf courses require an enormous amount of water every day and this can result in water scarcity. Furthermore, golf resorts are more and more often situated in or near protected areas or areas where resources are limited, exacerbating their impacts.
An average golf course in a tropical country such as Thailand needs 1500kg of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides per year and uses as much water as 60,000 rural villagers.

Important land resources include fertile soil, forests , wetlands and wildlife. Unfortunately, tourism often contributes to the degradation of said resources. Increased construction of tourism facilities has increased the pressure on these resources and on scenic landscapes.
Animals are often displaced when their homes are destroyed or when they are disturbed by noise. This may result in increased animals deaths, for example road-kill deaths. It may also contribute to changes in behaviour.
Animals may become a nuisance, by entering areas that they wouldn’t (and shouldn’t) usually go into, such as people’s homes. It may also contribute towards aggressive behaviour when animals try to protect their young or savage for food that has become scarce as a result of tourism development.
Picturesque landscapes are often destroyed by tourism. Whilst many destinations nowadays have limits and restrictions on what development can occur and in what style, many do not impose any such rules. High rise hotels and buildings which are not in character with the surrounding architecture or landscape contribute to a lack of atheistic appeal.
Forests often suffer negative impacts of tourism in the form of deforestation caused by fuel wood collection and land clearing. For example, one trekking tourist in Nepal can use four to five kilograms of wood a day!
There are also many cases of erosion, whereby tourists may trek the same path or ski the same slope so frequently that it erodes the natural landscape. Sites such as Machu Pichu have been forced to introduce restrictions on tourist numbers to limit the damage caused.

Tourism can create great pressure on local resources like energy, food, and other raw materials that may already be in short supply. Greater extraction and transport of these resources exacerbates the physical impacts associated with their exploitation.
Because of the seasonal character of the industry, many destinations have ten times more inhabitants in the high season as in the low season.
A high demand is placed upon these resources to meet the high expectations tourists often have (proper heating, hot water, etc.). This can put significant pressure on the local resources and infrastructure, often resulting in the local people going without in order to feed the tourism industry.
Tourism can cause the same forms of pollution as any other industry: Air emissions; noise pollution; solid waste and littering; sewage; oil and chemicals. The tourism industry also contributes to forms of architectural/visual pollution.

Transport by air, road, and rail is continuously increasing in response to the rising number of tourists and their greater mobility. In fact, tourism accounts for more than 60% of all air travel.
One study estimated that a single transatlantic return flight emits almost half the CO2 emissions produced by all other sources (lighting, heating, car use, etc.) consumed by an average person yearly- that’s a pretty shocking statistic!
I remember asking my class to calculate their carbon footprint one lesson only to be very embarrassed that my emissions were A LOT higher than theirs due to the amount of flights I took each year compared to them. Point proven I guess….
Anyway, air pollution from tourist transportation has impacts on a global level, especially from CO2 emissions related to transportation energy use. This can contribute to severe local air pollution . It also contributes towards climate change.
Fortunately, technological advancements in aviation are seeing more environmentally friendly aircraft and fuels being used worldwide, although the problem is far from being cured. If you really want to help save the environment, the answer is to seek alternative methods of transportation and avoid flying.
You can also look at ways to offset your carbon footprint .

Noise pollution can also be a concern.
Noise pollution from aircraft, cars, buses, (+ snowmobiles and jet skis etc etc) can cause annoyance, stress, and even hearing loss for humans. It also causes distress to wildlife and can cause animals to alter their natural activity patterns. Having taught at a university near London Heathrow for several years, this was always a topic of interest to my students and made a popular choice of dissertation topic .

In areas with high concentrations of tourist activities and appealing natural attractions, waste disposal is a serious problem, contributing significantly to the environmental impacts of tourism.
Improper waste disposal can be a major despoiler of the natural environment. Rivers, scenic areas, and roadsides are areas that are commonly found littered with waste, ranging from plastic bottles to sewage.
Cruise tourism in the Caribbean, for example, is a major contributor to this negative environmental impact of tourism. Cruise ships are estimated to produce more than 70,000 tons of waste each year.
The Wider Caribbean Region, stretching from Florida to French Guiana, receives 63,000 port calls from ships each year, and they generate 82,000 tons of rubbish. About 77% of all ship waste comes from cruise vessels. On average, passengers on a cruise ship each account for 3.5 kilograms of rubbish daily – compared with the 0.8 kilograms each generated by the less well-endowed folk on shore.
Whilst it is generally an unwritten rule that you do not throw rubbish into the sea, this is difficult to enforce in the open ocean . In the past cruise ships would simply dump their waste while out at sea. Nowadays, fortunately, this is less commonly the case, however I am sure that there are still exceptions.
Solid waste and littering can degrade the physical appearance of the water and shoreline and cause the death of marine animals. Just take a look at the image below. This is a picture taken of the insides of a dead bird. Bird often mistake floating plastic for fish and eat it. They can not digest plastic so once their stomachs become full they starve to death. This is all but one sad example of the environmental impacts of tourism.
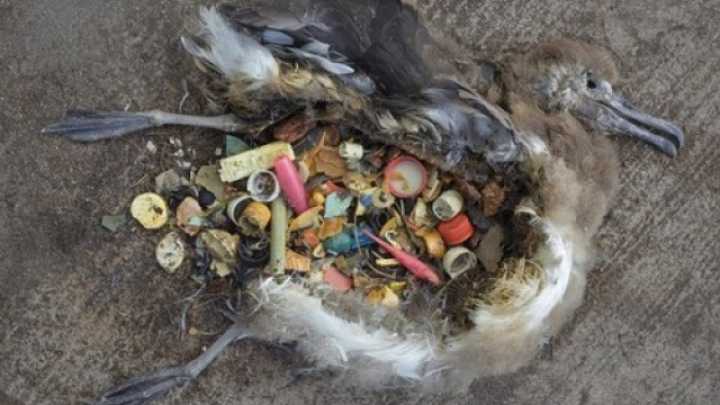

Mountain areas also commonly suffer at the hands of the tourism industry. In mountain regions, trekking tourists generate a great deal of waste. Tourists on expedition frequently leave behind their rubbish, oxygen cylinders and even camping equipment. I have heard many stories of this and I also witnessed it first hand when I climbed Mount Kilimanjaro .

The construction of hotels, recreation and other facilities often leads to increased sewage pollution.
Unfortunately, many destinations, particularly in the developing world, do not have strict law enrichments on sewage disposal. As a result, wastewater has polluted seas and lakes surrounding tourist attractions around the world. This damages the flora and fauna in the area and can cause serious damage to coral reefs.
Sewage pollution threatens the health of humans and animals.
I’ll never forget the time that I went on a school trip to climb Snowdonia in Wales. The water running down the streams was so clear and perfect that some of my friends had suggested we drink some. What’s purer than mountain fresh water right from the mountain, right?
A few minutes later we saw a huge pile of (human??) feaces in the water upstream!!
Often tourism fails to integrate its structures with the natural features and indigenous architecture of the destination. Large, dominating resorts of disparate design can look out of place in any natural environment and may clash with the indigenous structural design.
A lack of land-use planning and building regulations in many destinations has facilitated sprawling developments along coastlines, valleys and scenic routes. The sprawl includes tourism facilities themselves and supporting infrastructure such as roads, employee housing, parking, service areas, and waste disposal. This can make a tourist destination less appealing and can contribute to a loss of appeal.
Physical impacts of tourism development

Whilst the tourism industry itself has a number of negative environmental impacts. There are also a number of physical impacts that arise from the development of the tourism industry. This includes the construction of buildings, marinas, roads etc.

The development of tourism facilities can involve sand mining, beach and sand dune erosion and loss of wildlife habitats.
The tourist often will not see these side effects of tourism development, but they can have devastating consequences for the surrounding environment. Animals may displaced from their habitats and the noise from construction may upset them.
I remember reading a while ago (although I can’t seem to find where now) that in order to develop the resort of Kotu in The Gambia, a huge section of the coastline was demolished in order to be able to use the sand for building purposes. This would inevitably have had severe consequences for the wildlife living in the area.

Construction of ski resort accommodation and facilities frequently requires clearing forested land.
Land may also be cleared to obtain materials used to build tourism sites, such as wood.
I’ll never forget the site when I flew over the Amazon Rainforest only to see huge areas of forest cleared. That was a sad reality to see.
Likewise, coastal wetlands are often drained due to lack of more suitable sites. Areas that would be home to a wide array of flora and fauna are turned into hotels, car parks and swimming pools.

The building of marinas and ports can also contribute to the negative environmental impacts of tourism.
Development of marinas and breakwaters can cause changes in currents and coastlines.
These changes can have vast impacts ranging from changes in temperatures to erosion spots to the wider ecosystem.

Coral reefs are especially fragile marine ecosystems. They suffer worldwide from reef-based tourism developments and from tourist activity.
Evidence suggests a variety of impacts to coral result from shoreline development. Increased sediments in the water can affect growth. Trampling by tourists can damage or even kill coral. Ship groundings can scrape the bottom of the sea bed and kill the coral. Pollution from sewage can have adverse effects.
All of these factors contribute to a decline and reduction in the size of coral reefs worldwide. This then has a wider impact on the global marine life and ecosystem, as many animals rely on the coral for as their habitat and food source.
Physical impacts from tourist activities
The last point worth mentioning when discussing the environmental impacts of tourism is the way in which physical impacts can occur as a result of tourist activities.
This includes tramping, anchoring, cruising and diving. The more this occurs, the more damage that is caused. Natural, this is worse in areas with mass tourism and overtourism .

Tourists using the same trail over and over again trample the vegetation and soil, eventually causing damage that can lead to loss of biodiversity and other impacts.
Such damage can be even more extensive when visitors frequently stray off established trails. This is evidenced in Machu Pichu as well as other well known destinations and attractions, as I discussed earlier in this post.

In marine areas many tourist activities occur in or around fragile ecosystems.
Anchoring, scuba diving, yachting and cruising are some of the activities that can cause direct degradation of marine ecosystems such as coral reefs. As I said previously, this can have a significant knock on effect on the surrounding ecosystem.

Habitats can be degraded by tourism leisure activities.
For example, wildlife viewing can bring about stress for the animals and alter their natural behaviour when tourists come too close.
As I have articulated throughout this post, there are a range of environmental impacts that result from tourism. Whilst some are good, the majority unfortunately are bad. The answer to many of these problems boils down to careful tourism planning and management and the adoption of sustainable tourism principles.
Did you find this article helpful? Take a look at my posts on the social impacts of tourism and the economic impacts of tourism too! Oh, and follow me on social media !
If you are studying the environmental impacts of tourism or if you are interested in learning more about the environmental impacts of tourism, I have compiled a short reading list for you below.
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
Liked this article? Click to share!
Mass Tourism: History, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages, Destinations and Its Impacts
Mass tourism is a form of tourism that involves the movement of large numbers of people to popular holiday destinations. It is often associated with package holidays, all-inclusive resorts, and organized tours. Mass tourism aims to provide travellers with a hassle-free vacation experience, where everything from transportation to accommodation and activities is planned and delivered by a single operator.
While mass tourism has been a boon for many destinations, it has also been criticized for its negative impact on local cultures, economies, and environments. The sheer number of tourists can overwhelm local infrastructure and resources, leading to overcrowding, pollution, and strain on natural resources. In addition, mass tourism can also lead to the commodification of local cultures, where traditional practices and customs are adapted to suit the needs and expectations of tourists. This can result in the loss of cultural authenticity and homogenization of local cultures.
Despite its drawbacks, mass tourism remains a popular form of travel for many people. It offers convenience, affordability, and the opportunity to visit popular destinations without worrying about the logistics of planning a trip. However, it is essential to consider the impact of mass tourism on local communities and the environment and to make responsible travel choices whenever possible.
Table of Contents
History of mass tourism.

Mass tourism has a long and exciting history from the 19th century. The growth of leisure travel and its importance resulted from increased spending power, personal mobility, the development of public transport, and internationalization in modern communities.
Mass tourism began in 1851 when Thomas Cook led a mass of tourists to the Great Exhibition in London. A British entrepreneur, Cook is the father of modern tourism. He organized the first package tour , which involved people travelling together on a pre-planned itinerary. Cook’s innovation made travel affordable and accessible to the masses and quickly became popular.
The introduction of paid holidays in the early 20th century further fueled the growth of mass tourism. Workers were given time off from work to travel and explore new destinations. The concept of paid holidays was first introduced in the UK in 1938, and it quickly spread to other parts of the world. This increased the number of people travelling, creating a new market for the tourism industry .
The post-World War II period saw a significant increase in mass tourism. The airline industry’s growth , the development of new destinations, and the introduction of new technologies, such as the jet engine, made travel faster, cheaper, and more comfortable. This led to an explosion in the number of people travelling, creating a new industry that catered explicitly to mass tourism.
In conclusion, mass tourism has a rich and fascinating history that dates back to the 19th century. The growth of leisure travel, the introduction of paid holidays, and the development of new technologies have all contributed to the growth of mass tourism. Today, mass tourism is a significant industry that generates billions of dollars in revenue and employs millions worldwide.
Types of Mass Tourism

Mass tourism refers to the movement of a large number of organized tourists to popular holiday destinations for recreational purposes. It is a phenomenon which is characterized by the use of standardized package products and mass consumption. Here are some types of mass tourism:
- Cultural Tourism : This type of mass tourism involves visiting historical and cultural sites, museums, art galleries, and other places of cultural significance. Cultural tourism is popular among tourists who want to learn about a particular region or country’s history, traditions, and customs.
- Adventure Tourism : This type of mass tourism involves activities such as trekking, hiking, mountaineering, rock climbing, and other outdoor activities. Adventure tourism is popular among tourists seeking excitement and thrill during their holidays.
- Beach Tourism : This type of mass tourism involves visiting coastal areas, beaches, and islands. Beach tourism is popular among tourists who want to relax, sunbathe, swim, and engage in water sports.
- Ecotourism : This type of mass tourism involves visiting natural areas, wildlife reserves, and national parks. Ecotourism is popular among tourists who want to experience nature, observe wildlife, and learn about conservation efforts.
- Medical Tourism : This type of mass tourism involves travelling to another country for medical treatment. Medical tourism is popular among tourists who want to access medical treatments that are not available in their home country or are too expensive.
- Sports Tourism : This type of mass tourism involves travelling to attend or participate in sports events such as football matches, cricket matches, tennis tournaments, and other sporting events.
- Cruise Tourism : This type of mass tourism involves travelling on a cruise ship to visit multiple destinations. Cruise tourism is popular among tourists who want to relax, socialize, and enjoy onboard entertainment while visiting various destinations.
Mass tourism has positive and negative impacts on the environment, economy, and society. It is important to manage mass tourism sustainably and responsibly to minimize its negative effects and maximize its benefits.
Advantages of Mass Tourism

Mass tourism has several advantages, making it an essential part of the tourism industry. Here are some of the benefits of mass tourism:
Boosts Local Economy
Mass tourism can significantly boost the local economy of a tourist destination. It generates much revenue for local businesses, such as hotels , restaurants, and souvenir shops. This, in turn, creates job opportunities for the locals and helps improve their living standards. Mass tourism can also contribute to infrastructure development, such as roads, airports, and public transportation, which can benefit the local community even after the tourists have left.
Increases Cultural Exchange
Mass tourism can increase cultural exchange between tourists and locals. Tourists can learn about the local customs, traditions, and way of life, while locals can learn about the visitors’ culture. This cultural exchange can help to promote understanding and tolerance between different cultures and can also help to preserve the local culture by promoting it to a wider audience.
Provides Affordable Travel Options
Mass tourism provides affordable travel options for people who may not have the means to travel otherwise. The package deals offered by mass tourism companies can be significantly cheaper than individual travel arrangements. This makes travel more accessible to a wider range of people, including those on a budget.
Supports Conservation Efforts
Mass tourism can also support conservation efforts in tourist destinations. The revenue generated by mass tourism can be used to fund conservation projects, such as wildlife conservation and habitat restoration. This can help preserve the destination’s natural beauty and protect it for future generations.
Mass tourism has several advantages, making it an important part of the tourism industry. It can boost the local economy, increase cultural exchange, provide affordable travel options, and support conservation efforts. However, it is important to balance the advantages of mass tourism with its potential negative impacts, such as overcrowding, environmental degradation, and cultural homogenization.
Disadvantages of Mass Tourism

Mass tourism has become increasingly popular in recent years but has drawbacks. Here are some of the disadvantages of mass tourism:
1. Environmental Impact
One of the most significant disadvantages of mass tourism is the environmental impact. Mass tourism can lead to pollution, degradation of natural resources, and damage to ecosystems. The large number of tourists can put a strain on local resources, such as water and energy, and contribute to climate change.
2. Overcrowding
Mass tourism can lead to overcrowding in popular tourist destinations, which can cause inconvenience and discomfort for tourists and locals. Overcrowding can also lead to safety concerns and increase the risk of accidents and incidents.
3. Cultural Impact
Mass tourism can have a negative impact on local cultures and traditions. The influx of tourists can lead to a loss of cultural authenticity and homogenization of local cultures. This can also lead to losing traditional ways of life and displacement of local residents.
4. Economic Impact
While mass tourism can bring economic benefits to a destination, it can also have negative economic impacts. The reliance on tourism can lead to an unstable economy, and the profits from tourism may not benefit local communities. In some cases, tourism can also lead to inflation and increased living costs for locals.
5. Sustainability
Mass tourism is often unsustainable in the long term. The strain on local resources and ecosystems can lead to irreversible damage, and focusing on short-term profits can lead to neglecting long-term sustainability goals.
While mass tourism can bring economic benefits and opportunities for travellers, it is essential to consider its negative impacts on the environment, local communities, and cultures.
Mass Tourism Destinations

Mass tourism has become popular for people to explore new destinations and experience different cultures. The most popular mass tourism destinations include beaches, mountains, national parks, and historical sites. Here are some examples of popular mass tourism destinations:
Beaches are a popular destination for mass tourism. Some popular beaches include Goa in India, Santorini in Greece, and the Harbor Islands in Boston. These destinations offer beautiful beaches, crystal clear waters, and a variety of activities for tourists to enjoy.
Mountains are another popular destination for mass tourism. Central Massachusetts and the Greater Merrimack Valley are popular destinations for tourists who want to experience the beauty of the mountains. These destinations offer breathtaking views, hiking trails, and other outdoor activities.
National Parks
National parks are also popular destinations for mass tourism. Cape Cod National Seashore is a popular destination for tourists who want to explore the area’s natural beauty. The park offers hiking trails, beaches, and other outdoor activities.
Historical Sites
Historical sites are also popular destinations for mass tourism. The Pyramids of Giza in Egypt and the North of Boston are popular destinations for tourists who want to explore the history of the area. These destinations offer a glimpse into the past and a chance to learn about different cultures.
Overall, there are many popular mass tourism destinations for tourists to explore. Whether you are looking for a beach vacation, a mountain retreat, or a chance to explore historical sites, there is something for everyone.
Impact on Local Communities
Mass tourism significantly impacts local communities, and the effects can be positive and negative. While tourism can bring economic benefits to a region, it can also negatively impact the local culture, jobs, infrastructure, local businesses, gentrification, and over-tourism.
One of mass tourism’s most significant negative impacts on local communities is the erosion of local culture. As more tourists flock to a destination, the local culture can become homogenized, and the unique traditions and ways of life can be lost. This can lead to a loss of identity for the local community and a decline in cultural heritage.
Another negative impact of mass tourism is the effect on jobs. While tourism can create jobs in the hospitality and service industries, it can also lead to a decline in traditional industries. For example, in some regions, farming and fishing have been replaced by tourism, leading to a loss of traditional jobs and a decline in local economies.
Infrastructure can also be negatively impacted by mass tourism. As more tourists visit an area, the demand for infrastructure such as roads, airports, and hotels increases. This can lead to overcrowding, traffic congestion, and strain on local resources.
Local businesses can also be impacted by mass tourism. While some businesses may benefit from increased tourism, others may struggle to compete with larger international chains. This can lead to a decline in local businesses and a loss of economic diversity in the region.
Gentrification is another issue that can arise from mass tourism. As more tourists visit an area, property prices can rise, leading to the displacement of local residents. This can lead to social and economic inequality, as the local community is pushed out of its own neighbourhood.
Finally, mass tourism is a growing concern in many popular tourist destinations. When the number of tourists visiting a destination exceeds the region’s carrying capacity, it can lead to overcrowding, environmental degradation, and a decline in the quality of life for local residents.
In conclusion, while mass tourism can bring economic benefits to a region, it is essential to consider the impact on local communities. The negative impacts of mass tourism can be significant, and it is crucial to find a balance between economic growth and sustainable tourism practices.
Economic Aspects of Mass Tourism
Mass tourism can have a significant impact on the economy of a destination. It can generate income and create employment opportunities, but it can also put a strain on resources and infrastructure.
One of the main benefits of mass tourism is the income it generates for local economies. Tourists spend money on accommodation, food, transportation, and activities, which can contribute to the local economy. According to a report by the Massachusetts Office of Travel and Tourism, travel expenditures in Massachusetts in 2018 generated over $24 billion in direct spending, which supported over 150,000 jobs and generated $1.6 billion in state and local taxes.
However, mass tourism can also put a strain on resources and infrastructure. Popular tourist destinations may struggle to accommodate the influx of visitors during peak season, leading to overcrowding and strain on local resources such as water and energy. Additionally, the increased demand for goods and services can drive up prices, making it harder for locals to afford basic necessities.
Another economic aspect of mass tourism is profit. Large tourism companies may benefit from the high volume of tourists by making significant profits. However, smaller local businesses may struggle to compete with larger companies, leading to a concentration of wealth in the hands of a few.
Overall, the economic impact of mass tourism is complex and multifaceted. While it can generate income and create employment opportunities, it can also strain resources and infrastructure and concentrate wealth in the hands of a few.
Tourist Behavior and Expectations
Tourist behaviour and expectations play a crucial role in the mass tourism industry. Tourists are individuals who travel to different places for leisure, business, or other purposes. They have certain expectations and requirements from their travel experience, which can influence their behaviour during their stay.
One of the primary expectations of tourists is to have a comfortable and enjoyable experience. They expect high-quality accommodations, transportation, food, and entertainment options. Tourists also expect to be treated with respect and hospitality by the locals and the service providers. They want to feel welcomed and appreciated during their stay.
Another important aspect of tourist behaviour is their spending habits. Tourists tend to spend significant money on their travel, which can boost the local economy. However, they also expect value for their money and are likely to avoid places that are overpriced or do not meet their expectations.
Family tourists are a significant segment of the mass tourism industry. They have unique expectations and requirements, such as child-friendly accommodations, entertainment options, and safety measures. Family tourists also tend to plan their trips well in advance and are likely to choose destinations that offer a variety of activities for all members of the family.
Responsible tourism is another emerging trend in the mass tourism industry. Responsible tourists are conscious of their impact on the environment and the local communities. They expect the destinations and service providers to follow sustainable practices and reduce their carbon footprint. Responsible tourists will likely choose eco-friendly accommodations, participate in local conservation efforts, and support local businesses.
Overall, understanding tourist behaviour and expectations is essential for the success of the mass tourism industry. Service providers and destinations that meet and exceed these expectations will likely attract more visitors and generate higher revenues.
Role of Media and Internet
The role of media and the internet has greatly influenced the rise of mass tourism. With the advent of social media platforms such as Instagram, travellers are constantly exposed to images of exotic destinations and experiences, which can influence their travel decisions. In fact, a study suggests that social media has a significant impact on tourists’ choices of travel components, with most studies focusing on the impact of social media on behavioural intention.
The media has also played a vital role in promoting tourism, especially in countries where tourism is a major source of revenue. The media is often used to showcase a destination’s natural beauty, culture, and attractions, which can attract tourists. For example, television shows such as Anthony Bourdain’s “Parts Unknown” and Samantha Brown’s “Places to Love” have helped to promote off-the-beaten-path destinations to a wider audience.
The internet has also revolutionized the way people plan and book their travel. Travellers can now easily research and book flights, accommodations, and activities through online travel agencies and booking platforms. This has led to increased independent travel, where travellers can plan their own itineraries and customize their travel experiences.
However, the internet has also brought about challenges for the tourism industry. With the ease of access to information, travellers are now more aware of the negative impacts of tourism, such as overcrowding, environmental degradation, and cultural commodification. This has led to a rise in sustainable and responsible tourism practices, where travellers seek to minimize their impact on the environment and local communities.
Overall, the role of media and the Internet in mass tourism cannot be overstated. While it has brought about challenges, it has also opened up new opportunities for travellers to explore the world and for destinations to promote themselves to a wider audience.
Tour Operators and Travel Agents

Tour operators and travel agents play a significant role in mass tourism. They are intermediaries between the tourists and the service providers, such as hotels, airlines, and transportation companies. Their main function is to package and sell tours to holiday destinations, including flights, accommodation, and other services.
Travel agents are professionals who provide travel-related services to clients. They offer advice on travel destinations, make reservations for flights, hotels, and other services, and provide information on travel insurance, visas, and other travel-related documents. They earn a commission from the service providers for the services they sell.
On the other hand, tour operators specialize in organizing and selling packaged tours to holiday destinations. They create tour packages that include transportation, accommodation, meals, and other services. They work with travel agents to sell their tour packages to clients. Tour operators profit by buying services from service providers at a discounted rate and selling them to clients at a higher price.
Mass tourism has led to the growth of travel agents and tour operators. They have become essential players in the tourism industry, providing clients with a wide range of services. They have also contributed to the growth of the tourism industry by promoting tourism destinations and creating new tourism products.
One of the main advantages of using travel agents and tour operators is convenience. They provide a one-stop shop for all travel-related services, making it easy for clients to plan their holidays. They also offer expert advice on travel destinations and provide assistance in case of any problems during the trip.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using travel agents and tour operators. One of the main disadvantages is the cost. Travel agents and tour operators charge a commission for their services, which can add up to a significant amount. Moreover, some travel agents and tour operators may not provide accurate information or may misrepresent the services they offer.
In conclusion, travel agents and tour operators are essential players in the mass tourism industry. They provide clients with a wide range of services, including packaged tours, flights, accommodation, and other travel-related services. While they offer convenience and expert advice, they also have disadvantages, such as cost and potential misrepresentation of services.
Environmental Concerns
Mass tourism has been associated with a wide range of environmental concerns. One of the most significant environmental concerns is the impact of tourism on the natural environment. The increase in tourist activities has resulted in a higher demand for natural resources, such as water, energy, and land. This has led to the degradation of natural habitats, deforestation, and soil erosion in some areas.
Another environmental concern is the amount of waste generated by mass tourism. Tourists generate significant waste, including plastic bottles, food packaging, and disposable items. This waste often ends up in landfills or littered in the environment, leading to pollution and negative impacts on wildlife.
Sustainable travel is an approach that seeks to minimize the negative impact of tourism on the environment. This includes promoting green tourism practices, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing waste, and conserving natural resources. Sustainable travel also involves educating tourists about the importance of responsible tourism practices and encouraging them to participate in environmentally friendly activities.
Carrying capacity is another important concept in mass tourism. It refers to the maximum number of tourists a destination can accommodate without causing negative impacts on the environment. When the number of tourists exceeds the carrying capacity of a destination, it can lead to overcrowding, pollution, and damage to natural habitats.
Finally, carbon emissions associated with transportation and accommodation significantly contribute to climate change. Mass tourism is responsible for significant carbon emissions contributing to global warming. Sustainable travel practices, such as using public transportation, choosing eco-friendly accommodations, and offsetting carbon emissions, can help reduce the impact of tourism on climate change.
Future of Mass Tourism
Mass tourism has been a significant contributor to the global economy for decades. However, recent events have highlighted the need for a more sustainable and responsible approach to tourism. The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a significant decline in mass tourism, leading to the closure of many businesses and job losses. The future of mass tourism is uncertain, and it will likely require significant changes to adapt to the new reality.
One of the most significant challenges facing mass tourism is sustainability. The industry significantly impacts the environment, and there is a growing awareness of the need to reduce this impact. Governments and tourism organizations increasingly focus on sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, and protecting natural resources. The future of mass tourism will depend on its ability to adapt to these new practices and become more sustainable.
Another challenge facing mass tourism is the changing preferences of travellers. Many people are now looking for more authentic and immersive travel experiences rather than traditional mass tourism offerings. This trend will likely continue, and mass tourism must adapt to meet these changing preferences.
Technology is also likely to play a significant role in the future of mass tourism. Advances in technology are making travel more accessible and convenient, and this trend will likely continue. For example, virtual reality technology is already used to provide immersive travel experiences, which will likely become more widespread.
In conclusion, the future of mass tourism is uncertain, but it is clear that significant changes will be required to adapt to the new reality. Sustainability, changing traveller preferences, and technology will likely be the key drivers of change in the industry. The industry’s challenge will be adapting to these changes while continuing to provide high-quality travel experiences for its customers.
In conclusion, mass tourism is a significant part of the tourism industry, associated with package holidays, popular tourist attractions, and well-known resorts. However, the growth of mass tourism has led to several challenges, including over-tourism, environmental degradation, and cultural homogenization.
The future of mass tourism is uncertain, with several factors influencing its growth and development. The rise of sustainable tourism, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences will likely impact mass tourism’s future.
Despite the challenges, mass tourism continues to provide economic benefits to many destinations. However, balancing economic benefits with environmental and social sustainability is essential to ensure the industry’s long-term viability.
Overall, the future of mass tourism is complex and multifaceted, with several challenges and opportunities. It is crucial to adopt a holistic approach to tourism development, taking into account the economic, social, and environmental impacts of mass tourism.
Faced with too many tourists, France’s natural sites push back
Several of France’s heavily visited natural sites are sounding the alarm. Access to some of the Calanques coves in Marseille and Corsica is now limited in order to limit erosion. Other villages struggling with mass tourism, such as Étretat in Normandy, are rethinking how they handle the influx of visitors.
Issued on: 10/07/2022 - 17:13
Can the cliffs of Étretat in Normandy really handle their million visitors every year? As France heads into the high season of summer holidays, Shaï-Hannah Mallet-Bitton, an activist with the Étretat Demain association, is preoccupied with this question. “Every year it gets worse, and it’s happening more quickly. I’m only 28 years old and even I can see how much the site has been degraded,” sighs the lawyer, who spent part of her childhood in this village of 1,400 inhabitants in Normandy.
The signs of overtourism are everywhere: overflowing rubbish bins, hollowed-out hiking trails from so much foot traffic, more-frequent landslides, up to 400 kg of pebbles a day carried away from the beaches . Jean-Baptiste Renié, an Étretat city councillor, is concerned that the area’s wastewater treatment facility is being pushed too far, as it was “not developed to handle the 5 to 6,000 visitors a day on top of the local population”. The system had to be closed for maintenance last year “due to overuse”.
“After every big weekend, once all the tourists have left, the town is extremely dirty. When you visit the cliffs, you see papers everywhere, masks, cigarette butts”, says Shaï-Hanah Mallet-Bitton.
Volunteers from the Étretat Demain association clean cigarette butts from the beaches.
Voir cette publication sur Instagram Une publication partagée par É T R E T A T D E M A I N (@etretatdemain)
“We need tourism but a balance needs to be found. The tourists themselves would benefit the most. Many of them leave angry after having spent several hours in the car without being able to find parking, some place to eat, or toilets, because there isn’t enough infrastructure. This mass tourism satisfies nobody.”
“Healthy” regulation
Due to an excessive number of visitors, several French natural sites have gone so far as to impose obligatory timeslot reservations for tourists. Marseille’s Calanques National Park now limits the number of people who can visit the Sugiton and Pierres Tombées calanques to 400 a day. Both sites have been made more fragile due to ground erosion from the foot traffic of several thousand summer visitors previously. Three of Corsica’s top tourist sites (the Lavezzi islands, the Bavella Needles mountain ridge and the Restonica valley) also instituted daily quotas starting in July.
For Julien Buot, director of the association Agir Pour un Tourisme Responsible (“Act for Responsible Tourism”), which brings together ecologically aware travel operators, this new trend towards regulation is “healthy”. “There is growing awareness among local elected officials and tourism operators at all levels that we cannot wait until things get worse. The idea is to handle the situation early enough to prevent having to close the sites entirely.” He points to new ways of managing tourism traffic, such as how the Provence-Alpes-Côte-d’Azur region has partnered with the Waze navigation app to suggest users return to the busiest sites at later hours. This initiative has also been adopted by Normandy’s Mont-Saint-Michel, which is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site . Its abbey alone recorded 608,421 visitors in 2021. Waze indicates when the island is full to capacity and lists notable tourist attractions from the surrounding area.
Since the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic, many of the French have set aside the idea of vacationing in foreign destinations in favour of French sites. “Some people decided to improvise as ‘wild adventurers’ out in nature, but they weren’t used to visiting natural areas and these sites weren’t prepared to host so many people,” says Julien Buot. Chartreuse Natural Park in the Alps, finding itself taken by storm, had to forbid bivouac camping last summer. “If too many hikers pitch their tents and light fires, this disturbs the natural environment – flora, fauna – and also the local inhabitants.”
Instagram overwhelms natural sites
Another recent phenomenon upending normal tourism patterns is Instagram . “Between the moment UNESCO listed a site and the moment tourists started to arrive en masse, there used to be a period of several years. We had time to prepare. Today, an ‘influencer’ can post a photo of a location from off the beaten track, and in a few weeks or even just a few days, the site will be visited by hundreds of people.”
The Marseille Calanques
Voir cette publication sur Instagram Une publication partagée par WeAreMarseille (@weare.marseille)
Volunteers from the Clean my Calanques group collect trash left behind by visitors.
Voir cette publication sur Instagram Une publication partagée par Clean my Calanques (@cleanmycalanques)
The important role social media plays in overtourism is not a new idea for Shaï-Hanah Mallet-Bitton, who sees numerous tourists taking selfies from the edge of the Étretat cliff to create striking posts. “We’re going to have to think about roping off the trails, because a real security issue is being created.” Two women died this year after falling from the edge while posing for pictures.
Improving trails, reworking signage, increasing waste collection and upgrading to account for mass tourism comes with a cost that the community is struggling to cope with. For this reason, Jean-Baptiste Renié, the city councillor, is very happy that the Étretat cliff will soon be officially labelled a “Grand site of France”: “This will allow us to set the whole zone aside, obtain financing for its preservation and better manage the stream of tourists.”
This article was translated from the original in French.
Daily newsletter Receive essential international news every morning
Take international news everywhere with you! Download the France 24 app
- Environment
- social media
- Sustainable development
- French economy
The content you requested does not exist or is not available anymore.

10 Environmental Impacts That Overtourism Can Have On The World
- Overtourism, or too many tourists in a location, is destroying tourism itself as well as the environment and ecosystems of popular destinations. This can lead to the loss of the very qualities that made a place attractive to tourists in the first place.
- Overtourism contributes to increased carbon emissions due to the high demand for transportation, such as flights, ships, and road vehicles. Travelers can help reduce carbon emissions by booking non-stop flights and opting for eco-friendly modes of transportation like bicycles and public transport.
- The negative impacts of overtourism include the accumulation of plastic waste, destruction of natural ecosystems, sewage problems, greenwashing by hotels, noise pollution, loss of cultural identity, suffering of local businesses, inflation, and overconsumption of resources. Travelers can combat these issues by choosing eco-friendly accommodation, reducing plastic waste, respecting local cultures, supporting local businesses, and being mindful of resource usage.
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization, 1.5 billion international tourist arrivals were recorded in 2019 globally. Today's interconnected world depends on people's ability to travel, interact and explore.
Tourism has come to account for a large part of this travel, and a big chunk of the world economy now depends on it. In this endeavor for economic prosperity, the world seems to have missed a trick in terms of the impact that overtourism can have on society and, more importantly, on the planet.
A simple explanation of overtourism is that there are too many tourists at any given place and time, which is too much for the capacity of the infrastructure that supports it. There isn't an easier way to understand this except that overtourism is destroying tourism. Eventually, people will stop visiting a destination that has been undone through overtourism because the very reason they traveled to that place will no longer exist.
While the positive results of expanding tourism have always been easily measured, the environmental impact of overtourism has just started to be fully understood. Although there is no absolute solution to these issues, it may be time to take a deep dive into how this affects the world and what can be done to combat it. These are some of the many environmental impacts of too many tourists on a place.
Related: Here Are 10 Ways You Can Be Eco-Minded When Visiting National Parks Sustainably
Increased Carbon Emissions
With the increase in tourist travel, more flights, ships, and road vehicles are being produced and used across the world, resulting in higher pollution and carbon emissions. Places that attract visitors from all over the world are battling the impact of higher CO2 levels.
The magnificent Taj Mahal in India is a case in point about how pollution impacts tourism .
Ways To Reduce Carbon Emissions When Traveling
- Among the most to least sustainable modes of transportation , airplanes are definitely one of the "least". It's not always possible to forgo a flight, though, especially if traveling extremely long distances. Booking non-stop flights helps reduce pollution, as each take-off and landing of an airplane increases its carbon emissions.
- Bicycles, public transport, and walking are great alternatives to renting a car. It is a more eco-friendly mode of travel, is cheaper on the pocket, and helps the local economy.
Plastic Waste That Harms Wildlife And Ecosystems
The indiscriminate use of plastic water bottles is sadly a common phenomenon seen in many places, especially warm destinations where people naturally need to stay hydrated more regularly.
It is important to remember that disposable plastic bags and water bottles are non-degradable and will likely end up in landfills. This plastic finds its way to oceans, rivers, and forests, affecting marine life and wildlife, not to mention the blocking of sewage treatment plants.
Ways To Reduce Plastic Waste When Traveling
- When visiting places where tap water isn't drinkable, as is the case in some of the beautiful locations in Africa and Asia, using stainless steel bottles instead of disposable plastic ones is a more eco-friendly choice.
- Eating fresh food instead of plastic-enclosed pre-packaged meals is not only a healthier option, it's also more environmentally friendly.
The Overall Destruction Of Natural Ecosystems
Flora and fauna are usually the first to suffer overtourism in many of the world's popular nature destinations, whether it is beach destinations, wildlife sanctuaries, or areas known for skiing. Environmental issues such as deforestation have further led to the destruction of entire ecosystems, and many times, this situation is irreversible.
Plus, as global warming and mass tourism are irreparably ruining coral reefs due to bleaching and habitat destruction, they are part of a natural system that is slowly becoming extinct. Globetrotters can learn to understand the importance of protecting coral reefs while traveling and how it impacts the environment.
Ways To Reduce Ecosystem Destruction When Traveling
- If travel to such places is done during off-season times, it gives nature time to heal and repair.
- Using eco-friendly modes of travel, such as paddle boats, bicycles, and skis, instead of motorboats, ATVs, and snowmobiles, is a better way to promote eco-friendly tourism and minimize the risk of harm to the environment and ecosystems.
- Try to avoid visiting nature spots that are already suffering from overtourism. In many cases, a place needs to be left alone to recover.
- If hiking, stay on marked trails; taking shortcuts or exploring off designated trails can harm ecosystems.
- Select eco-friendly tour companies that respect the environment when booking experiences like camping, hiking, snorkeling and diving excursions, boat trips, safaris, and other trip types.
Sewage systems all over the world are designed for a certain volume of local and tourist population - and these systems need to be supported through drainage and waste management.
Overtourism, by definition, means that the number has been unmanageably exceeded, and sewage systems are not able to cope with it.
Ways To Reduce The Risk Of Sewage Problems As A Traveler
- Choosing unpopulated or off-beat places that are becoming overridden with tourists is not recommended, as these destinations will not be in the best position to handle large volumes of visitors, eventually resulting in garbage and subsequent diseases and pollution from malfunctioning sewers or outright sewer failure.
- Peak season travel will always test any local infrastructure while also being the most expensive time to travel; therefore, it's best to choose travel times that are off-season to make a better financial and environment-friendly choice.
- Avoid flushing items that are not supposed to be flushed; things like wipes, certain sanitary products, and even toilet paper in some places may cause problems with local sewage systems.
Related: Sustainable Travel: 10 Easy Ways That You Can Be Eco-Friendly During Your Next Vacation
Greenwashing
In the current day, when everyone wants to know what ecotourism is and why it's so important , corporations have jumped on the trend. That's where greenwashing comes in. Greenwashing is a practice where marketing and PR language is intentionally misleading and often used to convince customers that a hotel is better for the planet than it really is. It is also a common assumption that smaller boutique hotels will be greener just because they are smaller, but this isn't necessarily correct.
As such, eco-conscious travelers who want to enjoy an environmentally friendly vacation should check that their accommodation is indeed as eco-friendly as it claims. As an example, Marriott is a big hotel brand that decided to end its use of single-use plastic straws across all of its properties.
Overall, there are plenty of eco-hotels all around the world in most destinations, and many will prove their track record of green and sustainable initiatives by sharing what efforts they effectuate on their website and social media channels. Some even have official eco-status and awards, so these are always good to look for when determining if a hotel is actually eco-friendly.
Ways To Spot Greenwashing And Choose Eco-Friendly Accommodation
- Look for overly flowery "eco" language that doesn't really tell people how a hotel is actually eco-friendly. Environmentally friendly hotels that are genuinely so will show what their green initiatives are and prove how they achieve and maintain them, not just say they're eco. They should practice what they preach.
- See if a hotel has an official green or eco status - some countries, like Sweden and Bonaire, have their own eco-certification for accommodation.
Hotel and homestay owners should read about eco-friendly practices that have a minimal investment criteria to be certified green or eco-friendly.
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution can be a nuisance for local residents of a place. Moreover, it has an enormous environmental impact and does very serious damage to animal life, including wildlife. Experts say noise pollution can interfere with breeding cycles and rearing and is even hastening the extinction of some species.
With the craze for wildlife tourism at an all-time high, forests and sanctuaries all over the world have introduced noise abatement policies to protect wildlife.
Ways To Reduce Noise Pollution While Traveling
- Vehicular traffic is the single largest contributor to noise pollution. Using bicycles, carpools, and public transport wherever possible, and most importantly, less honking, especially in areas already marked as silent zones, all go a long way in reducing noise pollution.
- Loud music, especially at night, is very harmful to birds and other small species in both urban and non-urban ecosystems.
Related: The Most Polluted Countries In The World (And The Cleanest)
Loss Of Cultural Identity
Popularity brings in the crowd, and so is the case with tourism. Unfortunately, mass tourism often leads to local businesses feeling the need to change their traditional style of functioning for economic survival, thereby losing their own cultural identities and generating a sense of resentment towards tourists.
Tourists must abide by any such cultural restrictions that can be considered offensive.
Ways To Reduce The Loss Of Cultural Identity And Be A Respectful Traveler
- Research a place before traveling to it; check what the local laws, cultures, and customs are like.
- Learn about the destination's religion, if applicable, and learn more about the cultural norms, attitudes, and practices before visiting. Respect for local cultures and rituals is an important part of good tourism, and tourists must be aware of the local laws and customs.
- Alcohol, nightlife, dress codes, and sometimes even music can be sensitive cultural issues in some parts of the world.
Suffering Local Businesses
As tourism increases at any place, bigger corporations start to come in and set up businesses to cash in the advantage.
It's very likely that small local companies are not able to compete with them, so locally sourced products stop selling. Eventually, small local businesses may be forced to close down due to competition with big brands and corporations that cater to tourists.
Ways To Support Local Businesses While Traveling
- Although this is unlikely to deter overtourism, buying local products will help local small businesses stay afloat and counter some of the ill effects that mass tourism brings - like big corporations moving in and creating competition.
- An example of this would be to eat freshly cooked local food at a locally owned restaurant, cafe, or food stall rather than searching out a meal from a chain or corporation like McDonald's or KFC. Buying food from a local market instead of going to a big supermarket is also a great example of supporting small businesses in the local area.
Small businesses at tourist locations run the risk of being under capacity to deliver for overtourism in terms of financial investment or real estate capacity. Therefore, they often end up either selling out or migrating from the traditional area of work.
Inflation is simply the result of too much demand and too little supply, and this is one of the most immediate but indirect impacts of overtourism on the environment.
In the hyper tourism that started across the world after the COVID-19 pandemic, fast food and takeaway food services reported the sharpest inflation rate in travel and tourism services. Meanwhile, hotels and similar accommodation services also started showing a higher inflation rate than ever before.
What Else To Note About Inflation From Overtourism
- With overtourism, locally available products run short in supply, and so higher imports and cargo services have to be engaged, resulting in higher pollution and more waste.
- Not just government policy but tourists can also help change this equation by making eco-friendly choices while traveling and opting for sustainable and environmentally friendly ways of travel in the world. Lesser pressure of demand will keep prices in check and allow healthy tourism to flourish.
Related: 15 Countries Leading The Way In Environment Care (10 Falling Severely Behind)
The Overconsumption Of Resources
Many countries in Asia and the Mediterranean tend to favor mass tourism without implementing the necessary eco-friendly infrastructure. It is the short-term economic benefit versus long-term environmental damage.
Water, for example, is at the epicenter of human existence, and it is being wasted at an alarming rate. Hotel swimming pools in hot countries that are constantly refilled without recycling to cater to incoming tourists are a classic case in point.
Ways To Minimize Resource Overconsumption
- Wastage is a common result of overtourism, and it adds to an already under-supplied system. Being careful and thoughtful while shopping or consuming to avoid any waste is a big part of being eco-friendly towards the environment. The principle of buying and using only what one needs is a good methodology.
- Try to avoid being tempted by too many salesy deals, like "buy two, get one free", as this can make people more inclined to over-consume (and then potentially waste) resources or goods that aren't necessarily needed.
- Be mindful of water usage while traveling, especially when doing simple everyday tasks like showering, bathing, and brushing teeth (not leaving the tap on while brushing, for instance)
Overtourism and its ill effects in terms of wastage and overconsumption can be controlled by tourists themselves by raising self-awareness and making eco-friendly choices in terms of travel season, choice of transport, and accommodation, as well as consumption of resources.

Tourism and Sustainability in Turkey: Negative Impact of Mass Tourism Development
- First Online: 09 December 2016
Cite this chapter

- Istvan Egresi 3
Part of the book series: GeoJournal Library ((GEJL,volume 121))
1172 Accesses
5 Citations
Mass tourism has played a critical role in Turkey’s strategy for economic development. However, mass tourism development has not been without costs. This chapter will critically examine the impact of mass tourism on destination areas in Turkey. This chapter argues that tourists tend to consume more vital resources than local people and generate more waste and pollution. We also found that local people have benefited very little from tourism development. The main benefit for them is the provision of jobs, but most of these are seasonal, part-time, low-skilled, and low-paying. Tourism has also brought them higher prices and a de facto segregation from tourists in the coastal areas, where they appear to have lost the right to access beaches and other coastal lands which used to be public in the past but seem to be reserved for tourists nowadays.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Average water consumption is 140 L per person, per day, in rural areas and 250 L in urban areas (EEA 2001 ).
Total water consumption by the tourism industry in Alanya has increased from 4.6 billion liters in 2002 to 6.1 billion liters in 2008 (Tosun and Caliskan 2011 ).
Water consumption per guest, per day, in a five-star hotel is at least double compared to that in a two-star hotel. The share of five-star hotels in total water consumption of the tourism industry in Alanya is 34 %, and the share of four-star hotels is 11 % (Tosun and Caliskan 2011 ).
Besides the direct use of water in tourism, the indirect use of water is also very important—for example, for the preparation of food; with the increased preference for all-inclusive, this is projected to increase (Hadjikakou et al. 2013 ; Tortella and Tirado 2011 ).
The Blue Flag is a certification by the Foundation for the Environmental Education (FEE) that a beach meets its (high) standards for water quality and safety.
To be fair, we should note that, more often than not, the development of coastal mass tourism leads to an increase in the development gap between the coastal and the inland regions, especially in the developing nations. Andriotis ( 2006 ), for example, has reported a very similar situation on the island of Crete (Greece), where most development has taken place along the coast (stimulated by mass tourism), while the interior of the island is still used mainly for agriculture.
It is estimated that approximately 20 km 2 of agricultural lands have been lost in Alanya alone to tourism development (Tosun and Caliskan 2011 ).
Akkemik, K. A. (2012). Assessing the importance of international tourism for the Turkish economy: A social accounting matrix analysis. Tourism Management, 33 , 790–801.
Article Google Scholar
Alipour, H. (1996). Tourism development within planning paradigms: The case of Turkey. Tourism Management, 17 (5), 367–377.
Altunel, E., & Hancock, P. L. (1994). Pollution of the Pamukkale travertine as a consequence of urbanisation: What future for a unique natural Turkish Monument? 47 Turkiye Jeoloji Kurultayi 1994 Bildiri Ozleri; Cevre Jeolojisi Oturumu . Izmir: Dokuz Eylul Universitesi.
Google Scholar
Alvarez, M., & Korzay, M. (2011). Turkey as a heritage tourism destination: The role of knowledge. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management, 20 , 425–440.
Amelung, B., & Viner, D. (2006). Mediterranean tourism: Exploring the future with the tourism climatic index. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 14 (4), 349–366.
Andriotis, K. (2006). Researching the development gap between the hinterland and the coast: Evidence from the island of Crete. Tourism Management, 27 , 629–639.
Antakyali, D., Krampe, J., & Steinmetz, H. (2008). Practical application of waste-water reuse in tourist resorts. Water Science and Technology, 57 , 2051–2057.
Bianchi, R. V. (2004). Tourism restructuring and the politics of sustainability: A critical view from the European periphery (the Canary Islands). Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 12 (6), 495–529.
Blue Plan. (2012). Seaside tourism and urbanization: Environmental impact and land issues. Blue Plan notes: Environment and development in the Mediterranean, May 21.
Briassoulis, H. (2002). Sustainable tourism and the question of the commons. Annals of Tourism Research, 29 (4), 1065–1085.
Briassoulis, H. (2007). Golf-centered development in coastal Mediterranean Europe: A soft sustainability test. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 15 (5), 441–462.
Buhalis, D. (2000). Relationships in the distribution channel of tourism: Conflicts between hoteliers and tour operators in the mediterranean region. International Hospitality, Leisure and Tourism Administration Journal, 1 (1), 113–139.
Burak, S., Dogan, E., & Gazioglu, C. (2004). Impact of urbanization and tourism on coastal environment. Ocean and Coastal Management, 47 , 515–527.
Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. The Canadian Geographer, 24 (1), 5–12.
Çetinel, F., & Yolal, M. (2009). Public policy and sustainable tourism in Turkey. Tourismos: An International Multidisciplinary Journal of Tourism, 4 (3), 35–50.
Claver-Cortes, E., Molina Azorin, F., & Pereira-Moliner, J. (2007). Competitiveness in mass tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 34 (3), 727–745.
De Stefano, L. (2004). Freshwater and tourism in the Mediterranean . Rome: WWF Mediterranean Program. www.panda.org/Mediterranean
Duman, T., & Tosun, C. (2010). Current developments in Turkish tourism. Anatolia: An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research, 21 (1), 5–9.
Duzgunoglu, E., & Karabulut, E. (1999). Development of turkish tourism: Past and present. Istanbul: TURSAB (Association of Turkish Travel Agencies).
EEA. (2001). Environmental signals . Copenhagen: European Environmental Agency. http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/signals-2001/page000.html
EEA. (2003). Europe’s water: An indicator-based assessment . Topic report No. 1, European Environmental Agency. http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/topic_report_2003_1
Egresi, I., Bayram, B., Kara, F., & Kesik, O. A. (2012). Unlocking the potential of religious tourism in Turkey. GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites, 5 (1), 63–80.
Erdogan, N., & Baris, E. (2007). Environmental protection programs and conservation practices of hotels in Ankara, Turkey. Tourism Management, 28 , 604–614.
Eroglu, T. (1995). Yuksek okul adina yapilan konusmalar. In Kapadokya Toplantilari II: Turizm Endustrisi—Turizm Isletmeciligive Otelcilik Yukesek Okulu Isbirligi Imkanlari (pp. 30–33).
EurActive. (2010). Turk Turizmi Ekonomik Krizden Neden Daha Az Etkilendi? http://www.euractive.com.tr
Gezici, F. (2006). Components of sustainability: Two cases from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research, 32 (2), 442–455.
Gezici, F., Yazgan Gül, A., & Alkay, E. (2006). Analyzing coastal development pattern of tourism in Turkey. 46th Congress of European Regional Science Association, 30 August–3 September, Volos, Greece.
Gossling, S. (2001). The consequences of tourism for sustainable water use on a tropical island: Zanzibar, Tanzania. Journal of Environmental Management, 61 , 179–191.
Gossling, S. (2006). Tourism and water. In S. Gossling & C. M. Hall (Eds.), Global environmental change, ecological, social, economic and political interrelationships (pp. 180–194). Abingdon: Routledge.
Gossling, S., Peeters, P., Hall, C. M., Cevon, J.-P., Dubois, G., Lehmann, L., et al. (2012). Tourism and water use; supply, demand and security: An international review. Tourism Management, 33 , 1–15.
Göymen, K. (2000). Tourism and governance in Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research, 22 , 1025–1048.
Hadjikakou, M., Chenoweth, J., & Miller, G. (2013). Estimating the direct and indirect water use of tourism in the Eastern Mediterranean. Journal of Environmental Management, 114 , 548–556.
Kaya, Z., & Raynal, D. J. (2001). Biodiversity and conservation of turkish forests. Biological Conservation, 97 (2), 131–141.
Kaya, L. G., & Smardon, R. (2000). Sustainable tourism development: The case of Antalya, Turkey. In Proceedings of the Northeastern recreation symposium, Bolton Landing, New York, USA (pp. 222–228).
Kent, M., Newham, R., & Essex, R. (2002). Tourism and sustainable water supply in Mallorca: A geographical analysis. Applied Geography, 22 , 351–374.
Kocasoy, G. (1989). The relationship between coastal tourism, sea pollution and public health: A study case from Turkey. Environmentalist, 9 (4), 245–251.
Kuvan, Y. (2005). The use of forests for the purpose of tourism: The case of Belek Tourism Center in Turkey. Journal of Environmental Management, 75 , 263–274.
Kuvan, Y. (2010). Mass tourism development and deforestation in Turkey. Anatolia: An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality Research, 21 (1), 155–168.
Kuvan, Y., & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management, 26 , 691–705.
Medeazza, G. M. (2004). Water desalination as a long-term sustainable solution to alleviate global freshwater scarcity: A north-south approach. Desalination, 169 , 287–301.
Okumus, F., Avci, U., Kilic, I., & Walls, A. R. (2012). Cultural tourism in Turkey: A missed opportunity. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management, 21 (6), 638–658.
Okumuş, F., & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis: Evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research, 32 (4), 942–961.
Ozden, S., Atmis, E., & Menemencioglu, K. (2004). Negative effects and recent unplanned expansion on highland ecosystems in Turkey. Mountain Research and Development, 24 (4), 303–306.
Perry, A. (2006). Will predicted climate change compromise the sustainability of Mediterranean tourism? Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 14 (4), 367–375.
Reid, D. G. (2003). Tourism, globalization and development: Responsible tourism planning . London: Pluto Press.
Sabban, M. (2013). Report on sustainable tourism in the Mediterranean. Assemble Regionale et Locale Eyru-Mediterraneene—Euro Mediterranean Regional and Local Assembly (ARLEM). http://cor.europa.eu/en/activities/arlem/activities/meetings/Documents/sudev-report2012-tourism-en.pdf
Sari, D., Ozkurt, N., Hamamci, S.F., Ece, M., Yalcindag, N., Akdag, A., et al. (2014). Assessment of noise pollution sourced from entertainment places in Antalya, Turkey. Inter-noise conference proceedings, November 16–19, Melbourne, Australia. http://www.acoustics.asn.au/conference_proceedings/INTERNOISE2014/papers/p141.pdf
Scoullos, M. J. (2003). Impact of anthropogenic activities in the coastal region of the mediterranean sea. In International Conference on the Sustainable Development of the Mediterranean and Black Sea Environment, May, Thessaloniki, Greece.
Seckelmann, A. (2002). Domestic tourism—A chance for regional development in Turkey? Tourism Management, 23 , 85–92.
Shaw, G., & Agarwal, S. (2007). Introduction: The development and management of coastal resorts: A global perspective. In S. Agarwal & G. Shaw (Eds.), Managing coastal tourism resorts: A global perspective (pp. 1–20). Clevedon: Channel View Publications.
Sönmez, S., & Sirakaya, E. (2002). A distorted destination image? The case of Turkey. Journal of Travel Research, 41 , 185–196.
Tavmergen, I. G., & Oral, S. (1999). Tourism development in Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research, 26 (2), 451–453.
Tezcan, B. (2004). Developing alternative modes of tourism in Turkey (M.A. Thesis), Middle Eastern Technical University, Ankara, Turkey.
Tortella, B. D., & Tirado, D. (2011). Hotel water consumption at a seasonal mass tourist destination. The case of the island of Mallorca. Journal of Environmental Management, 92 , 2568–2579.
Tosun, C. (1998). Roots of unsustainable tourism development at the local level: The case of Urgup in Turkey. Tourism Management, 19 (6), 595–610.
Tosun, C. (1999). An analysis of contributions of international inbound tourism to the Turkish economy. Tourism Economics, 5 (3), 217–250.
Tosun, C. (2001). Challenges of sustainable tourism development in the developing world: The case of Turkey. Tourism Management, 22 , 289–303.
Tosun, C. (2002). Host perceptions of impacts of tourism: A comparative tourism study. Annals of Tourism Research, 29 , 231–253.
Tosun, C., & Caliskan, C. (2011). An analysis for achieving a better level of sustainable tourism development at local scale . Sophia Antipolis: Plan Bleu.
Tosun, C., Okumus, F., & Fyall, A. (2008). Marketing philosophies: Evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research, 35 (1), 127–147.
Tosun, C., & Timothy, D. (2001). Shortcomings in planning approaches to tourism development in developing countries: The case of Turkey. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 13 , 352–359.
Tosun, C., Timothy, D. J., & Öztürk, Y. (2003). Tourism growth, national development and regional inequality in Turkey. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 11 (2–3), 133–161.
Tosun, C., Timothy, D. J., & Öztürk, Y. (2004). Tourism growth, national development and regional inequality in Turkey. In B. Bramwell (Ed.), Coastal mass tourism: Diversification and sustainable development in Southern Europe (pp. 85–113). Clevedon: Channel View Publications.
Tucker, H. (2010). Peasant entrepreneurship, a longitudinal ethnography. Annals of Tourism Research, 37 (4), 927–946.
Var, T. (2001). The state, the private sector, and the tourism policies in Turkey. In Y. Apostopoulos, P. Loukisas, & L. Leontidou (Eds.), Mediterranean tourism: Facets of socioeconomic development and cultural change (pp. 91–111). London: Routledge.
Williams, S. (2009). Tourism geography: A new synthesis . London: Routledge.
Yarcan, S. (2007). Coping with continuous crises: The case of Turkish inbound tourism. Middle Eastern Studies, 43 (5), 779–794.
Yüksel, F., Bramwell, B., & Yüksel, A. (1999). Stakeholder interviews and tourism planning at Pamukkale, Turkey. Tourism Management, 20 (3), 351–360.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Fatih University, 34500, Buyukcekmece, Istanbul, Turkey
Istvan Egresi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Istvan Egresi .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Geography, Fatih University, Istanbul, Turkey
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Egresi, I. (2016). Tourism and Sustainability in Turkey: Negative Impact of Mass Tourism Development. In: Egresi, I. (eds) Alternative Tourism in Turkey. GeoJournal Library, vol 121. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47537-0_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-47537-0_3
Published : 09 December 2016
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-47535-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-47537-0
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Why tourism in Venice is doing more harm than good and what we can do about it
The current state of tourism is hurting venice.
The ever-increasing offering of low-cost travel transportation, housing, and planning has helped the tourism industry to boom in the past decades.
The year 2019 alone counted over 1.5 billion international arrivals.
However, most major stakeholders of the tourism industry focus on profit, not on sustainability.
Today, tourism hotspots are affected by mass tourism – when visitors arrive in masses of tens of thousands of people – and the industry in the most popular destination has turned into a problem, rather than a resource. Venice is one of them, and it is suffering a lot.

Venice residents dropped from 175.000 in 1951 to 50.000 in 2022. Why?
Data shows that the population in Venice has been constantly decreasing for several decades.
Several factors can explain why this is happening:
- An increased cost of living
- Higher cost of housing
- A decrease in quality of life (traditional shops replaced by low-quality souvenir shops, constant, for example)
- Lack of spaces for the youth
- Lack of rewarding job opportunities
All of the above can be linked directly to the impact caused by the dramatic increase in mass tourism in Venice.
Indeed, some local entrepreneurs and several foreign investors exploit this situation to target tourists and generate great profits. Meanwhile, authentic activities and shops have and are being strangled by: ever-increasing rents, a constantly decreasing market size of the local population, and the competition of tourist traps seducing tourists with their cheap mass-produced products or frozen food.
Want more tips, tools and stories from Venice, Italy?
We're on a mission to make it easy and fun to discover and support the authentic Venice. Try our email and see for yourself!
Thanks for signing up! If there is no e-mail in your inbox in the next hour, remember to check your spam folder and to add us to your contact list. Thank you! Get access to our live videos and even more content: like us on Facebook to add daily goodness to your feed. A presto!
Oops! We're sorry, something went wrong. We'll fix it soon. In the mean time, you can like us on Facebook to stay in touch!
By signing up you agree with Venezia Autentica's privacy policy
Venice is a beautiful and unique city that must and can only be preserved by locals, who are the only people with the knowledge (and love) necessary to do so.
This is why one of the biggest threats to the survival of Venice is the disappearance of its citizens.
Without citizens, Venice loses the mastery and the know-how that keeps and kept Venice alive for thousands of years.
Alas, however, younger generations are forced to move out of the historical centre because they can not find rewarding jobs and unaffordable housing, having to give up on their dream of living in their city.
Currenlty, the Venice I.V. (“indice di vecchiaia” or “age index”, which represents the ratio between people over 64 and children under 15) is well above 2,80.
In other words, there are almost 3 people over 64 for every child under 15.
This, coupled with a 35% decrease in the population aged 20 to 34 between 2001 and 2011 (just 10 years!), does not leave much hope for the city.
To give Venice a chance of survival, strong measures must be taken to repopulate the city.
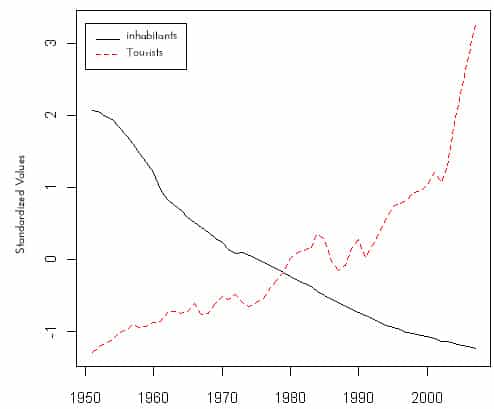
The above trend represents the number of locals and the number of tourists in Venice since 1950.
One of the reasons behind the constant increase of tourism arrivals is the decrease of international transportation.
Since 2015, Venice counts up to 30 million stays every year. And that in a city of fewer than 8 km 2 (or 3 square miles)!
This increase, however, has also been coupled with a decrease in the average length of the stat of tourists and a shift of touristic behaviour that is harming deeply Venetian inhabitants and local businesses.

These changes in tourism and the daily saturation of tourists within the city has led to an invasion of mass-produced souvenir shops and tourist traps, that are putting many local enterprises and artisans’ shops out of business by causing an increase in the cost of living and renting.
The consequences of this are a decrease in life quality and opportunities for the locals, as well as a worsened experience for responsible and caring visitors.
Related: You don’t want to be that tourist, watch out for these common tourist traps in Venice
Why are we speaking of a decrease in quality of life for the inhabitants as well as a decrease in quality of the stay for visitors?
Until the early 2000s, most visitors would come and stay in Venetian hotels for a few nights, taking a few days for exploring the city as a whole, visiting Venice beyond the landmarks, discovering the local life and culture.
In recent years, along with a yearly staggering increase in the number of the visitors, the way of visiting the city has changed: many tourists now come to Venice as a day/hour trip, as part of a cruise, for example, dramatically modifying social, logistic, economic and touristic aspects of the city.
Related: Good or bad? The truth about cruise ships in Venice
A vivid effect of this shift towards day-trips is that the only walkways used by dozens/hundred of thousands are the main streets connecting Piazzale Roma and the Train Station (the arrivals area) with the Rialto Bridge and Saint Mark’s square.
For 11 months a year, Venice assists to an almost daily gigantic human wave arriving in the city and trying to quickly move to and back from the two most known Venetian landmarks, resulting in a total jam.

To make things worse, Venice cannot provide picnic or resting areas because of its small size and its morphology, resulting in visitors sitting down for resting and eating on bridges, narrow alleys, house doors and shop windows blocking even further the already jammed city.
Even though they are not perceived as such, alleys and bridges in Venice are the equivalent to streets and crossroads in other cities. Blocking them is a guarantee for Venetians to get angry at you.
Related: You asked, We answered: 19 things you might not know about Venice, Italy
Another effect of this approach to visiting the city is the impossibility for day-trippers themselves to take the time to appreciate the city and to understand what is genuine and worth their money, and what is absolutely not.
Foreign investors and investment funds have decided to take advantage of this situation by purchasing shops on the busiest paths to display their cheap/very cheap merchandise, luring in the passing tourists and selling mass-produced plastic goods which, at best, are of no value. At worst, they have been found to be toxic.
One more problem is that Italy has a high unemployment rate but no minimum wage, and these businesses, in particular, exploit the situation even further: employees struggle to live even in Mestre (which has much lower rents), while the company they work for is destroying local and family businesses and artisans’ shops.

Unlock a discount at the best local businesses in Venice
The investment race for selling 99cents souvenirs has led to a spike in the price of shops and rents that forced many genuine local activities, which were not aiming at masses, to try and move to less visited and therefore less expensive areas.
Because of the day-trip approach and the ever-decreasing local population, however, those less-visited areas struggle to have enough customers, leading an ever-increasing number of local activities to close and never to open again.
Related: Interactive Local Map Of Venice, Italy
This lack of opportunities and the negative outlook for young Venetians is leading more and more people to leave the city, well knowing that they will never be able to come back unless the current situation changes.
Are the negative effects of mass tourism in Venice really that bad?
The situation we just described could seem to be a bit too gloomy to you, maybe a result of a pessimistic approach.
The considerations we made, however, are perfectly in line with UNESCO’s last report about the current situation of “Venice and its Lagoon”, which lead the institution to consider putting Venice on the UNESCO World Heritage in Danger list in 2017.
Related: Venice to be or not to be a UNESCO World heritage site, that is the question
Is there any chance for Venice?
We are convinced there is still hope for Venice, of course!
Our strong determination and optimism make us believe it is possible to change this very negative trend and to improve the life of the Venetians, the health of the city, and the quality of the stay of the visitors… but we don’t trust the authorities for making this change happen.
We believe that Venice can prosper again, but only thanks to the people like you and us.
We believe that YOU can make a difference! Travel Responsively, please.

Book an authentic experience in Venice
Here's how you can start making a positive impact in venice.
- Unlock your discount at our partner selected authentic local shops, bars & restaurants. You’ll help us build a better future for Venice and the Venetians
- Book an authentic experience or walk with a local
- Eat, Shop, Drink local: Visit and Support our certified local businesses
- Experience Venice like a Venetian: See our interactive map of Venice and our tips
- Hire Venetians to help you with your needs and services in Venice
Make sure to check out the resources below to make the best out of your stay in Venice, while making a positive impact on the local community.
We count on you!
YOU CAN SUPPORT VENICE AND THE VENETIANS BY TRAVELING RESPONSIBLY
I'm visiting Venice. Why should I follow your recommendations?
The way you visit Venice has an impact both on the quality of your experience and on Venice itself. Chilling, exploring , shopping , eating and drinking where the locals do, can make a huge impact both on the memories you bring home and on the local economy and community.
POPULAR POSTS LIKE THIS
- Best Places where to eat and drink like a local in Venice
- Interactive map of the best authentic local businesses and places where to eat & drink in Venice
- Why eating and drinking at authentic local businesses matters
Liked this article? Don’t forget to share the love!
Home >> Visiting Venice >> Tips and Inspiration >> You’re Here
Tips and Inspiration to experience Venice
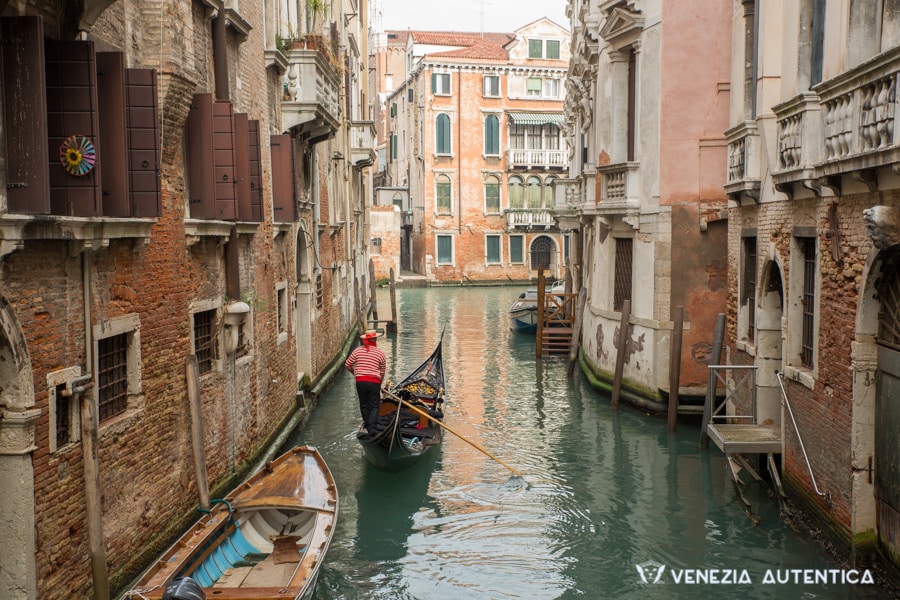

Want to go on a gondola ride in Venice? Here’s everything you need to know!

How’s the weather in Venice, Italy? We’ve got you covered!
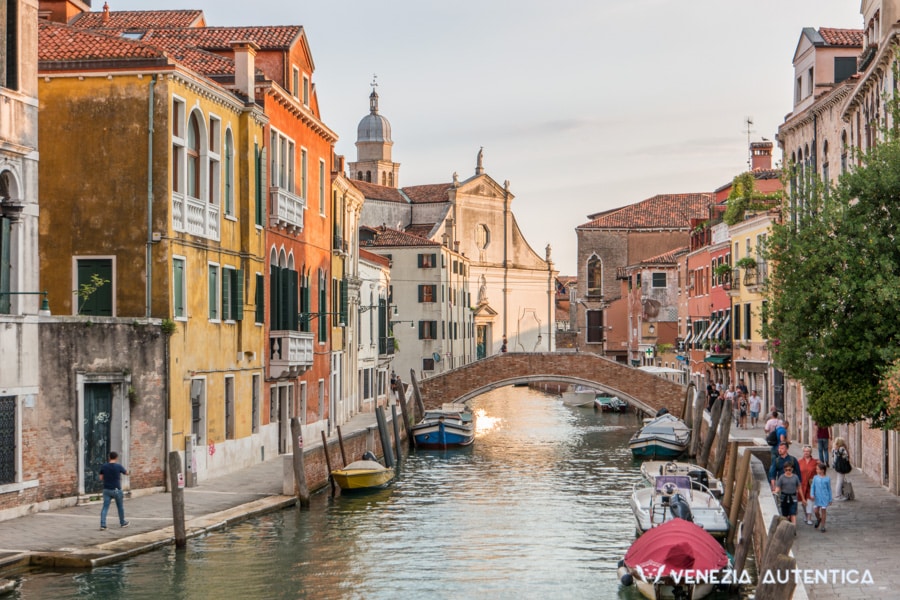

The ultimate guide to the top 10 things to do and see in Venice, Italy
More in Visiting Venice
Go to Visiting Venice >>
- February 12, 2022
You might also like

Want to go on a gondola ride in Venice? Here’s everything you need to know!

How’s the weather in Venice, Italy? We’ve got you covered!
![positive effects of mass tourism on the environment From a local event to an international rowing appointment in Venice, Italy: La Vogalonga [VIDEO+PHOTO] - Venezia Autentica | Discover and Support the Authentic Venice - In Venice, tourism is not sustainable. Discover the impact of the travel industry on Venice and how sustainable tourism can help saving the city](https://cdn1.veneziaautentica.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/0i5c0448-custom-560x315.jpg)
From a local event to an international rowing appointment in Venice, Italy: La Vogalonga [VIDEO+PHOTO]
- ONLY PRIVATE TOURS AND ACTIVITIES
We make it easy to experience Venice with local guides and experts
- 100% GUARANTEED LOCAL AND IMPACTFUL
Looking for things to do in Venice? Experience Venice with a local!
We’d love to chat.
Let us know
how we can help

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The images have drawn global attention and created a bad rep for single-use plastic items, making us (consumers) more aware of the true impact. #2 Tourism for skills learning and education. This is a special side of tourism but plays also an important role in positive impacts of tourism on the environment.
Mobilizing such a substantial human tourist's mass is most likely to trickle environmental pollution along with its positive effects on employment, wealth creation, and the economy. ... Kuvan Y (2010) Mass tourism development and deforestation in Turkey. ... Azizov M (2019) Re-evaluating the environmental impacts of tourism: does EKC exist ...
CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993; Hall & Lew, 2009; ... The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ... This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a ...
The most obvious consequences of uncontrolled tourism growth characterized by overtourism symptoms are given below as a summary of those collected by Jordan et al. ( 2018) and Peeters et al. ( 2018, p. 17-39): Environmental deterioration, including waste, noise, air quality, and water pollution issues.
There are many positive aspects to tourism. Around two billion people travel each year for tourism purposes. ... Each link in the chain can impact the environment - positively or negatively. If you prefer to leave the planning to someone else, be sure to pick an operator that prioritizes the environment, uses resources efficiently and respects ...
The Environmental Impact Of Mass Tourism And How To Help Manage It. Mass tourism is a somewhat recent social phenomenon, with its numbers rising dramatically in current years. This negative side of tourism saw its first growth boost in the 1930s, and nowadays, people making over a billion international trips a year, so this phenomenon still ...
It revealed that positive impacts of tourism have a significant positive correlation with residents' well-being, whereas negative tourism impacts do not have a convincing effect. The positive ...
"Tourism that takes full account of its current and future economic, social and environmental impacts, addressing the needs of visitors, the industry, the environment and host communities" Sustainable tourism development guidelines and management practices are applicable to all forms of tourism in all types of destinations, including mass ...
Climate action is understood as the efforts to measure and reduce GHG emissions and strengthen adaptive capacity to climate induced impacts.1. There is a growing consensus among tourism stakeholders as to how the future resilience of tourism will depend on the sector's ability to embrace a low carbon pathway and cut emissions by 50% by 2030.
Sustainable tourism is defined as the growth of all. types of tourism, tourist management, and tourism. marketing that considers natural, social, and economic. environmental in tegrity whil e e ...
Tourism and the environment can be mutually supportive. In a number of destinations, tourism helps to ensure higher water quality and better protection of nature and local natural resources. It can generate additional resources to invest in environmental infrastructures and services. A social dimension. Eco-tourism also has an active social ...
The most commonly noted positive environmental impact of tourism is raised awareness. Many destinations promote ecotourism and sustainable tourism and this can help to educate people about the environmental impacts of tourism. ... Natural, this is worse in areas with mass tourism and overtourism. Trampling. Photo by Vlad Bagacian on Pexels.com ...
For determining the tourism impacts, the socio-economic characteristics should be explored taking into account the destination characteristics and visitors' profile. The economic, socio-cultural and environmental impacts of tourism can be positive or negative for residents.
Mobilizing such a substantial human tourist's mass is most likely to trickle environmental pollution along with its positive effects on employment, wealth creation, and the economy. The local pollution at tourist destinations may include air emissions, noise, solid waste, littering, sewage, oil and chemicals, architectural/visual pollution ...
Mass tourism has positive and negative impacts on the environment, economy, and society. It is important to manage mass tourism sustainably and responsibly to minimize its negative effects and maximize its benefits. ... One of the most significant disadvantages of mass tourism is the environmental impact. Mass tourism can lead to pollution ...
Though tourism has many apparent positive repercussions, its negative impact can't be ignored. In the prevailing literature, many studies revealed that the negative effects of tourism outstrip the positive effects as the coal-based industries like coal mining and arid climate with improper maintenance have emerged as the main factor of environmental degradation.
The aim of this study is to present the effects of tourism on the economy, and environment. The study is divided in to sub-titles like the effects of tourism on environment-immigration-lifestyle of rural areas-foreign real estate and the structural change of a city. Munir Ozturk Keywords: Manavgat, Side, Tourism, Tourism in Manavgat, Transhumance.
In 2022, 415 million tourists traveled worldwide due to mass tourism, which has both positive and negative impacts on the environment and locals. Some cities attract millions of visitors each year, which can have adverse effects. Mass tourism: what are the consequences for the environment? We are mainly discussing pollution and environmental ...
Other villages struggling with mass tourism, such as Étretat in Normandy, are rethinking how they handle the influx of visitors. Issued on: 10/07/2022 - 17:13 4 min
Learn about the positive and negative impacts of tourism and how it can be managed sustainably in this guide for KS3 geography students aged 11-14 from BBC Bitesize.
According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization, 1.5 billion international tourist arrivals were recorded in 2019 globally. Today's interconnected world depends on people's ability to ...
Spatial and temporal concentration of tourism development has been identified as an important cause for environmental problems in many local tourist destinations (Tosun 2001).Evidence shows that coastal destinations face greater environmental pressure than inland destinations (Gezici 2006).Much of the development of mass tourism in Turkey has happened without any consideration for the ...
An increased cost of living. Higher cost of housing. A decrease in quality of life (traditional shops replaced by low-quality souvenir shops, constant, for example) Lack of spaces for the youth. Lack of rewarding job opportunities. All of the above can be linked directly to the impact caused by the dramatic increase in mass tourism in Venice.