Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Updated: April 17, 2024
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2022? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map at the last second?

The thing is — understanding your customer base can be very challenging. Even when you think you’ve got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

Download Now
While it isn’t possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a convenient tool for keeping track of critical milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents

What is the customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, benefits of customer journey mapping, customer journey stages.
- What’s included in a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Customer Journey Design
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer’s journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I’ve worked with were confused about the differences between the customer’s journey and the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don’t wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process of considering, evaluating, and purchasing a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand’s place within the buyer’s journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer’s journey. When you create a customer journey map, you’re taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey instead of leaving it up to chance.
For example, at HubSpot, our customer’s journey is divided into three stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
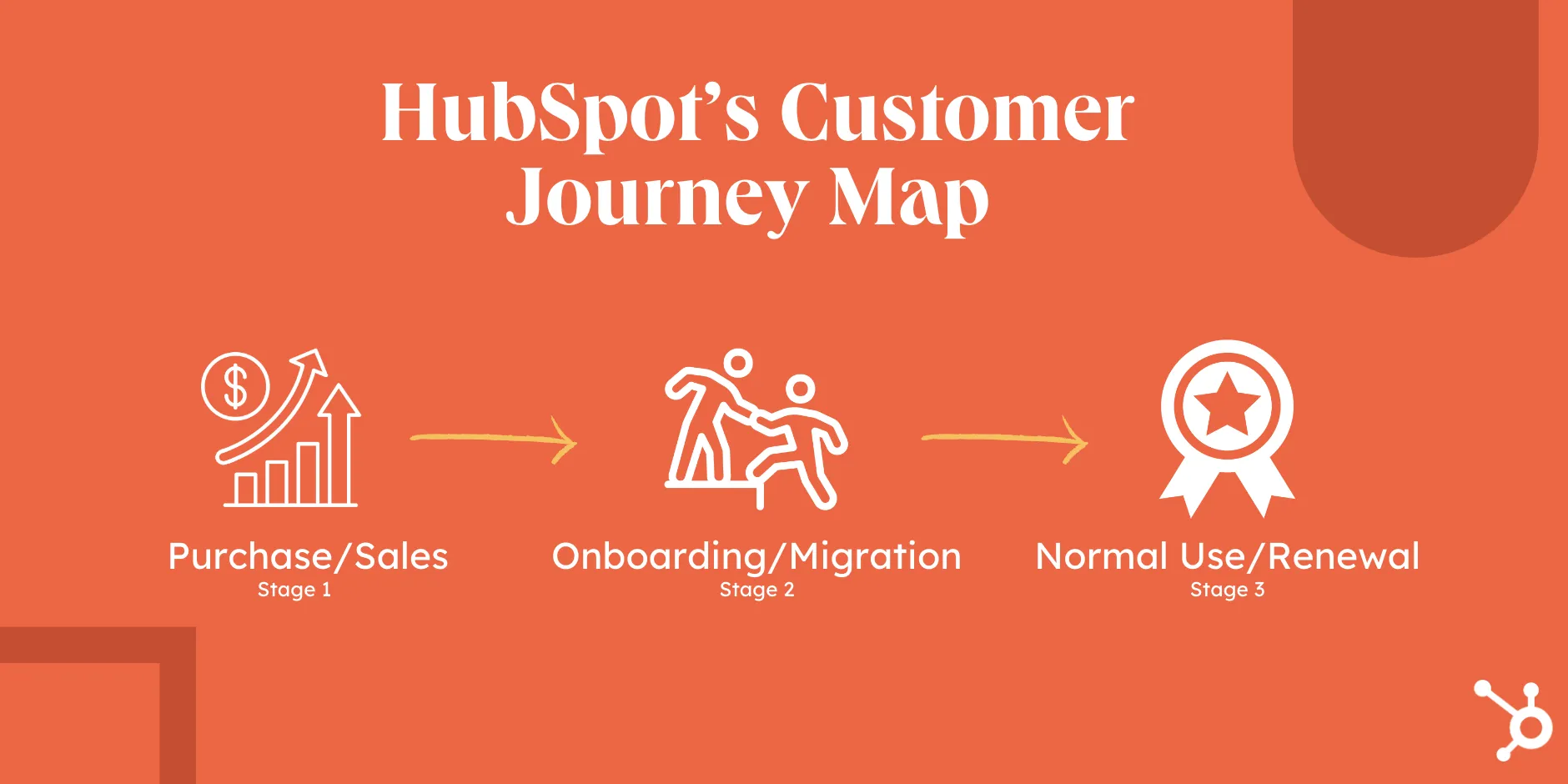
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot’s free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer’s journey, a day in your customer’s life, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company’s buyer persona. This will improve your product and customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you’re creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don’t have one, I recommend creating a buyer persona . This persona is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics of your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics ready.
Don’t have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot’s Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Questionnaires and user testing are great ways to obtain valuable customer feedback. The important thing is to only contact actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you’ve learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a customer journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company. If you group too many personas into one journey, your map won’t accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it’s best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don’t worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
What is a touchpoint in a customer journey map?
A touchpoint in a customer journey map is an instance where your customer can form an opinion of your business. You can find touchpoints in places where your business comes in direct contact with a potential or existing customer.
For example, if I were to view a display ad, interact with an employee, reach a 404 error, or leave a Google review, all of those interactions would be considered a customer touchpoint.
Your brand exists beyond your website and marketing materials, so you must consider the different types of touchpoints in your customer journey map. These touchpoints can help uncover opportunities for improvement in the buying journey.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there’s no overlap.
This is essential in creating a customer journey map because it provides insight into your customers’ actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they’re quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you must also look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels.
- Email marketing.
- Third-party review sites or mentions.
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
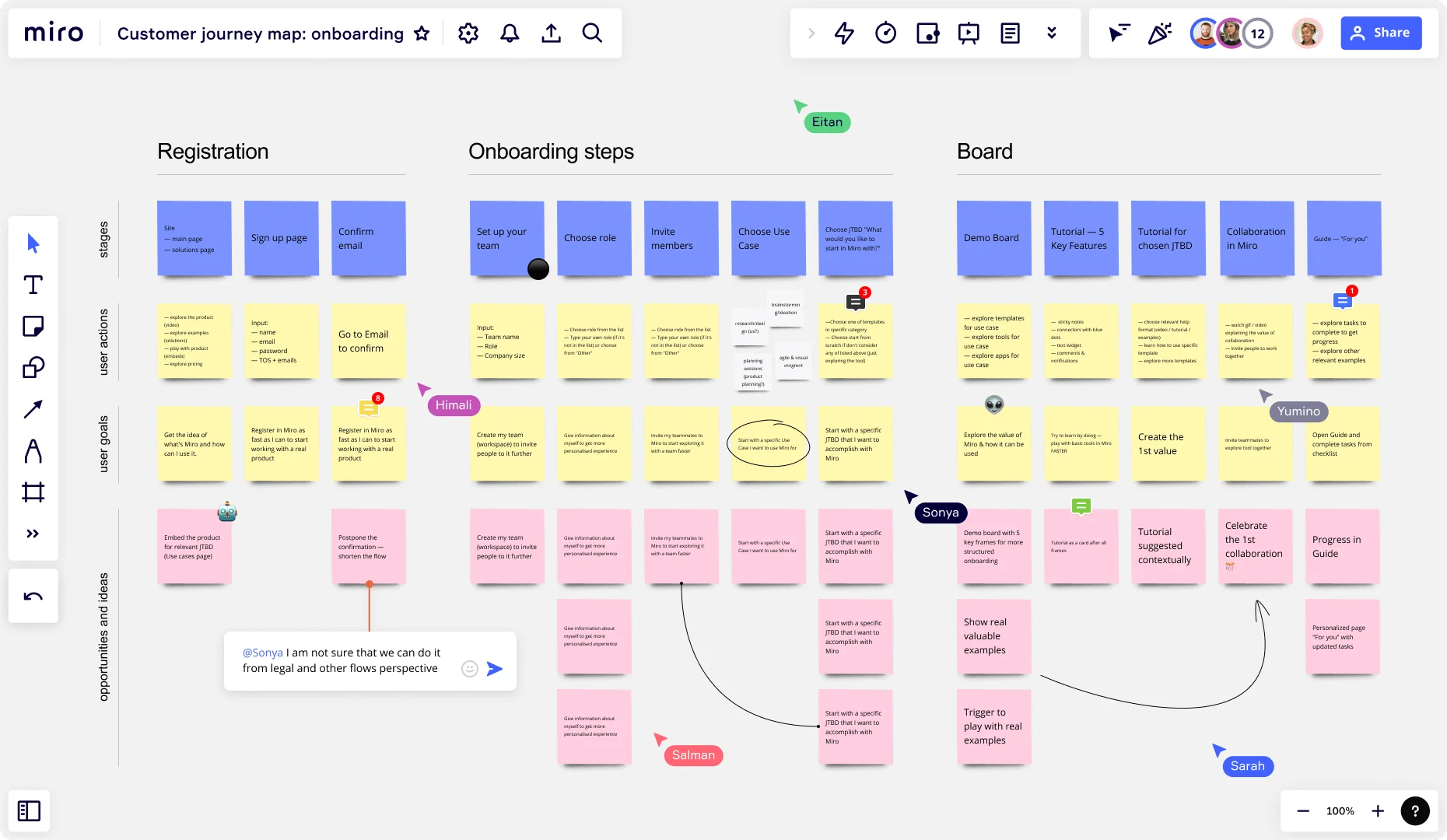
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding — you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![customer journey how to How to Measure Customer Experience: 8 Metrics 1000+ Service Reps Prioritize [+Data]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/customerexperiencemetrics.webp)
How to Measure Customer Experience: 8 Metrics 1000+ Service Reps Prioritize [+Data]
![customer journey how to How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey how to How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey how to Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
![customer journey how to How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office

How to create a customer journey map
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 8 min
How to Make a Customer Journey Map
- Conduct persona research
- Define customer touchpoints
- Map current states
- Map future states
Steve Jobs, the genius behind Apple’s one-of-a-kind customer experience, said, “You’ve got to start with the customer experience and work back toward the technology, not the other way around.”
Nowadays, a clear vision and strategy for customer interactions is no longer an optional “nice-to-have”—it’s essential. As you refine your customer experience, a customer journey map is one of the most powerful ways to understand your current state and future state.
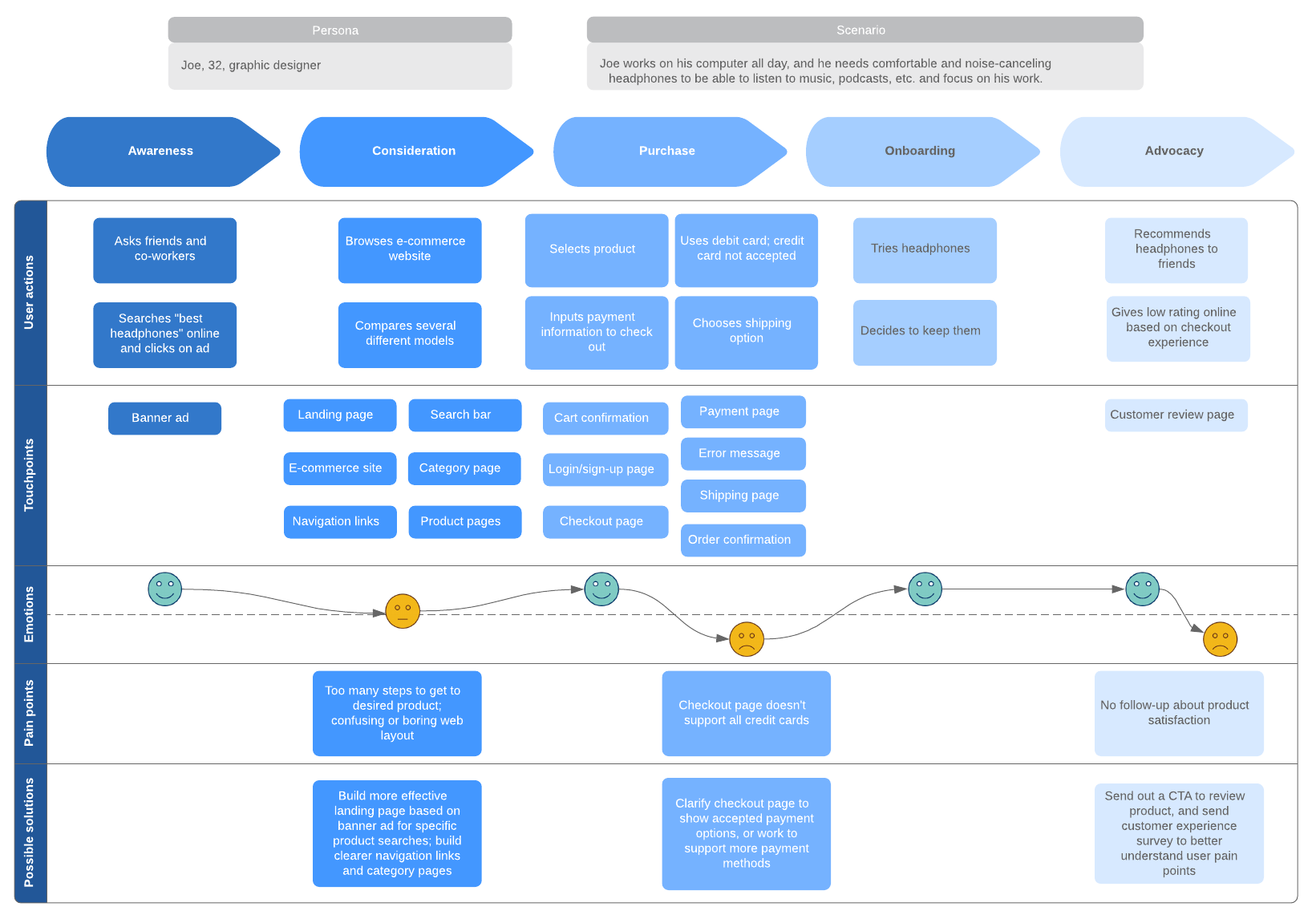
A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the process your customers go through in interacting with your business, such as an experience on the website, a brick and mortar experience, a service, a product, or a mix of those things.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with your brand. These visuals tell a story about how a customer moves through each phase of interaction and experiences each phase. Your customer journey map should include touchpoints and moments of truth, but also potential customer feelings, such as frustration or confusion, and any actions you want the customer to take.
Customer journey maps are often based on a timeline of events, such as a customer’s first visit on your website and the way they progress towards their first in-product experience, then purchase, onboarding emails, cancellation, etc.
Your customer journey maps may need to be tailored to your business or product, but the best way to identify and refine these phases is to actually talk to your customers. Research your target audiences to understand how they make decisions, decide to purchase, etc. Without an essential understanding of your customers and their needs, a customer map will not lead you to success. But, a well-constructed and researched customer journey map can give you the insights to drastically improve your business’s customer experience.
The benefits of customer journey mapping
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool for uncovering insights into your customer experience, driving business goals, and building resilience in a changing market. In a 2022 report, Hanover Research found that 94% of businesses said their customer journey maps help them develop new products and services to match customer needs. Another 91% said their maps drove sales.
But understanding a customer’s journey across your entire organization does so much more than increase your revenue. It enables you to discover how to be consistent when it comes to providing a positive customer experience and retaining customer loyalty.
This was especially evident in recent years as top of improving marketing, customer journey maps emerged as a valuable way to understand evolving buyer behavior. In fact, 1 in 3 businesses used customer journey maps to help them navigate the changing landscape during the pandemic.
When done correctly, customer journey mapping helps to:
- Increase customer engagement through channel optimization.
- Identify and optimize moments of truth in the CX.
- Eliminate ineffective touchpoints.
- Shift from a company to a customer-focused perspective.
- Break down silos between departments and close interdepartmental gaps.
- Target specific customer personas with marketing campaigns relevant to their identity.
- Understand the circumstances that may have produced irregularities in existing quantitative data.
- Assign ownership of various customer touchpoints to increase employee accountability.
- Make it possible to assess the ROI of future UX/CX investments.
Following the process outlined above, customer mapping can put your organization on a new trajectory of success. Yet, according to Hanover Research, only 47% of companies currently have a process in place for mapping customer journeys. Making the investment to map your customer journey and solidify that process as part of your company’s DNA can result in significant advantages in your competitive landscape, making your solution the go-to option that customers love.
Customer journey maps can become complicated unless you keep them focused. Although you may target multiple personas, choose just one persona and one customer scenario to research and visualize at a time. If you aren’t sure what your personas or scenarios might be, gather some colleagues and try an affinity diagram in Lucidchart to generate ideas.
1. Set goals
Without a goal, it will be difficult to determine whether your customer journey map will translate to a tangible impact on your customers and your business. You will likely need to identify existing—and future—buyers so you can set goals specifically for those audiences at each stage of their experience.
Consider gathering the key stakeholders within your company—many of whom likely touch different points of the customer experience. To set a logical and attainable goal, cross-functional teamwork is essential. Gather unique perspectives and insights about each part of the existing customer journey and where improvements are needed, and how those improvements will be measured.
Pro Tip : If you don’t already have them in place, create buyer personas to help you focus your customer journey map on the specific types of buyers you’re optimizing for.
2. Conduct persona research
Flesh out as much information as possible about the persona your customer journey map is based on. Depending on the maturity of your business, you may only have a handful of records, reports, or other pre-existing data about the target persona. You can compile your preliminary findings to draft what you think the customer journey may look like. However, the most insightful data you can collect is from real customers or prospective customers—those who have actually interacted with your brand. Gather meaningful customer data in any of the following ways:
- Conduct interviews.
- Talk to employees who regularly interact with customers.
- Email a survey to existing users.
- Scour customer support and complaint logs.
- Pull clips from recorded call center conversations.
- Monitor discussions about your company that occur on social media.
- Leverage web analytics.
- Gather Net Promoter Score (NPS) data.
Look for information that references:
- How customers initially found your brand
- When/if customers purchase or cancel
- How easy or difficult they found your website to use
- What problems your brand did or didn’t solve
Collecting both qualitative and quantitative information throughout your research process ensures your business makes data-driven decisions based on the voice of real customers. To assist when conducting persona research, use one of our user persona templates .

Discover more ways to understand the Voice of the Customer
3. Define customer touchpoints
Customer touchpoints make up the majority of your customer journey map. They are how and where customers interact with and experience your brand. As you research and plot your touchpoints, be sure to include information addressing elements of action, emotion, and potential challenges.
The number and type of touchpoints on your customer journey map will depend on the type of business. For example, a customer’s journey with a SaaS company will be inherently different than that of a coffee shop experience. Simply choose the touchpoints which accurately reflect a customer’s journey with your brand.
After you define your touchpoints, you can then start arranging them on your customer journey map.
4. Map the current state
Create what you believe is your as-is state of the customer journey, the current customer experience. Use a visual workspace like Lucidchart, and start organizing your data and touchpoints. Prioritize the right content over aesthetics. Invite input from the stakeholders and build your customer journey map collaboratively to ensure accuracy.
Again, there is no “correct” way to format your customer journey map, but for each phase along the journey timeline, include the touchpoints, actions, channels, and assigned ownership of a touchpoint (sales, customer service, marketing, etc.). Then, customize your diagram design with images, color, and shape variation to better visualize the different actions, emotions, transitions, etc. at a glance.
Mapping your current state will also help you start to identify gaps or red flags in the experience. Collaborators can comment directly on different parts of your diagram in Lucidchart, so it’s clear exactly where there’s room for improvement.
5. Map future states
Now that you’ve visualized the current state of the customer journey, your map will probably show some gaps in your CX, information overlap, poor transitions between stages, and significant pain points or obstacles for customers.
Use hotspots and layers in Lucidchart to easily map out potential solutions and quickly compare the current state of the customer journey with the ideal future state. Present your findings company-wide to bring everyone up to speed on the areas that need to be improved, with a clear roadmap for expected change and how their roles will play a part in improving the customer journey.
Customer journey map templates
You have all the right information for a customer journey map, but it can be difficult to know exactly how to start arranging the information in a digestible, visually appealing way. These customer journey mapping examples can help you get started and gain some inspiration about what—and how much—to include and where.

Don’t let the possibility of a bad customer journey keep you up at night. Know the current state of the customer journey with you business, and make the changes you need to attract and keep customers happy.

Customer journey mapping is easy with Lucidchart.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
What is a customer journey map?
Table of Contents
Definition of customer journey mapping.
A customer journey map (or CJM) is a visual representation of the process your customers go through when interacting with your company. This diagram takes you through the exact steps that lead to a customer choosing your specific product and buying it from your business. Creating a customer journey map will provide you with a visual storyline of how a buyer or a customer persona engages with your business at every touchpoint. From seeing your brand on social media to going into the store to buy the product — the customer journey will document the entire story. Customer journey maps are especially useful when they chart the experience of a single persona. By taking one specific customer persona, such as a small business owner or a single mother, the journey map can be detailed and specific — providing you with data and information about how to target specific customers. If you include too many personas on one customer journey map, you risk your diagram becoming too generic, and you may overlook new opportunities. You’ll likely need multiple customer journey maps to accurately depict the many personas of your target audience. But of course, you’ll need to define those personas first. Miro has a user persona template that can help you represent your target audience and better understand how to satisfy their needs with your product.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
Ever wondered what makes a customer buy a specific product from a certain company? The answer often lies in the journey the customer takes above all else. Here’s why mapping the customer journey is so important for every business, no matter how big or small.
Makes complex customer journeys easy to understand
Like other diagrams and concept maps, turning a complex process like a customer journey into a visual representation brings clarity and shared understanding. Instead of trying to describe a customer journey model exclusively with words, the diagram gives everyone on your team a visual overview of the entire customer experience.
Most customer journey touchpoints are mapped on a timeline, which creates a chronological understanding of the needs and wants of the customer at each stage of the process. Having a tool that makes it easier for your team to understand these complex journeys is crucial, as often, a customer journey doesn’t align with one specific department. For example, marketing, sales, customer service, and technical support may all need to be involved in creating an ideal user experience.
Everyone from each of these departments needs to be clear on how the journey works, where the handoffs are, and how to maximize the experience. By having one diagram act as a point of reference, different departments can ensure they are on the same page and can make informed, collaborative decisions.
Puts you in the customer’s shoes
An effective customer journey map helps you learn not only customer behavior but also how customers interact with your product. It also helps you understand your customers on an emotional level, acknowledging what causes them frustration, happiness, and excitement. By putting yourself in a customer’s shoes, you can follow their entire journey from brand awareness to advocacy. This allows you to gain deeper insights into the customer’s pain points and what compelled them to choose your company’s product. Based on this analysis, you can tailor your business processes to attract similar personas and increase conversions.
Creates a clearer understanding of your customer’s expectations
Customer journey mapping is a strategic approach that allows your company to understand customer expectations as well as what attracts certain personas to buy your product. By taking the time to understand the customer’s journey, you can understand what they expect from their experience with your business and product. This deeper understanding of what they need from your business allows you to proactively support them. It may also identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
Contributes to long-term customer retention
Striving to understand what the customer needs and following their journey will allow you to optimize their experience with your company. This will make your customer feel heard and appreciated, and, as a result, brand loyalty among your customer base will increase. In turn, this will lead to high customer retention and, hopefully, an increase in purchase frequency, which will benefit your company greatly in the long term.
The benefits of customer journey mapping
Many great tools can help you understand the customer journey. Why should you care about this one? Here are a few reasons why CJMs should be an essential part of your business toolkit.
Build better experiences
Customer journey mapping gives you a big-picture experience of your customer’s interaction with your brand. Think of a CJM as a map of a physical location like a city or a town. Once you have a map spread out in front of you, it’s easier to understand where you might run into roadblocks. It helps you plan ahead, and make adjustments to help customers overcome those obstacles.
Once you can visualize all phases of your customer’s journey, you can see where you’re not meeting their expectations. Armed with that knowledge, you can build a customer experience that’s seamless and satisfying. That translates into improved products and processes, more sales, faster sales cycles, and greater customer retention.
Enable customer success
For your business to succeed, your customer must also succeed. Customer journey mapping helps you see what is and isn’t working for your customer so you can set them up for success. Even a stylized picture of your customer’s journey can empower you to create, monitor, adjust, and enhance touch points.
Work better as a team
Even if your objectives are different, everyone in your organization is working toward the same goal: satisfying your customers. But it’s easy to lose focus. Engineering teams are busy coding, marketing teams are writing ad copy, sales teams are trying to sell to their prospects.… How do you all stay aligned?
Customer journey mapping is powerful because it keeps everyone focused on the customer. By creating a CJM, you can gain deep insight into what your customers want and need. For the marketing team, that means building better campaigns. For the sales team, that means deeper engagement with customers and prospects. For engineering, that means a holistic understanding of what programs are meant to achieve. Customer journey mapping makes it easy to equip every team member with a sophisticated understanding of your customers.
Set yourself apart from the competition
A recent report shows that 90% of the organizations that use customer journey mapping saw a decrease in churn and customer complaints. Customers and prospects respond positively when they feel like a brand understands their desires and pain points. The data is clear: customer journey mapping can set you apart from your competition.
5 customer journey stages
The customer journey map can be split into five important stages, as seen in this customer journey mapping template pack . Each customer will go through these stages as they interact with your company during their journey.
1. Awareness
Awareness is the moment when a buyer first becomes aware of your company, product, or brand. This can happen through a variety of mediums, from social media advertising to a word-of-mouth referral from another customer. Your brand can increase awareness and attract more customers through marketing practices and brand advertising. Paying attention to how your target audience grows their awareness of your brand enables you to optimize your marketing approach, budget, and channel prioritization.
2. Consideration
After your customer has become aware of your brand, they move into the consideration stage. This is a stage of ideation in which the customer considers whether they need the product or service your business is offering. They may also consider other companies that offer the same product. This stage proves the importance of good advertising at the awareness stage. If your company markets itself well, the customer will likely consider your product even more closely at this stage.
3. Purchase/Decision
After the customer has considered all of their options, it’s time to decide on the product or service they are going to purchase — or whether they’re going to make a purchase at all. Should they decide against buying, that will be the end of their personal customer journey. If that is the case, your company should focus on improving the awareness and consideration stages by working on its customer service or trying out new advertising or personalized promotional techniques.
4. Retention
Remember: the customer journey doesn’t end once they’ve made a purchase. Every company wants a loyal base of customers who return time and time again, which is why your team should analyze what needs to be done to stop customers from leaving. Fostering brand loyalty is a great way to improve your business’s general income. You can aim to retain customers by providing things like incentives, better customer support, and reminders about new products through digital marketing.
5. Advocacy
The last stage in the customer journey is advocacy — letting other people know about your brand or the service that you offer. Customers are more likely to advocate for your company if they are completely satisfied throughout each stage of the customer journey. This shows the interconnectedness of every step and how the journey is a circular pattern, even if it focuses on different personas.
What are customer journey touchpoints?
Throughout the five customer journey stages, there are different customer touchpoints . These are the moments in the customer journey when the customer interacts or engages with the business. Let’s take a closer look at the three types of touchpoints.
1. Pre-purchase touchpoints
A pre-purchase touchpoint includes any time when the customer interacts with your business before making a purchase decision. Pre-purchase touchpoints can occur in the awareness and consideration stages. They can also happen when another customer that has already gone through the entire customer journey refers your business. Pre-purchase touchpoints can happen if a buyer comes into contact with your business by visiting your website, seeing a post about you on social media, or hearing about your product from a friend. This point of the customer journey is all about persuasion and explanation. You need to make sure that when the customer discovers your business for the first time, you demonstrate that you can fulfill their buying needs.
2. Purchase touchpoints
Purchase touchpoints take place during the decision/purchasing stage of the buyer’s journey. This can happen in-store or online. You should optimize this stage to be as efficient and streamlined as possible so that the customer doesn’t change their mind during the purchase. For example, having a slow website that isn’t mobile optimized or forcing the customer to jump through hoops with a sales assistant to make a purchase will affect the buying process. Optimizing this touchpoint is essential to retaining customers, as a quick and easy purchase process could compel them to return in the future.
3. Post-purchase touchpoints
Post-purchase touchpoints include the journey’s advocacy and retention phases. The success of these touchpoints depends on how well-optimized the previous stages in the journey were. If the entire journey up until this point was enjoyable for the customer, they are more likely to refer your product or service to their friends and family. You should try to stay in regular contact with the customer to remind them about the journey and your company, as this will encourage them to return in the future.
What’s the difference between a customer journey map and a user story map?
Although customer journey maps and user story maps resemble each other, their functions are slightly different.
User stories are used to plan out features or functionalities, typically in an Agile model. In a user story, you describe a feature or functionality from user perspectives. That way, you can understand what the user wants to do and how that feature can help them accomplish it. Use a customer problem statement template to help you craft these perspectives.
Typically, a user story takes this form: “As a [type of user], I want to [goal], so that [benefit].” For example, “As a UX designer, I want to sketch on an online whiteboard, so I don’t have to be in the same location as my collaborators.”
You can then visualize that user story with a user story map. For example, if you wanted to visualize the user story above, you would start by detailing the various steps the user will take when using that functionality. In this case:
Sketch on the whiteboard
Share with teammates
See teammates sketch in real time
Then, you would document the features required to take each step. Once you’ve done that, you would write these features on sticky notes and rearrange them based on their corresponding functionalities.
In short, user story maps allow you to plan and implement changes to the customer journey. Customer journey maps allow you to discover and understand what those changes might look like.
How to create a customer journey map
Creating a great customer journey map can be challenging. You need to get into the mind of a specific customer persona and understand not only their needs but also the different ways in which they interact with your company. With Miro’s customer journey mapping tool , you can streamline the process of creating one of these maps for your specific needs. Or, if you'd rather not start from scratch, follow these steps when filling out Miro’s customer journey map template :
1. Set clear objectives for the map
Before diving into the creation of your customer journey map, ask yourself why you need to know this information. Are you looking to optimize certain touchpoints? Are you looking to see why customer retention is low? Do you want to determine why customers decide against your product? Figuring out why you’re building the map is essential to the success of the exercise.
2. Identify profiles and personas
As previously mentioned, you need to focus on a specific persona when examining the customer journey. It’s important to remember that the customer journey map should focus on one specific audience at a time. This will help you figure out exactly who your target customer base is and gain an in-depth understanding of the buyer’s needs that your company is attempting to fulfill.
3. List the customer journey touchpoints
Next, you need to understand what happens each time the customer comes into contact with your company. These points in the process will tell you which areas of the journey you need to streamline and optimize to improve the customer experience.
4. Take the customer journey yourself
For the customer journey map exercise to be productive, you need to put yourself in the shoes of the customer and be honest with the experience that you have. This is the best way to see if your customer journey mapping is accurate and identify areas for improvement in the customer journey.
Customer journey mapping example
Here are some customer journey mapping examples for you to draw inspiration from and better understand what goes into a customer journey model.
Alex Gilev’s Practical Customer Journey Map
Alex Gilev is a certified UX expert and product leader experienced in creating highly usable and intuitive web applications. His practical customer journey map example created in Miro is based on the idea that you want to create an irreplaceable product for your customers. This customer journey map is divided into four phases: Discovery, Onboarding, Scaffolding, and Endgame.

This take on a customer journey map allows you to figure out practical fixes that will increase your competitive advantage over other businesses in the same industry. It helps you identify the value metrics that make your product desirable to the specified persona so that they’ll want to use your product frequently and repeatedly.
Build a customer journey map suited to your needs
As we’ve shown, creating a customer journey map with your team has many benefits. This exercise can help you create the ideal experience for anyone who may come into contact with your company. It could be invaluable to the future of your business and help you build a loyal customer base.
Are you ready to get started with customer journey mapping? Try the Customer Journey Map Template , the ideal foundation on which to begin. This template is tailored to help your company identify touchpoints so that you can meet your customers’ needs.
How to make a customer journey map?
Benefits of a customer journey map
Customer experience vs. customer journey map
Service blueprint vs. journey map
What is consumer decision-making process?
Buyer journey vs customer journey
The 7 steps of the customer journey
What is service blueprint?
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Are you an agency specialized in UX, digital marketing, or growth? Join our Partner Program
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
The definitive 8-step customer journey mapping process
In business, as in life, it's the customer's journey that makes the company's destination worth all the trouble. No customer wants to jump through several different hoops to get to your product: they want it fast and they want it now.
Following certain customer journey mapping stages helps you improve your user's experience (UX) to create a product they love interacting with, ensures you stay ahead of key workflow tasks, and keeps stakeholders aligned. But a misaligned map can derail your plans—leading to dissatisfied users who don’t stick around long enough to convert or become loyal customers.
Last updated
Reading time.

This article walks you through the eight key stages of great customer journey mapping, and shows you how to adapt each to your unique business and product to optimize the customer experience from start to finish.
Learn how customers interact with your product and website
Hotjar's Observe and Ask tools let you go ‘behind the scenes’ to understand your users’ product experiences and improve their customer journey.
An 8-step process for effective customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a visualization of every point of interaction a user has with your company and product.
Mapping out the customer journey gives you insights into your buyers’ behavior to help you make changes that improve your website and the user flow between touchpoints. This helps you increase online sales and turn users into loyal customers and brand advocates.
Follow these eight proven steps to understand—and enhance—the customer experience.
Note: every business is distinct, so be sure to adapt these steps to your particular user and business needs.
1. Define your purpose
The first step to creating a successful customer journey map is to define your product's vision or purpose. Without a clear purpose, your actions will be misguided and you won’t know what you want users to achieve during their journey on your website, product page, or web app.
To define your purpose, consider your company’s mission statement and incorporate your specific user pain points as much as possible.
Make your purpose specific to your company’s needs and goals—for example, the purpose of an ecommerce brand looking to help users navigate several different products and make multiple purchases will differ from that of a SaaS company selling subscriptions for one core product.
2. Make sure your team is aligned and roles are clear
Cross-functional collaboration is essential when mapping out your brand's or product’s user journey. Get insights from different teams within your organization to find out exactly how users engage with key touchpoints to derive a holistic sense of the user experience (UX), which will help you improve every aspect of the customer experience.
Lisa Schuck , marketing lead at Airship , emphasizes the importance of keeping “anybody that has a touchpoint with a customer” involved. She advises teams to “figure out how to align your external marketing and sales with your internal operations and service.”
Although sales, product, and marketing departments are often the key players in customer journey mapping, also involve your operations and design teams that are responsible for creating the user flow.
If you have a SaaS company, for example, marketing creatives, sales teams, product owners and designers, and your customer experience department all need to participate in the process. Clearly define who’s responsible for different aspects of the map, and regularly check in to make sure your final map isn’t missing any important perspectives.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Highlights feature to collect and organize key product experience (PX) insights and data on user behavior from teams across your organization to help you build your customer journey map. Then use Hotjar’s Slack integration to quickly share learnings with your relevant stakeholders to get buy-in and ensure everyone is aligned.
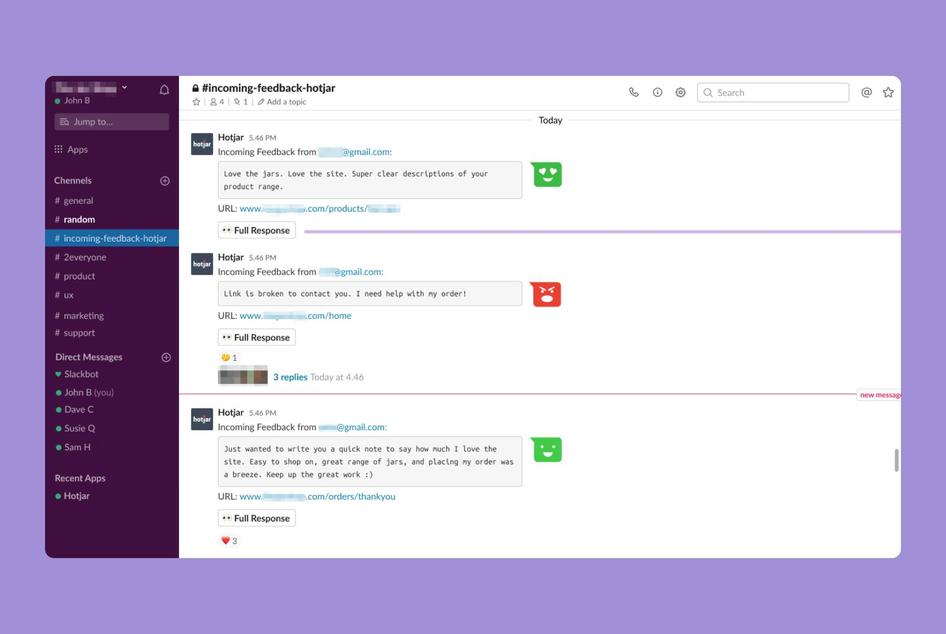
Hotjar’s Slack integration Slack lets teams discuss insights in the moment, so they’re up to date with critical issues
3. Create user personas
Once you’ve defined your purpose and involved all relevant stakeholders, it’s time to design your user personas . Use resources like UXPressia and HubSpot’s Make My Persona tool to help you design various product personas .
Create a range of user personas to understand what each type of buyer needs to curate a journey that’s easy and enjoyable for every customer. This is an important early step in the customer journey mapping process—because if you don’t understand your users, you won’t be able to fully comprehend how they interact with your brand to better it.
Create user personas for all your product’s possible buyers—for example, to map out a B2B customer journey for a company in the hospitality business means developing personas for a range of different customers, from large chain hotel managers to small vacation rental owners.
4. Understand your user goals
Once you’ve designed your user personas, it’s time to define their jobs to be done . What do your users hope to accomplish when they search for your product or service? What do they want to do when they click on your website? Address and answer these questions to build a deep understanding of your users’ goals and pain points to inform your customer journey.
In a SaaS customer journey , perhaps users are looking for helpful comparisons of product features on your website, or want to easily sign up for a trial account in the hopes that your product will solve their problems. But you won’t know until you ask .
Once you have users or test users, get direct insights from them with Hotjar's Feedback tools and Surveys to ask buyers exactly what their goals are as they browse different pages of your website or interact with product features.
Since user goals are at the center of your customer journey map, define them early on—but keep speaking to your users throughout the entire process to make sure you’re up to date with their needs.
5. Identify customer touchpoints
After you understand your users and what their goals are, it’s time to identify the ways they interact with your company and your product.
"Touchpoints are the moments the customer interacts with your brand, be it through social media channels, your product, or customer support. The quality of these experiences affects the overall customer experience, which is why it’s important to be aware of them. Consider what happens before, during, and after a customer makes a purchase or uses your product."
Key customer journey touchpoints for a website or product include your homepage, landing pages, product pages, CTA buttons, sign-up forms, social media accounts, and paid ads.
Collaboration is key to identifying touchpoints throughout the entire customer journey. Include insights from different teams and stakeholders —your marketing and sales teams will have a strong understanding of the touchpoints involved pre-purchase, while the customer experience department can shed light on post-purchase touchpoints.
Post-purchase touchpoints can help turn users into loyal customers and even advocates for your brand.
In the words of Lisa Schuck, "When you create a raving fan, or a brand advocate, who goes out and tells the world how wonderful you are, you get social credibility and validity. It’s becoming more and more important to have advocates."
Pro tip : speak with your users regularly to get direct voice-of-the-customer (VoC) insights on what they love and what frustrates them on their journey. Place Hotjar Feedback widgets and Surveys at key website touchpoints like your homepage and landing pages to get valuable user insights on what you can improve. Use Hotjar’s survey templates to get inspiration for your survey questions.
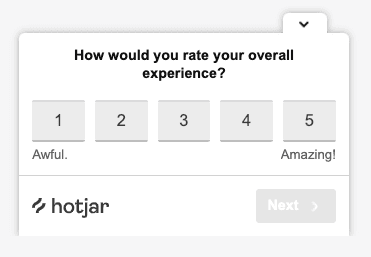
An example of an on-site Hotjar Survey
6. Map out the customer journey
Once your user and product research are complete and all roles are distributed, it’s time to map out the full customer journey.
First, map out an overarching customer journey by putting your key touchpoints in order and identifying how your various user personas interact with them. Then, home in on the details, looking at how customers engage with specific aspects of your website, product, or social media accounts.
Breaking down the mapping process into smaller phases will ensure you don’t miss any key interactions.
Here’s how an ecommerce brand could lay out general touchpoints, then narrow each down into more specific actions:
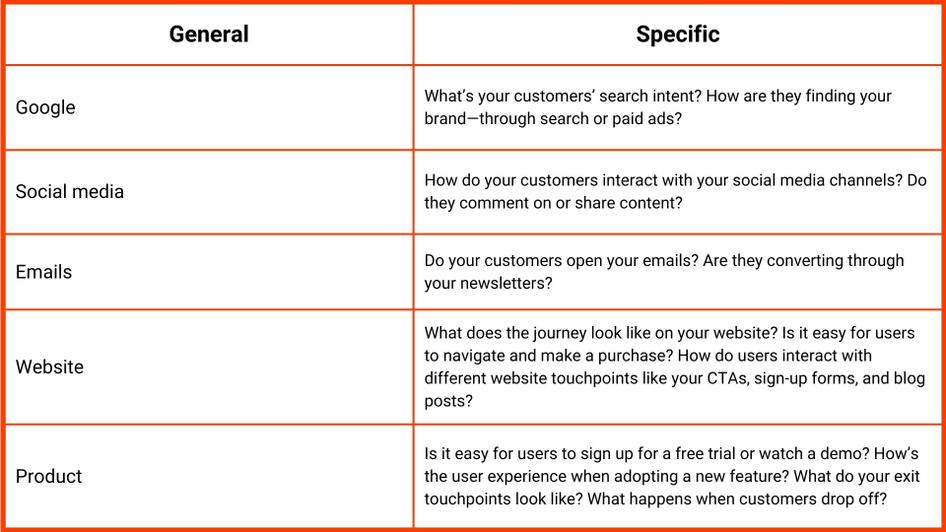
Pro tip : it’s helpful to think of the user journey in terms of different functions when mapping it out, like:
Connect: how are buyers connecting with your brand?
Attract: how are you convincing them to convert?
Serve: how are you serving customers when they want to purchase?
Retain: how are you promoting brand advocacy and customer retention ?
7. Test the customer journey
Once you’ve mapped out the customer journey, it’s time to take it for a spin. You can’t understand how your users move through customer touchpoints unless you test out the user flow yourself.
Start with an informational Google search, then visit your website, check out your social media pages, and simulate the purchase process. This will help you get a better sense of how users interact with each touchpoint and how easy it is to move between them.
Be sure to try out the journey from the standpoint of every relevant user persona. For an enterprise software company, this could mean looking at how decision-makers move through the user flow vs. the employees who’ll use your software day to day.
By walking through the customer journey yourself, you can identify issues and difficulties that users may have to address them proactively.
Try out the user flow with test users to get a realistic perspective of the user experience. Be sure to use focus groups that represent every one of your user personas.
8. Use continuous research to refine your map
Continuously map out, analyze, and evaluate the customer journey by observing users and getting their feedback. Hotjar Heatmaps and Recordings help you understand how your users are experiencing the customer journey on your website: create heatmaps to see whether users are clicking on CTAs or key buttons, and watch recordings to find out how they navigate once they reach your homepage.
Then, use Google Analytics to get an overview of your website traffic and understand how customers from different channels move through the user journey.
Finally, once you have these combined user insights, use them to make changes on your website and create a user journey that is more intuitive and enjoyable.
Pitfalls to avoid during the customer journey mapping stages
Jamie Irwin , director & search marketing expert at Straight Up Search , says companies should avoid these three common mistakes when mapping out the customer journey:
Don't map out the entire customer journey at once
Don't forget about the ‘hidden journeys’
Don't make assumptions about customer behavior
To sidestep these common pitfalls:
Start by mapping out the overall journey, and only drill down into more detail once you have a broader, higher-level overview of the customer journey
Factor in every way that customers interact with your brand, even the ones you don’t have as much visibility on, like ‘dark social’ communications about your brand shared in private channels. Talk to your users to find out what they’ve heard about your brand outside of public channels , and use sticky share buttons to keep track of when your content’s shared through email or social media messengers.
Take a data-informed approach: don’t assume you already know your users —test out your hypotheses with real users and qualitative and quantitative data.
Follow proven steps to successfully map out the customer journey
Take the time to understand your business goals and users, involve the right teams, and test frequently to consistently improve your customer journey and make the decisions that will help you map out an experience that will get you happy and loyal customers.
FAQs about customer journey mapping stages
What is the purpose of customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping helps you visualize how users interact with your business and product, from the moment they find it until long after they make their first purchase.
The purpose of customer journey mapping is to gain insights into the buyer's journey to create a more enjoyable, streamlined, and intuitive experience for your customers.
What are the benefits of following a customer journey mapping process?
The main benefits of a customer journey mapping process are: :
Building on tried-and-tested processes
Not missing any key steps
Considering all buyer personas
Keeping all relevant stakeholders involved
Creating a valuable customer journey map
Improving user experience
What happens if you don’t follow key steps in customer journey mapping?
If you don’t follow key steps when mapping out the customer journey, your map likely won’t give you the insights you need to enhance the experience users have with your most important touchpoints —like your homepage, landing pages, CTAs, and product pages.
This can result in high bounce rates, low conversion, and unsatisfied users who fail to become loyal customers.
CJM benefits
Previous chapter
CJM touchpoints
Next chapter
Send us an email
What is a customer journey map and how to make your own [examples included]
Written by by Kiran Shahid
Published on November 2, 2023
Reading time 12 minutes
Do you know what your customers see and do before they purchase from you?
They see your ads, interact with you on social media and explore your website before they buy. All these interactions—from the first ad impression to every “Please help” DM customers send—define your customer journey. To keep up with it all and better inform your social media marketing strategy , create a customer journey map as a blueprint to help you understand your customers at each stage.
Let’s explore what customer journey mapping is and how it helps your brand.

Social Customer Care by Sprout Social
What is customer journey mapping?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of each point of interaction your customers have with your company. You can style the map like a flowchart, timeline, table or even on sticky notes.
Creating the map is a great internal exercise. Along the way, you might find pain points or touchpoints you didn’t know existed. A basic customer journey map includes the buying stages (and support touchpoints) a customer goes through.

More detailed maps include:
- actions your customers take
- good and bad emotions your customers experienced
- departments involved in customer touchpoints
- content types you serve your customers
- solutions to pain points
What is a customer touchpoint?
A touchpoint on the customer journey map is the point of interaction a customer has with your brand. It doesn’t need to be a two-way interaction. Seeing a social media ad, getting a branded newsletter and asking a friend for a product recommendation are all touchpoints.
Customers may experience emotions and actions at touchpoints. When someone asks for product recommendations, people might mention your brand. You might not serve that recommendation to them directly but someone still introduces you to a potential customer.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
A customer journey map puts the customer first by giving you a deeper understanding of how your customers interact with your brand. This enable you to make better decisions and improve customer experiences.
When coupled with social media market research , they help brands:
- Provide an overview of the resources your customers use . This helps determine the ROI of customer-centric engagement and service. For example, if blogs are your highest traffic sources, investing more in those channels makes sense.
- Identify content gaps . Pain points without solutions are an excellent source for content ideation and development . If customers need help with a specific product issue, for example, but find limited guidance, create in-depth video tutorials to address this pain point.
- Identify inefficiencies . Maybe some processes are repetitive, or some solutions cause more friction. If your customers have trouble checking out due to a complicated form, for example, simplify it to reduce cart abandonment rates.
- Generate marketing campaign ideas . A clear understanding of customer motivations and journey stages creates targeted campaigns. You can provide them with relevant content and incentives to move them closer to a purchase.
- Guide multiple departments. Streamline content creation, social customer care strategy and messaging optimization across every touchpoint. Departments use the customer journey map as a central reference to ensure a consistent and customer-focused approach.
- Enhance customer communication . Customer journey maps reveal critical touchpoints, like social media interactions, for timely and meaningful engagement. In fact, The Sprout Social Index™ shows 51% of customers believe the most memorable brands on social respond to customers.
Every business and industry has its unique customer journey maps, but the fundamentals remain the same.
Recently, our social team talked about using social media for the customer journey in the auto industry. Watch the video below to hear their discussion on touchpoints, customer experience and how legacy brands are going beyond traditional tactics like targeted ads to tell their story.
It’s a great example of how industry-specific customer journey follows the fundamentals but also has touchpoints specific to them.
What’s included in a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is like a detailed travel itinerary for your customer’s experience with your brand. It includes elements like:
1. The buying process
The buying process is the step-by-step path a customer follows to make a purchase decision. It tells you where customers drop off or face obstacles during making purchases.
Use prospecting tools, content management systems (CMS) and behavior analytics tools to gather data. Facebook Shops, Instagram Shopping and TikTok Shop data also provide valuable insights into how customers find products and engage with content via social commerce .
Pro tip : Categorize the journey into stages like awareness, consideration and decision to map these steps horizontally on the customer journey map.
Don’t forget to integrate feedback mechanisms, such as customer surveys or user testing. These offer qualitative insights into the buying process. Understanding the “why” behind customer behavior can be as important as knowing the “what.”
2. Emotions
Emotions show how customers feel at different touchpoints in their interaction with your brand. Emotions heavily influence purchase decisions and brand loyalty which is exactly why it’s so important to include them.
Think about it: When someone has a great experience with your brand and feels happy, they’re more likely to buy from you again. On the flip side, if they feel frustrated or unhappy, they’ll knock on your competitor’s door.
Use surveys or feedback forms to ask customers how they felt during their experience. You might have come across these smileys during your own shopping experience:

These scales are a convenient way to gauge how your customers feel at any point.
Pay attention to what they say on social media and in reviews. You can tell if they’re happy or upset by their tone.
Tools like Sprout Social use AI-driven sentiment analysis to dig into social listening data to give you insights on what people think about your brand.

These insights are handy when creating emotional marketing campaigns . When you know how customers feel, take actionable steps to solve any negative experiences and encourage positive ones.
3. User actions
User actions are the steps customers take when they interact with your brand. They include steps like visiting your website, clicking on a product, adding items to their cart or signing up for your newsletter.
Actions highlight what people do at each stage. Each of these actions tells you something about what customers are interested in and how close they are to making a purchase.
Analytics tools for your website or app are your best bet for such data. These tools show you which pages customers visit, what they click on and where they drop off.
Once you have this information, tailor your marketing efforts and content to align with the actions customers take at each stage.
4. User research
User research examines what customers search for or where they turn for information during the buying process. This part of the customer journey map helps you understand how customers gather information.
For example, in the awareness stage, buyers often rely on search engines like Google to research solutions to their problems. But it’s not just about where they go—it’s about what they’re looking for. Knowing their specific research topics allows you to address their pain points.
What’s the trick? Keep an eye on what customers search for online. Tracking keywords and phrases they use on search engines, as well as social media market research are good places to start.
Also, monitor discussions and conversations to get a deeper understanding of the questions, concerns and topics that are top-of-mind for your potential customers.
The key is to use this information to provide potential customers with what they need at each stage. Targeted content delivery positions your brand as a valuable source of information.
5. Solutions
This section outlines the actions and strategies your brand implements to address customer pain points and improve their overall experience.
It documents the specific solutions or improvements applied at each stage of the customer journey. These include steps like changes to website design that resolve issues and improve the customer experience.
It visualizes how your brand responds to customer needs and challenges at different touchpoints. Besides that, it’s a good reference to ensure your team implements the solutions and refines them to increase customer satisfaction.
What are the 7 steps to map the customer journey?
A strategic approach to building a map ensures you capture every touchpoint, anticipate customer desires and address potential pain points. Here are seven steps to build a journey map unique to your customers and business needs.
1. Set your goals
What do you want to get out of this process? And why does it matter to your business? Knowing your goals sets the stage for how you assemble your map.
Some examples of goals include:
- Identify the top three customer pain points. Use these pain points to create content.
- Understand customer interests and motivations to develop better products and services.
- Total the cost of customer interactions to set a better social media budget .
2. Decide on a customer journey map type
There are several different customer journey maps and each one has its advantages. When you decide which map to work with, you know which details to focus on.
These are four of the most common types of customer journey maps: current state, future state, day in the life and service blueprint. We’ll go further into detail on each one later on.
Understanding your goals and where your brand stands in its evolution will guide you in selecting the appropriate map type.
3. Create and define your customer personas
Which customers will you focus on? It’s difficult to map a customer journey if you don’t have a customer in mind. Customer personas are fictional characters that represent each of your target customer groups. They’re detailed with everything from demographics to interests to buying behavior.

If you’ve already created social media personas to understand your audience, you’re more than halfway there. But if you haven’t, then our buyer persona template or Xtensio’s will be useful. To really get to know someone’s purchase decisions and shopping processes, interview existing customers.
Pro tip: If you have distinctively different personas—such as, if you serve both a B2C and B2B market—set up different customer journey maps.
4. Break it down: touchpoints and stages

The customer journey map is divided into stages that usually fit within the funnel illustrated above. List out the stages to begin. Next, list out the main customer touchpoints that exist for your company. When you’re done with both lists, place the touchpoints into the different stages.
To get even more detailed, assign department owners to each touchpoint. You can identify where certain social media channels fit into the mix. And, you can assign predicted customer sentiment or emotions to different stages of the journey. It’s up to you how detailed you want the map to be.
5. Gather data and customer feedback
You need rock-solid data on how customers interact with your brand to create an accurate customer journey map. Focus on these three aspects:
Analyze existing data
Jump into the data you already have—more specifically website performance, chats with customer support and sales records. This information can tell you loads about how customers act, what they like and what frustrates them.
This quantitative data offers a foundational perspective on how customers interact with your brand, helping you identify both strengths and areas of improvement.
Conduct customer interviews
Get personal with one-on-one chats with customers. Ask them about their experiences, what bugs them and what they expect when they deal with your brand. These talks reveal qualitative insights that numbers can’t, like understanding the emotional and psychological aspects of the customer journey.
Create surveys and questionnaires
Turn to surveys and questionnaires for a more structured and broader approach to gathering feedback. Send them out to a bunch of customers and get structured feedback. Ask questions about their journey with your brand, how happy they are and where they think things could get better.
A combination of these three aspects gives you a 360-degree view of what your customers really experience with your brand.
6. Test and identify pain points
To confirm your customer touchpoints, you probably checked in on various departments and spoke to customers. This is great work but you need to take another step further: test it yourself. Go through the customer journey from the viewpoint of the customer.
While you’re testing the journey, keep an eye out for challenges, confusion or any frustrating moments. For example, if the website takes forever to load, if instructions aren’t clear or if reaching customer support is a headache, make detailed notes of these issues.
It’s also a smart move to collect feedback from both colleagues and customers who’ve gone through the journey. This way, you double-check and confirm your findings for a more complete picture.
A hands-on approach ensures your customer journey map reflects the real-world experience and equips you to take targeted actions to improve the overall customer journey.
7. Make changes and find solutions
So your map is complete. What’s next? You need to find or create solutions to the pain points you identified in the previous step.
Now’s the time to check in on the goals you established in step one and make the moves to smooth out the journey. Give yourself time and space to implement some of the solutions, whether a quarter or six months, and check back on the map to update it.
As you put these changes into action, make sure to watch your customer journey map closely. Don’t forget to keep it up to date to show the improvements and how they affect the customer experience. This keeps your customer journey map fresh and super useful for steering your brand toward delivering an exceptional customer experience.
4 types of customer journey maps and examples
Let’s take a look at the four most common customer journey maps and examples of each.
1. Current state
Current state customer journey maps are like an audit. You document how your customers experience their buying and service paths in your company’s current state. These are especially helpful to establish a baseline for your customer service experience.
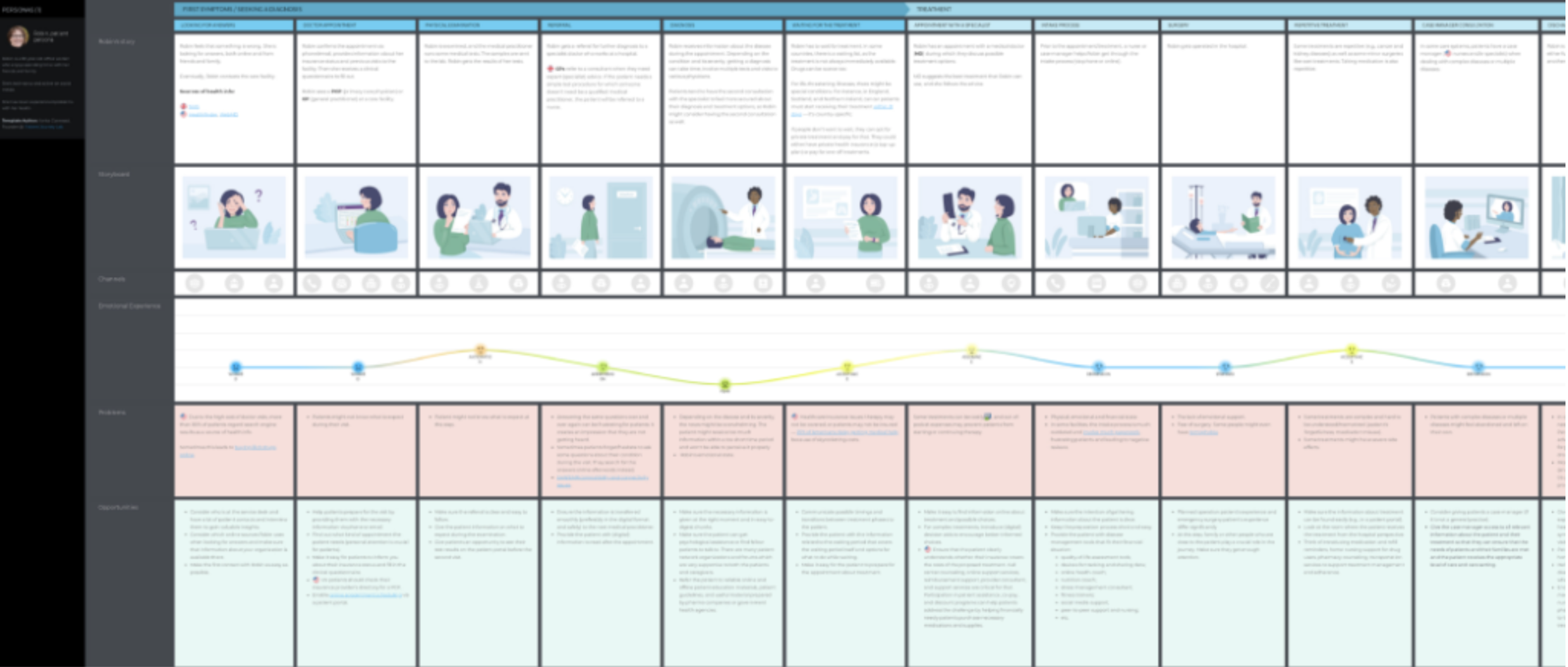
Take a look at this simplified current state customer journey map from Nielsen-Norman.

The map follows the journey of “Jumping Jamie” as they navigate the process of switching to a different mobile plan. The map defines the current journey into four stages. Apart from the journey, it also highlights opportunities and metrics to track.
Current state maps are fantastic for sharing user frustrations with all departments. This helps you get everyone on board with investing in solutions and brainstorming ways to address user pain points.
2. Future state
Future state customer journey maps follow the same format as current state maps except they represent the ideal journey. You can use them alongside your current state maps to identify painpoints and areas to improve.
Here’s an example of a future state journey map:

Why does this visual work? It covers different states, feelings and even touchpoints in a cohesive format.
The map visualizes the best-case scenario to create a north star vision for your brand. It aligns your efforts toward achieving the ideal customer journey.
3. Day-in-the-life
Day-in-the-life customer journey maps outline one of your persona’s schedules as they go about their day. The interactions may or may not involve your company. Creating one of these maps helps you identify the best times and areas to interact with your customer.
Here’s a “day-in-the-life” visual from Pipedrive.

The map doesn’t just highlight when the persona does something, but it also highlights different touchpoints and the different people they interact with throughout the day. And, notice those thumbs ups and downs? Those highlight how the child feels during different activities too.
4. Service blueprint

A service blueprint customer journey map focuses solely on when you provide customer service. It ignores components like ads that might exist in other maps.
Miro, a collaborative online whiteboard for teams, created the above map with a bank in mind. You’ll notice how this map is only about a customer’s visit to the bank. This type of map helps brands look at individual service areas and interactions. It’s a macro version of the current and future state maps.
Get started with customer journey map templates
Creating a customer journey map doesn’t have to be overwhelming. There are plenty of free and paid templates out there to help you create one. If you think you’ll need more guidance or many maps, some companies offer special software to design a custom map. Build your first journey map or improve your existing one with these options.
- Current state template , provided by Bright Vessel.

- Customer journey map template by Moqups, a design and collaboration tool.

- Service blueprint template by Miro

- Customer journey map template by Mural, a planning tool.

- UXPressia’s customer journey map online tool , made specifically to create presentation-ready customer journey maps.
Create a strong foundation with a well-integrated customer journey map
A customer journey map gives you the recipe for crafting personalized, impactful interactions that build customer satisfaction and loyalty.
When you know what they are and why they’re important, it’s time to make yours. Use data to create a solid customer journey map that exceeds customer expectations at every touchpoint.
Check out how you can turn your B2B social media data into a revenue-driving powerhouse and create a memorable brand.
- Customer Experience
- Marketing Disciplines
Grow your brand with customer-centric marketing
How a sentiment score improves your brand strategy
- Customer Care
How to build customer relationships with social media
Omnichannel customer experience: exploring seamless customer journeys
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
- Case studies
- Expert advice
How to create a customer journey map — a step-by-step guide with examples
Learning more about client experience is the best way to understand and improve it. As you are reading this article, you already know that 😉
Here, you will find a detailed step-by-step guide on making a customer journey map (CJM), examples, expert tips, templates, and a PDF guide to download and save for later.
- 1 What is a customer journey map?
- 2 Benefits of client journey mapping
- 3.1 Step 1: Define your persona
- 3.2 Step 2: Set customer journey stages
- 3.3 Step 3: Define journey map sections
- 3.4 Step 4: Set customer goals
- 3.5 Step 5: Define touchpoints
- 3.6 Step 6: Processes and channels
- 3.7 Step 7: Problems and ideas
- 3.8 Step 8: Emotional graph
- 3.9 Step ?: Be Creative!
- 4 Customer journey map examples
- 5 A customer journey mapping checklist
- 6 The free guide to download
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is the final output of the collaborative visualization process called customer journey mapping. This process lets you reveal typical experiences the customers have over time when interacting with your organization, service, or product. A finished map provides insights into their actions, processes, goals, needs, channels, emotions, and many other aspects shaping the customer experience.
Journey maps can be of different scopes. For example, a broad-scope map would include multiple customer journey stages like ‘Awareness’, ‘Decision’, ‘Purchase’, ‘Support’, and ‘Renewal’. In contrast, a map with a narrower focus would look at a few specific stages like ‘Decision’ and ‘Purchase’.

CJMs focusing on the current experience are AS-IS maps, while journey maps visualizing the future, desired, state of the experience are called TO-BE maps.
There’s also a similar technique, customer experience mapping, which is often used interchangeably with journey mapping. Experience maps are variations of CJMs, but they typically cover a wider range of interactions and contexts beyond a specific consumer-business relationship.
Benefits of client journey mapping
Why make journey mapping your tool of choice? There are plenty of reasons, the major of which include:
- Gaining a deeper understanding of your customers
For instance, a high-end fashion retailer may discover that its younger customers prefer online shopping, while older customers enjoy the in-store experience.
- Getting a single view of your customer within the organization
Journey mapping will help you turn a fragmented vision of the customer experience into a unified, organization-wide one. It will have a massive impact on the decision-making process, encouraging you to consider how your actions will affect your clients and become customer-focused.
- Breaking corporate and cross-department silos
To make the way toward delivering a great customer experience, you will need to collaborate with others. Understanding why this collaboration is essential, departments and employees will be more inclined to participate in conversations and collaborate.

- Improving customer experience, retention, and loyalty
While working on a map, you will discover customer pain points at different stages of their journey with you. Fixing the most crucial one as quickly as possible will do you a good turn by eliminating the reasons for leaving you. If fixes take much time, look for quick wins first.
For instance, adding details about your shipping policy on the website will take a developer half an hour, while it will set the right expectations among customers. They won’t be expecting the delivery the next day anymore, bombarding your customer support team with frustrated messages. Another example is a subscription-based video streaming service that can personalize content recommendations to keep subscribers engaged and less likely to cancel their subscriptions.
- Better conversion and targeting of your target customers
Sometimes, it makes sense to focus on a specific segment or, talking journey mapping terms, specific personas. Customer journey insights will help you with this endeavor by giving you a glimpse into these people’s minds and ensuring the higher effectiveness of your marketing.

How to build a customer journey map
Although there is no gold standard for creating a customer journey map, we’ll try to create a somewhat generalized map. So that you can use it as a reference when making maps of your own.
We’ll be using our CJM Online tool along the way for two reasons. Because it’s easy to use and lets you create a CJM fairly quickly without wasting time setting up the environment. Oh, and there's a Personas building tool that comes with it 😉

We’ll take a pizza restaurant as an example of business and learn how to make a customer journey map together.
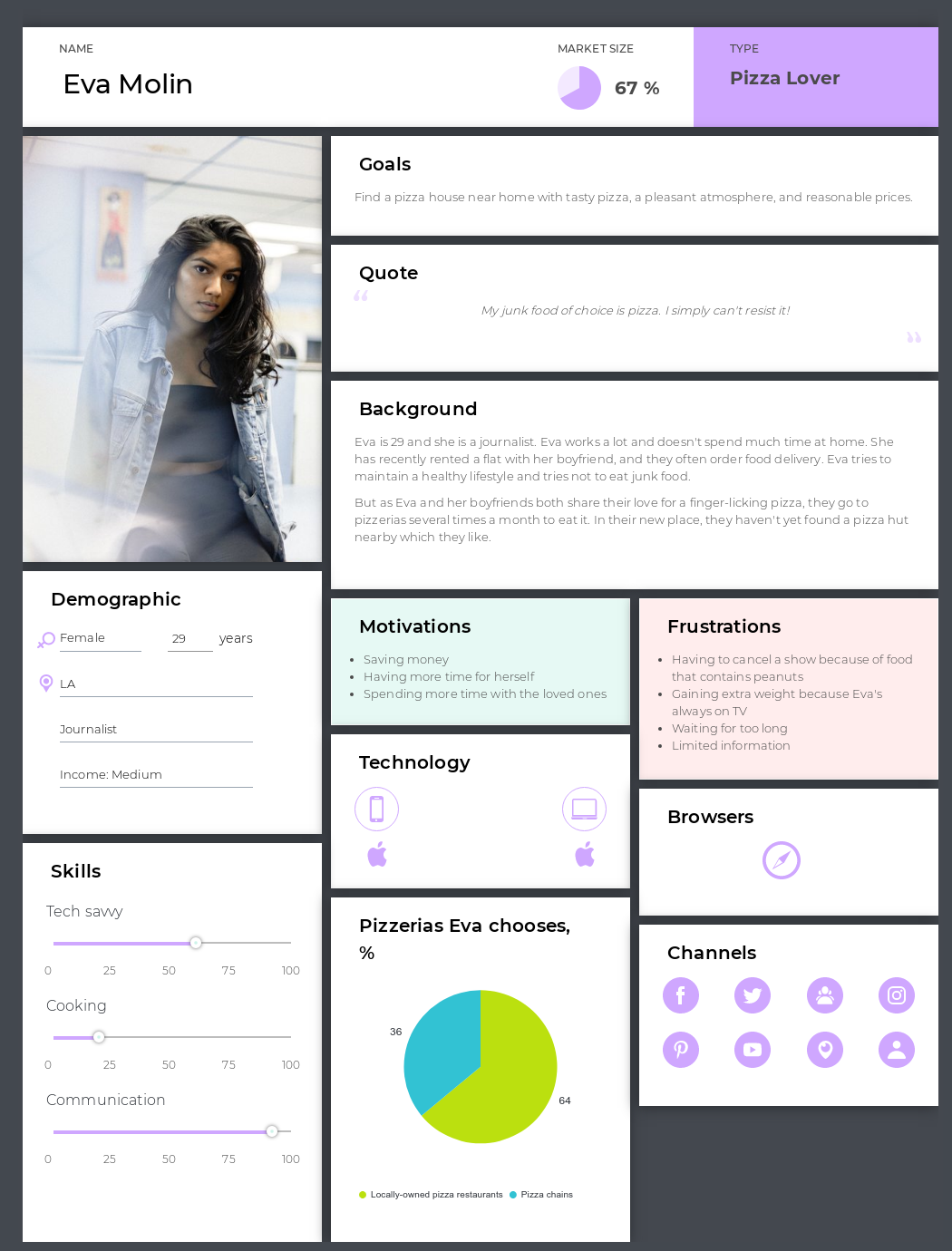
Step 1: Define your persona
Creating personas is a crucial part of customer experience service and journey mapping in particular. We won’t go into details — you can find them in this post about defining personas .
Let’s just say that our persona’s name will be Eva Moline — 29, works as a journalist and loves pizza. Eva is not really tech-savvy, and she tries to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Step 2: Set customer journey stages
Stages are the steps customers take when interacting with a business. The easiest way to identify them is to think of all the actions the person has to take throughout their journey, organize them into logical groups, and name these groups. These will be your map stages.
The number of stages varies from business to business, but we’ll take 8 for this example:
💡 Expert tips:
- If you’re unsure about the order or names of the stages, don’t worry about that. You can change both at any time when working on the map.
- If your stages are complex, you can break them into smaller ones. Read this blog post about defining customer journey stages to learn more.
Step 3: Define journey map sections
Sections are horizontal rows with data that, together with the stages you defined, make up a customer journey map.
When picking sections for a map, your choice will depend on your journey’s type and purpose.
As for UXPressia’s Journey Map tool, it offers a set of more or less universal sections for all kinds of maps.
We’ll use some of the sections in the current example.
Step 4: Set customer goals
Setting customer goals at each stage is great for multiple reasons:
- It helps you understand how your business goals align with the goals of your customers.
- You can meet your customers’ needs better, gaining their loyalty by helping them achieve their goals at each stage.

Above, you can see some of the goals we set for Eva. They are self-explanatory, so there’s no need for extra details.
Step 5: Define touchpoints
Touchpoints are encounters that happen between your business and customers. In the pizza restaurant example, touchpoints happen:
- At the Awareness phase, when Eva is actively looking for a pizza place nearby. She is asking around, searching locations on Google Maps, etc.
- At the Research phase, when she is trying to find out what people say about the place by asking her friends and reading online reviews.
- At the Arrival stage, when Eva searches for a parking spot and enters the restaurant to get seated after parking the car.
- At the Order stage, when she makes an order and waits for it.
- Time to eat! At this stage, touchpoints occur when Eva is being served and when she is eating her meal.
- At the Leave stage, Eva interacts with the waiter, pays for the meal, etc.
- At the Feedback stage, she goes to the pizzeria’s website and drops a few lines on Instagram.
- At the last stage, Eva gets a promo email from the restaurant with discounts or other special offers.
Defining all the touchpoints is critical because each touchpoint leaves some impression, and your main goal is to keep it up to the mark.
You can also have a separate section to describe the actions your persona takes:
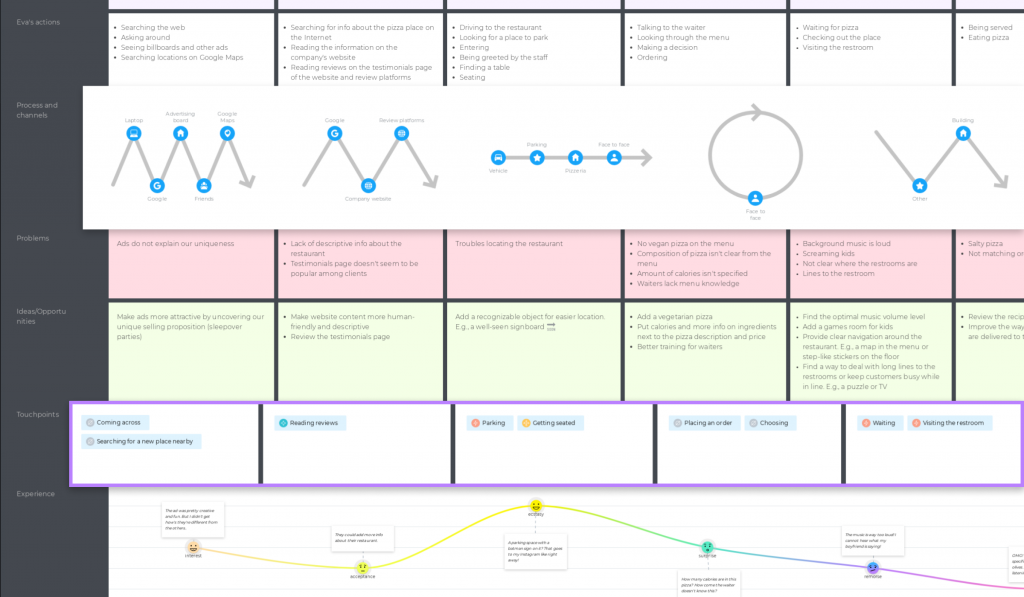
Step 6: Processes and channels
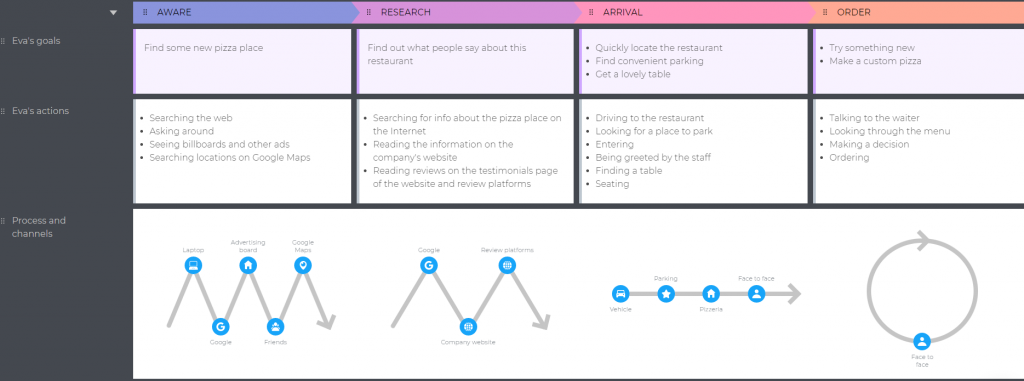
Now, you may want to add some processes and channels to the map. Just to see what channels your persona uses and what types of processes are in their journey. Luckily, our tool lets you do it in the most awesome way. Processes can be linear, non-linear & time-based, cyclic, or bi-directional. In UXPressia, you can specify up to 10 channels per process.
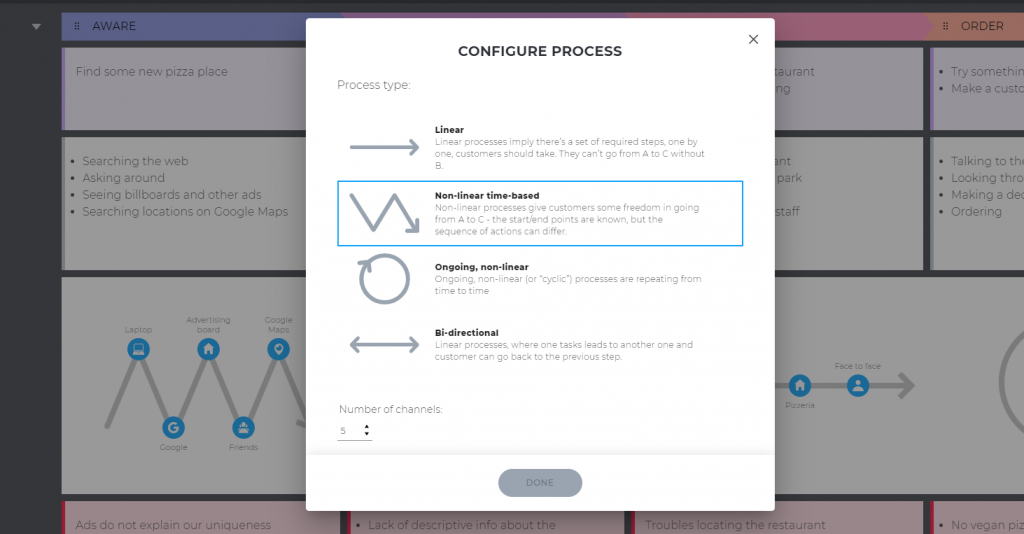
Step 7: Problems and ideas
It’s time to explore problems Eva might have when using our service. It could be a lack of info about the pizza house. Few reviews and ads do not show how our pizza differs from others.
Upon arriving, Eva may struggle with locating the place due to unclear information on signboards or just because of a hard-to-find location.
When making her order, Eva may look for detailed info on dish ingredients to learn whether it contains peanuts she’s allergic to. Descriptions may not be as detailed as she’d want them to be.
While waiting for the pizza, Eva may want to check out the place. Finding a restroom can turn into a nightmare if you don’t have clear signs showing what’s where in the restaurant.
Once you’re done with problems, it’s time to find solutions to these problems. Brainstorm for some ideas on how this or that problem can be solved. Here’s what we brainstormed for Eva’s case:

Step 8: Emotional graph
Never underestimate the power of visualization. And our Customer Journey tool is all about it. We added an emotional graph to see where our service example shines and where it stinks. Plus, we filled text boxes with Eva’s thoughts:
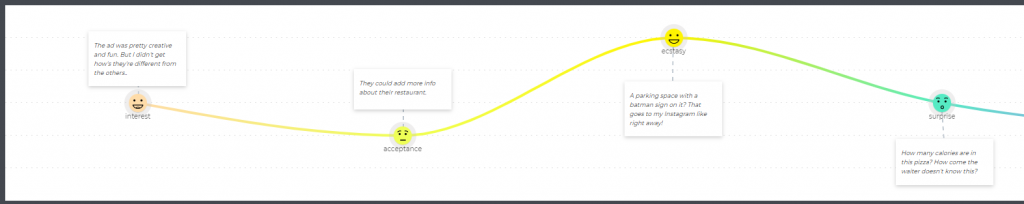
There’s also a special section ( “Think & feel” ) to put personas’ thoughts.
Step ?: Be Creative!
This is a good start, but the map is far from being complete. So, keep exploring Eva’s journey to find more insights and then add all of them to the map.
If you use our tool (which we highly recommend you to do), check out other CJM sections:
- Image section for screenshots, photos, or any other relevant imagery. You can even turn it into a storyboard , describing the journey from beginning to end with your images or those from our library.
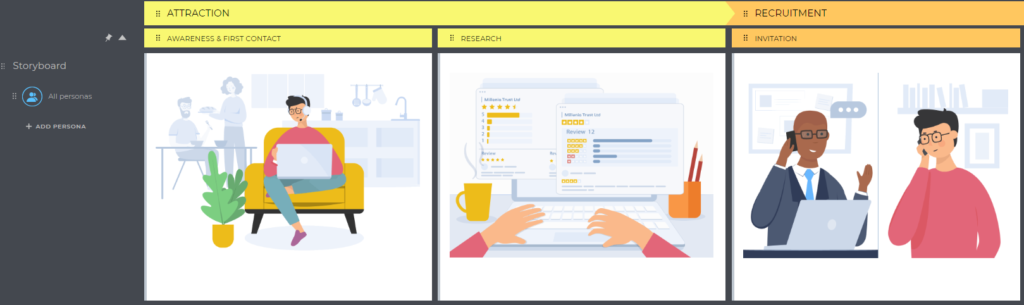
- Charts section for communicating data in a visual and meaningful way, just like we did it in the persona:
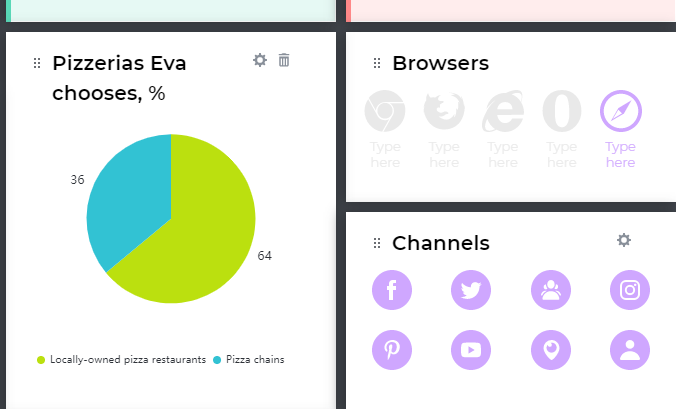
- Video and document sections for journey-related videos and documentation (e.g., an annual marketing report).
- Personas section for visualizing different personas’ interactions within the same journey.
💡 Expert tip: The section with the persona’s questions works like a charm for marketing and content purposes. So be sure to add one 😉
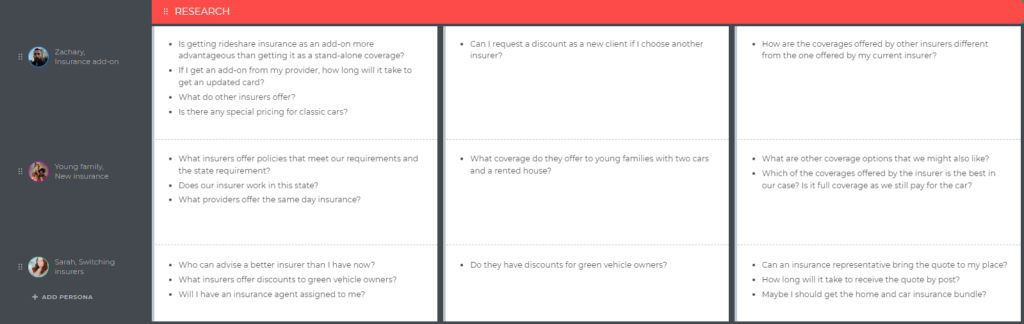
Customer journey map examples
There are also a whole lot of free CJM templates for all sorts of journeys in our library. Here are three examples we picked for you.
- Example 1: a mobile user journey
This user journey map template covers the digital experience of the persona who discovers a new mobile app, installs it, and uses the app for some time before deleting it.
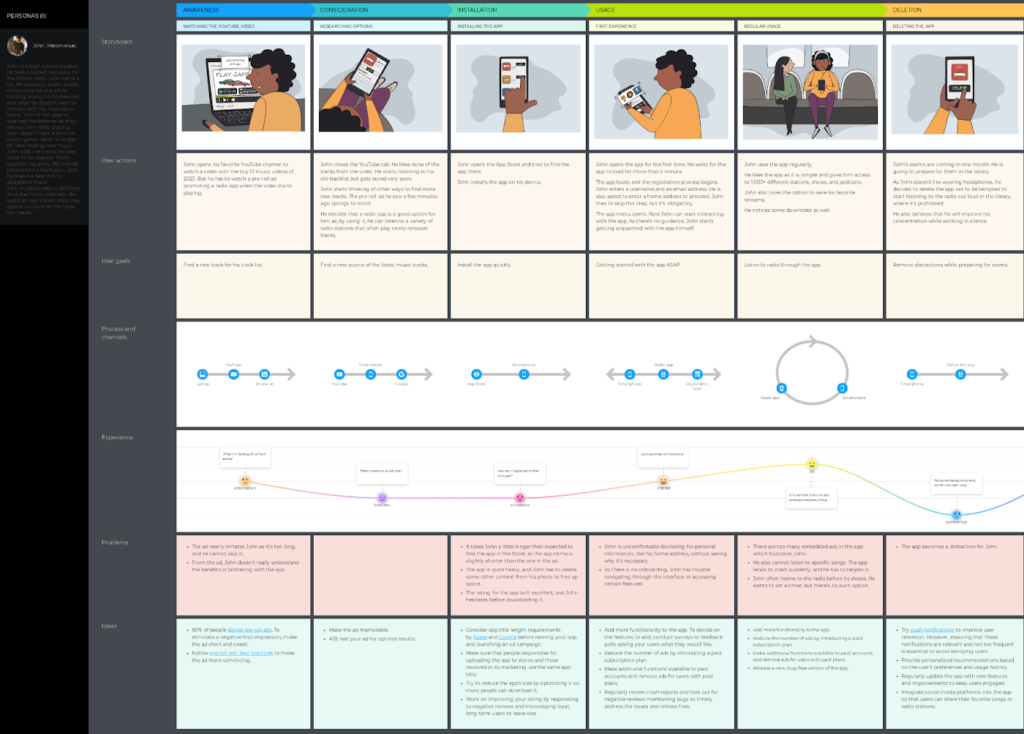
- Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank
This free template is an example of a multi-persona, B2B customer journey. The key persona is a newly opened company looking for a bank to run their business. The CJM also visualizes interactions between the personas involved.
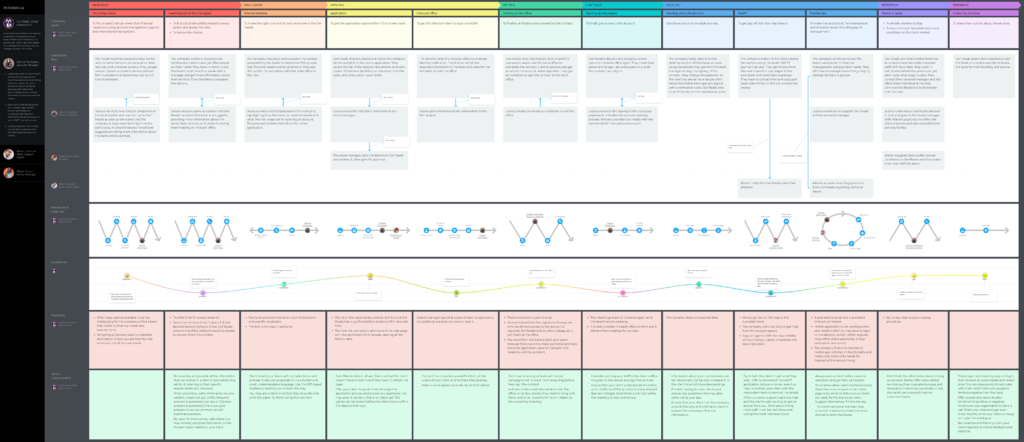
- Example 3: a digital customer journey
This customer journey map example shows the digital journey of three customer personas who want to buy a new pair of sneakers online. They go through the same stages, but if you look at the map, you will be able to see the differences in customer behavior, goals, and actions. It’s also a multi-persona journey map .
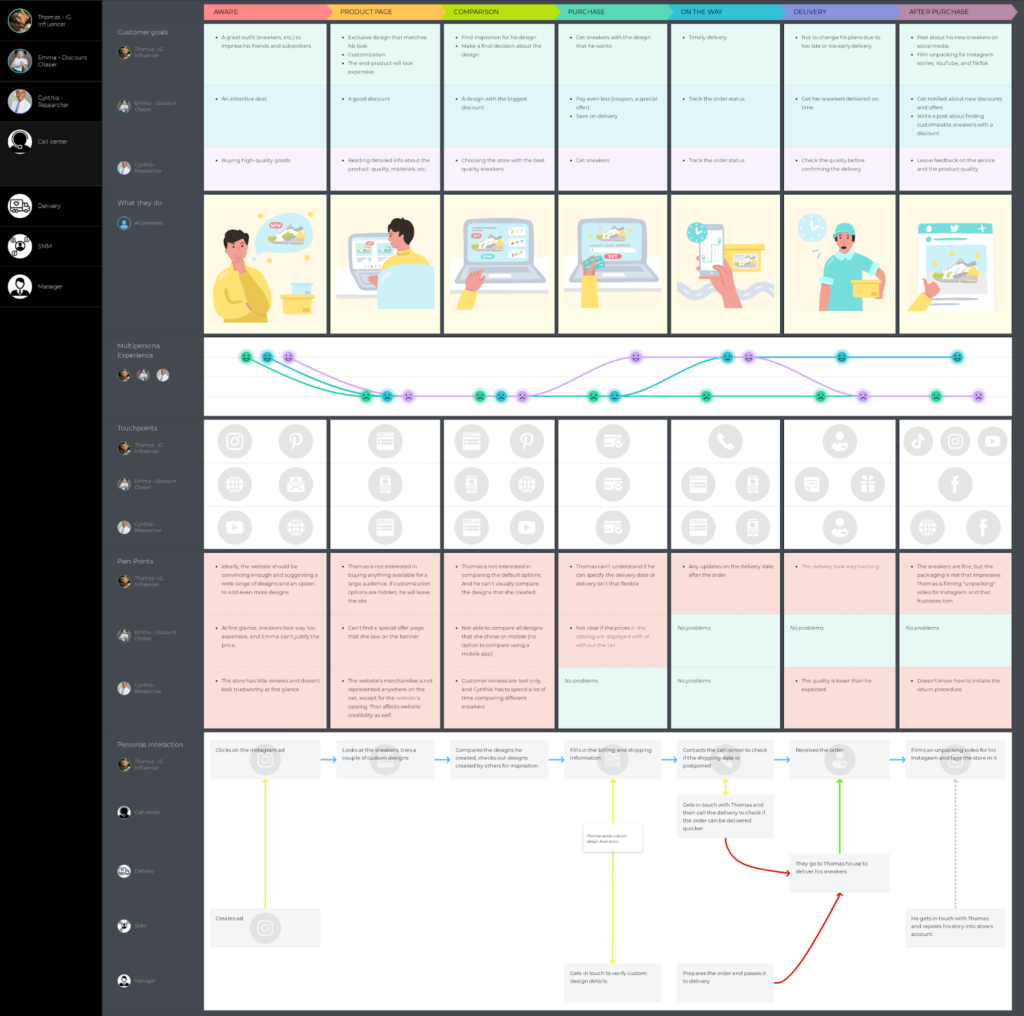
A customer journey mapping checklist
As a quick recap, here is a checklist with key steps to follow when creating a customer journey map:
- Do research
To represent real people, your real customers, and visualize their journeys, you must base your personas and journey maps upon actual data.
- Define your customer persona(s)
Identify your target personas. Create detailed profiles focusing on information relevant to your journey mapping initiative. Include such details as background, customer needs, motivations, channels, etc.
- Specify journey map stages
Determine the stages you want to have on your map and come up with their names.
- Decide on the map sections
Determine which sections to include in your map (e.g., actions, touchpoints, emotions, channels).
- Set customer goals for each stage
Make sure that it is your customers’ goals, not your business goals.
- Identify touchpoints between the persona(s) and your organization, product, or service
Consider both online and offline interactions.
- Map out processes and channels
Visualize the journey-specific processes and the channels your customers use at each stage. Include both digital and physical channels.
- Highlight problems and look for opportunities
Identify any pain points and issues customers might encounter. Brainstorm potential solutions and quick wins to improve the experience.
- Add details about the emotional experience
Visualize the persona’s emotional journey. Include thoughts and feelings where it’s relevant.
- Use more sections
Include illustrations, images, and charts to make the map visually engaging and easy to understand. Enrich your journey map with more data, like KPIs related to journey stages.
Feel free to tailor this checklist to the specific context of your business and your project's needs.
The free guide to download
As a bonus, download our free customer journey mapping guide. Fill in the form below to get a PDF file as an email.
Related posts
The post was originally written in 2017.
Rate this post
first of all, excellent example and I’m very happy to I could understand how to create user journey map, due to for a long time I can’t understand it and how, many thanks for your efforts 🙂 I have some question about ser journey map. I hope to open your chest for me,
1-no there are rules for user journey map? 2-I need another example ?(for example Uber)?further understand 3-have I create user journey map without customer?
Hello, Karim!
I am very glad that this article helped you understand customer journey mapping 🙂
In regards to your first question, I would say that journey maps differ from business to business. However, they tend to have the same structure give or take. So no matter what industry you make a CJM for, you will end up having several stages and a bunch of sections we mentioned in this post.
If you’re looking for CJM examples of Uber customers, here is one: https://www.mindomo.com/doc.htm?d=92be818b774d422bad7eab790957ebc0&m=7d286174ccf1450bbb77c921a609ff65 Plus we have a lot more on our template page: https://uxpressia.com/templates
As for your last question, yes. You may have a journey map without a customer (persona) and use target audience segments instead (or have a generic map without personas at all, though I don’t recommend the latter as in this case it will be hard to empathize with real people). So you will certainly have to introduce a customer down the road to gain a deeper understanding of the journey.
many thanks for your reply to me and again I have some questions
1-why you don’t use in your example? user experience, empathy maps such as use goal touch point, and how to create it 2-As for the previous example (Uber) very confuse for me not as your example
Could you please rephrase your first question? And as for the Uber map, well, that’s all I managed to find. 🙂 But again, here you can find a hundred of map examples of all stripes and colors: https://uxpressia.com/templates
welcome again, my question is? what’s different between Aware and Research
The differences come from the names.
At the aware stage your client realizes that there’s a need for a service/product. Or they find out that your company exists and offer a desired service.
While at the research stage they either do research on your business (e.g. visit your website or ask their friends if they used your service) or they research what is out there on the market that can help them.
Makes sense? 🙂
Thank you for this,
I am wondering , Have you done examples on B2B services. I work in Accreditation & Certification, this seems to be the least visited topic in marketing platforms and blog sites.
We have some B2B templates in our Template Library . Type B2B tag in the search placeholder and you will see all categories with the fitting templates. You can also explore the B2B mapping guide here .
Good luck and happy customers!
Great article, well articulated and detailed. I am starting off with service design and was wondering if I could get some advice mapping out a customer journey for a specific project. I was mapping out how do one approach to repair services?
Hi Shreya, glad you liked the article!
If you’re dealing with home repair, I might suggest our pre-filled template for an interior design agency customer journey: https://uxpressia.com/templates/real-estate . Templates can be a great starting point even if they’re not a 100% match to your use case.
Other than that, you will need to create a persona. If you don’t have any research data yet, do it based on your assumptions. Then, try to visualize what their experience across all stages and interactions with the repair service might be. Once you have the first draft, you can proceed with validating it and adding more data as it comes in.
If you have more context on the project, I can look into it and come up with specific tips 🙂
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Thank you for sharing, it was something I researched.
Hi Rok! Happy mapping 🙂


Effective customer journey maps and how to create them
Mapping your customers’ journeys can feel daunting. There are many steps involved, and you may even need to create different maps for different types of customers.
Once you learn to break down the journey mapping process step-by-step, however, creating customer journey maps becomes not just manageable, but simple. This post explains what customer journey maps are, why they’re important, how to create them, and how to make them as effective as possible.
As you'll learn, there are a variety of resources available to help create customer journey maps. The more you leverage them, the faster and more efficient your mapping process will be.
What is a customer journey map?
The benefits of using customer journey maps, how to create a customer journey map, optimizing your customer journey map, customer journey map resources.
A customer journey map is a visualization of the steps your customer goes through during the process of engaging with your company. It’s visual storytelling that helps you understand and optimize customers’ experiences with your business.
Most customer journey maps are designed chronologically, meaning they represent the customer experience as a timeline of events. But in reality, customer journeys — the series of steps from brand awareness to customer loyalty — are often not linear. Instead, customers follow a cyclical, multichannel set of steps as they engage with your business. For example, they may make purchases online as well as offline during the same period (if you operate both types of sales channels).

Customer journey maps need to account for the nonlinear nature of customer journeys, even as they also represent customer experience in a chronological fashion. To achieve the right balance, journey maps should include:
- Customer touchpoints. Every time your customer has some type of contact with your brand, even if it’s indirect, that touchpoint should be noted on the customer journey map.
- Customer moments of truth . Customer moments of truth happen when an event changes a customer’s perception of your brand. These are pivotal engagements and should be noted as such on the customer journey map.
- Customer pain points. Barriers or challenges that a customer experiences when interacting with your brand — such as hiccups in digital sales tools or delayed shipments — should be included on the map so you know how such events correlate with overall brand perception.
- Desired actions. Your customer journey map should note the actions you intend for customers to take, such as engagement with content or the completion of a purchase.
- Completed actions. Note the actual actions your customers take so that you can determine how often their behavior aligns with desired actions. When your customer journey maps include all of the above information, you end up with holistic information that can help you deliver maximum benefits.
Understanding your customers’ experiences is critical. Investing in the customer experience leads to revenue increases in 84% of cases, according to research from Dimension Data. And PwC reports that poor customer experiences are the primary reason that people sever brand loyalties.
Increasing return on investment (ROI) and building a stronger brand are definitely sufficient goals, but how does customer journey mapping do it? Journey maps provide detailed benefits, including:
- Targeted customer insights. The more you know about your customers, how they behave, and what they like and dislike, the better you can optimize marketing and sales processes.
- Increased customer engagement. Customer journey maps provide insights you need to create the kind of interesting and informative content your customers want to see, improving the effectiveness of your inbound marketing efforts.

- Optimized touchpoints. Some customer touchpoints are more successful than others, and customer journey maps help you identify the most effective ones. They may reveal, for example, that a certain ad channel is associated with low rates of engagement — so to address that, you could redirect your marketing spend to a more effective touchpoint.
- Better customer focus. Mapping the customer journey helps to place customers at the forefront of your company’s operations and get ahead of challenges that could undercut their experiences. For example, if you are expecting a customer surge, you can proactively inform your customers of the expected delay and launch alternative resources for them.
- More new business. The more you know about the journeys of your current customers, the better positioned you are to expand on what works to engage new types of customer personas through campaigns tailored to them.
- Fewer business silos. Customer journey maps help every department visualize its respective impact on the customer experience. In turn, these maps help increase cross-unit functionality with regard to serving customers. In short, customer journey maps help stakeholders from a variety of business units to understand customers better — and that drives success across the business.
Successful customer journey mapping can be broken down into five key steps.

1. Set goals
First, you need a clear goal. Rather than creating a customer journey map just to create one, decide what you are hoping to accomplish through the map, which customers you are targeting, and which types of experiences you want your maps to highlight. In addition, your goals for creating the customer journey should reflect your overall company goals, such as increased revenue or improved customer retention.
Be sure to also decide on relevant metrics you can track as you create and use your customer journey maps. Setting clear goals is worthless if there’s no standard for measuring them.
2. Define your personas
Determine which customer personas you want to target when creating maps.
If you don’t have well-developed personas, or you need to update them, you can get the insights you need through surveys, interviews, testimonials, reviews, and feedback from customer relations teams. These teams tend to have a good perspective on the pain points that lead to falloffs during the buying journey.
The more specifics you can collect about who your customers are and what they want, the more effective your customer journey maps will be.
3. Determine your touchpoints
Identify the touchpoints that you’ll represent on your customer journey maps. Touchpoints are any point of engagement between customers and your brand, and they are the foundation for your customer journey map.
Consider all of the places where the customer may interact with your business. Be sure to factor in indirect engagements, like reviews of your brand that customers read on third-party sites, in addition to direct touchpoints that you maintain. Each and every touchpoint can drive customer conversion, so it’s critical to represent all the possibilities.
4. Map the current buyer journey
Once you’ve identified your customers and touchpoints, you can map the steps that buyers follow on their way to making purchases. Be sure to represent every variation on the buyer’s journey, including different types of sales channels, multiple product versions, and small-volume as well as large-volume purchases.
5. Map the ideal buyer journey
The journey you want customers to take may vary from their actual journey, especially if you release new products or services and the desired buyer journey changes as a result. Be sure to represent the ideal buyer journey alongside actual buyer journeys on your maps.
Creating customer journey maps is a huge step toward increased visibility into the customer experience, an enhanced ability to reach new personas, and better cross-unit functionality within the business. No customer journey map is ever truly “done,” though. They need regular reviews and updates to keep them optimized.
Whenever your product or service offerings change, your customer journey maps will need to change too. Likewise, whenever you detect new types of customer roadblocks — challenges related to pricing, brand credibility, or product functionality — you’ll want to add them to your customer journey maps.
You can also optimize these maps by investing in tools that automate omnichannel marketing . These tools can make it more efficient to generate and update customer journey maps, especially in cases where customers engage with your business through multiple channels at once.
Although creating customer journey maps may seem complicated at first, they’re actually quite simple once you break the process down into manageable steps.
Adobe Analytics can help you optimize both online and offline interactions so that you can optimize your customer journeys using data to create comprehensive customer journey maps. Likewise, Adobe Customer Journey Analytics can help you to visualize cross-channel customer interactions.
The better your ability to automate the process of tracking and interpreting the customer experience, the more efficient and effective your customer journey mapping process will be.

Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Management
Try Qualtrics for free
The complete guide to customer journey management.
14 min read Effective customer journey management requires a keen understanding of how your customers move from touchpoint to touchpoint. Here’s how to understand and optimize every customer’s journey – and how to make proactive changes that boost the entire customer experience.
The interactions your customers have with you are never one-off moments, and they don’t happen in a vacuum. Instead, they form part of an overarching customer journey, which incorporates every single stage of each customer’s road to purchase – and beyond.
Understanding those customer journeys, and building experiences with every step in mind, is how you’ll create interactions that people love, remember, and recommend.
Delivering on those next-level customer journeys requires a deep understanding of how people discover your brand and buy your products, and that means working on a few core practices:
Customer journey mapping
Customer journey orchestration, customer journey optimization, customer journey analytics.
In this article, we’ll be going through the what, why, and how of customer journey management – as well as what mastering it will mean for your customers.
Deliver next-level customer journeys with Customer Journey Optimizer
What is customer journey management?
Customer journey management is the art of being able to understand, map, design, and improve the interactions and processes that make up the entire customer experience.
It’s a discipline stemming from the idea that no matter how a customer interacts with your brand, that interaction is one part of a larger journey and not just an individual event.
It doesn’t matter if a customer is actively researching your products, passively encountering a social media post, browsing in a physical store, or contacting customer support – whatever the interaction, it’s happening as part of an overall journey.
Managing that journey really just means making those isolated moments better, but also ensuring that they’re interconnected and aligned.
When exploring and visualizing customer journey data, we are assessing:
- Customer behavior What is your customer trying to do?
- Customer attitudes What is your customer feeling/saying?
- The on-stage experience Who/what is your customer directly interacting with? (This includes various channels, such as TV ads or social media)
- The off-stage experience Who/what needs to be in place but which your customer is NOT directly aware of?
The purpose of customer journey management is ultimately to finetune the customer experience until it’s as seamless as possible, that the path towards purchase is frictionless, and that each touchpoint works as part of a broader CX strategy.
Successfully managing customer journeys, then, requires that you can master a mixture of customer data, behavioral science, customer feedback, industry insight, and a dash of business instinct.
Customer journey management: A mindset shift
Building customer journey management processes into your business requires a mindset shift. It’s not something that you can do once and forget about, and nor is it something that’s a quick change. That’s because customer journey management is a multi-faceted task that asks a little bit of every department.
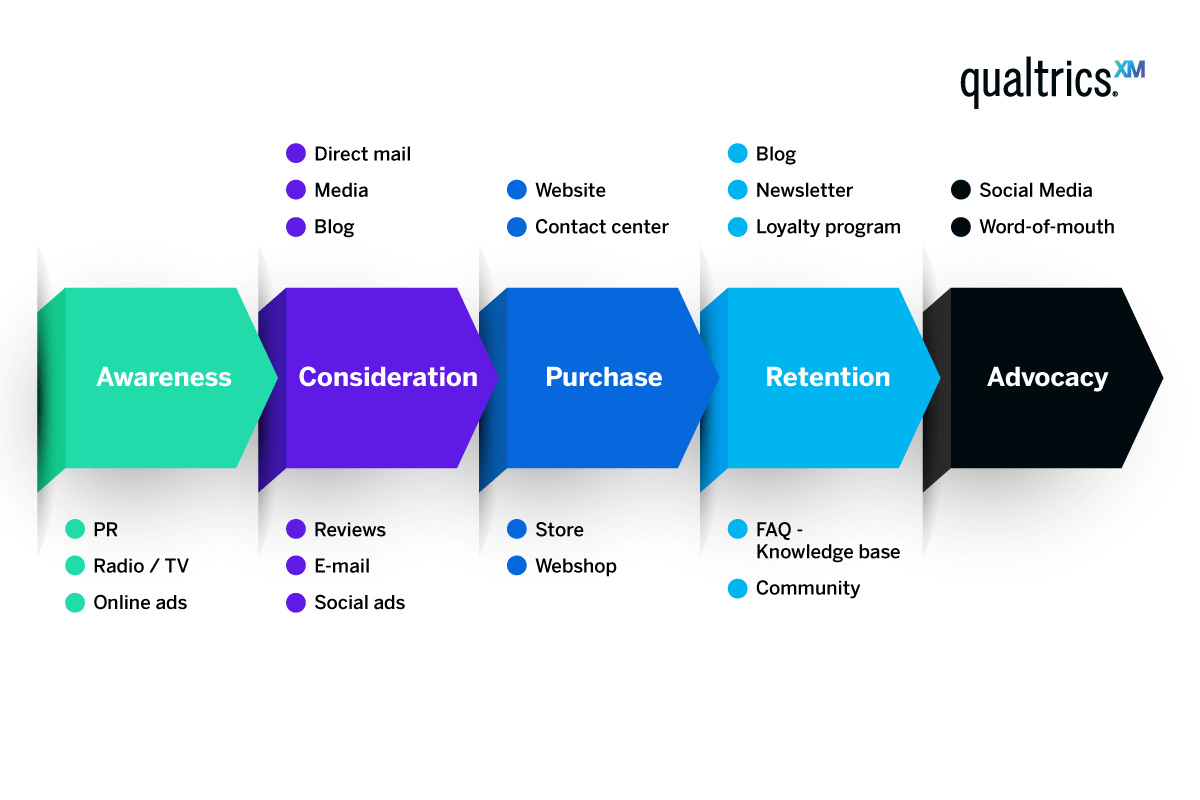
Instead of siloed teams looking after their individual touchpoints or KPIs, true customer journey management needs to have an omnichannel focus. You’ll need to work across departments to deliver more a seamless customer experience no matter how your customers choose to interact with you.
Customer journey management is about pooling your resources to answer the following questions:
- What journeys are your different customer segments taking?
- Are customers able to get the answers and solutions they need?
- Can you track and pinpoint where experience gaps lie?
- How can you work to proactively fix those pain points?
- Are you able to monitor the results of those changes?
Customer expectations are higher than ever, and people are much more careful with where they spend their hard-earned money. So it’s vital to be able to offer them journeys that offer zero resistance.
In that sense, customer journey management needs full company buy-in. It’s top-down, as well as bottom-up – where customer journey data informs both individual channels as well as your overarching business strategy.
The benefits of customer journey management
There are two core benefits to customer journey management: stronger business outcomes, and a better customer experience. But you needn’t just take our word for it; there’s strong evidence for both.
PwC , for example, cites that 65% of consumers are likely to become long-term customers if the entire customer journey offers a positive experience, while some 86% will leave a brand after two poor interactions, according to Emplifi. In fact, that same research says that 49% of consumers have done just that, with poor customer experience being the key driver of churn.
From a business outcomes perspective, there are plenty of reasons to ensure that your customer journeys are as polished as possible. Customer journey management means being able to offer customers a more personalized experience, for example, which is a great way to grow an audience of loyal customers.
Some 60% of consumers will become repeat buyers if the experience on offer is a personalized one, and 66% are willing to share personal data if it helps them get that. That shows an appetite for journeys that work better on an individual level. In our own 2022 research , we found that:
- 63% of consumers said companies need to get better at listening to their feedback
- 62% of consumers said that businesses need to care more about them
- 60% of consumers would buy more if businesses treated them better
And then there’s the fact that orchestrating and fine-tuning the customer journey will result in a stronger omnichannel experience – which also boosts sales. Omnisend research found that omnichannel campaigns and experiences can drive as much as 494% more orders than single-channel ones.
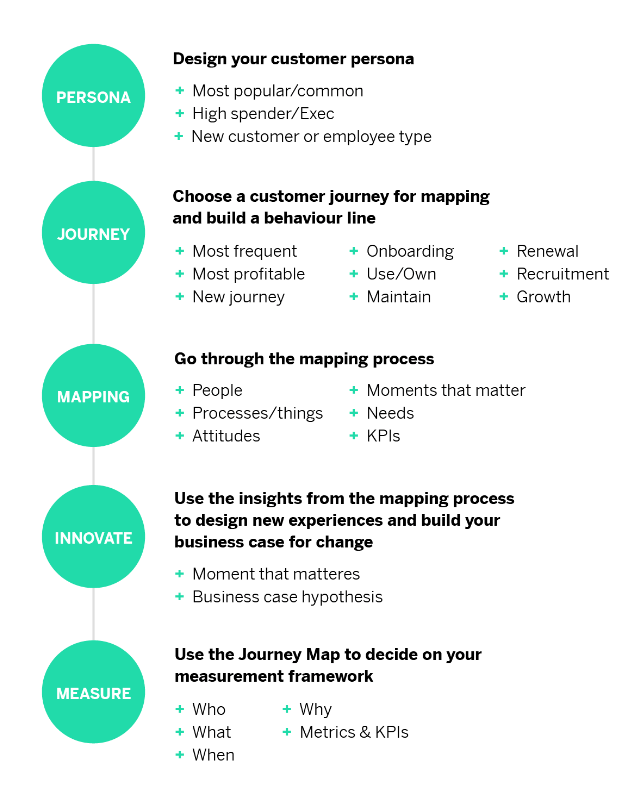
If you remember nothing else, remember this: customer journey management is an incredibly worthwhile practice to build into your business for three main reasons:
1. You become more customer-focused Customer journey management is about putting your customers at the forefront of your business practices and processes. 2. You can offer more personalized experiences You’ll know more about what makes your customers tick, which will let you tailor your offering to them in a more bespoke way. 3. You’ll break down siloes Customer journey management requires total transparency and teams that talk regularly to one another.
The building blocks of customer journey management
Let’s take a look at each part of the customer journey management framework:
A customer journey map is a theoretical version of the steps a customer persona or segment will take to achieve what they’re trying to do. That might be making their first purchase, making a repeat purchase, or seeking customer support.
The idea, then, is to create multiple customer journey maps for all of these different experiences and list out the steps and touchpoints along the way. This’ll give you an idea of the various processes that take place in any given journey.
You’ll normally create these maps as a team, as part of a journey mapping workshop. There are two stages here: defining your audience personas and outlining their various journeys.
Fo audience personas, you’re really asking who your customers are. What’s their age and location? What do they do for a living? What’s their family status? And what are their goals in relation to your product?
Their journeys can be understood by answering a series of behavioral questions. Who’s involved in the journey? What are the processes and stages? What does the customer think during these stages? What’s the greatest moment of emotional load? What are your customer needs at this moment? How do their needs change if this experience goes badly?
For the most part, this is an experience-driven process, rather than a data-driven one – in that your team should be able to create a customer journey map for a range of customer journeys based on instinct and understanding. These assumptions can then be tested by asking customers as part of your workshopping process.
Need more info? We’ve got a full guide to customer journey mapping here.
Customer journey orchestration and optimization
Once you know what your customer journeys look like, you can think about how to design ones that work best. If your customer journey mapping is a top-level exercise, then customer journey orchestration and optimization are more practical. These use customer data and a cross-team approach to ensure that customers can move from touchpoint to touchpoint smoothly.
Customer journey orchestration often relies on a dedicated team made up of marketing, product, and service personnel, who can work together to create more compelling journeys.
Imagine, for example, that you a customer has recently installed your SaaS tool, but now they’re experiencing an issue. Your customer service team will naturally spring into action here, but great customer journey orchestration would also mean that other teams know what’s happening.
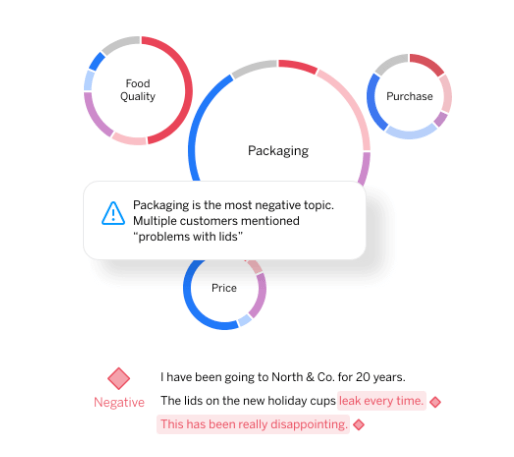
Your marketing team, for instance, would know not to bombard that customer with collateral about how great the product is until their issue has been fixed. The product team, meanwhile, would know about the issue the customer is facing and would be proactively working to ensure that the issue doesn’t arise for anyone else.
In other words, orchestration is about designing processes that can be standardized as a ‘best practice’ framework for each and every customer journey.
If orchestration is about designing flows that offer the best possible experience, then optimization is about looking at the ones currently in place, identifying pain points, and working to fix them.
Optimizing customer journeys is a cyclical process, rather than a ‘one and done’ job. Here, you’ll use customer data points, insight from analytics, social listening tools, regular customer feedback, and survey responses to build a picture of both customer behavior and high-priority pain points.
Armed with all that knowledge, you’ll be able to take active steps to improve the customer experience wherever you can.
Imagine, for example, that you know that a lot of your target audience arrives on your website via Instagram ads, but that a high percentage of them bounce without making a purchase. One way to optimize that journey could be to build a series of landing pages that are unique to each segment – with each targeted social ad sending people to a more personalized product offering.
Whatever the case, it’s essential to monitor the success of these initiatives and learn if they’ve worked, or if things still need changing. Optimization is about being holistic and agile, and not ignoring the data and insight available to you.
This brings us to the last part of the journey management process…
While instinct and some level of customer insight will help you map out a range of customer journeys, the ability to orchestrate and optimize things relies on access to customer data.
Customer experience management software is the answer here. The right customer journey management tools can provide masses of insight into the customer experience, help you track KPIs, and offer areas for improvement.
This information can come from a variety of sources. Customer behavior tracking can be baked right into digital products and work across platforms to help you better understand their journeys, while AI and natural language processing can listen to and understand customer effort, intent, and sentiment.
When it comes to customer journey management, software like this can help you:
- Audit journeys you think are happening
- Find ones you didn’t realize were happening
- Hear customer feedback from every touchpoint
- Understand where things need to change
- Measure the success of those change tactics
Information like this, both real-time and historical, can not only help you monitor the success of your customer journey management efforts but also provide a list of next steps to try, in order to attain better business outcomes.
Because of that, you can think of journey analytics as the engine behind an effective customer journey management approach.
Customer behavior: Bringing it all together
The three-part customer journey management framework is really a series of overlapping processes. Mapping informs orchestration and orchestration informs optimization, but the right analytics and data can inform all three.
So, in order to drive your desired business outcomes, you need to adopt the right tools. Customer experience management platforms, like the one offered by Qualtrics, can help you figure out what your customers are doing, saying, and thinking – and why.
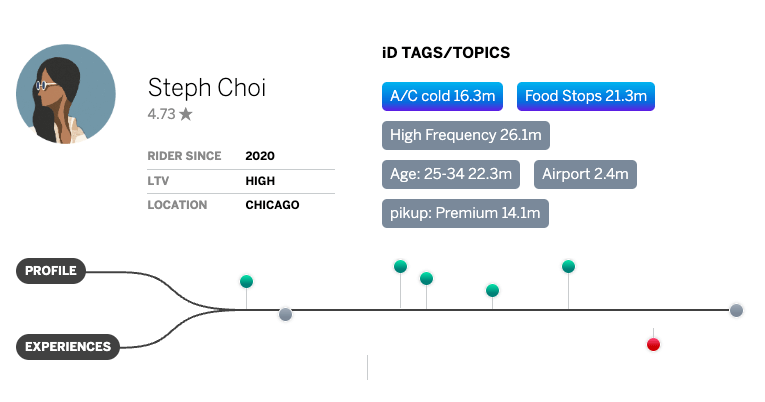
That information, alongside a much deeper understanding of who your customers actually are, can help you build personalized customer experiences that allow people to effortlessly float from touchpoint to touchpoint in a way that feels tailored to them.
The Qualtrics CustomerXM™ Platform has been designed to turn customers into fans. It allows you to hear every customer’s voice, fix every broken experience, and increase customer loyalty and spend. Click here to learn more.
Related resources
Customer Journey
Customer Journey Stages 12 min read
Buyer's journey 16 min read, customer journey analytics 13 min read, how to create a customer journey map 22 min read, b2b customer journey 13 min read, customer interactions 11 min read, consumer decision journey 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
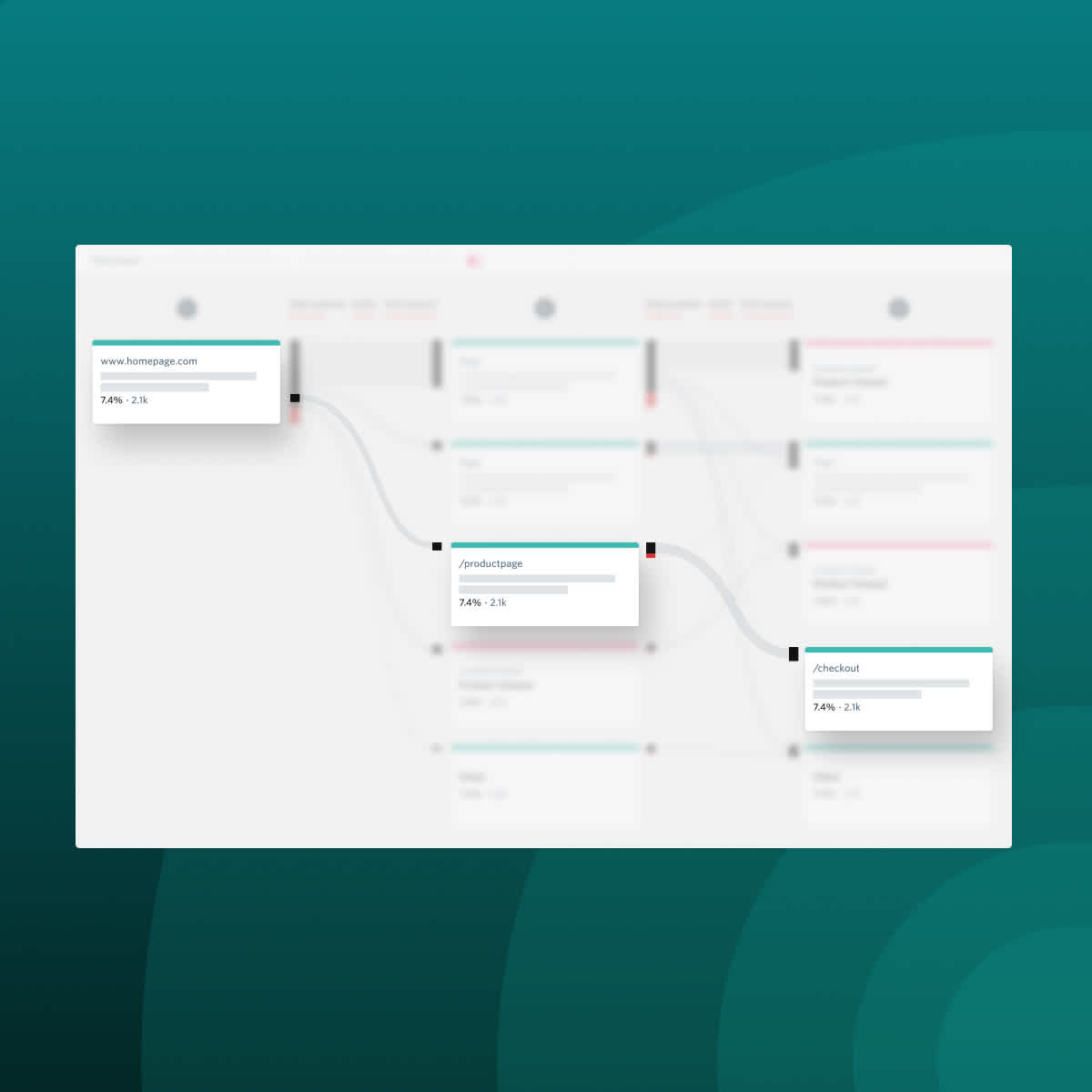
Customer journey maps: Understand, use, & build
A customer journey map is key to building a solid marketing strategy. We cover everything you need to know about customer journey maps, their different types, examples, and the steps to making your own.
What is a customer journey map?
Why do you need a customer journey map, characteristics of customer journey maps.
- What are touchpoints?
- Different types of customer journey map
Journey map variations
- How to create a customer journey map
Customer journey map tools
- How to build an empathy-based, data-backed customer journey map
- How to use empathy to create stronger customer journey maps
- Customer journey tools: Top rated and best available
The customer journey is a long and often unpredictable road. Understanding it can be even more complicated.
That’s why customer journey maps were invented: to understand the roadmap of a customer, from the very first touchpoint throughout the lasting life of their relationship with your business.
Customer journey maps (or user journey maps) can be an invaluable resource for companies, from marketing to sales to UX, and are known to help businesses increase their ROI by 13–22% if done correctly.
Below we cover journey maps from top to bottom, their importance, characteristics, and review examples, along with what you need to make your own.
>> Jump to get started learning how to create a customer journey map
Key takeaways:
Customer journey mapping is a strategic (and successful) approach to truly understanding your customers.
There are real and valuable business reasons to journey map.
There are six basic types of customer journey maps.
Customer touchpoints are every instance of interaction or engagement that happens along the journey.
There are current- and future-state customer journey maps that can help predict future behavior .
A customer journey map (sometimes called a user journey map, UX map, or CJM) is a visualization of the steps and experiences a customer has with a brand, from first contact to ongoing engagement, revealing both seen and unseen interactions.
User journey mapping lets you create personalized experiences across all touchpoints —for every individual—across all channels.
Companies can use this shared understanding to identify opportunities for innovation and improvement.
These maps can be simple or complex, depending on what you're looking to gain from them.
For any company, a customer journey map helps to enhance the customer experience and increase customer loyalty.
A customer journey map can prove invaluable for optimizing across multiple departments—marketing, sales, product, and customer service—in many, many ways. Journey maps can help you:
Promote a customer-centric culture internally and externally
Identify your ideal buyer and connect with customer needs
Glean customer journey insights into your audience that can drive revenue
Improve sales funnels & conversion rates authentically
Amplify customer experience by understanding the customer’s perspective
Reduce customer support tickets by locating customer pain-points
Aid in marketing campaigns
Generate repeat business
Decrease customer churn and increase customer lifetime value
Together, these advantages translate into higher sales for your business.
A typical customer journey map includes:
Actors—or potential profiles of customers—usually align with personas and their actions in the map are rooted in data . These actors will be the foundation of your map, and they will dictate the actions needed to create the desired outcome.
Customer personas and buyer personas: What’s the difference?
A buyer persona is a profile that showcases your ideal customer based on existing customer data and market research. Buyer personas help humanize the ideal customer you are trying to attract, which helps you understand them better and pick the right marketing strategy to convert them.
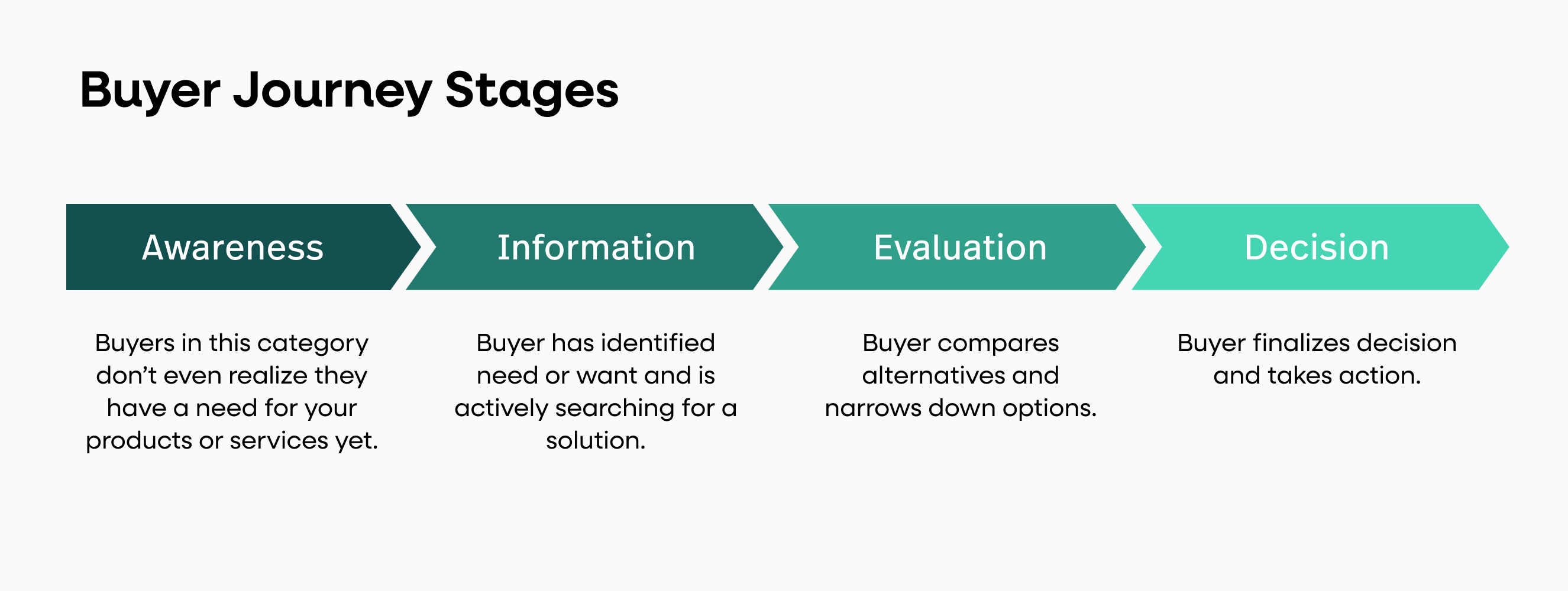
A buyer persona is your ideal customer—they’re in research mode. You can have more than one buyer persona for your company, and understanding this buyer is the key to creating a successful customer experience. This buyer will turn into your customer.
Here’s what makes up your buyer persona:
Demographics —including personal, professional, and specific (age, gender, location, education, income, marital status, skills, routines, etc.)
Goals —including personal and professional, priorities, and challenges
Values —including personal and professional, and what they find to be important in products and companies
Preferences —including the content they consume, their communication choices, communities, groups, or associations, and how they spend their day, on and offline
All of these characteristics make up customer journey maps on the buying path.
Journey phases
Journey phases are the different high-level stages in the customer roadmap. They provide organization for the rest of the information in the journey map (actions, thoughts, and emotions).
The stages will vary from scenario to scenario, and each organization will usually have data to help it determine what these phases are for a given scenario. Often you will see awareness, research, evaluation, and decision making in the customer phases.
Customer expectations
Journey maps are best for scenarios that involve a sequence of events, describe a process, or might involve multiple channels.
Pain points are a specific problem that customers or prospective customers of your business are experiencing in the industry.
Scenarios can be real (for existing products and services) or anticipated—for products that are yet in the design stage.
Actions, mindset, and sentiment
Every customer has a particular action that they take, because of a mindset that they have and will express it in their own sentiment.
Actions: When a customer engages with your brand with a purpose.
Mindset : Correspond to users' thoughts, questions, motivations, and information needs at different stages in the journey.
Emotions : How customers feel about your brand, whether positive, negative, or neutral. Plot these emotions in a single line across the journey phases, signaling the emotional highs and lows of the experience.
Opportunities
Opportunities of a customer journey map are desired outcomes. Maps should include key components, which can depend on the goal of the user journey mapping initiative.
Opportunities are also insights gained from mapping—they speak to how the user experience can be optimized.
To create a customer journey map, identify the personas, map the triggers that lead to desired outcomes, and discuss opportunities.
What are customer journey touchpoints?
Customer journey touchpoints are individual transactions through which the customer interacts with a business.
There are about 5–7 minimum touchpoints along a customer journey. Customer journey touchpoints for omnichannel brands are everywhere:
social media posts
product demos
advertisements
brick and mortar visits
website(s) clicks
You’ll also have the added returning customer touchpoints to consider—like how engaged they are with your product, if they are returning to your website or if they are attending your events for the second or third time.
Examples of customer touchpoints
Identifying each touchpoint is crucial for creating a customer journey map that will drive a better customer experience. Once you’ve identified the touchpoints, list out possible customer actions for each.
Some actions that derive from customer touchpoints might be:
Downloading an eBook
Clicking on your FAQ
Requesting a demo or call
Subscribing to your blog
Clicking a paid ad
It’s important to know which touchpoints to invest time and resources into. Your map maps out the areas you can improve, retain and scale.
Types of customer journey maps
Each customer journey map has a different objective and business focus. There are six types to familiarize yourself with:
Current state —These illustrate what customers do , think, and feel as they interact with your business currently.
Future state —These illustrate what customers will do, think, and feel as they interact with your business in the future.
Day in the life —These examine everything that customers or prospects do, think, and feel (within a specific area), whether that involves your product or not.
Service blueprint —This is a diagram that usually starts with a basic version of an existing or future state journey map.
Circular —These are used for subscription-based models to visualize the customer journey as a circle or loop. This helps reinforce the importance of customer retention and lifetime value.
Empathy —These are used to create a shared understanding around the wants, needs, thoughts, and actions of a customer.
Journey maps are meant to be used as a strategic planning tool. Use these definitions to guide you towards aspects of other methods that your team has not previously considered.
Journey map vs. experience map
A journey map is specific to a product or service, while an experience map is more general and can be used outside of a business's scope.
Since experience maps are more generic in nature, they can also be used to find pain points in a product or service for a future journey map.
Journey map vs. service blueprint
If journey maps are a product of experience maps, they will need a blueprint to direct them there.
Service blueprints are a continuation of journey maps in the service industry. They lead the roadmap for service-based customer journeys.
Journey map vs. user story map
User stories are used in Agile to plan features or functionalities, much like a future customer journey map.
In the user story map case, each feature is condensed down to a deliberately brief description from a user’s point of view. The typical format of a user story is a single sentence:
“As a [type of user], I want to [goal], so that [benefit].”
How to create a customer journey map
When you set out to create your own journey map, try drawing everything out on a whiteboard or digitizing it on a spreadsheet to get the big picture. The goal is to find and resolve any customer pain points. Here are eight steps to creating your own customer journey map.
Step 1: Set your objectives for the map
Before the whiteboard comes out, it’s important to set up clear objectives for the map. How do you do this?
Collect customer feedback from all company stakeholders, your team, and your customers. You can do this by forms, surveys, interviews, spotlights, or good old-fashioned conversation.
Ask questions like:
How do you feel about this feature?
How easy was it to find us?
Were there any points of frustration during your interaction with us?
Set goals within the customer journey map like seeing your product through your customer’s eyes, ways to improve your product or service, and how it all impacts your future.
Step 2. Define your customer persona
Your customer is the core of your journey map, so the first step is defining your target customer persona.
A customer or buyer persona is an in-depth understanding of who your customer really is, what they are trying to solve, and how they interact with your business.
The first thing you need to decide is which type of journey you’re going to map:
Persona —a profile of a specific customer type
Target —a profile of a potential customer
Market —a segment of customers
If you're creating your first map, it's best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
From the point of interest to the product lifeline, track each step along the way to get a true sense of your target persona.
Once you've created distinct personas, you can use them to dictate customer journey maps that describe each persona's experience at various points during their lifecycle with your company.
Step 3: Highlight your target customer personas
Take your journey map persona list and pinpoint your target customer. To do this, dig deep and understand what each customer wants to achieve as they go through the customer journey.
A great way to go about doing this is to first identify the paths that your customer may take on your site.
For instance, if your customer is a member, the first thing that they might do is to log in. These instances will help you determine engagement for each customer.
Here are some different ways to obtain and understand customers' goals:
Survey or interview different customer groups
Conduct user testing feedback
Study customer support correspondence
With this insight, you can then determine where your customer will go along their journey.
Step 4. Determine customer stages
Journey maps are organized by customer stages (sometimes referred to as phases ).
Each stage represents a goal your customer is trying to achieve in their journey. You should build a customer journey map with stages that represent your customer's goal-oriented journey, not your internal process steps.
Based on the persona, define the stages that your customer experiences with you over time. To figure out your stages, answer this question:
What does it take for a customer to start from awareness to decision throughout the buying process?
The typical customer journey map stages are:
Awareness —how they found out about you
Research —how you can solve their problem
Evaluation —how you compare against others
Decision —how they chose you
The goal : to determine how, when, and where they discover you, choose you over competitors, purchase from you, and maintain a relationship with you.
Step 5. Identify customer touchpoints
Your buyer journey map will be built off of customer touchpoints. Customer touchpoints are your brand's points of customer contact, from start to finish.
For example, here are a few ways customers may find you:
Search inquiry
Customer review
Social media post
These are just a few touchpoints; there are many more. Identifying these customer touchpoints is an important step towards creating a journey map and ensuring your customers are satisfied every step of the way. It’s also a pivotal part of how you will define your map.
Step 6. Map the current state
It’s time to conduct customer research for your map. This will include information about your customer’s intentions, motivations, digital footprint, and interpretation of your brand.
Most customers are happy to help if they believe you are genuinely interested in their experience and will use your feedback to improve things for others.
For each stage of the journey, try to identify:
What are my customer’s goals?
What type of experience do they want?
What steps are needed to complete that process?
How do they feel during each touchpoint?
What other thoughts, feelings or frustrations do they have during certain stages?
Beyond this information, be sure to look at patterns of how they conduct themselves online, where they frequent, and what they share.
Step 7. Understand motivations, frustrations, and resources
This step involves looking at the totality of the customer experience (CX) with your company.
Every business will look through the lens of its customer personas uniquely. Walking through each journey map stage with your team will help you identify any friction points within the customer experience.
You know your customers best. Here are a few example questions to get you started:
Where could friction appear in this particular touchpoint?
Are people abandoning purchases because of this?
Are customers unaware of this solution that you've provided? If so, why not?
These questions can be answered with customer behavior data, using a behavioral data platform like Fullstory , which delivers a complete, retroactive view of how people interact with your site or app. By finding out how visitors engage with your product and service, you can understand what resources you will need for growth.

Examine customer emotions and motivations.
Every action your customer takes is motivated by emotion. The emotional driver of each of your customer's actions is usually caused by a pain point or a problem.
So, get to know what roadblocks are stopping customers from making desired actions (again with digital intelligence) and get in front of motivation.
Overcome obstacles like cost, product friction , and onboarding frustration with customer experience intelligence.
Take the customer journey yourself.
Follow the customer journey yourself. Analyze the results to show where customer needs aren’t being met by seeing it through your customer’s point of view.
Pro tip: Document the customer journey for each of your personas and make note of the differences. It will help for future user journey maps.
Determine the resources you have and the ones you'll need.
It's important to take inventory of the resources you have and the ones you'll need to improve the customer's journey.
Using your map, you can advise leadership to invest in the right tools that will help your team manage customer demand. Do you have what it takes to solve the customer’s problem?
Step 8: Evaluate, adjust and scale
As with any process, you’ll need to test it over time. Data analysis is used to identify customers’ behavior and pain points that need changing along the way.
Use digital experience and customer intelligence to keep you informed on the user journey. This means relying on a solution to let your customers show you what’s actually happening. With features like session replay , you can understand exactly what they are going through and proactively fix it.
Always include your team and keep stakeholders involved to keep the roadmap clear.
Your customer journey map checklist
This guide on creating a customer journey map should help you truly understand the impact of your product or service. By stepping into your customer’s shoes, you will gain the insight needed to improve the entire experience.
Now, you’re ready to create your map. Here are the questions you will ask yourself while creating a customer journey map:
☑ Set clear objectives for your map ☑ Define your customer persona ☑ Highlight your target personas ☑ Determine customer stages ☑ Identify customer touchpoints ☑ Map the current state ☑ Understand motivations, frustrations, and what tools you’ll need ☑ Evaluate, adjust, and get ready to grow
Use the data and let your customers do the rest.
6 customer journey map templates
Having a template is a great way to get started. There are a few different templates to choose from:
Current state
The current state journey map visualizes the current experience with your product or service. It involves defining the scope of the customer experience with customer touchpoints.
This type of customer journey map is designed with the considerations, thoughts, feelings, and actions of your customers in mind. Current state mapping is a practical approach to identify existing pain points and create a shared awareness of the end-to-end customer experience.
Day-in-the-life
A day-in-the-life journey map is another simple grid map based on time, created especially for the daily grind of the customer. Instead of different journey stages, it represents times in the day related to actions based on decisions in the path of purchasing.
This template helps you visualize your customer’s daily routine even if these actions are outside your company. It typically is organized chronologically to systematically show the course of the habits of the day.
Day-in-the-life's are great for giving you insights into all the thoughts, needs, and pain points users experiences throughout their day. You can use this type of map to evaluate when your product or service will be most valuable in your customer’s day.
Future-state
With a future-state journey map template, your goal is to learn how your customers feel about a new product launch or about how they will require your service in the future.
Future-state journey mapping is a useful approach to explore possible customer expectations and to create new experiences. Mapping out a future customer journey helps to align your team around a common goal—the betterment of the customer experience.
Service blueprint
A service blueprint helps you design a roadmap of your service process—much like building a house. The goal is to be able to make projected changes to the service where needed and to be able to visualize each step in the eyes of the customer.
Service blueprint maps reflect the perspective of the organization and its employees and visualize the things that need to happen behind the scenes in order for the customer journey to take place.
Service blueprints are created when making procedural changes, or when trying to pinpoint solutions to roadblocks in the customer journey on a website.
A circular customer journey map is just that—circular instead of linear or graph-like to showcase a different type of business model. For instance, a SaaS company may find it more useful to visualize the customer journey as a loop or wheel.
This subscription-based journey map does a nice job of portraying both the customer interactions and sentiments, as well as their journey from awareness to purchase.
The empathy journey map is a bit different because it aligns with the customer's feelings and emotions. Empathy is a big factor in the customer journey and this template is designed to help teams align their customer journey mapping exercise with these types of needs.
With empathy, you can get into your customer’s shoes and truly feel what they feel as it pertains to your product or service.
As with anything, you’ll need a customer journey mapping tool to help you. The key is to find the right tool that works with your team and workflow.
Here are a few tools to consider:
PowerPoint or Google Slides
With the right map and the right tools, you can overcome roadblocks and open a path to scalability and success.
Enhance your journey mapping process with customer intelligence. Look at behavioral data points like heatmaps , scroll maps , and other insights you can glean from session replay . Combining these quantitative and qualitative insights will help you in your journey-mapping process.
Using journey maps to drive organizational change
It may not be easy to get buy-in to support the changes in strategic planning that result from customer journey mapping.
You can use what insights you’ve gleaned from the current state journey map in these beneficial ways:
Align your organization around the customer viewpoint. Engage with each department and set up a commitment to put the customer experience moments top of mind with an initiative for growth.
Enlist team members and partners to generate empathy for customers. Use your journey map to bring together relevant teams to train on customer experience best practices.
Supplement a new strategy with internal communications that encourage better customer service. As new initiatives roll out, use internal channels to communicate how you’re improving the experience of the customer, and how team members can help.
Optimize your user journeys with Fullstory
Understanding your users' digital experience and optimizing your most important touchpoints can be make-or-break.
With Fullstory Journeys, you can easily see how users explore your site or app and see step-by-step page navigations and other key interactions along the way. This lets you identify if users are using your site how you intended; what the most common navigation paths are; and how users typically arrive at your most critical pages.
It's no longer a guessing game—it's data-driven and actionable.
Fullstory's behavioral data platform combines the quantitative insights of customer journeys and product analytics with picture-perfect session replay for complete context that helps you uncover opportunities.
Sign up for a free 14-day trial to see how Fullstory can help you combine your most invaluable quantitative and qualitative insights and eliminate blind spots.
Frequently asked questions about customer journey maps
Who uses customer journey maps.
For any brand or company that wants to learn their customer, from the point of motivation to the turning point of frustration, a customer journey map is the best tactic to do so. Journey maps are best for scenarios that describe a sequence of events. You might want to map multiple scenarios for one persona, depending on your project goals.
How often should I update a customer journey map?
If business goals change, so could your customer’s goals. If you roll out a new product or service, you may want to edit or update your customer journey map. Keeping your maps updated can help you reach your goals as a team.
How many customer journey maps do I need?
The number of different customer journey maps needed all depends on your target audience. If you have multiple customer personas, it would be best to create different journey maps to suit each one.
At the very least, be sure to create a customer journey map for the current and future state so you can aid in predicting future trends of the customer journey in alignment with your product and service.
Who should be involved in the mapping process?
Anyone that is involved in making your product or service successful should have a hand in the mapping process. Sales, marketing, customer success, and product teams all should be involved in customer journey mapping. Every team member will benefit from truly understanding their customers to make for a better customer experience.
What is a user journey map in design thinking?
User journey maps for design thinking is an iterative process of studying the user so that they can engage with a system with more agility. It redefines customer problems in an attempt to identify alternative solutions that might not be obvious with the initial level of understanding.
Related resources and further reading
Jennifer Pyron from brand performance agency Mighty & True on building a customer journey map.
What is a customer journey map, how does it relate to product and marketing teams, and where can empathy help? Let's find out.
Fullstory helps you visualize customer interactions so you can understand and improve customer experience, one glowing review at a time.
A comprehensive guide to product analysis and analytics platforms, how important they are, and why they’re a valuable asset for your bottom line.
Journey mapping tools help marketers identify pain points, tailor interfaces, and cultivate efficient, enjoyable experiences for customers.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Customer Journey: What it is & Examples [Free Template]

Have you ever thought that all the purchases we make involve a buying process before the time of the transaction? We call this process the customer journey, which encompasses all the phases a person/buyer persona goes through from the moment they identify their need until they acquire a product or service to satisfy it.
This process can be as short as a few minutes in the case of low-cost products that we buy impulsively (food in a supermarket, for example). The purchasing process may also last for months or more than a year (for instance, when acquiring a car or purchasing a customer experience management software ).
This article will cover the customer journey, its phases, and how we can define it in our customer experience strategy.
Remember to download the free Customer Journey Map template at the end of this guide!
What is a Customer Journey?
By book definition, a customer journey is the set of interactions that a customer has with a brand in buying a service or product. Put plainly, and It considers the complete interaction roadmap – from brand discovery to purchasing and beyond.
The focus isn’t only on transactions and how the customer feels after every interaction with the brand. In other words, the customer journey can be used as a strategy to gain insights into the customer’s experience throughout their buying process.
The objective of these journeys is, on the one hand, to measure and evaluate how you are taking care of your customers and, on the other. In this way, you can enhance and bring further delight to their experience with your brand measurement .
Excellent products, a praiseworthy website, and an on-call customer service team may seem like the perfect mix to capture prospective clients. However, when customers feel something is off in your communication, they’re more likely to seek competitors.
By improving the customer experience at each touchpoint in the customer journey, you focus your business on your customers, putting them at the heart of all. This builds a loyal fan base and keeps customers coming back time and again, fostering a strong connection throughout the entire customer journey. This builds brand loyalty as a positive outcome, leading to having satisfied customers and an influence over their lives, choosing your brand above others.
The brands that gain the most loyalty are the ones that influence their clients’ lives. It is the outcome of so many variables —some of which we can control and others we cannot— and understanding how those variables play out in our markets is a crucial first step to understanding what causes brand loyalty.
Customer Journey Stages
Now that you know what a customer journey is, it’s time to look more closely at what you can do to commit to your present and potential clients. Various stages make up the complete journey.
These three steps generally make up most journeys: Awareness, Consideration, and Conversion . These customer journey stages are most suitable for offline purchases.
With the progress of digital platforms, two critical additions appear in the customer experience: Retention and Advocacy . These new stages of the customer journey explore brand touchpoints with online shoppers.
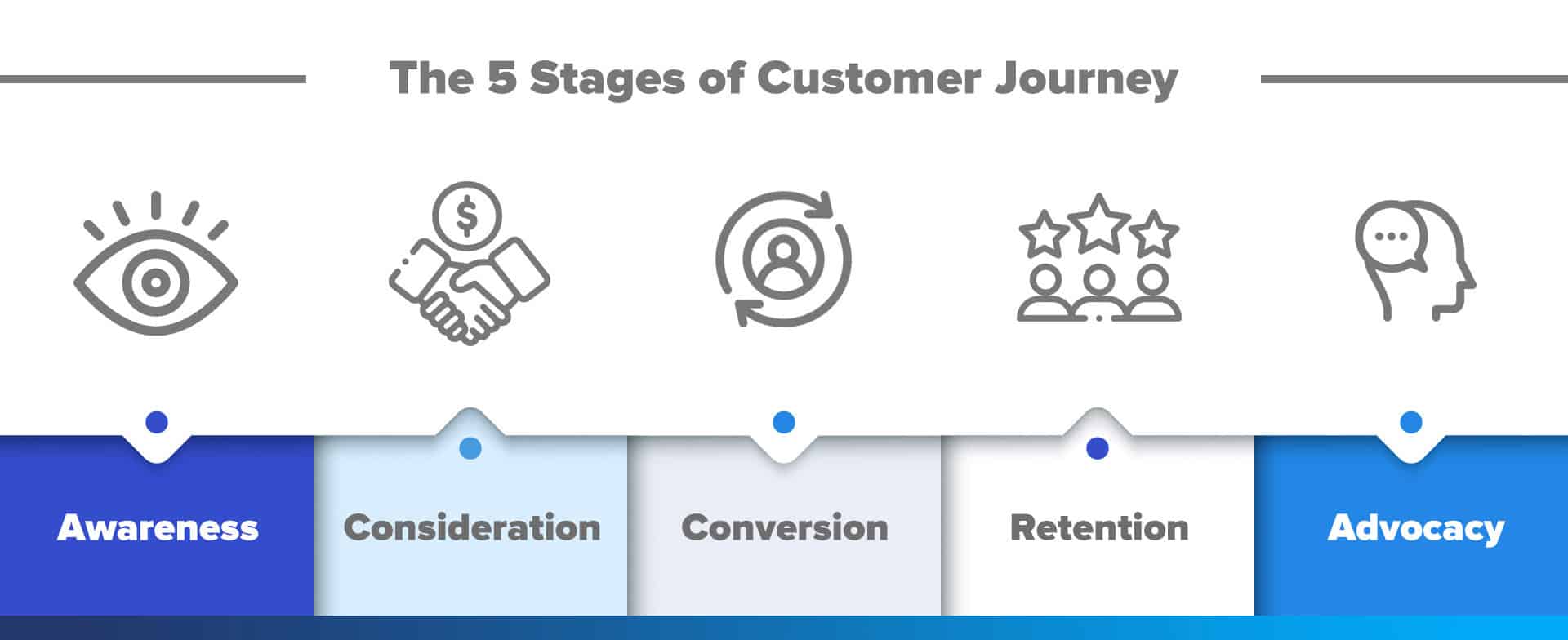
1. Awareness: The first stage
Awareness involves spreading general information about your products and services to your target audience (s).
During the customer awareness stage of the customer journey, consumers search for solutions and encounter multiple brands and products. Hint: This is the time to shine if you want to make a good first impression.
What consumers are doing : During this customer journey step, consumers are likely conducting research. This can include searching online for solutions to keyword problems, reading blog posts and news articles, browsing online forums, and first meeting brands.
What brands can do : You might think consumers are doing all the heavy lifting at this stage of the customer journey because they’re asking questions and browsing content.
However, you don’t want to approach brand awareness passively. You have to be there already, where the consumer is looking at alternatives. By “being there,” we mean taking the form of an educational blog post or video, providing the solution or information they want. Bringing valuable resources to the consumer is vital in this initial customer journey phase.
Read about the consumer decision journey .
2. Consideration: The second stage
Brands focus on promotion during the consideration stage of the customer journey. This is where customers begin to look for alternatives to past purchases. During this journey phase, your business strives to convince potential buyers to include you on the list of available options.
Your brand will most likely be considered alongside others, so make sure every impression you make counts.
At this point, consumers are directly interacting with your brand, and you want them to stick around for the next step in the customer journey.
What consumers do : Research specific brands and products, compare competitors, and evaluate your priorities. This could include looking closely at your product and service specifications and features, examining customer support policies, and turning to direct comparison reviews.
The consideration phase of the journey varies because consumer-centric channels can come in many forms.
What brands can do : Value the importance of the user experience (UX). Continuously optimize the UX across all your touchpoints, including e-commerce transaction and description pages.
Little things like making sure the descriptions and processes are clear and that all the buttons work correctly go a long way when someone considers you against a competitor on their customer journey.
For instance, a person becomes aware they’re hungry and could be scouting for a place to eat on an app like Google Maps.
Suppose your business has a strong presence there, i.e. , with information about what kind of food you sell, the menu, photos of the place and the food, phone number, and truthful, positive customer reviews. In that case, you might make them consider that you could be an excellent alternative to what they’re looking for.
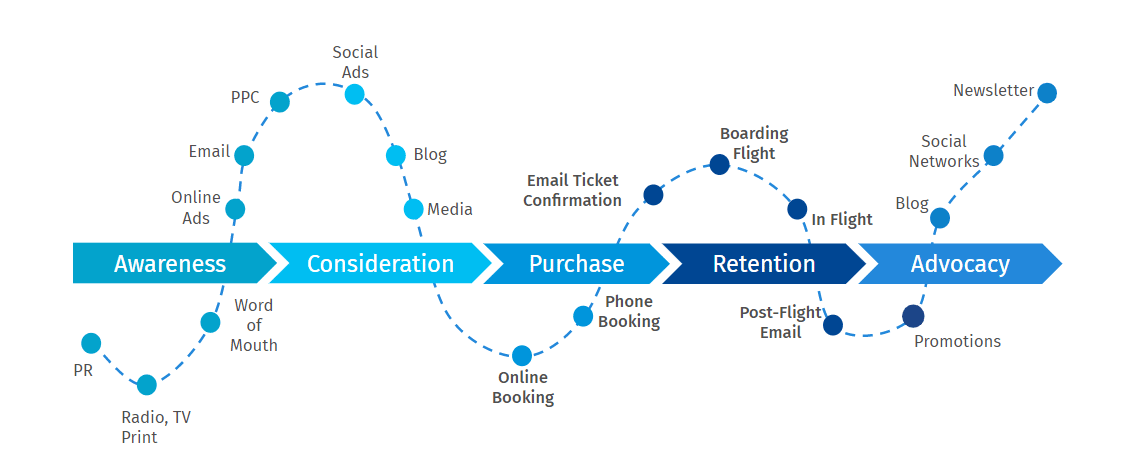
3. Conversion: The third stage
This stage of the customer journey prompts visitors to take a particular action. Using a dedicated call-to-action (CTA), you encourage customers to make a purchase, subscribe to a mailing list, or sign up for services. You should use this phase to sell your product as the best fit to solve a visitor’s problem.
It is your moment to make or break during the Customer Journey. Once potential customers are satisfied with researching and comparing their options, they will eventually decide.
Sometimes, they find that none of the brands they’ve been considering offer what they’re looking for. If they make a favorable decision, they want to make the process easier by choosing their trusted products.
What consumers are doing : They are considering factors like price vs. value, customer service responsiveness, company values, and policies as part of the existing customer journey. When they’re in the decision phase, it’s not just about product specifications or the shopping experience but how these elements fit into their customer journey design.
Consumers want to support a brand they trust to provide a quality solution to their problems, ensuring a positive customer journey begins and continues throughout their interaction with the company.
What brands can do : To anticipate this customer journey step, you must go further. This could include marketing strategies where you offer incentives to potential customers who have already visited your website or engaged with your business.
Ensure your return and refund policies are easy to find and train your customer support team to answer key decision-making questions.
Note that the following two customer journey stages, Retention and advocacy, were optional in previous business models. Nevertheless, the increase in online purchases makes these stages of the customer journey as significant as the others.
Read about the customer value journey and what it is.
4. Retention: The fourth stage
At this point in the customer journey, you already have a new customer – Congratulations! All that planning and asset building is paying off when they get to this phase. The journey refers to the consumer’s path from initial awareness to making a purchase, and in this phase, they have decided to navigate their purchase journey with you. But don’t assume it’s a done deal.
A loyal customer brings an organization consistent business and costs less than the effort to bring in new customers. A study by Bain & Company discovered that loyal customers are 50% more likely to try new products and spend 31% more than new customers. This demonstrates the value of nurturing and maintaining relationships with customers throughout their customer journey.
Retention includes keeping customers happy with a relationship management/customer success team to stop them from leaving and take them as many as possible to the next and final stage of the customer journey- make them so loyal to your brand that they want to advocate for your product and service.
What consumers are doing : Depending on your business model, customers are taking advantage of this moment to buy your products online, with a physical retailer, or are booking a service they plan to experience soon.
Once they have the product or service as a part of their consumer journey, they will start to implement their purchase, and if they go through the phase successfully, you will earn their customer loyalty.
What brands can do : Optimize the transaction experience in the Journey. Ensure the quality of your e-commerce site or physical store, and regularly review how your competition optimizes customers’ experience for each customer touchpoint .
5. Advocacy: The fifth stage of customer journey
Most organizations acknowledge the benefits of word-of-mouth. However, few companies commit to a plan for boosting customer advocacy . Encouraging each customer to share reviews can take time and money. Reaching out to influencers or guest bloggers is an effective alternative to traditional word-of-mouth.
Enthusiastic customers are more likely to recommend your brand and products to a friend, which can be a deal-breaker for many as it enhances the entire customer journey.
When you keep your customers happy and exceed their expectations with innovation and excellent customer service, the customer journey shortens, and transaction costs decrease.
What consumers are doing : At this point in the customer journey, customers are using your offerings to address their needs. The better the results and experience they get with your product, the more likely they will buy again and recommend you.
They can also begin to engage with your brand more casually on social media and plan their next purchase.
What brands can do : Take the initiative to contact customers in a friendly and supportive manner during their journey. A short customer experience survey is an excellent way to let them know you care about their feedback.
Consider starting a loyalty program for referrals and future transactions. This is also an excellent opportunity to keep consumers returning to some relevant assets you create to build brand awareness.
This could include blog content with tips to enrich your product experience , a newsletter with updates, promotions, and occasional opportunities to provide further feedback.
Are you thinking about improving your understanding of your customers? Dive into QuestionPro’s latest blog on their Customer Insight Platform!
Benefits of Understanding the Customer Journey
Identifying customer journeys allows us to understand better how they buy to meet their needs and expectations and what role a specific business plays in this process.
Furthermore, being aware of all their journey interactions (customer touchpoints) through any channel, such as email or social networks, allows for a better shopping experience while delivering a consistent message across all communication channels.
Next, we will explain the benefits of implementing a customer journey strategy in your business.
A better understanding of customer emotions.
Building a customer journey framework puts you directly in the mind of the consumer. Understanding why a customer makes a particular choice sets your business up for success.
Knowing how customers feel encourages you to improve how the organization functions because it allows you to identify the friction points throughout their customer journey, making them easier to fix.
Analyze the stumbling blocks in products/services.
Mapping the journey gives your organization insights into where your customer communications fall short. For instance, if your support staff is undermanned, customers don’t receive help when needed. Your customers become angry because they expect prompt replies. You resolve the issue by hiring another support team member to tackle more customer questions.
Creating a customer journey map provides the customers’ viewpoint of a business. The map is a visual representation of the transactions and emotions that lead through each touchpoint with customers that helps to identify weak points in your messaging.
Improve employee and customer satisfaction.
As issues are resolved, confidence levels among customers and employees alike increase, leading to a more positive customer journey. Employees are encouraged to continue doing great work, increasing overall customer satisfaction.
Create a united team.
To develop unique customer experiences, the teams in your organization need to be on the same page. Marketing, product development, sales, and customer service must work together to improve customer journey processes within the organization. As the teams work together, the efficiency and effectiveness of each team increase, positively impacting the customer journey mapping process.
Make sure to check these 10 customer journey benefits for mapping
Customer Journey Analysis
Understanding the organization from the customer’s point of view brings new ideas and opinions to the table. Customer Journey Analytics does precisely that – it analyzes customer viewpoints about products so that you can make appropriate changes to keep customers loyal to your brand. Use data from customers to implement improved marketing strategies.
The analysis involves three stages: gathering accurate information, developing customer personas , and analyzing customer interactions.
Here is how customer journey analysis is beneficial in gathering information:
- Clearly defines all customer interaction points.
- Evaluates how the customer journey progresses from beginning to end.
- Analyzes the impact on customer loyalty and brand shareability according to customer interaction points.
- Highlights areas that waste a customer’s time to improve efficiency.
- Generalize the customer journey of similar audiences to make improvements and keep customers satisfied.
Learn what Customer Journey Monitoring is and the benefits of implementing this systematic activity.
Customer Journey Communication Channels
Your map is a 360-degree view of customer feedback from each step in their journey. Customer journey mapping is a proven model for understanding how, when, and where your customers experience your brand.
To start, here are some places to measure experience on an ongoing basis:
- On-site: Capture feedback at the moment customers visit businesses with physical locations. For example, let’s say you run a restaurant. Give diners a short survey to complete along with their bill at the end of their meal, allowing you to gather valuable insights into their customer journey.
- Email: Sending emails is one of the easiest ways to get customer feedback. Set up your sales system to trigger an email after a customer completes a purchase.
- Call center: After every customer interaction, you can collect feedback via email or phone-based survey.
- In-App: For app developers, collecting responses without leaving the app is ideal. An in-app survey allows users to continue enjoying the app while still providing you with feedback, contributing to a seamless customer journey.
- Website: Your prospects browse your site to consider becoming customers. Once customers continue visiting for support and account access, gathering feedback on your website is essential to a holistic customer experience approach.
If you like reading about what the customer journey is, you might find it interesting to learn about the in-store customer journey: definition, importance and stages .
Elements of the Customer Journey
There are various elements that are essential when creating your Customer Journey and that will help you have a better customer analysis.
Each of these elements will help you identify the points that you should improve on your journey:
Buyer persona
Buyer personas are iconic representations of your ideal customer. They are based on research, data, facts, and real interviews with recent buyers (and may even include perspectives from people who postponed a purchasing decision or purchased a competitive solution).
By creating a buyer persona correctly, marketing managers will be able to segment their messages better, targeting different people with the most appropriate content and offers; develop new products/services based on the needs and wants of its key customers; and reach the right people, thus pre-qualifying potential customers by attracting them.
Let’s remember that the journey of a customer is the story of a customer’s experience, and it helps you explain what happens along the way, to whom, and how it happens. Therefore, it is necessary to know who makes the trip to tell the story. The buyer persona represents the customers whose journey you are mapping.
Contact points or touchpoints
Where are the customer contact points? Touchpoints encompass all interactions between a brand and a customer at any point in the customer journey.
These individual touchpoints can influence how a customer perceives your overall brand experience. Every touchpoint represents an opportunity to guide and delight the customer. Touchpoints can occur through web and offline channels and may or may not be controlled by the brand.
These are some channels you can use to stay in touch during the journey:
- In the place
- Via telephone
- Social networks
- Word-of-mouth recommendations
- Evaluation sites
The number of customer touchpoints and the time it takes to complete each step can vary depending on multiple factors, including:
- Customer preferences (i.e., preferred mode of searching, purchasing, support, etc.).
- Relevance and importance of the goal (for example, buying a car compared to buying food for your dog)
- The channels chosen by companies to interact with their customers.
Performance indicators
A key role is to identify critical opportunity areas based on understanding your customers’ perceptions of the experiences.
You can use common indicators that indicate positive/neutral/negative or exceeds/meets/does not meet expectations. This generalized approach to performance indicators can be used effectively to identify and evaluate areas of opportunity.
Because qualitative research is typically conducted with smaller sample sizes, quantitative research with a large sample size can strengthen confidence in qualitative insights.
Quantitative research provides an opportunity to capture customer experience metrics for specific journey stages or touchpoints. By integrating metrics into the customer journey map, they become a useful tool for measuring customer experience initiatives over time. Some useful metrics you can include are:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) or other customer loyalty measures
- Customer satisfaction metrics
- Quantitative assessments of the primary emotions customers are experiencing at specific stages or touchpoints in their journey
- Effort metrics
- Measures of importance, usefulness, etc. from a specific point of contact
The metrics collected and included in the Customer Journey will help you measure the health of the customer experience, now and in the future. And in doing so, there must be a commitment to making value decisions based on customer experience performance.
Customer experience map
The customer experience map helps you list the following elements that will help satisfy users and compel them to move forward. Consider these examples:
- Consumer activities and questions
- Touchpoints such as websites, forums, and advertisements
- Assets such as paid media, blog posts, videos, and webinars (some assets are customer touchpoints)
- Strategies such as SEO, social networks, managing virtual communities, and creating referral programs
- Tools like engagement reports and online surveys.
How to Define a Customer Journey Effectively?
After learning what Customer Journey is and the elements that make it up, it is time to build a journey map that converts prospects into loyal customers and creates the best strategy.
Follow these 5 steps to ensure your customers get the products they need for their needs and enjoy a customer experience that will keep them coming back to your business.
1.- Understand what you have to offer and who benefits from it
Each member of your team should know how to communicate the benefits of your products and services. You can’t share something when you don’t know what it is! In the same way, you need to know who your ideal client is.
Ask yourself, “Who needs this solution most?” This is a good opportunity to take advantage of online surveys, which allow you to identify your target audience, their primary needs related to your offers, and any other considerations you need to make to attract them.
2.- Create your ideal client
Once you have a general idea of who your target audience is, create a few profiles to give them a name and a face. When you have a well-developed sense of who to include in your demographic segmentation, you’ll have a clear understanding of the variations in your customers’ journeys.
For example, you may discover that your reusable water bottles will solve problems for athletes of all ages, sustainability-conscious millennials, and adults with limited mobility. Avoid expanding your market too much because that can blur your focus and make your market strategies less efficient.
Create a customer archetype for each of these groups within your target audience, taking into account these imaginary but realistic variables:
- Economic situation/income range
- Interests and hobbies
- Main sources to communicate and obtain information
- Consistent touchpoints
- Favorite brands and products
- Consumption habits
3.- Identify any specific details of your industry
The next strategy to create an effective Customer Journey is to obtain details of your industry. Generally, customers’ stops along their journey will be similar. However, their specific needs should influence your value propositions and the assets you create to market your product.
4.- Optimize your value propositions
The Customer Journey is personal, and your value propositions must be consistent in each encounter with consumers.
As you become familiar with your target market, refine your value propositions to be inclusive, communicative, and aspirational. Use these statements as a guide in your customer journey map and your company’s marketing assets.
It’s time to put your customer experience map into practice. Consider what each of your customers would need and do so throughout the entire process while assigning these elements to each phase of the customer journey map.
5.- Build assets for each touchpoint in the Customer Journey
By mapping out the customer journey, you’ll have a clearer idea of what your ideal consumers will ask of you, the brands they might be considering, and the types of content they’re likely to consume to move from one phase to the next.
Depending on your industry, customer touchpoint content may include the following asset types:
- Associated or influential content
- Print or email newsletters
- Infographics
- Information on social networks
- Videos (ads, tutorials, webinars)
- Promotional flyers
- Sample kits or demos
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) tells the story of your customer’s experiences with your brand across every touchpoint – all on the same canvas. Or Customer Journey Map (CJM) as a key tool to improve the customer experience. Depending on the objective of the CJM, it can be more or less complex.
The things your customer feels, sees, and hears as they interact with your business, builds the foundation for their experience.
Understanding these experiences allows you to map and control the customer journey accurately.
Example of Customer Journey Mapping
Starbucks, for example, masters the concept of customer intimacy and uses customer journey maps to control the experience. The customer journey is calculated from the moment you step in the door.
Imagine a trip to your local Starbucks. As you walk inside, you smell the aroma of roasted coffee beans. The barista behind the counter greets you with a smile. As the muffled chit-chat disappears into the tranquil background music, you feel the coziness around you.
When you receive your coffee, you see your name handwritten by one of the friendly baristas, a personalized moment clearly indicated on the customer journey map. If you’re a regular, the staff knows you by name and can make your order from memory.
The coffee giant doesn’t just sell a product. It sells what people are best at remembering – the experience. The company retains loyal customers by packaging the product with an unforgettable experience. They’re also able to charge up to 10 times more than their competitors. Starbucks clearly understands customer experience and infuses that into the core of its business strategy.
Learn More: Click here if you’d like to review 7 more Customer Journey Examples.
Below, you will find a customer journey map template in case you need a reference to create your own. If you’d like to download the customer journey map template, keep reading! Or scroll down a little bit more 😉
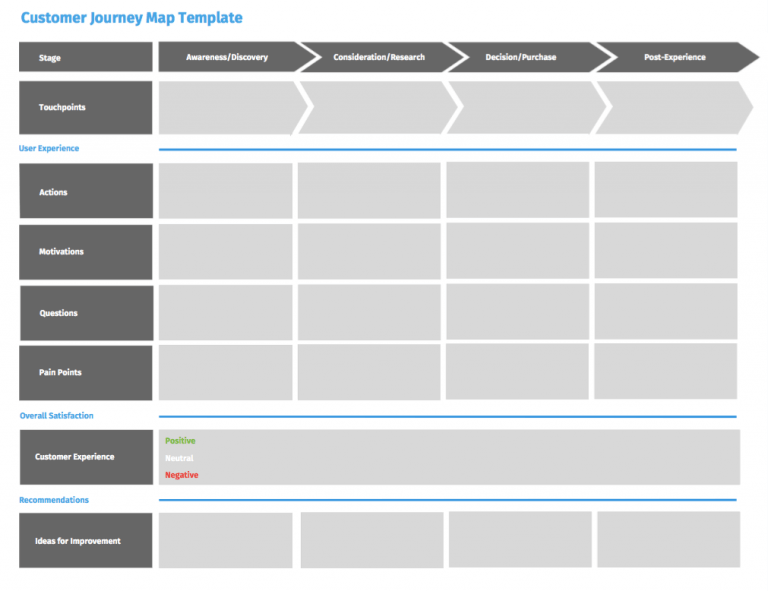
Your customer journey could take place over a few hours or more than several weeks. The simplest way to start is to create a timeline. Using your customer knowledge, fill in what’s happening with your customer at each stage of your customer journey timeline.
The customer journey mapping framework includes the following alongside the timeline:
- Actions: What is your customer doing? What are the key actions a customer takes to move to the next customer journey stage? What actions does a person take when they don’t move on?
- Motivations: What drives the customer to proceed to the next stage of the customer journey? What is the goal? Are they trying to solve a problem? What are they feeling?
- Questions: What are the customer’s uncertainties? Are they looking for something specific? Are they confused? Identify which stage of the journey customers have the most questions and quickly address them.
- Pain points: What obstacles prevent your customers from moving to the next stage? Is it the process? Price?
Direct customer opinions are the most effective way to get answers. Send surveys or conduct interviews to learn more about your customers and their needs. Input the data you receive into the framework above so you can see your company from your customer’s perspective.
Free eBook: The Hacker’s Guide to Customer Experience – CX= Emotion x Value
Halfway there? Congratulations! Luckily, you’ve learned a bit more about what Customer Journey is and its interconnection with customer experience. If you’d like to go the extra mile and learn more about how customer experience can help you gain happier , loyal customers and increase your business growth, download our free eBook: The Hacker’s Guide to Customer Experience – CX= Emotion x Value.
DOWNLOAD EBOOK FOR FREE
Tips for Conducting a Customer Journey Mapping
If you’ve made it this far, you would probably agree that knowing your customer’s journey is critical to creating a great customer experience. But how do you make the most out of it?
Let’s take a look at some of the following tips to create an effective Customer Journey Map:
Tip #1: Building a customer journey map is a team effort
It is not easy to reflect on the Customer Journey Map of all the interactions a customer goes through. The task can be further complicated when the people responsible for interaction cannot be found in the different departments.
This takes for granted the phases or interactions the client goes through with the company. What’s worse, it sometimes leads to mapping a Customer Journey Map that has more emphasis on departmental silos than the overall customer journey.
Remember, your team cannot forget the goal. It seeks to map the Customer Experience from its perspective. This is most effectively achieved when different company profiles are brought together. Only in this way will the final result reflect the knowledge that each one has of the client.
The idea is to dedicate a workspace with the different professionals, with and without client contact. If this is impossible, performing at least one validation with each department is vital. This will allow you to turn your Customer Journey Map into a shared responsibility tool.
Tip #2: Know your customer thoroughly
Understanding your customers at each intersection or checkpoint in their customer journey is critical. This allows you to develop content, products, and services that meet their needs. Rather than gathering occasional data from customers, employ continuous surveys to collect information.
You’ll enjoy the ability to adjust your marketing or product development in real-time to meet customer needs as the market changes.
Tip #3: Obtain a comprehensive view
The customer journey starts before potential customers purchase or sign up for services. Prospects begin their customer journey as they learn about offerings on your website, online review sites, or advertisements. After the awareness and discovery stages of the customer journey, consumers enter the purchase process. Customers experience your products and services when making a purchase and then form opinions.
Throughout these stages of the customer journey, you must know how customers feel about your business and products. For example, do you know what factors cause customers to choose you over the competition? How do customers perceive your sales staff? What do customers like about your products? Is your support team answering customer questions with accuracy?
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
There are six main steps to creating a customer journey map :
Step 01: Understand the target buyer’s persona: An organization must define its ideal buyer’s persona before journey mapping.
Step 02: Acknowledge the target audience’s intent: What does a buyer hope to achieve by interacting with a brand? What are their expectations?
Answer these questions by:
- Sending out online surveys to all the customers
- Organizing focus groups or one-on-one interviews
Then, develop action plans using the results of your research to meet buyer expectations.
Step 03: Note the touchpoints: Map all interaction touchpoints every time new customers visit your website or contact a sales team member. Include interactions before, during, and after purchase in your customer journey map.
Your organization should understand:
- Where customers obtain information about your website – Google search, social media, or Google ads.
- Which pages do most customers visit? What’s the average time spent on each?
- Did the customers enjoy shopping with the organization? Did they face any difficulties, and how helpful was the customer service team?
Step 04: Ask crucial questions: It’s essential to ask questions such as:
- Does my organization satisfy all the requirements of my target audience?
- In which stages of the customer journey do customers face common problems?
- Which website pages have higher bounce rates than what is acceptable?
If you interact directly with customers, be sure to ask them:
- How did you know about our organization?
- What were your expectations from our organization’s website?
- Were your expectations satisfied?
- What prompted you to purchase from our organization?
Step 05: Make a list of priorities: You can optimize customer journey mapping by identifying the areas that need immediate attention. Once you know common problems, you can take steps to limit their impact on customer loyalty.
Step 06: Put all ideas to paper: Most marketers prefer drawing the entire map on a whiteboard or using customer journey mapping tools to create a digital customer journey . Refer to your copy when you need to make decisions to improve customer experience.
Learn: What is the buyer’s journey , and what is its difference from the customer journey?
Free Customer Journey Map Template
At QuestionPro, we know that all this information can be overwhelming, and starting to create your Customer Journey without help can be intimidating.
That is why we have created a Customer Journey Map Template that we hope can help you start sketching the stages, UX, and overall satisfaction of your customers with your brand.
DOWNLOAD CUSTOMER JOURNEY MAP TEMPLATE (PDF)
How to Use Customer Journey to Improve Your Customer Experience?
Customers expect every exchange with a brand to be seamless from the start. Understanding the interactions at each customer journey touchpoint helps you satisfy customer needs and improves your business’s efficiency.
“Customer-centric companies are 60% more profitable than those not focused on the customer.” – Deloitte and Touche
To accurately map the customer journey, consider each stage of buying a product. At each customer journey stage, write down what a customer feels and the actions they must take to move forward.
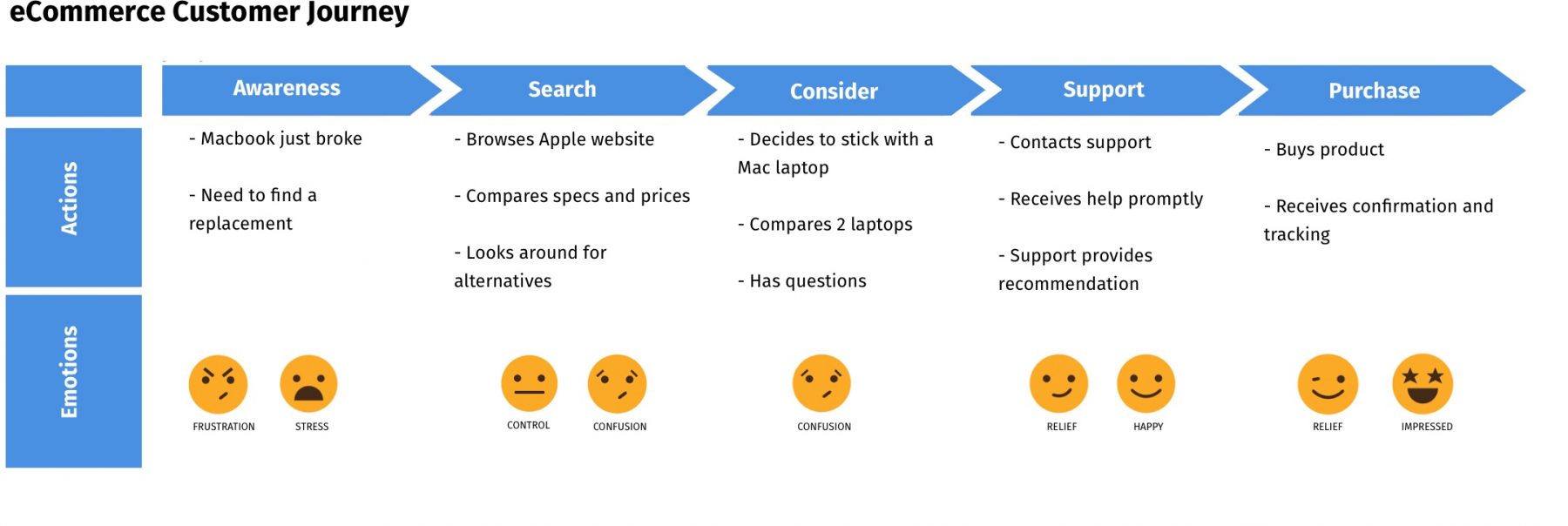
Examine the emotions at each touchpoint and rate the experiences. Is it positive or negative?
Begin to connect the dots and identify which gaps are falling short of your customer’s expectations. This exercise will help you formulate and decipher where you can have the most significant impact on improving the experience.
Learn more about the Customer Journey Canvas
Collect customer satisfaction feedback for more accurate results
Include your customer satisfaction scores as you map out your customer journey template. This additional information helps validate gaps or assumptions you make from mapping.
For example, your customer rates a CSAT score of 3 at their point of purchase and gives a score of 8 post-purchase. You immediately know that your point of sale requires attention.
Look at multiple customer satisfaction scores to find the most crucial pain points. If there is a customer journey touchpoint that ranks poorly for most customers, start your improvements there.
Start following your customer’s journey and create a detailed customer journey map. QuestionPro offers some of the most advanced customer experience tools available. Gain valuable insights into your customers’ thoughts and emotions using QuestionPro CX today.
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 10 Knowledge Management Tools to Enhance Knowledge Flow
Jul 10, 2024

CX Shenanigans: Booth Duty and Beyond — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Jul 9, 2024
Negative Correlation: Definition, Examples + How to Find It?

Customer Marketing: The Best Kept Secret of Big Brands
Jul 8, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing Customer Journey Map: What It Is & How to Create One
Customer Journey Map: What It Is & How to Create One
Written by: Jennifer Gaskin Dec 10, 2021

Creating a customer journey map gives a business the opportunity to visualize the path a person takes to become a loyal customer with your organization. A customer journey map is an excellent way to understand how consumers interact with your business.
Many companies use the customer journey map creation process to identify areas of improvement in their internal processes to help ensure all consumer interactions are the best they can be.
With Venngage’s Customer Journey Map Maker , you can easily create a customer journey map that aligns with your brand guidelines and helps all team members better understand your target customer.
Click to jump ahead:
What is the customer journey, what is customer journey mapping, why do businesses need to map their customer journey, steps to map a customer journey, how to create a customer journey map with venngage, customer journey map templates.
- FAQs about customer journey maps
Broadly, the customer journey describes how your customers or users interact with your organization. It is a way for companies to understand the complete customer experience and learn how to optimize it.
For a brick-and-mortar shop, that could be physical interactions like taking their trip through your store.
For companies that produce mostly digital products and services, the customer journey describes the consumer’s perspective as it relates to your company and its goods and services.
Mapping the customer journeys means understanding the path a person takes from becoming a lead or potential customer to transforming into a loyal patron of your business, so that you can visualize how a customer interacts with your organization at various points, as in the example below.

This customer journey map describes the journey the average customer of GLIDE App will experience, divided into different stages. You also see the steps the customer is expected to take, which customer touchpoints they’re going to interact with and how each touchpoint is coordinated with each business department.
As we’ve touched on, customer journey mapping means creating a visual representation of the entire customer journey: how existing and potential customers interact with your business. Some customer journey maps are map-like, while others are more linear, flowing in a straight line, and still others have unique shapes.
What all customer journey maps have in common is that they focus on the customer experience as it relates to the product you make or the services you sell.

This customer journey map is represented in a circle: customer journey begins with Discovery and ends in Conversion. You can also tell that this customer journey map illustrates the importance of continual customer engagement even after leads have turned into customers.

In this customer journey map, activities, motivations, emotions and barriers are all plotted against the stages of the buyer’s journey. At the start, customers have little to no awareness of the product and by the end, they are reliable returning customers — in an ideal world. Of course, to make this even more seamless, customer training software can be deployed as it helps understand customers’ use of products in their daily life.

This infographic takes the traditional customer journey map a step toward the customer by depicting a theoretical client, lead or consumer—or in other words, a buyer persona. This allows the organization to ensure they’re keeping the buyer top of mind at all times.
To learn more about buyer or customer personas, check out our posts:
- 10 Buyer Persona Templates, Examples & Marketing Tips
- 20+ User Persona Examples, Templates and Tips For Targeted Decision-Making

Taking into account the customer perspective, this customer journey map template plots the buyer’s activities along the top, from the moment they realize they need to purchase something until they’ve paid for it. The business can then populate the cells with the appropriate answers based on the metrics they are attempting to visualize; in this case, emotions, experiences and customer expectations.
Mapping the customer journeys can help businesses understand bottlenecks or pain points they didn’t realize existed. And it can help organizations diagnose internal issues by enabling them to visualize things from their customers’ perspective.
In short, customer journey maps give businesses a chance to develop a deep well of knowledge about their consumer beyond the metrics of sales or engagement. Putting themselves in the customer’s shoes and understanding why consumers behave as they do can empower an organization with all the tools it needs to better serve consumers. Moreover, integrating call center software helps businesses better understand and serve customers by managing inquiries efficiently and gathering valuable data.

This eCommerce customer journey map, for example, can allow a savvy sales, marketing or operations team to optimize customer satisfaction by correlating a bad customer experience with poor UI/UX design or other issues.

Customer journey maps are also useful for simplifying and visualizing only one aspect of the journey. In this case, the focus is the outreach tools a business uses to reach potential customers, but it’s easy to customize this type of design to apply to many other segments of the buyer journey or add details that can aid decision-making.

Use this type of customer journey map to visualize the content you’ll use in your marketing efforts at each stage of the buyer’s journey or sales funnel . Remember that it’s important to consistently offer leads and prospects something new to maintain their interest.
The first step to any successful journey is understanding where you want to go. In the case of mapping your customer journey, the first step is determining your end goal. Do you want to identify bottlenecks in your process, increase conversions or push new products? Think about what you want to get out of the process before you begin.
Once you’ve outlined your goals, you can begin the steps to mapping a customer journey.
Step 1 . In most cases, a customer’s journey should first be broken down into a timeline or customer stages. This typically follows the buyer’s journey (Awareness—Consideration—Decision) or a variation of that.
Here’s an example of a customer journey map that divides the common 3-stage customer’s journey into 5 stages:

Step 2 . From there, you should determine what should go down the side of your customer journey. In the case of the above example, the customer’s approach and resulting experience are listed.
Step 3 . List or visualize the customer touchpoints.
The template below does that by including a row in the graphic for physical and digital touchpoints. In some cases, you may consider listing these as pain points if all customers or this particular persona in question have to deal with a lot of hurdles to successfully move on to the next phase of the journey. This could be something like price or product availability.

Step 4 . Include solutions or opportunities for your organization to optimize the customer experience at each step. That could mean removing pain points or roadblocks, such as offering them discounts or other incentives to select your company.
Visualizing your customer’s journey can be difficult without using the right customer journey mapping tools.
Venngage makes it very easy to create a customer journey map by offering dozens of templates that you can quickly customize with your company’s information. With just a few clicks, you can list out the steps of your customer journey and detail the experiences at each point.
Check out our library of customer journey map templates you can easily customize:

Notice the Smart Templates? They are created with our Smart Diagram editor. You can easily add icons, move things around and space the design elements however you like. As you add or delete text, the editor will automatically adjust so you won’t need to resize anything.
For businesses that want to have consistent branding across their customer journey design, you can use My Brand Kit to apply brand colors or logos to your customer journey map in one click:
Here are a few more effective customer journey map examples to inspire you as you work to create your buyer’s journey to better understand your consumer.

This customer journey map lists the stages of the process across the top and the categories the organization must consider down the side. Organizing your buyer’s journey in this way allows you to visualize each issue at a glance and make correlations between segments and outcomes.

Similarly, use this customer journey map to quickly see which channels apply to what phases and what opportunities exist for reaching out to potential buyers during each segment along the way.

Buyer’s journey maps can also lean toward the simple size, as in this example, which is appropriate for companies that need to list digital and physical touchpoints along with opportunities that could help convert leads to customers.

When considering your customer journey, it’s important to think about how your customer has changed after every contact with your organization. In the beginning, they may not know exactly what they need, and then by the end, they should be more confident about what you can do for them.

Remember that not all customers are the same, and pain points for one person may not be pain points for another. So, it’s best to make customer journey maps for your major buyer types or personas.
FAQ about customer journey maps
Do you have more questions about customer journey maps? We’ve got answers.
What are the 7 steps to map the customer journey?
When creating a customer journey map, many experts recommend the following seven steps:
- Set targets
- Create buyer personas
- Identify motivations and define barriers or pain points
- Visualize buyer journey
- Maximize touchpoints
- Identify opportunities to establish trust
- Test and revise
What do you use a customer journey map for?
Customer journey maps are useful for visualizing a buyer’s interaction with your company. This can help you understand your buyer and their motivations better, as well as helping you identify reasons why they might not choose your business, thus changing strategy or decision-making to make your organization more attractive.
Ultimately, creating a customer journey map can help you learn what the customer needs and know how to provide consistently excellent service to acquire new customers as well as retaining customer loyalty.
What are touchpoints in customer journey maps?
A touchpoint in a customer journey map describes a moment in which your customer interacts with your company or brand, and a customer journey map should include all touchpoints along the way.
In summary: Optimize the customer experience by creating a customer journey map
With Venngage’s Customer Journey Map Maker , you can quickly and easily visualize your customer journey so you can eliminate pain points, resolve bottlenecks and better understand how to give your customers what they want. It’s free to get started.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Customer Journey Map (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]
Home » Customer Journey Map | 🕑
Gust de Backer
June 29, 2024.
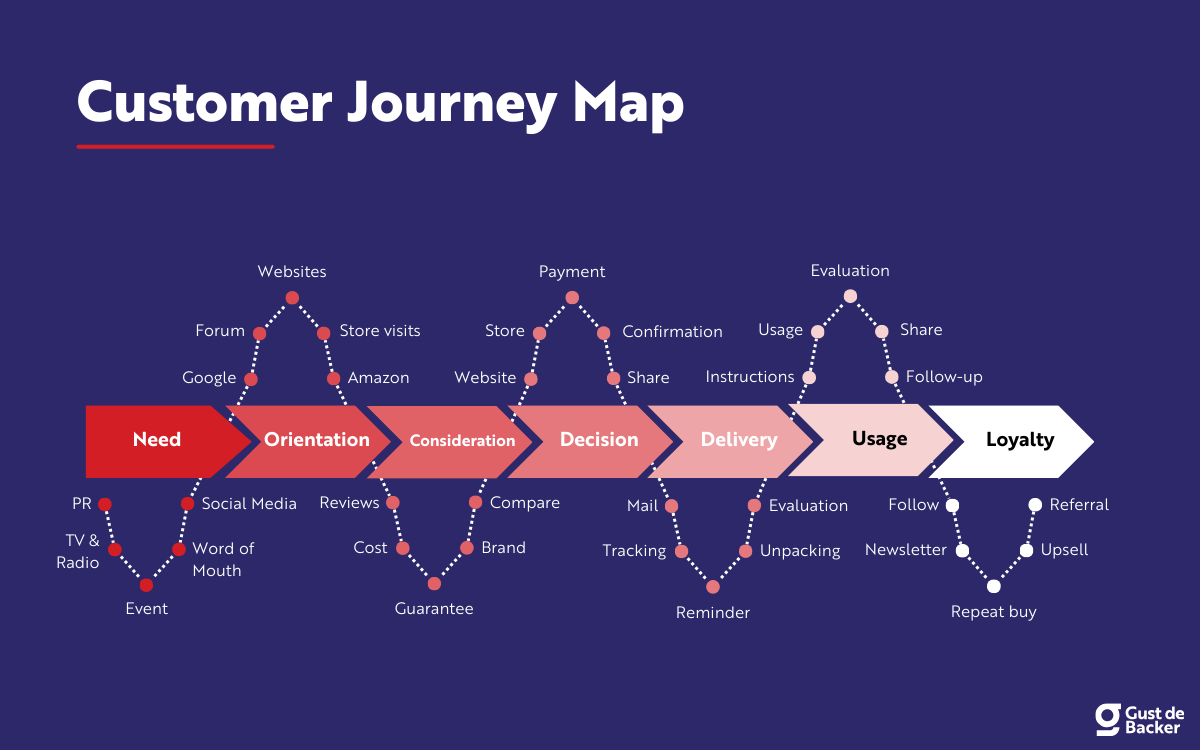
👉🏻 Workshop / Keynote / Consultancy
The Customer Journey is the process your customers go through with your company. This then covers the first to last interaction someone has with your company.
Many companies do not have a map of how their customers orient, what they care about or when the company comes into the potential buyer’s mind.
Not having enough mapping of the Customer Journey puts you at risk of having, perhaps unknowingly, negative touchpoints with your (potential) customer.
I’m going to show you:
- What the Customer Journey is
- How to create your Customer Journey
- And what good examples of a Customer Journey are
Let’s get started…
Table of Contents
What is the Customer Journey?
The Customer Journey is the process that maps every interaction with your brand:

The first interaction someone has with your brand is the beginning of the Customer Journey. If you find yourself in a niche market, it can also be interesting to map interactions with your niche.
The Customer Journey for B2B and B2C often looks quite different:
The Customer Journey is relevant to any business, but particularly important for companies that:
- Are customer-centric
- Want to improve customer satisfaction
- Want to increase sales
In general, you often see in companies that the marketing department is responsible for ensuring that (potential) customers have a positive experience with the brand.
A nice trend you see is that marketing/growth teams are becoming more responsible for the entire funnel rather than just reaching and bringing in new customers.
7 Stages of the Customer Journey
There are different models you can use to map out the Customer Journey, but in the end they all boil down to the same thing:

Keep in mind the different roles of the Decision-making Unit , but essentially there are 7 steps you can include in the Customer Journey….
Your (potential) customer can have 2 types of needs:
- Latent need : the person does not yet know he needs something. If you are going to buy a car you are not yet directly concerned with insurance.
- Concrete need : the person knows they have a certain need, here it is important to be visible with your brand. For example, think of buying a phone when your old one is broken.
Every Customer Journey basically starts with a certain need.
In practice, you can encounter 5 types of customers in this:
- Unaware : don’t realize they have a problem or need.
- Problem Aware : realize they have a problem or need.
- Solution Aware : they know there are solutions to their problem or need, but they don’t know you.
- Product Aware : they know you, but haven’t bought you yet.
- Most Aware : brand ambassadors.
2. Orientation
The orientation process has changed a lot in recent years thanks to digitalization, which makes it extra important to map it out using research.
You want to be visible with your brand at least in the orientation phase so that you will eventually be included in the consideration phase .
Some examples of behavior in the orientation phase:
- Concrete keywords in search engines
- Asking acquaintances for their opinions
- Checking out inspiration platforms such as Pinterest, TikTok or Instagram
3. Consideration
In the consideration phase, we examine which option from the orientation phase best meets the customer’s wishes and needs.
Here it is important to know which decision criteria weigh most heavily for the customer; this should be properly researched.
Some examples of decision criteria:
- Brand awareness
4. Decision
In the decision phase, a product or service from a specific vendor is actually chosen.
There are a number of things that make it easier for the customer to choose your product or service:
- Make it easy to compare
- Provide a good selection in different options
- Offer a good deal, make sure your customer can’t say no
- Provide a smooth payment process
- Increase engagement in your brand by providing valuable content, offers and support
Provide as few distractions as possible during the decision phase, people who are still Googling “[company name] discount code” from the checkout want to be convinced to convert.
5. Delivery
After someone has become a customer, a product or service will need to be delivered.
Here the first moments of evaluation will be whether someone actually made the right choice to choose your company, product or service.
- Make sure you deliver on time and that your product arrives in the right condition or that your service is of high quality.
- Give clear instructions on how to use or what the added value of the service is.
- Provide good support if the customer experiences problems in using your product or service.
In the use phase it is important that customers get the most out of your product or service and that they really see the added value .
You can stimulate this in a number of ways:
- Include tutorials
- Measuring and communicating impact
- Aftersales phone call
This is the ultimate evaluation moment ; if your product or service did not help the customer well, there is little chance that they will make a repeat purchase or become a brand ambassador .
In any case, it is important to prevent people from talking badly about your brand, so make sure that in the earlier stages you already make sure that people who are not ideal customers for you are excluded and that you make sure that customers see the added value of your product or service.
It is 5 to 7 times cheaper to retain a customer than to bring in a new customer. This is precisely why it is so important to encourage loyalty.
Loyalty can be expressed in the number of repeat purchases or upsells a customer eventually makes with you. You can encourage this by offering valuable content, offers and support.
The goal is for people to remain loyal to your brand and not switch to a competitor or go out of business in the first place.
There are different forms of loyalty:
- Transactional Loyalty : getting customers to make repeat purchases by giving offers.
- Social Loyalty : interacting with your customers on social media, for example.
- Engagement Loyalty : you reward people who engage with you where you can receive points for subscribing to a newsletter, for example.
- Emotional Loyalty : if your brand is positively aligned with your customer’s emotions, you can’t get this kind of loyalty with offers. In this, you want to make people feel part of something.
- Behavioral Loyalty : a level of loyalty in which you want to make customers do something like buy higher volumes where you give a third product for free after buying 2 products.
- Advocacy Loyalty : you are going to reward people who recommend others to become customers of your brand.
Customer Journey Mapping
Download the Customer Journey Canvas:

Good choice! Check your e-mail for the resources...
How do you complete the Customer Journey Canvas?

Once you know who all is in your Decision-making Unit, you can start creating personas and empathy maps so you can better understand the behaviors, needs, problems and wants of those individuals.
Determine what questions you would like to have answered after doing your Customer Journey Mapping research. Some common questions are: – When do you experience X? – On a scale of 1 – 10, how much would you like a solution to X? – How much are you willing to pay for a solution on X? – How would you orient yourself to a solution for X? – What brands would you consider in a solution for X? – What should a solution for X satisfy you in? – How would you go about determining if the solution was effective?
The threshold in terms of time and cost is often somewhat lower for quantitative research than for qualitative research. In it, you can gather good insights about your target audience from a helicopter perspective. Consider, for example: – Questionnaire – Post-purchase survey – Exit-intent Survey – Search volume
Once you have a high-level validated understanding of your target audience, you can begin to supplement your findings at a detailed level using qualitative research. Consider: – Customer interviews – User tests – Screen recordings
If you have made your Customer Journey Map comprehensible, you have gathered many insights on which you can improve your Customer Journey. To prevent it from becoming a dusty document that is no longer looked at, it is important to determine follow-up actions and evaluate them accordingly.
Common mistakes
There are a number of mistakes that you often see passed in Customer Journey Mapping:
- Based on assumptions : often you see that a Customer Journey is completely based on assumptions and not on validated research.
- Wrong scope : critically determine in advance where you want your Customer Journey to begin and end otherwise you quickly lose focus and overview.
- No customer perspective : reason the Customer Journey from your persona or customer and not from your company.
- Inside-out : if you start from how you do it as a company you are not customer-centric and there is going to be a mismatch in how the customer experiences something and how your company does it. Make sure your Customer Journey is actually completed from the customer’s perspective.
- Stakeholders : it is important to involve all relevant stakeholders so that you start creating support for the Customer Journey.
- End goal : the Customer Journey is not an end goal, but a starting point. It is something that will continuously play out and needs to be changed.
And now you…
Now you’re armed with enough knowledge to start visualizing your Customer Journey.
I’m curious, what has been the biggest insight for you in understanding your target audience?
Let me know in a comment.
P.S. if you would like additional help you can email me at [email protected]
Frequently Asked Questions
The 7 steps of the Customer Journey are: need, orientation, consideration, decision, delivery, use and loyalty.
A customer journey is a term used in marketing and customer experience management to describe the path a customer takes through the stages of awareness, consideration, purchase and use of a product or service. The term can also be used to describe the path a potential customer takes.
A customer journey map is a visualization of a customer’s experience with a company, product or service. It begins when the customer first becomes aware of a need and ends at the level of loyalty. The map tracks all the contact moments the customer has with a brand, both online and offline. Customer journey maps can help companies understand where they need to make improvements to provide a better experience for their customers.
The Customer Journey for every business is different. It is important to research for your business what the most ideal customer journey is, in doing so you want to validate all assumptions.
I try to help business surpass their growth ceiling with my content.
Sounds interesting?
Let’s connect on LinkedIn!
Account-Based Marketing | Business Strategy | Customer Development Process | Customer Journey | Decision-Making Unit | Digital Marketing | Lead Generation | Market Research | Marketing and Sales | Marketing Strategy
Gust’s Must-Reads 👇🏼
- TAM SAM SOM
- Value Proposition
- Decision Making Unit
- Product-Market Fit
- North Star Metric
- Market Research
- Customer Development
- Growth Hacking
- Brand Identity
- Customer Journey
- Account-Based Marketing
![customer journey how to Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/151-Cognitive-Biases.png)
Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]
Cognitive biases, there are so many of them... Decisions we make based on emotion, cognitive biases are irrational 'errors' that are programmed into people's brains and affect the decision-making process. Plenty of different articles have been written and an entire...

What is Growth Hacking? (2024): Best Strategy to Grow Your Business
The popularity of Growth Hacking is increasing rapidly, but what is Growth Hacking? Many companies lack a clear strategy for achieving growth and don't know how to manage a (marketing) team in it... Many marketers and entrepreneurs find Growth Hacking the best way to...
![customer journey how to Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Ultimate Guide [+ Checklist]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Conversion-Rate-Optimization-CRO.png)
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Ultimate Guide [+ Checklist]
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) aims to increase the conversion rate using experiments based on quantitative and qualitative data. Are you getting enough visitors, but would you like those visitors to convert faster, better or more often? You suspect there's a...
Ziet er zeer volledig en praktisch uit.
Bedankt Nicole!
Thanks! I’m trying to understand how to explain this approach in simple words, and your material is one of the best so far.
Thank you, Marie!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Customer Journey Map
You have successfully subscribed, proven (marketing) management tactics 12x / year.
✔ Discover the secrets of successful companies.
✔ Make better decisions and avoid bad choices.
✔ Never miss out on any growth for your company.
Function Owner C-Level Manager Marketer Sales Student
Thank you! You have successfully subscribed.
7-day free trial | No credit card required
10,000+ teams use Hiver to delight their customers!

Table of contents
A detailed guide to customer journey mapping.
Customer journey mapping. Sounds like a fun exercise, but is it actually helpful?
Done well, a customer journey map can be many things: a blueprint for business decisions, a shared vision for your team, and a yardstick to measure progress.
In this piece, we’ll unpack how you can create a customer journey map that’s actually useful, and best practices to make it more powerful.
Let’s go.
Table of Contents
What is customer journey mapping.
A customer journey map helps you understand how customers experience your product.
You trace the customer’s footsteps throughout your product and use feedback and other qualitative data to identify points of friction and delight. The goal is to enhance the overall product experience.
As per one report, customer experience beats price when it comes to buying decisions. Another PWC report found that 73% of customers consider customer experience as a key factor when purchasing a product.
Customer journey maps help you take that first step towards delivering a great experience .
The process of creating a strong brand identity starts with marking different customer touchpoints, including your website, landing pages, product pages, help documents, payment gateway, social media, chat, or phone support. This includes designing a visually appealing logo that represents your brand and can be displayed prominently on all these touchpoints, especially on your website and social media profiles. A well-crafted logo design can help increase brand recognition and credibility, and make your business stand out from the competition.
Then, at each stage, you label customer emotions based on feedback from surveys, social media, and support.
All of this comes together visually in a customer journey map that provides a complete picture of the customer’s frustrations and wins.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
We’ve seen why customer journey maps are important. But how do you actually build one that’s a source of truth for all teams, and not another vanity project?
Take a look.
1. Define the scope of your customer journey map
Before you start lining up the wall with sticky notes, you’ll need to ask a few questions.
Once you’ve set goals and objectives for your map, it’s time to get down to business.
2. Compile customer data
Depending on the buyer segment or persona you choose to focus on for your map, it’s time to go a-fishing for data and feedback .
What are we looking for? The different routes customers take inside your product, the ways they find your brand, and clues into how they feel while using your product. Here are some reliable sources to find this information:
If you use customer support software such as Hiver , you can easily create detailed reports to reveal trends in your customer service data.
3. List all possible customer touch points
Let’s say you run an e-commerce website that sells second-hand furniture. Some users may land up on your website through a social media post. These customers may casually browse through your product catalog and sign up for your newsletter.
A small number of those who sign up may open your newsletter. From there, they’ll probably click on a sale item and proceed to purchase. But, the journey isn’t over yet. The updates they receive on their purchase and the feedback they leave, if any, counts too.
Each of these stages – from social media to catalog to newsletter and onward – is a touchpoint in the customer journey. Every customer will forge a unique path inside your product. For instance, some customers may chance upon a PPC ad, browse your catalog, and head off from there. Others may become repeat customers.
Your goal is to visualize as many possible paths a given buyer persona may take, and note down all touchpoints along the way. It also helps to divide the buyer journey into three phases: before, during, and after purchase, to better segregate touchpoints.
4. Connect the dots
You’ve got your data and you’ve got a list of touchpoints, now it’s time to put two and two together. For each touchpoint, see if you have any customer data and qualitative feedback to analyze.
Let’s start with social media. Are customers aware of your presence? How much traffic does it drive to your website? It doesn’t matter if you have more escalations or shoutouts, you’re looking for ways to improve the touchpoint itself to add more value.
Look at your website next. How do customers land on it? Which pages do they click on most? Conversely, do they ignore prominent pages?
Then, dig deeper into the reasons. Is your website design and development user-friendly? What about site speed? Any complaints about your check-out process? Pages with 404 errors?
Another important question you want to ask: are there too many hoops customers have to jump through to get where they want to? Touchpoints, where customers drop off, are a good place to investigate this.
You’ll start to see a pattern of customer emotions emerge for each touchpoint in the journey. In certain areas, you’ll also find insights about why customers feel a certain way and how to improve their experience.
5. Take the journey yourself
The process of customer journey mapping will remain patchy if you don’t step into your customer’s shoes.
To get a real sense of customer frustrations, obstacles, and pain points, revisit each customer touchpoint yourself. Check if your emotions are in sync with those your customers may be feeling.
6. Make it visual
There’s a reason why visuals have a special place in marketing: they’re processed faster, they’re easily comprehensible, and they boost recall.
Thus, the best way to make your customer journey map easily accessible to all teams is to compile all of your findings and inferences into a handy map.
If you work on-site, you may do this with the help of post-its on a wall.
If you’d rather have a virtual copy of your customer journey map, use an online tool such as Google Sheets, Trello, or a dedicated mapping tool such as MindMeister to create a visual representation of your customers’ journey.
7. Let all teams pitch in
Customer journey mapping is incomplete without your team’s perspective.
Each team has its own set of data points and experiences to add more nuance to your findings.
The product team has a pulse on the features customers need, while your marketing team has a better handle on the optimum number of touchpoints. Your support team can add more color to customer feedback, explaining the backstory behind each request.
Let all teams brainstorm, so you can build a more comprehensive customer journey map.
8. Share results and next steps
Once you’ve built a complete picture of your customer’s journey, it’s time to identify roadblocks and come up with suitable solutions.
In some areas, the fix may be easy: bumping up website speed, fixing bugs, improving checkout processes.
Other problems may need more reflection: improving support resolution times, making your marketing memorable, launching a new app.
No matter what, don’t leave this exercise without assigning specific, actionable steps to each team.
Review your progress periodically and see if the journey becomes more fun and less of a hassle for customers.
Types of customer journey maps
Depending on the scope of your map and the types of insights you’re looking to mine, customer journey maps could take different forms.
These include:
1. Current state customer journey maps:
These maps reveal improvements you’ll have to make to your product, based on recent customer experiences. Here’s a current state customer journey map template you can use:
2. Day in the life customer journey map:
These provide you with snapshots of your customer’s day: their actions, touchpoints, and emotions. It may or may not involve your brand.
The idea is to get a general sense of your customers’ frustrations and motivations on a day-to-day basis. This helps you design moments of delight and remove friction from your product.
Here’s a day in the life customer journey map template you can use:
3. Future state customer journey maps:
While current state journey maps aim to uncover problems, future state journey maps are about envisioning the future. Ideally, you take existing journey maps and forge new paths to see if you can create new experiences for customers.
For example, if you have a website, you might want to create a future state map of how an app for your product might help your new and potential customers.
Here’s what a future state customer journey map template looks like:

Four benefits of customer journey mapping
A customer journey map is a window into your customer’s world. But it offers other benefits too, for your team and business. Take a look.
1. Align teams to a common goal
60% of business leaders believe that misalignment between sales and marketing could damage financial performance.
Often, marketing has little visibility into the questions the sales team gets asked. On the other hand, the support team may fail to share their learnings from customer interactions with the rest of the organization.
A customer journey map helps you fill in the gaps and build a sense of alignment among teams.
2. Increase customer retention
We’ve belabored the importance of customer experiences, but here’s another important finding: 91% of customers who have a poor customer experience won’t willingly do business with a company again.
Customer journey maps unveil the causes of poor customer experiences and help reduce customer churn .
3. Build moments of delight
As important as averting a bad user experience is, it’s equally essential to sneak in moments of delight in your product experience. These convert customers into fans and advocates.
Ease of use, proactive customer service, empathetic copy – all these are examples of weaving in ‘wow’ moments in your product.
4. Improve your messaging
Customer journey maps show you the different pitstops customers make, and whether or not you’re providing enough direction to guide customers. It might help you discover that there’s missing information in one of your product catalogs, or that the messaging on your pricing page is unclear. Some sites use deep linking to make it easier for customers to navigate through different product pages and blogs.
You can also gauge if you’re telling a cohesive brand story across different customer touchpoints: your social media page, website, product catalog, and emails.
Three best practices for customer journey mapping
Here’s a set of cheat codes to help you get the most out of your customer journey mapping exercise:
1. Map journeys for all customer personas
It’s not enough to map customer journeys for your most profitable customer segments, though that’s a good starting point.
Once you’ve mastered the art of building a customer journey map, repeat the exercise for different customer profiles. This will help you add more brand advocates and reduce detractors.
2. Make it accessible to everyone
A smooth customer journey requires teamwork. Don’t let your customer journey map exist in silos. Involve your team members. Let the map serve as the single source of truth guiding all business goals and decisions.
From customer support to product development to marketing, each team benefits from a closer view into customer behavior and motivations.
3. Update journey maps regularly
A customer journey map should be a living, breathing document that evolves just as your business does.
Add fresh insights, data points, new touchpoints, and feedback as often as possible.
Customer journey maps are the path to customer-centricity
Each team has its own definition of what customer-centricity means.
A customer journey map helps you bind all of these different viewpoints into one, cohesive narrative. It serves as a single reference point for all proposed changes your product may or may not need.
The next time you’re unsure about introducing a feature or wondering why a launch didn’t go as planned, take a careful look at the entire customer journey on your customer journey map and ask, “How did it affect the customer’s journey? How did they feel about it?”
That should give you some direction.
Deliver stellar customer support right from Gmail

Email Signature Templates for Gmail and Outlook
Email signatures are an important part of professional communication. They are more than just a way to sign off your emails; they...

Zendesk vs Intercom – A Detailed Comparison
Dive into our analysis of Zendesk and Intercom, focusing on their approaches to customer engagement and support. While Zendesk...

11 Customer Retention Strategies you shouldn’t overlook in 2024
In the immersive realm of the ‘experience economy’, businesses don’t just sell products or services – they craft...

Hiver has come along as a trustworthy, discerning, and dependable sidekick that has helped us manage our emails better and faster.

Hiver is extremely easy to use. We were able to hit the ground running right from day one. Plus, their customer service is fantastic!

We're 100% Gmail. Working on customer queries from Gmail was exactly what we needed. Moreover, moving to Hiver was a painless affair.

20 Customer Journey Touchpoints Examples + How to Optimize Them

Looking for examples of customer journey touchpoints?
If yes, you’re in the right place.
The article explores 20 major touchpoints in a SaaS product journey. And shows you how to optimize them for better conversions and higher customer satisfaction.
Let’s dive in.
- Customer journey touchpoints are moments or points of contact where customers interact with the product or brand.
- To identify the key touchpoints, first research customer expectations and needs. Then, study their interaction patterns at different journey stages using analytics and surveys.
- The purpose of the touchpoints at the pre-purchase stage is to capture the attention of potential customers and showcase product benefits .
- Examples of touchpoints at this stage include paid ads, blog articles, social media posts, marketing emails, webinars , customer reviews, and referrals.
- During the purchase phase, the touchpoints need to be optimized to enable customers to make informed decisions and to convince them to buy it.
- The purchase-stage touchpoints include free trials, demos , pricing and comparison pages, and customer testimonials.
- After the customers buy the product, the role of the touchpoints is to support customers and provide a positive experience . They are responsible for customer satisfaction, retention, and account expansion .
- Examples of post-purchase touchpoints include thank you and welcome emails, upsell and cross-sell messages, onboarding flows , self-service resources, and new feature announcements .
- Looking to optimize your customer journey touchpoints? Book Userpilot demo!
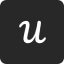
Try Userpilot and Take Your Customer Journey to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

What are customer touchpoints?
Customer touchpoints are all the points of contact between the customer and the brand or the product along the customer journey .
By ensuring a positive customer experience across all touchpoints, SaaS companies can increase customer satisfaction , boost conversions, and strengthen relationships with their customer.
How do you identify customer touchpoints?
First, research your customers to find out what their needs and expectations are.
Next, analyze customer interactions using analytics tools and collect feedback about their background.
Finally, create a customer journey map with all touchpoints and associated actions, challenges, opportunities, and user feelings.
Important customer touchpoints before the purchase
The touchpoints at this stage get your product on the potential customer’s radar. They showcase its value and encourage them to explore what it has to offer in more depth.
1. Advertising
Advertising isn’t the most organic way to promote your product, but it’s very effective.
That’s because you can get it in front of your audience immediately and target very specific customer segments. This is particularly the case with PPC ads, like those on Google or social media. And retargeting enables you to keep them engaged with your brand.
Targeting and retargeting have one more benefit: they allow you to personalize the messages. That’s how you can highlight specific use cases and product benefits to relevant audiences.
To optimize your ads, track the performance of your campaigns with tools like Google Analytics and run A/B tests to identify those that best convert into landing page visits.

2. Content marketing
Content marketing involves creating and distributing valuable content. Like blog posts, whitepapers, eBooks, or video tutorials .
Product-led content , which presents your product as a solution to customer problems, can be particularly effective at attracting new customers and converting them into free-trial or demo bookings .
To get a good ROI on your content, ensure it addresses genuine user pain points and offers actionable insights.
To help your users find it, optimize it for search engines and distribute it across other channels , like social media. And track its performance to identify content that best resonates with your target audiences.

3. Social media platforms
Social media platforms are the most popular marketing channel at the moment. Platforms like LinkedIn, X, Facebook, YouTube, or TikTok are spaces where you can engage with potential customers, share your content, and build brand awareness.
To get the most out of this touchpoint, choose the platforms where your target audience hangs out. Post regularly to keep your audience engaged and respond to their comments and messages to build a community around your brand.
Visual content resonates best with social media users, so invest in videos , high-quality images, infographics, and carousels.

4. Email marketing
Email marketing involves sending targeted emails to potential customers to nurture leads and drive conversions. These could be newsletters, promotional offers, or drip campaigns.
Just like with other types of touchpoints, personalization is the key to email marketing success. Segment your email lists to send relevant messages to different audience groups, for example, based on their interests.
To increase open rates, craft engaging subject lines. Questions and subject lines with numbers tend to perform particularly well.
Finally, include strong CTAs in your emails to drive desired actions.

5. Webinars and events
Webinars and life events are an excellent way to attract new customers. They also keep your existing customers engaged and help them maximize the product value .
The idea is to run events that address common customer problems. For example, our July webinar focuses on converting free trials into paid accounts , which is one of the cornerstones of product-led growth .
Here’s the kicker:
In the webinars, we show the audience how to tackle their challenges with Userpilot capabilities.

6. Customer reviews
Customer reviews on pages like G2 or Capterra can encourage potential customers to explore your product further, so they should be part of your customer touchpoint strategy.
How do you optimize this touchpoint?
- Make sure your product pages on the review sites are up-to-date.
- Actively encourage existing customers to leave reviews . You can do it by targeting them with in-app messages .
- Always respond to feedback, especially if it’s negative . This shows your commitment to customer satisfaction and builds trust .

7. Word-of-mouth marketing
Word-of-mouth marketing is the most effective marketing types, both in terms of conversions and cost . Customers are more likely to trust people they know than your marketing campaigns.
While most of your happy customers promote your product organically, you can motivate them to go that little bit further. Set up a referral program and reward them for every new customer they refer.
Just like Revolut, a UK-based bank, which offers £40 to every newly-referred customer who set up an account.

Important customer touchpoints during the purchase decision
Having captured the attention of the potential customers, it’s time to close the deals now. Here are the key touchpoints that can help.
8. Free trials
Free trials give users the chance to try out the product before they commit to the purchase. The principle is simple: instead of telling users what the product can offer, let them experience it firsthand.
How can you optimize the touchpoint?
- Use analytics to determine the ideal trial length . It needs to be long enough to activate users.
- Cap usage to let users experience value without satisfying all their needs .
- Create personalized onboarding experiences to reduce time to value .
Demos can quickly showcase product features and benefits to the customers.
Live demos are particularly useful for complex products whose value may be difficult to experience during the trial. By showing users how relevant features work, they allow them to use the free trial more productively.
For best results, tailor your demos to specific use needs and use cases and make them interactive so that participants can ask any questions that they might have. You can also email the recording to the participants so that they can review it at their own pace.

10. Pricing pages
Pricing pages provide detailed information about the various pricing plans, features included, and payment options available for the SaaS product.
To help customers make informed decisions, present the pricing details clearly and transparently: show the final price without any hidden fees. Add-ons make things unnecessarily complicated.
On your pricing page, include comparison tables to highlight the differences between plans.
To increase conversions , provide information about free trials, discounts, and special offers.

11. Comparison tools
Comparison tools help potential customers compare how your SaaS product stacks against competitors. These could be in the form of interactive web tools, downloadable comparison charts , side-by-side feature comparisons, or X vs. Y blog posts.
To do their job, the comparison data needs to be up-to-date. And keep the resources objective. Biased comparisons are easy to see through and erode trust in your brand.

12. Product reviews and testimonials
Customers trust reviews and testimonials more than your marketing materials. In fact, 88% of customers tend to trust reviews from strangers as much as from people they know.
They hinge on powerful psychological principles to build your credibility and authority. Customers who see that other well-known companies have chosen your product are more likely to ‘conform’ to become a part of the exclusive club.
Add testimonials and reviews to your money pages. Use images of real people, or even better, videos , as they convert the best.

Important customer touchpoints after the purchase
The customer swiping their credit card is just the beginning. The post-purchase touchpoints ensure they get adequate support and can get the value they’re paying for.
13. Thank you emails
Thank you emails are sent to users immediately after the purchase. To show your appreciation and confirm their transaction.
How do you write good thank you emails?
- Provide information on what the customer can expect next.
- Add a CTA that takes them to the login page or triggers an onboarding flow .
- Include links to additional resources, like tutorials .
- List well-known customers and include more testimonials to reassure the buyer they’ve made the right choice. In case they’re experiencing buyer’s remorse.
14. Upselling and cross-selling
Upselling and cross-selling involve promoting higher-tier plans or complementary products to existing customers to increase their lifetime value . And offer more value to customers.
You can achieve this through in-app messages that highlight the extra benefits of the add-ons or higher plans and prompt users to buy them.
Upsell/ cross-sell messages are most effective when they:
- Target users who are ready for the upgrade, for example, power users.
- Are triggered contextually when the user experiences the need for a premium feature or hits a usage limit.

15. Customer service touchpoints
Customer service touchpoints are interactions where customers seek help with their issues or questions. For example, via live chat, phone, or email.
Having frictionless access to support is essential for customer satisfaction. A lack of it can lead to churn as users’ patience runs out.
Here are some optimization tips:
- Provide support via multiple channels .
- Aim for quick response times.
- Train the customer service team to ensure product knowledge and excellent communication skills.
16. Welcome emails
Welcome emails are the first emails sent to new customers.
Just like thank you emails, they introduce customers to the product and provide essential information.
They follow the same rules: they are personalized , provide clear instructions on the next steps, and include links to onboarding resources, FAQs, and support contacts.

17. In-app onboarding
In-app onboarding involves guiding new users through the product’s features and setup process directly within the application. Using tools like tooltips , interactive walkthroughs , and checklists.
- Use progressive disclosure to introduce information gradually. Not to overwhelm users.
- Personalize it based on their use cases. To make it relevant.
- Use interactive elements and gamification to increase engagement and information retention.

18. Customer loyalty programs
Customer loyalty programs reward repeat customers with benefits like discounts, exclusive access, or reward points. The purpose? To strengthen relationships with customers and drive retention .
For example, you could create a points-based system where customers earn points for completing tasks or reaching milestones, and can exchange them for perks.
You can optimize this touchpoint by offering valuable and relevant rewards, clearly explaining how the program works, and keeping them informed about the rewards they’ve earned and new opportunities.
19. Self-service resources
Self-service resources, like knowledge bases, resource centers, or chatbots , allow customers to find answers and solve issues on their own without contacting support. 24/7.
How to optimize them?
- Ensure the resources cover the most common issues comprehensively.
- Keep content up-to-date with the latest information and product updates.
- Collect customer feedback to improve the resources.

20. New feature releases
SaaS teams can communicate new feature releases and updates via multiple touchpoints: email, in-app messages , blog articles, social media posts, and release notes, to name just a few.
To ensure the users engage with the new features:
- Clearly explain how they work and what benefits they offer.
- Showcase use cases.
- Create how-to guides , tutorials, and onboarding flows to drive adoption .

Well-optimized customer journey touchpoints provide potential and existing customers with the information they need and drive desired behaviors. This translates into higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. And better business performance.
If you’d like to learn how to use Userpilot to identify and optimize customer journey touchpoints in your SaaS , book the demo!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
9 customer experience software to improve customer satisfaction.
Aazar Ali Shad
Identifying and Optimizing Customer Journey Touchpoints
How to Create Customer Journey Maps You Can Actually Use
Customer journey maps tell the story of how people behave when interacting with your brand across different touch points. Creating a journey map helps businesses make sense of consumer behavior—ultimately helping to improve and optimize the user experience.
Lots of “experts” out there make this process way too complex.
At Crazy Egg, we take a simple and logical approach to creating customer journey maps–we cut out the noise and get straight to what matters.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map from Scratch (In Just Four Steps)
With a customer journey map, your business can easily visualize all of the steps and experiences a customer has with your brand. Framing this experience as a story helps put yourself into the shoes of buyers so you can better understand their wants and needs at every stage.
Using a visual representation of your customer journey provides a bird’s-eye view of every potential turn or action someone can make while interacting with your brand.
Then you can make critical changes to your marketing and business strategy to improve the customer experience based on all potential scenarios.
Step 1: Create Content for Each of the Five Purchasing Stages
The first thing you need to do is understand the five stages that drive every purchasing decision—awareness, consideration, conversion, retention, and loyalty.
Then, you need to have a good mix of quality content that appeals to buyers at different stages of the purchase process.
Here’s a closer look at the types of content you should have for each of these five stages:
Awareness — The goal here is to create content that attracts leads and encourages them to become customers. People in this stage may not even know what products or services you provide yet. So you’ll need to create educational and informative content, like a variety of blog posts , podcasts, ebooks, explainer videos, and social media campaigns to help boost awareness.
Consideration — By now the customer knows who you are and what you offer. You can use content like case studies, webinars, testimonials, and product comparison guides to help steer them toward your brand over market alternatives.
Conversion — All content in the conversion stage should directly trigger the consumer to make a purchase. Highly targeted email campaigns, free trials, free demos, and cart abandonment campaigns all fall into this category.
Retention — Retention content should always deliver some kind of value to your existing customers while also keeping your brand top of mind. At this stage, you could encourage users to download your mobile app or send them emails with helpful tips for getting the most out of your products or services. You can also create promotional content to encourage upgrades and cross-sells.
Loyalty — At the loyalty stage, everything you do should be about getting your retained customers to spend more money and increase their purchase frequency. Aside from creating customer loyalty programs, you can also develop referral programs at this stage that allow your best customers to become your biggest advocates.

We’re just barely scratching the surface here with the types of content you can create at each stage. That’s because this content will look really different depending on your industry and what you’re selling. That’s really a much larger topic that falls outside the scope of this guide, so let’s get our focus back to the journey map.
The goal of this step is to ensure you’re drawing in people from all parts of your conversion funnel.
If you’re missing content at different stages, spend some time to create high quality content that fills those gaps. This is super important, and it’s ok if it takes a while.
Step 2: Map Out All of Your Touch Points
The first step was identifying all of the content you have already and making sure you’re reaching people at every stage of the funnel–this next step involves laying them all out and organizing them into touch points.
Touch points are broader than pieces of content. Rather than an individual piece of content or asset, it’s a group of assets that share the same goal. A touch point could also be an interaction instead.
Here are some examples:
Social media ads — Simple and quick ways to boost awareness while customers are scrolling in a non-buying mindset.
Homepage — Should clearly articulate who you are and what you do, so the visitor understands your brand in a matter of seconds.
Landing pages — More specific product or service verticals that get reached as a visitor progresses further down your funnel.
Someone else’s social media posts — People might see your brand mentioned on social media by another customer or another business you’ve partnered with.
Third-party reviews — Either on specific customer reviews platforms (like Yelp or Tripadvisor) or in long-form blog-style reviews from third-party websites.
Your own blog posts — People can land on these pages through your organic SEO efforts or if you’ve sent them to a new blog though an email campaign or social media post. Unlike third-party reviews, in total control of what’s being said on your own blogs. You may have different types of blog posts, like top lists, comparisons, tutorials, or something else entirely. You can break these different types into individual touch points if each type has a different goal in mind.
Inbound phone calls — Customers and prospects can dial your call center for sales, support, or general questions. It’s important to give them this option, and it’s worth setting up a virtual call center even if you have a small or one-person business.
In-store or face-to-face — In many instances, customers visit your store with the intention of buying something. However, some face-to-face interactions may be accidental (like a shopping mall, where a buyer just happens to pass your store while browsing from something else).
Email — These can come in all shapes and sizes, like a newsletter blast to your entire subscriber list or a targeted cart abandonment email to specific users.
Live chat — Live chats are often prompted when a customer has questions about a product, order, or problem. But it can also be initiated by your business using a chatbot to encourage further interaction while a visitor is navigating your website.
Billing — Each time you send an invoice or automatic payment receipt to your customer, it counts as a touch point.
There are literally dozens of different potential touchpoints for your business. The list above is a good starting point, but make sure you go through all of the possibilities for your business.
To map them all out, we recommend Figma because it makes it really easy to stay organized–plus, you can use it for free. You can use whatever tool you want (pen and paper, Canva, etc.), just make sure each touch point you identified has its own box.
From there, tie all the pieces of content you identified or created in step one to your touch points.

Step 3: Tie Everything Together & Fill in the Gaps
By now, you should have a box for every touch point and all the content or assets you have for each one. Now, it’s time to map out how a customer will get from each touch point to your end goal.
For many businesses, the end destination is making a purchase. However, it could also be subscribing to your newsletter, clicking an affiliate link, buying a specific product, signing up for a free trial, or filling out a form.
Basically, how will a customer get from touchpoint one to the action you want them to take?
If they land on a blog post at the top of your funnel (the awareness stage), how do you get them to buy something from you? Shoving offers in their face isn’t going to work because they aren’t ready. You need to guide them to the consideration stage first. You could link to comparison guides, webinars, or case studies instead. And then within those, you can start showing offers as they get closer to the conversion stage.
Different touch points may have different end destinations, too. If someone’s calling you for help with something, they don’t want to buy anything–they just want help.
Your end goal may be providing an excellent experience so they’ll recommend you to their friends.
It’s all about understanding where they’re at in the purchasing process based on how they’re interacting with you. Then planning out how you’re going to nudge them towards an end goal.
This is where Figma really comes in handy. It allows you to visually map each journey from start to finish and add all of the content you need along the way.

Visualizing this makes it much easier to identify gaps and truly understand how customers flow through your business.
You’ll eventually come up with a bunch of different intended customer journeys that clearly outline the various paths someone can take from each touch point.
Now that you know what you want each journey to look like, you can update your content and touch points to ensure they’re all working harmoniously to get customers to the next step you want them to take. This could mean reorganizing your brick-and-mortar store, updating your landing pages with more direct calls to action, removing sales language from top of the funnel blog posts, training your call center agents, writing scripts, or something else entirely.
Step 4: Map Alternative Customer Journeys
Not every customer journey will do what you expect them to. Even if you’ve mapped out several intended journeys, some of your customers will break all the rules and create their own paths.
That’s totally ok.
But you should try your best to anticipate these variations. Even if a customer doesn’t do exactly what you want them to, you can map out alternative routes to ensure you don’t lose them. From there, you can create new content that will guide them back to your desired path or create completely new journeys for them.
For example, say you originally anticipated that someone would see a social media ad and then take one of four paths—click the ad, click your social profile, Google your website, or just keep scrolling.
But what if someone decides to go straight to YouTube and search for a video demo or review of your product instead? You can account for this by creating YouTube videos yourself or encouraging affiliates to create them for you.
Here’s another example: say someone subscribes to your email list. Most of your existing map may assume that this person wants to receive email communication from you.
But what happens if they opt out after the first message? You could try retargeting them on social media or a well-crafted opt-out email designed to bring them back in.
7 Ways to Use Your Customer Journey Map
Your customer journey map is done. Now what?
You can apply some different strategies to truly get the most out of your customer journey map, and these seven tactics are the best places to start.
Create Buyer Personas for Different Touch Points
Buyer personas that will help you zero in on who your customers are and what they want. The more detailed your personas are, the better.
The secret here is to think of your customers as human beings as opposed to numbers or data points. By humanizing your personas, you can get a more holistic picture of what they’re looking for—and then use that to further improve your journeys.
Here’s an example buyer persona :
Do you see how realistic and detailed this is? That should be your goal with each persona.
Based on Max’s occupation, you might assume that he’s more likely to interact with your brand via live chat. Whereas another persona of an elderly woman who isn’t as tech-savvy may be more likely to get help by calling your main phone number.
Create as many personas as possible for as many touch points as possible.
Get Really Targeted With Your Messaging
Once you understand exactly who will be interacting with different touch points at each phase of the journey, you can begin speaking directly to those individuals.
For example, you’ve mapped out how someone could potentially land on your ebooks landing page. From there, you might even have different personas or maps to specific ebooks.
So your CTAs and value propositions for downloading, “How to Create a Mobile App” can be different from your “How to Get More App Downloads” ebook.
This is a fairly obvious example, but you can break it down at a granular level for all campaigns by simply referring to your journey map. This will ultimately help increase your conversion rates .
Monitor Your Most Important Metrics
This is another instance where the metrics you track will vary slightly based on your business type. For example, B2C ecommerce KPIs will be a bit different from a B2B SaaS product.
But you’ll want to look at traffic, leads, conversions, sales volume, revenue, opt-ins, subscribers, email bounce rates , open rates, average order volume, etc.
You can also zoom in on channel-specific metrics. For example, you could look at something like page sessions, average time spent on page, or page-specific conversions without worrying about sales. This could help you correct any potential UI design mistakes that have a domino effect on the KPIs that drive sales.
What needs to be on each specific landing page to target potential buyers landing on it? Your customer journey map holds the answer.
Update and Optimize Existing Content
You don’t necessarily need to re-create every piece of content from scratch. Instead, it’s easier to identify existing content that just needs to be tweaked to target customers based on what they need to see in that particular buying phase .
Maybe you already have really good blog posts explaining how to use your products. But existing customers may not necessarily be using organic search to find tutorials.
So you could turn those into emails that get sent after a product has been delivered to focus on buyers in your retention phase. Or maybe you add tutorial videos to your product pages to provide more information to customers in the consideration stage.
Be More Strategic About What You Create
Your buyer persona can help provide you with a blueprint for content creation. Rather than just blindingly deciding to write more blogs or increase your social media posting frequency, you can refer to your customer journey map for inspiration.
Looking to fill content gaps is the most obvious place to start. But even after those gaps have been filled, you can continue expanding on your content to cover your most frequently traveled journeys or create content that covers your less traveled paths.
In either scenario, you’ll know who you’re speaking to and why. It’s much more effective to create content that speaks to a narrower group as opposed to your entire customer base.
A/B Testing for Continuous Improvements
You can run A/B tests at every stage and with nearly every touch point throughout your customer journey.
These tests are great for validating a particular hypothesis, but they can also be used to just make your content better. Why settle for what’s working if you can squeeze even more juice out of it?
Beyond A/B testing the obvious stuff like email subject lines or landing page CTA buttons , you can take this a step further and run tests on what content should be served up for various touch points.
You might think a customer subscribing to your email list from a particular landing page should be sent a whitepaper as the first message. But maybe you experiment with sending them a video introduction instead.
Add New Customer Journeys as Needed
Your first round of creating a customer journey map wouldn’t and shouldn’t be your last.
There will always be new journeys to map out, especially if you’re continuing to expand and launch new products or services. These launches are always a good time to assess your existing journeys and add new ones.
Just make sure you’re always being actionable with your journey maps. Creating them but not using them is a wasted effort. So don’t just add more for the sake of adding them. Each additional journey needs to serve a purpose.
Best Practices to Keep in Mind
Here are some pro tips and best practices to keep in mind as you’re creating your customer journey map and implementing it:
- Make it a team effort—working with sales, marketing, and service departments to get everyone’s input.
- Don’t be afraid to get hyper-specific. Once you’ve mapped out a particular journey for a certain persona, it’s ok to go really deep with those touch points even if it means neglecting other buyers. You can eventually target those other buyers separately.
- Think outside the box. Rather than focusing on how you want or hope customers will behave, get creative and think up some unconventional steps they might take along the way.
- Use data to back up your claims or strategies whenever possible. For example, visitor data from Google Analytics can be really helpful when creating buyer personas.
- Prioritize user experience with every touch point and at every buying stage.
- Keep your branding the same across different touch points. While your buyers might have different wants or needs, your branding should always stay consistent.
- Make sure your journey maps are organized and easy to read. Things can get complicated when you start adding lots of variations, which is why using a tool like Figma is super helpful.
- Don’t be afraid to ask your customers what they’re thinking. Rather than trying to guess what it’s like to be in their shoes, you can use surveys and run tests to actually see what they’re thinking.
- Take the customer journey yourself. Go through each stage of the map to see if it makes sense. This is the best time to brainstorm alternate routes.
- Make sure your journey map is shareable and can be easily accessed by your entire team.
- Start small and focused. Don’t worry about having everything mapped out on day one. Start with what can get you results, and you can always add more later.
- Use a low-fidelity map when you’re getting started. Don’t worry about the map looking perfect right now. Get what you need diagrammed, and you can have someone fix the aesthetics down the road.
Make your website better. Instantly.
Keep reading about conversion.

Customer journey maps tell the story of how people behave when interacting with your brand across different touch points. Creating a journey map helps businesses…

Best Auto Dialer Software Compared
Do you know the best-kept secret to selling over the phone? Not wasting time. That’s where autodialer software enters the picture. It eliminates wasted time…

What Is a Good Conversion Rate? The Answer Might Surprise You
What is a good conversion rate for your online business? And how do your company’s conversion rates stack up against the competition? These are questions…

Poor Sales? Maybe You Need a Website Redesign: Here’s How
Neil Patel co-founded Crazy Egg in 2005. 300,000 websites use Crazy Egg to understand what’s working on their website (with features like Heatmaps, Scrollmaps, Referral…

How to Start a Business for Less Than $100
An idea and a crisp $100 bill is all you need to start your new business. Seriously. And we’re about to show you how. In…

Growth Hacking: The 12 Best Techniques to Boost Conversions

Website Design – Beginner’s Guide
Creating a website simple. You don’t have to be a tech expert or designer. Anyone can create a stunning website today. There are tons of…

20 Tricks to Double Your Ecommerce Conversion Rate
Want to earn hundreds and thousands of dollars per year online? You can, with ecommerce. Whether you’re starting a new ecommerce shop from scratch or…

Hack Your Thank You Page: 5 Ideas for Driving Even More Conversions
When it comes to on-site optimization, landing pages, product pages and checkout pages receive the most attention. However, there is one page that a lot…

CRM Strategy – The Complete Guide
Here’s the truth. CRM solutions will not magically solve all of your problems. And adoption does not necessarily guarantee success. It’s not only about investing…

How to Optimize Your Website for SEO and Conversions
Learning how to optimize your website for SEO and conversions is crucial for your site’s success. It’ll ensure your website is working exactly as hard…

5 Advantages and Benefits Of SEO For Your Website
If you’re a marketer or business owner, you’ve likely been told that you should be using SEO (Search Engine Optimization) more than once or twice….

The 8 SEO Tracking Metrics That Really Matter
SEO tracking is essential for evaluating your site’s success. After all, If you’re going to invest the time and budget it takes to create and…

15 High-Converting Lead Magnet Examples and Ideas
Generating good lead magnet ideas can become a long process. Simply throwing together an e-book or whitepaper just because other businesses do it would be…

What is Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)?
Conversion rate optimization offers one of the fastest, most effective methodologies for turning your existing web traffic into paying customers. Also known as CRO, conversion…
Over 300,000 websites use Crazy Egg to improve what's working, fix what isn't and test new ideas.
Last Updated on May 18, 2022
Blog • Customer Experience
Customer Journey Stages: Guide, How-To & Best Practices

What Is the Customer Journey?
Why is it important to understand the different customer journey stages, how to create an effective customer journey, best practices for an efficient customer journey stages.
It’s easy to fall into an if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it mindset when thinking about customer journeys—why mess with a system that’s served you well so far? The rather unsurprising answer is that your customer journey isn’t nearly as efficient, enjoyable, and profitable as it could be.
According to McKinsey , when the average business makes systematic, targeted improvements to their customer journey, they increase revenue by 15-20% while also cutting service costs by 15-20%.
Interested in this win-win scenario? You’re going to need a solid understanding of the journey stages and what they mean to your business. And in this Customerly guide, we’ll be giving you a crash course to get you started.
Let’s dive in.
A customer journey is the life cycle of a customer’s relationship with your business—from the point of initial contact to post-purchase follow-up.
The customer journey is a fluid spectrum—but that’s not an especially helpful way of thinking about it. To simplify things, people usually break the customer journey down into stages (five, to be exact) that are defined by customer needs, behaviors, and touchpoints.
When you understand each stage, you’re much better equipped to give each customer the experience they’re looking for at any given moment.
Check out how Feed Donkey uses Customerly to engage with their clients at every stage of the journey.
What are those stages? Let’s go over them now.
The Stages of a Customer Journey
- Awareness : The customer becomes aware of your product or service. Maybe they saw an ad, or maybe they clicked on a blog post—the important point is that they know your company exists.
- Consideration : The customer isn’t simply aware of your existence; they’re actively considering your company as a solution to their problem(s). This usually involves fairly surface-level research and comparison.
- Purchase : This is the point when a customer has decided to purchase something from your company. They’ve put aside any hesitations or doubts and moved forward with their purchase.
- Retention : The customer made a purchase (congrats)—now your goal is to retain their business. In practice, that means offering incredible post-purchase support, demonstrating that you value the relationship (e.g., offers and rewards), and delivering an excellent overall experience.
- Advocacy : This is one of the most powerful stages in terms of impact on your bottom line. In this stage, the customer is not only satisfied—they actively champion your product or service to their friends and family. This can create a snowball effect that fast-tracks growth.
We already covered two very good reasons to care about customer journey stages—increased revenue and decreased costs. But those benefits are really side effects of far more important reasons:
Allocate Resources Effectively
Your customer journey is a complex mess of touchpoints, channels, mediums, features, benefits, use cases, landing pages… you get the idea.
When you understand the stages (and what they mean for customers), it helps you identify where to invest, what features and tools to prioritize, and how best to engage with customers along their entire purchase journey. The result is a system that’s working as close to maximum efficiency as possible when it comes to generating revenue.
Personalized Customer Experience
On a related note, these stages also give you a quick and easy way to segment leads and customers into intuitive groups. These groups are easy to target for personalized messages, tailored content, and relevant product recommendations.
With Customerly, you can build custom lists of customers in our CRM using a range of characteristics, including:
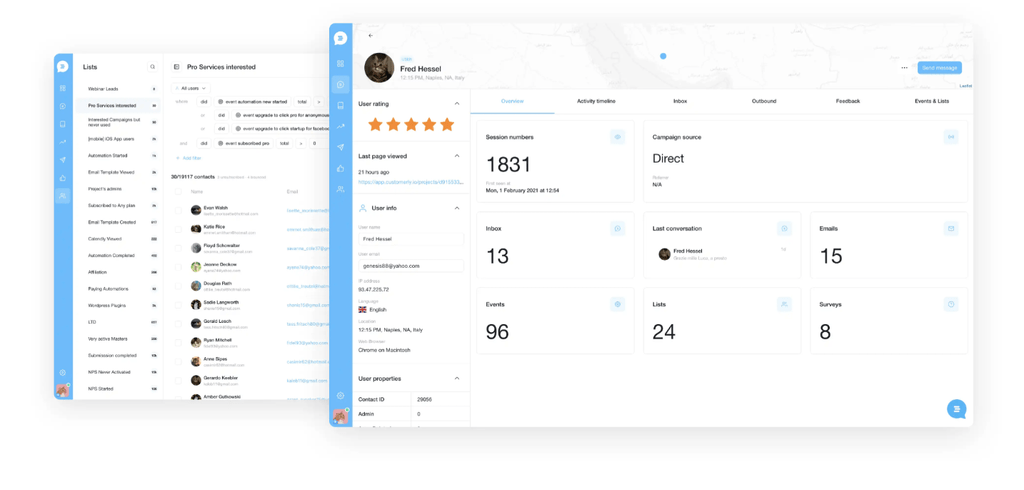
- contact properties
- company properties
This helps you create much more rewarding experiences for each customer group—the kinds of experiences that earn purchases, retention, and advocacy.
Build Longer-Term Relationships
Customers want their experiences with businesses to be simple, straightforward, and rewarding—no moments of confusion, no moments of frustration. If you consciously work to make that dream a reality, you’re setting yourself apart from the competition and earning long-term advocates.
1. Create a Customer Profile
If you want to create an effective journey for your customer, you need to know who that is—in clear, concrete terms.
A customer profile (or ideal customer persona ) is like a character sheet for a TV show, movie, or D&D campaign. It’s a generalization of a customer group that’s important to your business, either because they make up a sizable portion of your total customer base or revenue.
For each customer profile you create, you’ll want to cover:
- Demographics : Who the customer is (e.g., “Chief Customer Officer at a growing B2B SaaS”).
- Psychographics : What their needs and interests are (e.g., “looking for a partner to guide the process”).
- Goals : What they hope to achieve in their journey (e.g., “boost customer support efficiency”).
- Pain Points : What keeps them awake at night (e.g., “confusing onboarding processes”).
- Current Solutions : How (if at all) they’re meeting their needs without your solution.
To get your hands on the data needed to make these generalizations, you’re going to need to run surveys to supplement CRM data. With Customerly, you can create and run custom surveys or use our pre-built customer persona template to speed the process up.
All the data you collect is automatically added to your CRM for use in analysis and automated marketing campaigns.
2. Make a List of Customer Touchpoints
Once you have a customer profile, it’s time to make a list of the customer touchpoints—or, the points of contact between them and your business.
There are an absolute ton of touchpoints that you can use to your advantage, but there’s a caveat here—not every touchpoint is well-suited to every customer at every stage of their journey.
There’s some overlap, but here’s a simplified list of common touchpoints and the stages they apply to:
- Awareness : SEO, PPC, word-of-mouth, blog content, PR, etc.
- Consideration : Organic social, case studies, demos, website visits, etc.
- Purchase : Reviews, testimonials, sales staff, branded content, etc.
- Retention : Surveys, email campaigns, etc.
- Advocacy : Loyalty programs, offers, organic social, etc.
3. Identify the Pain Points
Pain points are reliable predictors of behavior.
If you really understand a problem someone is having and know for a fact that you can solve it, it’s much easier to make a sale. So, the next step in this process is listing the pain points that bring customers to you—either on a segment-by-segment basis or in general.
Not sure where to start?
A product positioning survey is a great way to find out why customers choose your company over the competition. Start by using Customerly to target a valuable segment (paid customers, perhaps?) and launch our product positioning template to start generating data.
4. Create a Customer Journey Map
Now that you have a customer profile, touchpoints, and pain points identified—you can create a customer journey map. This is an interactive diagram that shows (in broad strokes) how a customer segment progresses from awareness to advocacy.
The map should include key touchpoints, pain points, needs, customer emotions, and the owner(s) for each stage. You should also be creating a map for each persona you identified in the first step.
Here’s an example of what this might look like:
5. Determine the Course of Action
This final step is where you start using your customer journey map to fine-tune your processes.
Start by finding out which touchpoints are influencing customer satisfaction the most. Identify what’s working well and what needs improvement.
Then, brainstorm ways to improve each stage of the journey and measure success at each stage. This includes optimizing processes, running experiments, and implementing changes that will make customers feel heard and valued—ultimately leading to better engagement.
1. Establish a Good First Impression
The first impression is the most important one. That’s why it’s so important to establish a good one from the very start—especially in the awareness and consideration stages.
2. Understand What the Customer Is Getting and Why
In every stage of the customer journey, it’s important to understand what your customer is getting and why. Your messaging should be focused on communicating the value they get from your product or service—not just on pitching them something.
3. Demonstrate Value
Withholding value is an important sales tactic—but it’s important to find a balance. Demonstrate your product or service’s value without revealing too much. Simple, transparent free trials let customers experience the offering fully and allow you to showcase its value. The trial serves as a reference for informed decision-making once it ends.
4. Stay in Contact with Customers After-Sale
It’s not enough to just make a sale—you also need to stay in contact with customers after they’ve made their purchase. This will help you build a strong relationship with them and encourage repeat business. Make sure your post-sale messaging is focused on customer success—not just upselling or cross-selling.
5. Measure Your Success
To create an effective customer journey, measuring success is crucial. Track customer satisfaction , purchase frequency, and lifetime value to understand how your strategy is performing. Use tools like analytics software, surveys, and user tests.
Every well-designed customer journey begins with a deep understanding of the stages that make it up.
At Customerly , we arm businesses with all the tools they need to understand and enhance every stage of their customer journey. From marketing automation tools to intelligent live chat support, we’re here to help you create a seamless customer experience that will increase satisfaction and loyalty.
Want to see for yourself? Start your 14-day free trial and take Customerly for a test drive.
14-day free trial
Create a seamless customer experience that will increase satisfaction and loyalty
- Customer Advocacy
- customer experience
- Customer Journey Analysis
- Customer Journey Mapping
- Customer Journey Optimization.
- Customer Journey Stages
- Customer Pain Points
- Customer Relationship Management
- customer retention
- Customer Touchpoints
Luca Micheli
Luca Micheli is a serial tech entrepreneur with one exited company and a passion for bootstrap digital projects. He's passionate about helping companies to succeed with marketing and business development tips.
Related articles

The Role of AI Tools in Personalizing Customer Experiences for Marketing Success

Best Customer Satisfaction Software for Every Use
- Customer Service
- Marketing Automation
- Customer Satisfaction
- Video Live Chat
- Help Center
- Marketing Funnel
- Email Marketing
- Email Template Builder
- In-App Surveys
- Alternatives
- Success stories
- Terms Of Service
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Submit Guest Post
- Merchandising
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
7 ways to analyze a customer-journey map.

March 22, 2020 2020-03-22
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
A customer-journey map is an infographic visualization of the process that a persona segment goes through in order to accomplish a goal. Journey maps are useful in communicating the general narratives and themes uncovered by longitudinal research done to understand how a customer works toward a goal over time.

This journey map includes all the information necessary for understanding and analyzing the user experience of shopping for a new car. In this illustration, we have intentionally left out one key piece of the map — the insights and opportunities gleaned from the map. This section is often found at the bottom of a customer-journey map and highlights how the organization can optimize and improve the customer journey.
In this article we will demonstrate how to analyze a journey map and, thus, how to identify the insights and opportunities for improvement.
In This Article:
Analyzing the journey map.
Longitudinal research and analysis is necessary to create a map like this.
Every journey map will look different because the research insights and the resulting visual depend entirely on the context of the journey, its underlying activities, and the persona completing it. That said, there are 7 common elements you can and should look for when analyzing a customer journey.
1. Look for points in the journey where expectations are not met.
Users go into an interaction with an organization with certain expectations. When the interaction does not meet their expectations, you see pain points in a customer journey. To identify these instances, first reflect on who the persona is. Ask yourself; what is important to this persona, where did she come from before this journey, what has she seen and what does she know already? Putting yourself in the user’s mind space will allow you to understand which interactions conflict with user’s prior ideas and expectations.
Of course, you should look for places where users verbalized their concerns, but also use your logic to assess interactions with no explicit complaints or negative comments.
Sometimes people bring their expectations into the journey from other experiences. For example, users expect that when they pull up to a hotel, the bellman will open the door, because that’s what always happens when you pull up to a hotel with a bellman — it’s the mental model that they have formed for that situation. Some organizations set inaccurate expectations early in the customer journey. Others don’t set expectations at all, forcing users to make assumptions and possibly be disappointed if those assumptions prove wrong.
Find the trouble spot and work backward to identify the triggering factor and how the expectations were (or were not) set. Work to resolve the conflict between expectations and reality.
In the car-buying journey map, there were two clear points where Eric’s expectations weren’t met. These instances are annotated using red numbered circles.

2. Identify any unnecessary touchpoints or interactions.
Are there any steps in the customer journey that could be eliminated in order to streamline the total experience? Look for logical ways to optimize the process to reduce total interaction cost . That may mean removing an existing step that is no longer needed or adding something to the experience that bring efficiency to the overall journey.

3. Identify the low points or points of friction.
When you step back and look at the whole journey, you should be able to see where the user experiences the most pain or friction. These points are usually represented visually as dips in the journey diagram. See where the journey reaches its lowest point and compare it to other low points in the journey. These should be on your shortlist of optimizations. That said, not all fixes are created equal: there can be dependencies and constraints involved. Work with your team to decide which low points should be addressed first and which can come later. (Because of the peak-end rule , the lowest point in a journey will have a particularly ruinous impact on the branding effect of the user experience.)

4. Pinpoint high-friction channel transitions.
Many journeys take place across devices or channels . A lot of times the journey breaks down and friction appears when users change channels. For example, a user receives a newsletter about a specific offering from a company. She’s interested in the offering and clicks the call to action in the newsletter. However, instead of being taken to a landing page detailing that particular offer, the user lands on the company’s homepage. At this point, she has to put in effort to find the offer. Or, another user may begin filling out a form on the mobile phone, but wants to complete it on the laptop when it becomes too laborious. Doing so means losing work and starting over. These channel-transition pain points should be identified and streamlined. Think outside of the box: rather than forcing users to work hard, build a bridge for them to get to the other side easily.

5. Evaluate time spent. In your journey map, provide time durations for the major stages of the journey.
This information gives you another lens for analyzing the experience. Assess how long it takes users to achieve the underlying substeps. Are these times appropriate? Time spent often correlates to the amount of user effort. Call out areas of the journey where time and effort are problematic.

6. Look for moments of truth.
Some points in the journey are so important that the rest of the experience might hinge on them. Think about the personas’ attitudes, needs, and priorities. Is there a make–or–break moment in the journey for that persona? This moment may be where your research shows a lot of emotion or where you see a strong divergence between the paths different users take. If this moment goes well, it can save the experience. For example, think of the first time a car-insurance customer files a claim. She’s been paying her policy responsibly, and now she needs her insurance to come through seamlessly for her. The first interaction in the claim experience might be a moment of truth for this persona. If it goes wrong, the user may move to a competitor. Be sure to look for moments of truth and to call attention to them when you find them.

7. Identify high points or points where expectations are met or exceeded.
Good UX practitioners should always balance their analysis by pointing out things that are working well in any experience. Look at the high points in the journey — the interactions that users are happy with. Where do they express positive thoughts and emotions? These insights are also valuable. You may be able to amplify them or recreate similar experiences elsewhere in the journey.

Whether you’re evaluating journey research for the creation of a map or digesting a map created by another party, it’s important to know what to look for. As the creator of the map, you’ll want to identify and call attention to these important elements through visual emphasis and storytelling. As a consumer of the visualization, apply this checklist like lenses through which to view the map in order to find the most actionable insights.
Related Courses
Journey mapping to understand customer needs.
Capture and communicate UX insights across complex interactions
Omnichannel Journeys and Customer Experience
Create a usable and cohesive cross-channel experience by following guidelines to resolve common user pain points in a multi-channel landscape
Interaction
Customer-Journey Management
Establish and operationalize journey-level experience design work across functional groups for continuous improvement
Related Topics
- Customer Journeys Customer Journeys
Learn More:

The 3 Competencies of Journey Management
Kim Salazar · 5 min

Journey Management vs. Service Design
Kim Salazar · 4 min

Types of User Pain Points
Sarah Gibbons · 4 min
Related Articles:
How to Conduct Research for Customer Journey-Mapping
Kate Kaplan · 7 min
Good Customer Experience Demands Organizational Fluidity
Kim Salazar · 7 min
Journey Mapping: 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Alita Joyce and Kate Kaplan · 7 min
Remote Customer Journey Mapping
Kate Kaplan · 5 min
Journey Mapping in Real Life: A Survey of UX Practitioners
Customer Journeys and Omnichannel User Experience
Kim Salazar · 6 min
- Home > B2B Blog > 5 Top Tips for Running Effective Customer Journey Workshops
- 5 Top Tips for Running Effective Customer Journey Workshops

The importance of customer journey mapping
Whilst logic might tell us that happy and engaged customers should be a top priority for b2b brands, our research tells us that only 2 in 10 companies would consider themselves ‘CX Leaders’ – namely, those fully committed to delivering on customer needs and providing a seamless experience for their customers.
The core foundation to managing the experience of your customers, is to understand what your customer journey looks like end-to-end, so you can better establish what is working and where any challenges, pain points or roadblocks lie that might make life more difficult for your customers. For example, a customer’s initial interaction with our brand might be our website, but if this isn’t intuitive, clear, or easy to navigate, this can be a pain point. Similarly, we might have a seamless sales process when onboarding clients to our product or service offering, but we can erode the customer loyalty we have built if our aftersales is problematic and if it’s not easy for customers to resolve a business or time-critical issue they are facing.
Customer journey mapping is an important first step in creating a more deliberate, seamless, end-to-end customer experience. As implied, it involves mapping out all the individual touchpoints or interactions our customers have with us. In this blog, we’ll share our top tips for conducting an effective customer journey mapping workshop, as part of a wider customer journey research program.

Our 5 top tips for running an effective customer journey mapping workshop
Go all in – run the session in person
Without customers, we have no reason to exist. They are an organization’s most important asset and yet if you were to ask most organizations to describe the end-to-end journey their customers take, most would return a blank face!
Whilst it’s become more commonplace to run online meetings, we would always recommend running a journey mapping workshop in person. More than anything, you will give this exercise the undivided attention it deserves. The “light bulb” moments and transferable learnings that can be experienced on the day by having multiple internal stakeholders in the same room discussing the customer journey is unparalleled.
Get the right people in the room
The point of customer journey mapping is to allow internal stakeholders to put themselves in their customer’s shoes and think about all the interactions they have. Ultimately, every interaction that a customer has contributes to their perception of that brand. When doing this, it’s helpful to think about the five senses – what customers see, hear, touch, taste or smell. In other words, from the customer’s point of view, if they can see it, smell it, touch it, taste it, hear it, feel it, sense it, click it, hold it, carry it, use it, step on it, or step over it….it becomes a part of the customer experience and therefore the brand. Put another way, if there are interactions that take place in your organization that customers don’t see, these don’t count as part of the customer journey and are part of an internal process.
When creating a journey map, we might be focusing on a specific section of the journey or exploring the full customer journey end-to-end. A full journey map might start with how customers become aware of our brand through to making an enquiry, service delivery, aftersales and even what happens at the point at which they leave us or return as a returning customer. To ensure the workshop captures all these different interactions, it’s important to include a range of internal stakeholders and departments in the room; those that can input into different stages of the journey. For example, someone from Marketing that can input into how customers become aware of our brand, the Sales team for the sales process, the Project Delivery team, the Finance team and so on. Typically, you would aim for 10-20 maximum stakeholders at the workshop.
As with any planned exercise, you get out of this what you put in, so you don’t want to wing it, especially if you’ve gone to the trouble of getting the right people in the room. When preparing for a workshop, it’s important to decide on which parts of the journey you wish to explore, who will attend and then tailor the exercises on the day accordingly.
Before each workshop, we usually discuss options with our clients and then prepare the customer journey “spine”. The spine consists of overarching touchpoints or key stages in the journey where the main journey mapping exercise consists of asking stakeholders to think about all the specific interactions that might take place within each touchpoint.
As an example, our end-to-end journey “spine” might include the following overarching touchpoints:

If we take ‘Awareness’ as the first overarching touchpoint, examples of the individual interactions or touchpoints mapped out in the exercise might include things like word-of-mouth recommendations, the website, direct mail, seeing the brand logo on a delivery van, online searches, social media etc. These are all interactions our customers might experience when becoming aware of our brand. Taking this approach, you can see how a journey mapping exercise could easily identify a hundred or so different interactions that our customers experience with us!
More than this, as is true for many b2b organizations, there might be a range of different customer types we are serving and therefore variation in the touchpoints and interactions that take place. It’s therefore crucial to think carefully about who will attend the session, the time available and what we already know or don’t know, in order to make the most out of the workshop.
Allow the time needed to run multiple exercises over a day
Tied to the previous point, a detailed journey mapping can take some time and so we’d recommend, where possible, a full working day’s workshop dedicated to this. First and foremost, is the mapping of touchpoints as we’ve described already, but there are additional exercises you could run to get the most value from the day. We include some popular examples below:
Heat-mapping performance: Using colored pens or stickers, get all stakeholders to mark individual touchpoints as those which are “pain points” for customers now or those which are “moments of delight”. If time allows, we can also mark up the touchpoints which we see as the “moments of truth” i.e. those touchpoints which are the most important to customers and carry the most power to build or destroy loyalty over time.
Exploring emotions/sentiment: At each stage of the journey, we can also ask stakeholders to think about they key emotions they feel customers experience now (whether positive, negative, neutral or a combination) alongside the emotions we would ideally like them to feel.
Assigning departmental responsibility: Once all touchpoints have been mapped, it can be useful to review all of those identified and think about which department (or departments) have responsibility for delivering that touchpoint.
Brainstorming improvement areas: Given all the valuable learnings and discussion on the day, it can be useful to home in on the momentum that’s been built and capture some key learnings and immediate improvement areas or action points to consider.
Consolidate learnings to cascade
As is clear, there is a considerable amount of insight that can be captured during a journey mapping workshop. When preparing the outputs, we often find that there are the more detailed outputs and then something more high-level and visual that can be useful to cascade more widely. Whilst we have an in-house design team who can custom-create journey maps in our client’s own branding, another option is to hire a visual scribe to attend the session and capture a visual representation of what’s discussed in-the-moment.
Whatever you decide, think about how to cascade the findings – it’s valuable for everyone within an organization to be clear on the customer journey, since directly or indirectly, we all play a part in delivering the customer experience, no matter what department we sit in!
Learn more about our customer journey research >
To discuss how our tailored insights programs can help solve your specific business challenges, get in touch and one of the team will be happy to help.
Get in touch to discuss your research requirements >
Recent Articles
- B2B Insights Podcast #62: How to Achieve World-Class Quality in B2B Market Research
- 3 Use Cases for Kotler’s Five Product Levels Framework in B2B Research
- Using the Push-Pull Model to Successfully Bring New Products to Market
- B2B Insights Podcast #61: How to Ensure B2B Market Research is Strategic and Actionable
Speak to an expert...
- Keep up to date with our latest research
- First name *
- Last name *
- Company name *
- By subscribing to this newsletter, you are opting in to our marketing communications. Read our privacy policy for more information.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Privacy Overview
Travel invented loyalty as we know it. Now it’s time for reinvention.
Travel brands didn’t invent loyalty programs, which have been traced to as far back as the 18th century . 1 James J. Nagle, “Trading stamps: A long history,” New York Times , December 26, 1971. But ever since the first major airline frequent flier programs appeared in the early 1980s—soon to be followed by similar programs from hotel chains—the travel industry has become known for letting customers accumulate redeemable “miles” and “points.” Modern-day voyagers are deeply familiar with loyalty-related concepts such as status tiers, members-only lounges, and point-earning credit cards.
Travel loyalty programs were originally designed to influence travelers’ behavior. By offering rewards such as free flights and hotel rooms to frequent customers, a company might convince power users to consolidate their travel spending with its brand. Why fly airline X when you’re halfway to earning a free perk for remaining faithful to airline Y?
Over time, many travel loyalty programs became wildly successful—not just as a way to boost sales or strengthen customer relationships but as major profit centers in their own right. Travel companies found they could sell loyalty points in bulk to, for instance, banks, which in turn offered the points to their credit card customers as rewards for spending. In 2019, United’s MileagePlus loyalty program sold $3.8 billion worth of miles 2 Brian Sumers, “How is United Airlines’ loyalty program worth $22 billion?,” Skift, June 15, 2020. to third parties, which accounted for 12 percent of the airline’s total revenue for that year. In 2022, American Airlines’ loyalty program brought in $3.1 billion in revenue, and Marriott’s brought in $2.7 billion. 3 Form 10-K, fiscal year ending December 31, 2022, American Airlines Group, Inc.; Form 10-K, fiscal year ending December 31, 2022, Marriott International, Inc. Many loyalty programs have evolved into discrete divisions with their own profit-and-loss ledgers.
Along the way, however, some travel players have shifted their focus away from the original purpose of these programs. As loyalty programs have become powerful bottom-line enhancers, companies have sometimes been tempted to view them first and foremost as revenue generators instead of tools to sway customers’ behavior or to improve customers’ experiences . The postpandemic resurgence of travel demand has also pressured companies to shore up their loyalty programs’ viability by devaluing members’ points and miles and enacting rule changes that have at times caused customer frustration. At the same time, innovative loyalty programs in other industries are raising the bar, opening customers’ eyes to the value that loyalty programs can offer.
As a result of these factors, travel loyalty program members have become increasingly disloyal. For some customers, reaching the top tier of a loyalty program is still almost a facet of their personal identities—“Just a couple of more flights, and I’ll reach elite status!” But many loyalty program members now seem more inclined to play the field. The warm feelings at the heart of loyalty, which lead travelers to show allegiance to a brand and trust that their faithful behavior will be noticed, seem to fade when brands let their focus drift away from rewarding their most valuable and consistent customers.
Loyalty is about more than a program, a department, or a tangible redemption offer.
Loyalty is about more than a program, a department, or a tangible redemption offer. True loyalty is won through a genuine desire to forge bonds with customers and thereby maximize each customer’s lifetime value to the brand. Travel brands, therefore, should consider rethinking and reinventing their loyalty programs in ways that frame loyalty as something more than points and miles. A mindset shift, coupled with three practical actions, could help restore the luster of loyalty programs while bringing straying customers back into the fold.
A mindset shift, coupled with three actions, could restore the luster of loyalty programs while bringing customers back into the fold.
How we got here: Disruption, devaluation, and dissatisfaction
When travel came to a halt as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, many travel brands—hoping to keep customers happy—“froze” the loyalty program status levels of members who might have otherwise lost perks due to a lack of travel activity. When travel spending was slow to resume, brands changed their program rules to make status tiers significantly easier to reach and maintain. These moves made sense in the face of an unprecedented disruption, with far fewer miles and points being redeemed.
But as travel recovered, loyalty programs became burdened by increased redemptions and overpopulated high-status tiers (evidenced, for example, by the lines outside the doors of airport lounges). Some major travel brands have responded by adjusting loyalty program rules. They’ve ended the status extensions that were granted during the pandemic, and they’ve devalued points and miles—raising the bar to redeem them for free flights and rooms.
All these changes have, understandably, been made with an eye toward programs’ profit-and-loss statements. But collectively, they’ve resulted in widespread customer dissatisfaction. Program members have chafed at having their points devalued and benefits clawed back. Meanwhile, successful loyalty programs in other sectors have opened customers’ eyes to other types of value that these programs can provide, such as better customer experiences, richer communities, more tailored personalization, and exclusive access to events or offers.
Loyalty surveys conducted by McKinsey in 2021 4 The 2021 loyalty survey of roughly 10,000 American consumers covered multiple sectors (including airlines, hotels, cruise lines, banks, retail, grocery, and others). and 2023 5 The 2023 loyalty survey of 3,200 American travelers covered the airline, lodging, and cruise sectors. revealed a steep decline in the likelihood that a customer would recommend airline, hotel, and cruise line loyalty programs to a friend or colleague—even though the likelihood that customers would recommend the airline, hotel, and cruise line brands remained relatively steady (Exhibit 1).
A focus on a loyalty program’s bottom line can distract from its higher purpose
A travel loyalty program might be able—at least temporarily—to disappoint its members while inflicting minimal damage on its company’s earnings. This is because so much of a modern travel loyalty program’s importance comes from B2B sales of batched points or miles. The programs’ most relevant customers in terms of generating revenue are credit card companies, not individual travelers. And these B2B deals generally involve long-term contracts that guarantee sales years in advance. A travel brand can unilaterally issue more loyalty program points to sell to third parties at any time, as well as raise the redemption levels for flights or rooms if margins become undesirable.
Meanwhile, airline travelers have fewer options than they did in the past. Consolidation of major airline brands means it’s harder for frequent fliers to abandon one airline and its loyalty program for another without losing access to convenient flight routes or departure times. And customers who have already banked a large number of miles or points with one airline or hotel program can feel locked in.
For all these reasons, loyalty programs appear to be in a position of strength. But a narrowed emphasis on revenue and costs could lead to brands’ losing focus of the big picture. Travel loyalty programs were originally conceived as a clever way to influence customer behavior—and encourage customer loyalty. But it’s not clear if the programs are currently fulfilling either mandate as successfully as they could.
McKinsey research reveals that airline loyalty programs’ ability to change fliers’ behavior declined between 2017 and 2021, and again between 2021 and 2023 (Exhibit 2). During those time frames, it became less likely that a customer who was a member of a given airline loyalty program would report that they chose the associated airline over other options or increased the frequency of their spending with that airline. If this trend continues, it could eventually create a vicious cycle: airlines would cut loyalty program budgets if they deemed them ineffective at influencing customer behavior, lower budgets would lead to reduced program benefits, and less attractive benefits would result in customers perceiving program participation as having less value.
McKinsey research further shows that loyalty program members these days aren’t especially loyal (Exhibit 3). Hotel, cruise, and airline travelers are typically members of about three or four different loyalty programs within a given sector, our analysis finds. On a yearly basis, they consider traveling with about three different brands within that sector and ultimately transact with more than one of them. Travelers don’t even consolidate their spending with the brand they say they “prefer” within a sector: the median share of the customer’s wallet for preferred brands is only about 50 percent in lodging, 60 percent in cruise lines, and 60 percent in airlines—with the remainder of the customer’s spending spread around to other players within the same sector.
Evidence suggests this trend will persist. According to our 2023 survey on travel loyalty, younger generations are more likely to consider and transact with multiple travel players. Gen Zers and millennials consider about 1.7 times as many brands as do baby boomers and the Silent Generation and transact with about 1.3 times as many brands.
All this comes at a time when the travel loyalty market is becoming more competitive. Consumer banks, which were once content to offer cobranded credit cards featuring travel brands as the marquee partner, are now launching their own self-branded travel awards ecosystems and booking platforms. Travelers might wonder why they should put all their loyalty points in one basket with a single airline or hotel brand when a consumer bank might offer more flexible rewards redemption and possibly a better user experience. (It’s worth noting that our research suggests the likelihood that a customer would recommend some of the major consumer banks with travel loyalty initiatives to a friend or colleague is far higher than the likelihood that a customer would recommend a cruise line, lodging brand, or airline.)
How to reshape loyalty for a new travel landscape
Our research finds that experience —far more than tangible, “earn and burn” benefits—is what wins customers’ loyalty. Experiential factors, including “offering an experience worth paying more for” and “feeling taken care of,” have become more important over time and now account for three of the top five (out of more than 40) drivers of loyalty to cruise lines, hotels, and airlines. For hotels, experience has four times more impact than tangible benefits on purchase frequency, while for airlines, experience is more than twice as likely to influence frequency. Positive past experiences are the biggest factor in customers’ desire to travel more with a company in the future.
The following three steps could help travel brands adjust to this changing landscape and engender loyalty that goes beyond a mere quest for redemptions and perks.
Put experience at the core of loyalty programs
When our 2023 survey asked American respondents which company they’re most loyal to, Amazon received more votes than the top six travel players combined—despite the absence of any traditional, points-based loyalty program. How does Amazon win loyalty? By providing a frictionless experience.
How can travel brands learn from this and win customers’ love even when points and miles are worth less? By offering distinctive, satisfying experiences: making customers feel delighted is the key to their hearts, but McKinsey’s 2023 loyalty survey showed that only 20 percent of travelers were delighted by a recent travel experience.
Companies should strive to design loyalty programs around experiential benefits that make travelers feel special. This can be win–win, such as when Delta offered free in-flight Wi-Fi to loyalty members, which led to a better experience for the members while also boosting enrollment in Delta’s loyalty program. In retail, some programs bring together engaged communities of like-minded brand loyalists. Advance notice or exclusive access to offers can send loyalty members a signal that the brand considers them VIPs.
Brands should seamlessly integrate customer experiences between desktop, mobile, and physical locations—meaning that frontline workers have an important role to play. Proper execution of customer service is vital for getting experiences right, so companies should try to keep frontline workers top of mind. Workers should be given the proper training and tools to satisfy customers, and the effectiveness of this training should be measured.
When it comes to mitigating, or avoiding, a negative customer experience, saying “sorry” can go a very long way. Companies should proactively engage customers after service shortfalls, as a service challenge can actually lead to an increase in customer satisfaction if handled well. The form an apology takes might be made commensurate with a customer’s status level in the brand’s loyalty program, and any recompense can be informed by a predictive analysis of its impact —considering factors such as the magnitude of the lapse and the nature of the customer’s other recent interactions with the brand.
(Finally) use data to offer personalization to members
Travel brands have long had access to reams of customer data. Loyalty program members surf on travel companies’ Wi-Fi, sleep in their hotel rooms, fly on their planes, and cruise on their ships. But many travel brands haven’t yet captured the opportunity to use these unique data to offer their members personalization on par with other industries. Likewise, although airlines and hotels have incredibly sophisticated, lightning fast, AI-enabled pricing algorithms, they aren’t consistently harnessing their technology capabilities to power real-time customer personalization.
Nontransactional engagement opportunities, such as the daily interactions fostered by social communities, offer rich troves of data that can be used to hone personalization. In turn, personalization can drive engagement, as seen in Sephora’s Pocket Contour Class initiative, which lets users upload a selfie to get personalized makeup tips.
Personalization can be employed to tailor both experiences and offers for loyalty members. Our research has shown that 78 percent of consumers are more likely to make a repeat purchase when offered a personalized experience . The goal should be to achieve a hypersegmentation of program members that’s so nuanced, it results in a “ segment of one .”
Rethink partnerships to protect self-interests while delivering customer value
Since the 1980s, travel companies have been partnering with banks to launch cobranded credit cards. But several credit card brands now offer their own, self-branded travel rewards ecosystems. These ecosystems sometimes direct bookings to airlines, hotels, and cruise lines—but they can also serve as a way for credit card brands to steal away travelers’ loyalties. These types of transactional partnerships with consumer banks might eventually cease to be a winning play for travel companies. In time, travel loyalty programs could be driven to seek alternate sources of funding.
The best kinds of partnerships build richer connections with consumers while boosting engagement through thoughtful collaborations. Uber’s partnership with Marriott gives users the option to link the brands’ loyalty programs, tapping into two large customer bases and providing more convenient travel experiences.
One promising recent example of collaboration is a travel media network. A hotel company might, for instance, launch a media network that allows third-party brands to place relevant, nonintrusive, personalized advertisements in the hotelier’s owned spaces—websites, hotel lobbies, guest room TVs, and so forth. This type of partnership can offer travelers an elegant, curated experience while providing the travel brand with an alternate monetization route.
In general, travel companies should cultivate collaborations that protect their interests, generate new revenue streams, add personalization and value for loyal customers, and diversify touchpoints with those customers. Early action could prove vital here, as the travel space will not accommodate infinite partner ecosystems.
As other industries raise the bar and consumers grow increasingly dissatisfied with travel loyalty programs as they are designed today, travel industry leaders may need to ask themselves some hard questions. How can points and miles be paired with experiences and excitement? Which partners are truly adding value? What is causing customers to stray, and how can their loyalties be won back?
Travel brands were loyalty innovators. But travel loyalty programs might soon hit an inflection point. Now is the time to innovate and win back customers’ allegiances.
Lidiya Chapple is an associate partner in McKinsey’s Atlanta office, where Jillian Tellez Holub is a partner; Clay Cowan is a partner in the Dallas office; and Ellen Scully is a consultant in the Seattle office.
The authors wish to thank Bella Alfaro, Alex Cosmas, Marilyne Crépeau, Oren Eizenman, Austin Hack, Ryan Mann, Jacob Miller, Afiya Romeo, Matthew Straus, and Jamie Wilkie for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Seth Stevenson, a senior editor in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Prediction: The future of CX

Rebooting customer experience to bring back the magic of travel

Experience-led growth: A new way to create value
- Skip to main
- Skip to footer
- Board of Directors
- Walmart History
- New Home Office
- Working at Walmart
- Sam's Club
- Location Facts
- Contact Walmart
- Media Library
- Contact Media Relations
- Opportunity
- Sustainability
- Ethics & Integrity
- Belonging, Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Philanthropy
- ESG Reporting
- Health & Wellness
- Stock Information
- Financial Information
- Corporate Governance
- ESG Investors
- Investor Resources
- Supplier Requirements
- Apply to be a Supplier
- Supplier Inclusion
- Sustainability for Suppliers
- Investing In American Jobs
- Sam's Club Suppliers
- Walmart Growth Summits
- Ask Walmart
Walmart's Grocery Network Transformation: The Next Steps on Our Supply Chain Modernization Journey
By Dave Guggina, Executive Vice President, Supply Chain Operations, Walmart U.S.
July 10, 2024

Press Center
In the last several years, something has become very clear: Walmart customers love options. From the strength of our delivery business to our innovative aisles in-store and online, we’re witnessing shoppers make use of every opportunity to save money and live better.
As customers change the way they shop, we’re taking steps to build even more trust with them, ensuring the things they want – and need – are on shelves faster than ever before. To do that, we've been investing in data, increasingly intelligent software and automation – all to transform our business and create a more connected supply chain.
In the same way we added technology across our ambient and fulfillment networks, I’m excited to share more about the future of our grocery network. Our grocery transformation can be broken down into three distinct approaches:
- New builds — We’re building five brand new high-tech perishable distribution centers. Our first high-tech DC in Shafter, California has been operational since 2021. The second, located in Lancaster, Texas, is ramping operations and will be followed by Wellford, South Carolina; Belvidere, Illinois; and Pilesgrove, New Jersey. Collectively, these facilities bring around 2,000 new jobs into these communities and our supply chain network.
- Expansions — We’re expanding four traditional perishable DCs by adding over 500,000 square feet of automation per site to increase capacity for fresh product. We will expand facilities in Mankato, Minnesota; Mebane, North Carolina; Garrett, Indiana; and Shelbyville, Tennessee.
- Retrofits — Our Winter Haven, Florida perishable distribution center is getting upgraded, as we integrate the newest technology into the space. Our goal is to learn more about the feasibility and requirements of retrofitting an existing grocery building with automation technology – similar to how we have approached our ambient distribution center in Brooksville, Florida .
Investing in technology and our people
Our business is growing. Walmart is the largest grocery retailer in the U.S., with our grocery network supporting over 4,600 stores with a massive pickup and delivery business that continues to grow as customers seek the convenience and value we offer.
That’s why we’re adding state-of-the-art tech to our facilities: to enable greater speed and capacity that allows us to serve customers even more reliably. For example, these high-tech DCs can store double the number of cases and process more than twice the volume of a traditional perishable DC, more than doubling the number of cases processed per hour!
Here’s how the technology works:
- As cases come in from farmers and suppliers, they’re inspected for quality and de-palletized.
- The cases are then stored in an automated storage system that stretches nearly 80 feet tall and operates in a temperature-controlled environment.
- When it’s time to build a store order, the system retrieves the cases from storage to begin building store-ready pallets, which are built by department, making them easier to unload at the store.
- These intelligently layered pallets – with more fragile items, like eggs or fruit, toward the top – are then wrapped and loaded onto a truck for shipping.
We’re excited about what this technology will do for our business, but more than that, we’re excited about the opportunities it will create for associates. Technology is evolving physically demanding jobs into roles where associates are operating and maintaining high-tech systems, leading to an improved quality of life.
For example, associates who used to manually stack cases may work in a high-tech facility as an automation equipment operator and continue growing their career as an automation control center operator, automation technician or automation area manager. Plus, associates who have transitioned into these new roles tell us they are more enjoyable and satisfying, while also often resulting in higher base pay.
We remain committed to meeting customer demand, embracing technology and bringing our people alongside the technology as we transform our supply chain. With our investments in our associates and facilities, I’m confident we’re well-positioned to continue providing customers the items they want, whenever and wherever they want them, for years to come.
AI Transformation - An Enterprise Journey That Needs All of Us

COMMENTS
Customer journey mapping helps you keep track of customer touchpoints. Discover what a customer journey map is, how to create one, and best practices.
Discover how to start customer journey management using customer journey mapping, & how to improve journeys for the benefit of your customers.
A customer journey map is a visual overview of how customers experience your business across multiple touchpoints. Here's how to get started.
A customer journey map is a chart that displays the stages your customers experience when interfacing with your business. Here's how to create your own.
Customer journey maps are a powerful tool for understanding your customer's experience and adapting to meet their needs. Learn how to create a customer journey map (we even have free customer journey map templates available!).
A customer journey map (or CJM) is a visual representation of the process your customers go through when interacting with your company. This diagram takes you through the exact steps that lead to a customer choosing your specific product and buying it from your business. Creating a customer journey map will provide you with a visual storyline ...
This article walks you through the eight key stages of great customer journey mapping, and shows you how to adapt each to your unique business and product to optimize the customer experience from start to finish.
Customer journey maps are a powerful tool to understand and meet customer needs. Learn how to make your own customer journey map.
Here, you will find a detailed step-by-step guide on making a customer journey map (CJM), examples, expert tips, templates, and a PDF guide to download and save for later.
If you want to turn a potential customer into a lifetime one, you'll need to know all stages of the customer journey. We'll show you how.
A customer journey map is the key to understanding each segment of your target audience. Learn how to create customer journey maps that engage every audience.
Learn how effective customer journey management requires a keen understanding of how your customers move from touchpoint to touchpoint.
Customer journey mapping is key to building a solid marketing strategy. We cover everything you need to know about customer journey maps, their different types, examples, and the steps to making your own.
A customer journey is an entire customer experience while communicating with a brand. Learn more about the customer journey & how it impacts.
A customer journey map helps you eliminate pain points, resolve bottlenecks and optimize the customer experience. Here's how to create one.
A customer journey map is a visualization of a customer's experience with a company, product or service. It begins when the customer first becomes aware of a need and ends at the level of loyalty. The map tracks all the contact moments the customer has with a brand, both online and offline.
A customer journey map is a representation of the various experiences customers have while interacting with your company. Learn why you need one and how you can build it.
Looking for customer journey touchpoint examples? Read on to discover 20 touchpoints for different journey stages. Learn how to optimize them!
Using a customer journey map to analyze user behavior helps you understand how your customers travel through the sales process. Find out how to create one!
Dive into our in-depth guide on customer journey stages to drive customer satisfaction and loyalty throughout their journey.
The customer journey mapping process puts the organization directly in the consumer's mind to better understand the customer's processes, needs, and perceptions. A journey map lays out all touchpoints that your customer may have with your brand - from how they first heard of you through social media or brand advertising, to their direct ...
A customer-journey map is an infographic visualization of the process that a persona segment goes through in order to accomplish a goal. Journey maps are useful in communicating the general narratives and themes uncovered by longitudinal research done to understand how a customer works toward a goal over time.
Customer journey mapping is an important first step in creating a more deliberate, seamless, end-to-end customer experience. In this blog, we'll share our top tips for conducting an effective customer journey mapping workshop.
Create engaging Retail Customer Journey Map Slides in white and blue. Fully customizable and completely free to use. Get started now!
Members of travel brands' loyalty programs have become increasingly disloyal. We look at how the travel industry can bring these straying customers back.
Walmart's Grocery Network Transformation: The Next Steps on Our Supply Chain Modernization Journey Walmart's Grocery Network Transformation: The Next Steps on Our Supply Chain Modernization Journey. By Dave Guggina, Executive Vice President, Supply ... We remain committed to meeting customer demand, embracing technology and bringing our people ...
The transformation journey will take everyone in an organization, from top leadership to customer-facing team members, all of whom are enabled in their roles by the digital expertise found in the technology group.
Chatbots incorporate various behavioral and psychological marketing elements to satisfy customers at various stages of their purchase journey. This research follows the foundations of the Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM) and examines how cognitive and peripheral cues impact experiential dimensions, leading to chatbot user recommendation intentions.