Monkey: A Folk Novel of China
By wu ch'eng-en, monkey: a folk novel of china summary and analysis of chapters 13-20.
Summary and Analysis
Chapters 13 and 14 see Tripitaka set out on his journey with his two followers only to be captured by a band of ogres as a meal. His two followers eaten, Tripitaka is saved by the Spirit of the Planet Venus, disguised as an old man. Nevertheless, Tripitaka's journey continues to be fraught with peril as he is surrounded by deadly beasts only to be saved from a tiger by a hunter after many hours of fighting, who takes him in. During his time at the hunter's home, Tripitaka prays continually which saves the hunter's deceased father from the terrible underworld he has been tormented in and allowed him to be reincarnated -- as is revealed in a dream. The hunter and Tripitaka journey to the Mountain of Two Frontiers, where the land of the Tartars lies on the other side. Suddenly, the two hear a voice saying, " The Master has come." The hunter realizes that this is the voice of Monkey , who was imprisoned beneath this mountain (once known at the Mountain of Five Elements long ago. Tripitaka frees Monkey by taking away the seal Buddha placed on top of the mountain that reads OM MANI PADME HUM.
The hunter returns home, while Tripitaka and Monkey face off with another tiger, which Monkey dispatches with his magic iron much more quickly than the hunter did. He turns the tiger's skin into clothing and the two take refuge at the house of an old man and his wife. On the road again, six robber kings besiege them; Monkey kills them, and he and Tripitaka have a falling out over whether killing is acceptable. Monkey packs his things and leaves, while Tripitaka meets Kuan-yin disguised as a kindly old woman, who gives him a magic spell to keep Monkey obedient. Meanwhile, Monkey visits the Dragon King of the Eastern Ocean, who counsels patience and self-control, leading Monkey to return to Tripitaka. Tripitaka uses the Tight Fillet on Monkey, who promises to be good and obey him, just as Kuan-yin predicted.
In Chapter 15, the two travelers have their horse eaten by a dragon. Two deities sent by Kuan-yin, Lu Ting and Lu Chia, as well as the Gold-headed Guardian, descend to guard Tripitaka while Monkey confronts the dragon. The fight ends inconclusively, and they call the Bodhisattva for help. She confronts the dragon, who makes the excuse that Monkey did not announce who he was when asked. Kuan-yin transforms the dragon into the lost horse and he carries the travelers as he promised long ago. Before leaving, Kuan-yin gives Monkey three magic hairs to get him out of any trouble, and he returns to where Tripitaka has been waiting.
In Chapter 16, the two travelers make their way to Kao Farm, where a monster named Hog Fu-ling has carried off the farmer’s youngest daughter, Blue Orchid; a good exorcist must be summoned. Monkey offers his services to the despondent Mr. Kao and frees the daughter from her outhouse prison. He then disguises himself as Blue Orchid and has the monster tell him where he is from, before revealing his true form. Monkey's reputation precedes him and the monster runs away in fear. Throughout Chapter 17, the monster continues to flee and protests his merits, until Monkey mentions they are seeking scriptures, at which point the monster reveals that he was sent to wait for them by Kuan-yin. Tripitaka does not accept any of Mr. Kao's gifts of gratitude, but the monster, Pigsy , asks for a new jacket, which he receives.
Chapter 18 follows a similar vein, where the travelers again take a creature at the River of Flowing Sands for a monster who is actually a friend converted by Kuan-yin, in this case a deity named Sandy , who was banished from Heaven for breaking a crystal dish. He helps the travelers across the enormous river by giving them nine skulls that transform into a holy ship. Tripitaka has a dream in Chapter 19 where the ghost of the king of Crow-cock visits him and tells him of his misfortunes. After a massive famine, an imposter sits on his throne, and for the past three years no one has been the wiser. The king gives Tripitaka a white jade tablet so that his loved ones will recognize it is really the king who sends this message. Tripitaka takes Monkey in a small casket to the king's son the next day while he is hunting, and Monkey recounts what happened to the prince's father. He shows him the tablet and the prince rides off to his mother for confirmation.
In Chapter 20, after showing his mother the tablet and receiving confirmation that the king has been different these last three years, the prince returns to Monkey. He asks for game to keep up the pretense that he has been hunting all day and Monkey obliges by asking his deities. Monkey worries to Tripitaka that he overstated his abilities to the prince and might not be successful in removing the imposter form his throne and asks to take Pigsy with him. The two decide to steal treasure first, with Pigsy keeping the treasure and Monkey the fame. They set off to the Imperial Flower Garden and find a watery well with the Crystal Palace of the Dragon King of the Well at the bottom. Pigsy is lowered down on Monkey's magic iron and the dragon recognizes him, and gives him the king's body, which he has preserved with a magical pearl. Frightened, and wanting real treasure, Pigsy surfaces without the corpse and demands to be taken back up. Monkey refuses until Pigsy takes the corpse too, and the two bring it to Tripitaka who wails at the sight of the deceased king. Pigsy, wanting revenge, tells Tripitaka that Monkey could perhaps revive the king if properly motivated—say, by the headache-inducing spell or the painful Fillet.


Monkey: A Folk Novel of China Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for Monkey: A Folk Novel of China is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
Through their long journey to India to retrieve the scriptures, what do the main characters (Tripitaka, Monkey, Pigsy, Sandy) learn about themselves, each other, and their own beliefs? How do they react to various circumstances?
These are thematic ideas. You can find out about what they learned and how they grew at the themes link below:
https://www.gradesaver.com/monkey-a-folk-novel-of-china/study-guide/themes
Compare and contrast the role of two religions in Monkey. Do they always work in harmony? Do they have separate hierarchies? Conflicting ideologies? Do they provide sources of conflict? If so, how and why?
Thanks for your questions. This is only a short answer space but I can make a general comment.
Tripitaka is taking the journey from China in the east to India where Buddha has his holy scriptures so the religion of Buddha can spread and people can...
Analyzing how the writer used description/
Okay, so what writer/text is it? If you have an extract could you send it? You're only focusing on 'description', so stuff like language devices really: metaphors, similes, personification, [in poems especially, anaphora, enjambment, caesura,...
Study Guide for Monkey: A Folk Novel of China
Monkey: A Folk Novel of China study guide contains a biography of Wu Ch'eng-en, literature essays, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About Monkey: A Folk Novel of China
- Monkey: A Folk Novel of China Summary
- Character List
Essays for Monkey: A Folk Novel of China
Monkey: A Folk Novel of China essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of Monkey by Wu Ch'eng-en.
- Monkey and The Ramayana
- “The Monkey and the Monk”: An Allegory of Buddhist Teachings
Wikipedia Entries for Monkey: A Folk Novel of China
- Introduction
- Historical context
- Main characters

Journey to the West | Full Story, Summary & Moral Lessons
- February 19, 2024
“Journey to the West” stands as one of the pinnacles of Chinese literature, a riveting blend of mythology, folklore, humor, and spirituality .
Authored by Wu Cheng’en in the 16th century during the Ming dynasty, this epic novel has transcended its cultural origins to become a global literary treasure!
The narrative follows the perilous journey of the Buddhist monk Xuanzang, historically known, as he travels to India to obtain sacred Buddhist scriptures. Accompanied by his three disciples— Sun Wukong , Zhu Bajie, and Sha Wujing—each with their own unique abilities, their quest is filled with divine interventions, battles with demons, and moral lessons.
Many of which we will be getting to know today!
Table of Contents
Historical Context
The “Journey to the West” is deeply entwined with the real-life travels of Xuanzang (602-664 CE), whose pilgrimage to India and back took 17 years, a journey undertaken to obtain authentic Buddhist scriptures.
Wu Cheng’en’s fictionalized account, however, does more than narrate a religious quest; it weaves a rich story of Chinese myths, Taoist and Buddhist philosophy, and satirical commentary on the social issues of his time, making it a multifaceted work of art.
If you’re interested in watching the Journey to the West, I highly recommend the 1986 series as it’s often lauded as being not only the most accurate but also you can really feel the love and respect given to the adaptation.
Key Characters
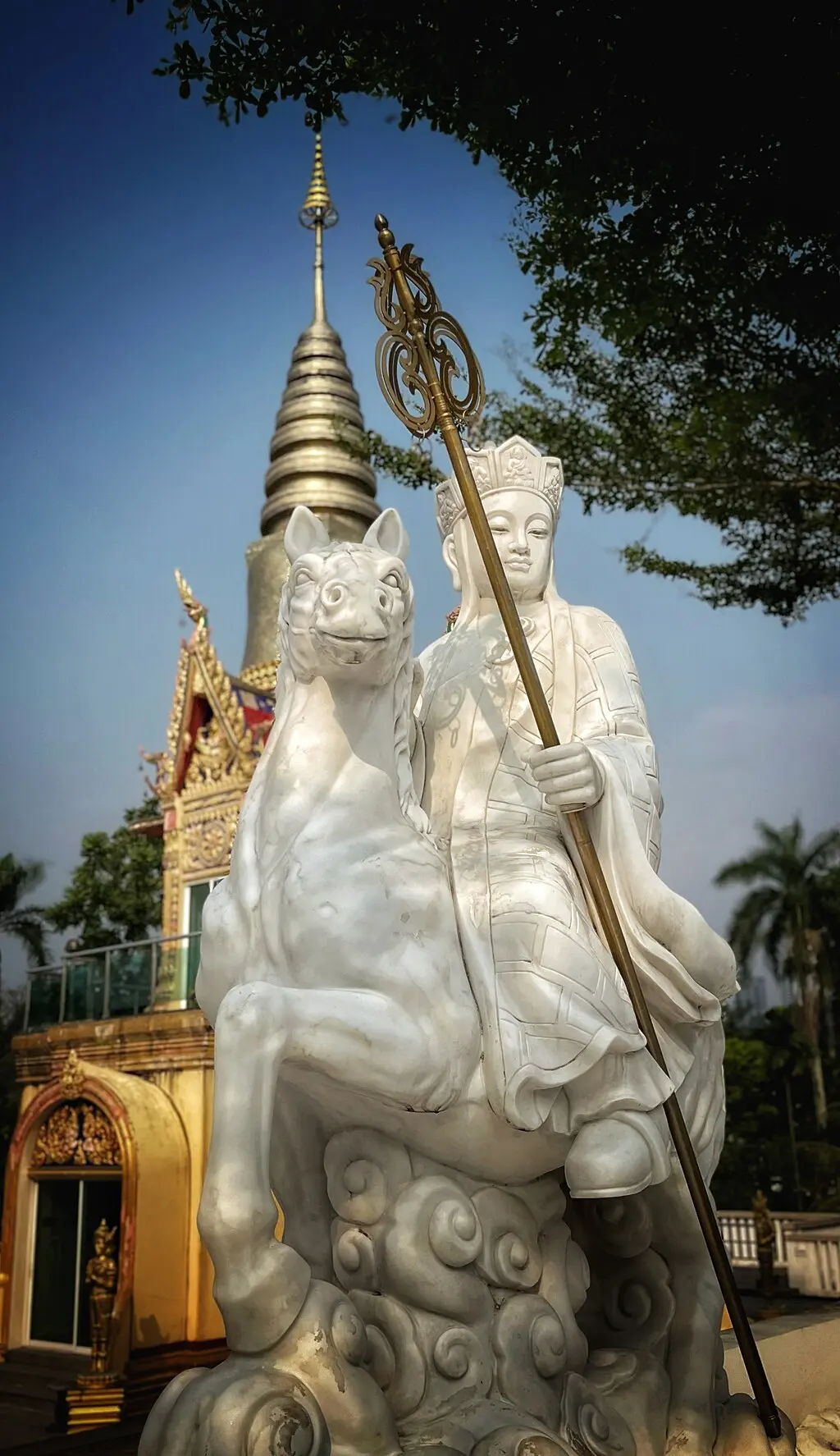

Tang Sanzang
Tang Sanzang, also known as Tripitaka , stands at the heart of “Journey to the West” as its protagonist. His mission to retrieve sacred Mahayana Buddhist scriptures from India serves as the narrative’s driving force. Tang Sanzang embodies virtues such as humility, compassion, and unwavering dedication to his spiritual quest.
His portrayal as the epitome of piety and moral integrity offers a rich canvas against which his interactions with disciples and various challenges unfold.
Tang Sanzang’s personality is a blend of devout faith and moral steadfastness. He is the moral compass for his disciples, guiding them not only towards their external goal but also on their internal journeys of growth and enlightenment .
Despite his virtues, Tang Sanzang is not portrayed as infallible. His naivety and strict adherence to religious doctrines sometimes lead him into trouble, requiring rescue by his more worldly and powerful disciples. This aspect of his character highlights the novel’s exploration of the balance between innocence and wisdom, as well as the necessity of worldly knowledge in achieving spiritual goals.
Throughout the novel, Tang Sanzang undergoes significant development. His journey is not only a physical one across dangerous terrains but also a spiritual odyssey that tests and refines his character. He learns to balance his strict moral codes with the practicalities of the world, growing in understanding and compassion towards his disciples and the beings they encounter.
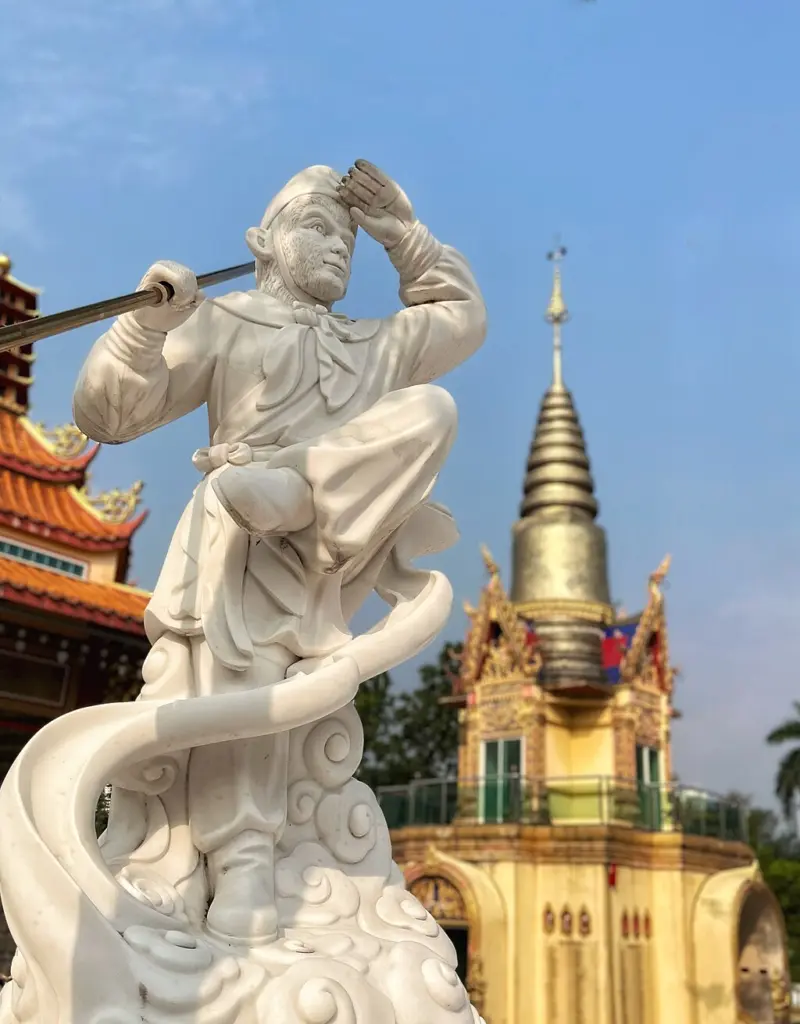

Sun Wukong , famously known as the Monkey King , is one of the most beloved characters in “Journey to the West.”
His origins are as magical as his personality; born from a stone egg on the Mountain of Flowers and Fruit, Sun Wukong acquires supernatural powers through Taoist practices.
His abilities include shape-shifting, immense strength, and the ability to travel vast distances in a single somersault. Despite his powers, Sun Wukong’s early journey is marked by rebellion and pride, leading him to challenge the heavens themselves.
His initial defiance against the celestial order and subsequent punishment—being imprisoned under a mountain by the Buddha—sets the stage for his redemption arc.
His release by Tang Sanzang and commitment to protect the monk on the journey to India is a turning point, marking his transition from a rebellious figure to a devoted disciple. This journey serves as a path of self-discovery and spiritual maturation for Sun Wukong, as he confronts challenges that test his ingenuity, patience, and fidelity.
The Monkey King’s personality is multifaceted; he is cunning and playful, yet capable of profound wisdom and bravery. His loyalty to Tang Sanzang is unwavering, and he becomes the monk’s most powerful protector, using his abilities to overcome demons and obstacles that the pilgrimage encounters. Sun Wukong’s transformation from a mischievous troublemaker to a protector embodies the novel’s themes of redemption and the possibility of spiritual growth regardless of one’s past.
In terms of symbolic significance, Sun Wukong represents the untamed mind and the potential for enlightenment within all beings. His journey from arrogance to enlightenment mirrors the Buddhist path, emphasizing the importance of humility, learning, and devotion.
Through Sun Wukong, “Journey to the West” explores the idea that even the most unruly spirits can achieve enlightenment through perseverance, guidance, and self-reflection.
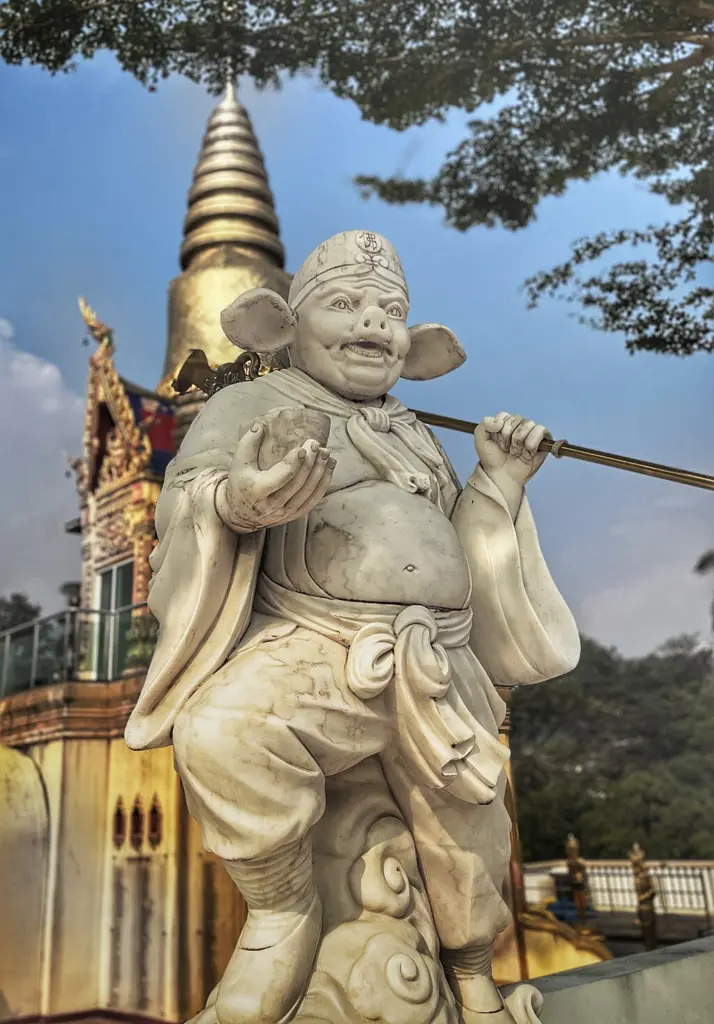

Zhu Bajie, often referred to as Pigsy , is known for his complex and somewhat contradictory character traits. Originally a marshal in the celestial army, Zhu Bajie was banished to the mortal realm as a punishment for his indiscretions in heaven, particularly with the Moon Goddess, Chang’e .
Transformed into a pig-human hybrid, his appearance reflects his base nature and penchant for indulgence, especially in food and women. Despite these flaws, Zhu Bajie becomes one of Tang Sanzang’s disciples, joining the quest to retrieve the Buddhist scriptures from India.
Zhu Bajie’s personality is marked by a mix of bravery and cowardice, loyalty and self-interest, wisdom and folly. He often provides comic relief in the story through his antics and bumbling mistakes, yet his character also displays moments of insight and bravery.
His earthly desires and tendencies towards laziness often put him at odds with his more disciplined and spiritually focused companions, particularly Sun Wukong, with whom he shares a rivalry.
While he deeply respects Tang Sanzang and is committed to the pilgrimage, his weaknesses often lead to complications and challenges for the group. However, these shortcomings make his moments of courage and sacrifice all the more significant, highlighting the theme of redemption and the possibility of moral and spiritual growth regardless of one’s past actions or nature.
Zhu Bajie’s character serves as a reflection on human nature, embodying the struggles between base desires and higher aspirations, between selfishness and altruism. His journey alongside Tang Sanzang is as much about his own redemption and transformation as it is about the physical pilgrimage to India.
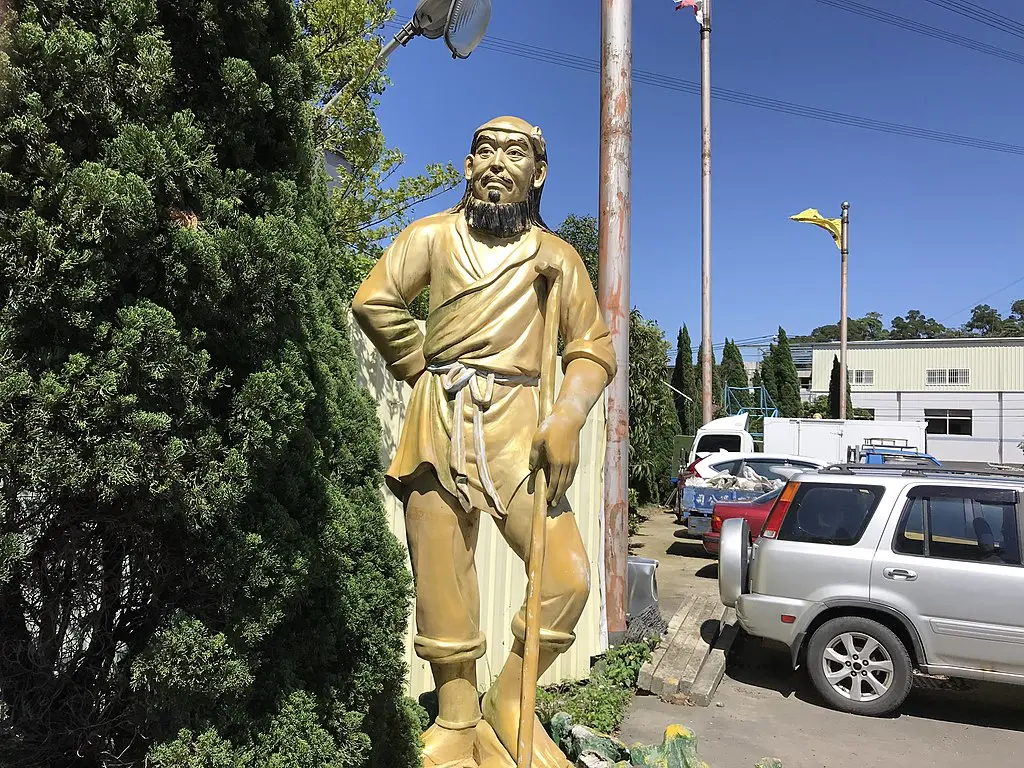

Sha Wujing, or Sandy , is the third disciple who joins Tang Sanzang. Once a celestial general, Sha Wujing was banished to the mortal world as punishment for a transgression in heaven, where he was transformed into a river ogre.
His frightening appearance belies a kind heart and a steadfast, loyal nature. Recognizing his past mistakes, Sha Wujing seeks redemption through service to Tang Sanzang on the perilous journey to the West.
Characteristically, Sha Wujing is the embodiment of stoicism and reliability. Compared to the more flamboyant Sun Wukong and the often comically flawed Zhu Bajie, Sha Wujing’s demeanor is subdued and earnest.
He is less prone to the antics and disputes that sometimes ensnare his fellow disciples, showcasing a level of maturity and wisdom that stabilizes the group. His role is often that of the peacemaker, bridging gaps between his more temperamental companions and ensuring the pilgrimage remains focused on its spiritual goals.
Armed with a magic staff that he uses to combat demons and other threats, he is a formidable fighter in his own right. His knowledge of aquatic environments also proves invaluable, as many of the journey’s challenges take place near or in water.
The Journey to the West

The Origins
In the lush, mystical expanse of the Mountain of Flowers and Fruit, a stone egg, nurtured by the elements and the heavens, gave birth to Sun Wukong, the Monkey King. This miraculous birth marked the beginning of an extraordinary being destined to leave an indelible mark on the realms of gods and mortals alike. Possessing incredible strength, agility, and a keen intellect from birth, Sun Wukong quickly established himself as the king of the monkeys, securing their loyalty through his bravery and wisdom.
Driven by an insatiable curiosity and the fear of death, Sun Wukong embarked on a quest for immortality. His journey led him to the tutelage of a Taoist sage, from whom he learned the secrets of magical arts, shape-shifting, and the way of immortality. These newfound powers, coupled with his natural cunning and prowess, made Sun Wukong a being of unmatched ability.
However, with great power came a great desire for recognition and respect. Sun Wukong’s ambitions soon turned him against the celestial order. Seeking to claim his place among the gods and immortals, he caused havoc in the heavens, challenging the authority of the Jade Emperor himself. His antics and defiance led to a celestial war between his monkey army and the heavenly forces.
The turmoil caused by Sun Wukong could not go unpunished. Despite his might, he was eventually captured by the combined efforts of the Buddha and the celestial army. To curb his rebellious spirit, Buddha imprisoned Sun Wukong under the Five Elements Mountain, sealing him with a magical spell for five hundred years. This punishment was not just a consequence of his actions but also a pivotal moment of transformation. Under the mountain, Sun Wukong was forced to reflect on his deeds and the consequences of his unchecked ambition.
This period of imprisonment was a crucible, tempering Sun Wukong’s fiery spirit with a newfound understanding of responsibility and the importance of humility. It was here, in the shadow of his actions and under the weight of the mountain, that the foundation was laid for his redemption and eventual role as a protector on the journey to the West.
The Calling of Tang Sanzang
In the empire of the Tang Dynasty, under the watchful eyes of celestial beings, the birth of Tang Sanzang was foretold with a prophecy. He was destined to be no ordinary monk, but one whose journey would mark a pivotal moment in the spiritual fabric of the world. From an early age, Tang Sanzang displayed an uncommon devotion to his Buddhist faith, his heart set on understanding the deepest truths of existence and alleviating the suffering of all beings. His life was filled with piety, scholarship, and an unwavering commitment to the path of enlightenment, setting him apart as a vessel for divine purpose.
The turning point in Tang Sanzang’s life came through a divine revelation, where the Bodhisattva Guanyin presented him with a mission of paramount importance. He was to travel to the Western regions of India to retrieve sacred Buddhist scriptures not yet available in China . These texts held the key to deepening the spiritual understanding and salvation for countless souls in his homeland. This was not just a journey across lands; it was a pilgrimage that would test the limits of his faith, endurance, and spirit.
The gravity of this mission was clear; the scriptures were vital for the propagation of Buddhism in China, promising a new era of spiritual insight and enlightenment. However, the path to the West was fraught with perils beyond imagination—demons, treacherous landscapes, and trials that would challenge the very essence of his being. It was a journey that no one could undertake alone and survive, let alone succeed.
Recognizing the monumental challenges that lay ahead, the Bodhisattva Guanyin promised Tang Sanzang divine assistance in the form of disciples who would protect and guide him through the dangers. These disciples, each with their own paths to redemption and enlightenment, were destined to be united with Tang Sanzang, forming an unlikely fellowship bound by a shared mission.
Thus began Tang Sanzang’s journey, a quest that was not only his own but one that carried the hopes and spiritual aspirations of the entire Buddhist community. With the divine mandate bestowed upon him, Tang Sanzang set forth, stepping into the annals of legend.
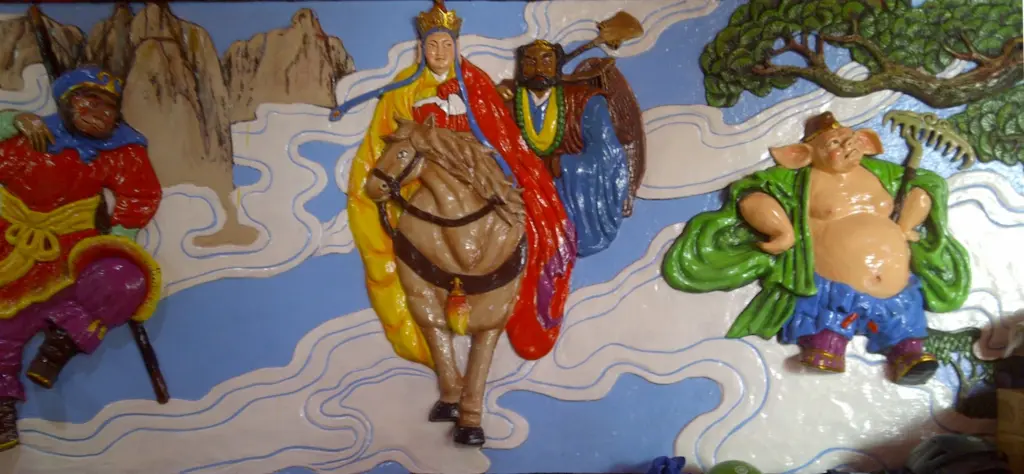

Assembling the Disciples
As Tang Sanzang began his perilous journey to the West, the first to join him was none other than Sun Wukong, the Monkey King. Freed from his five-century imprisonment under the Five Elements Mountain by Tang Sanzang himself, Sun Wukong was bound to him by a vow. This vow, forged in the fires of redemption (and the head-tightening band), was Sun Wukong’s promise to protect Tang Sanzang throughout the journey. The release symbolized not only Sun Wukong’s second chance but also the formation of an unbreakable bond between the disciple and his master. With his unparalleled martial prowess and magical abilities, Sun Wukong was a formidable protector, one whose loyalty and dedication to Tang Sanzang’s mission were beyond question.
The next to join this celestial mission was Zhu Bajie, once a marshal in the heavens, now living as a half-human, half-pig being as punishment for his lascivious behavior in the celestial realm. Encountered by Tang Sanzang and Sun Wukong, Zhu Bajie was persuaded to join the pilgrimage, seeking redemption for his past misdeeds.
Sha Wujing, the third disciple, was once a celestial general who, due to a grave mistake, was banished to a river, taking the form of a fearsome water ogre. His encounter with Tang Sanzang and the promise of redemption through service transformed Sha Wujing from a feared monster into a loyal disciple.
Together, these three disciples, each with their unique strengths, weaknesses, and backgrounds, formed the core of Tang Sanzang’s entourage. Their assembly was no mere coincidence but a divinely orchestrated gathering of souls seeking redemption, enlightenment, and the fulfillment of a sacred mission.
Trials and Tribulations
As Tang Sanzang and his newly assembled disciples embarked on their journey to the West, they were soon met with a series of trials that tested their resolve, unity, and individual capabilities. These challenges served not only as obstacles to be overcome but also as crucibles for character development and bonding among the pilgrims.
One of the first major trials they faced was the Black Wind Mountain, where a fierce demon known for capturing and eating travelers threatened their mission. It was here that Sun Wukong’s prowess and quick thinking were first put to the test, showcasing his ability to protect Tang Sanzang against seemingly insurmountable odds.
Another significant challenge came in the form of the White Bone Demon, a creature capable of changing its form to deceive and capture Tang Sanzang. This trial tested not only the physical strength of the disciples but also their wisdom and ability to see through deception.
These early trials also brought to the forefront the dynamics and interactions among the disciples. Sun Wukong’s impulsive nature and readiness to use force were often at odds with Tang Sanzang’s more compassionate and pacifistic approach, leading to tensions within the group. Zhu Bajie and Sha Wujing, each with their distinct personalities and strengths, found themselves navigating the complex dynamics between their desire for redemption and the often chaotic leadership of Sun Wukong.
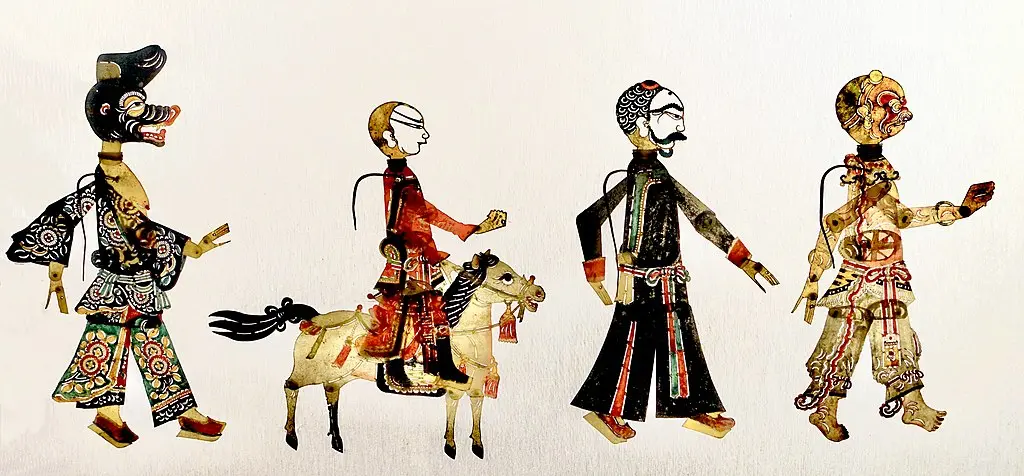

The Final Challenges
As Tang Sanzang and his disciples neared the end of their epic quest to retrieve the sacred scriptures from the West, they encountered the Fiery Mountain, a vast barrier of flames that seemed insurmountable. This natural obstacle was a metaphor for the burning trials of the spirit, a test of their resolve and unity. To pass, they needed the fan of the Princess Iron Fan, a task that proved to be as much about diplomacy and wisdom as it was about strength and courage. The quest for the fan was marked by deception and challenges that tested their patience and ingenuity, especially for Sun Wukong, whose confrontations with the Princess pushed him to find non-violent solutions.
Following this, the pilgrims faced the ordeal of the Tenfold Maze, a bewildering labyrinth that tested their mental endurance and faith. The Maze, crafted by powerful magic, represented the inner confusions and doubts that can lead one astray from the path of enlightenment. Each turn and dead end forced the disciples to rely not just on Sun Wukong’s strength or Zhu Bajie’s might, but on Tang Sanzang’s unwavering faith and Sha Wujing’s quiet determination. It was their unity and collective wisdom that eventually led them through the maze, symbolizing the triumph of shared purpose over individual despair.
Perhaps the most significant trial came in the form of a spiritual challenge directly from the Buddha. Before granting them the scriptures, Buddha tasked Tang Sanzang and his disciples with a final test of their virtues and understanding of the Buddhist teachings. This trial was not about battling demons or overcoming physical barriers but confronting their inner selves and the essence of their journey. Each disciple, including Tang Sanzang, faced manifestations of their past errors, fears, and desires, challenging them to apply the lessons of compassion, humility, and perseverance they had learned on their journey.
The confrontation with their inner demons was a profound moment for the pilgrims, especially for Sun Wukong, whose journey from rebel to protector had been fraught with pride and anger. For Zhu Bajie, it was a moment to transcend his baser instincts and desires, while Sha Wujing confronted the solitude and obscurity of his existence with newfound peace. For Tang Sanzang, it was the ultimate test of his faith and his commitment to his mission, proving his worthiness to receive the sacred texts.
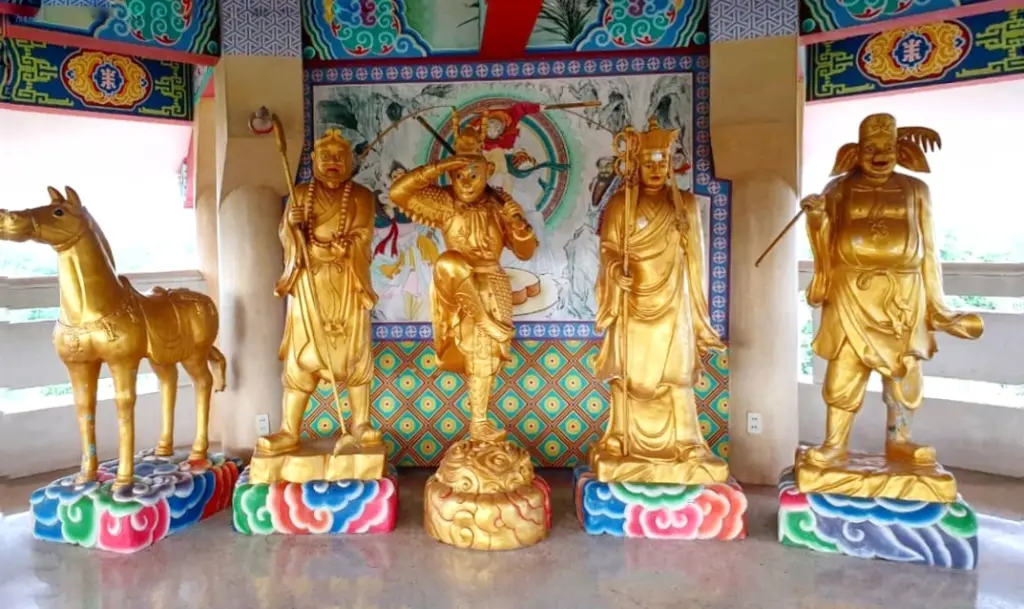
Arrival in the West
After overcoming the final, daunting challenges set before them, Tang Sanzang and his disciples reached their sacred destination in the West. It was here, in the presence of the Buddha, that they were finally granted the sacred scriptures.
The attainment of the sacred scriptures was an achievement of monumental significance. For Tang Sanzang, it represented the fulfillment of a divine mission entrusted to him, affirming his unwavering faith and dedication. The scriptures themselves were not just texts but beacons of wisdom, destined to enlighten countless generations to come. Their acquisition symbolized the bridging of divine knowledge from the West to the East, promising an era of spiritual awakening and understanding for Tang Sanzang’s homeland.
For the disciples, the journey to the West and the acquisition of the scriptures were transformative. Sun Wukong, once a rebellious figure driven by pride and the desire for immortality, emerged as a being of enlightenment, his actions tempered by wisdom and compassion. The journey refined his character, turning his immense power and cunning into instruments of protection and service to a cause greater than himself.
Upon their return to the Tang Empire, the pilgrims were received with reverence. The sacred scriptures were translated and spread, seeding the growth of Buddhism and its teachings throughout the land. The disciples, each awarded divine recognition for their service, achieved a form of enlightenment that transcended their former selves ( Both Sun Wukong and Tang Sanzang were turned into Buddhas .)

Summary of the Journey to the West
“Journey to the West” is a chronicling of the pilgrimage of the Buddhist monk Tang Sanzang and his quest to retrieve sacred scriptures from India. Alongside him are his three disciples: Sun Wukong, the Monkey King, with his unparalleled martial prowess and magical abilities; Zhu Bajie, the gluttonous and lecherous pig demon with a heart of gold; and Sha Wujing, the steadfast and reliable river demon. Each disciple, once celestial beings now seeking redemption for past transgressions, brings unique strengths and weaknesses to the journey, creating a dynamic and sometimes volatile mix of personalities.
The narrative begins with the birth and rise of Sun Wukong, who, after acquiring magical powers and challenging the heavens, is imprisoned under a mountain by the Buddha for his arrogance. Meanwhile, Tang Sanzang, chosen by the Bodhisattva Guanyin , embarks on a mission to the West to obtain Buddhist sutras that will enlighten the East. Along the way, he liberates and recruits Sun Wukong, Zhu Bajie, and Sha Wujing, who vow to protect him in exchange for their spiritual redemption.
Their journey is fraught with peril, encountering a series of demons and monsters intent on capturing Tang Sanzang for their own gain. Each challenge tests the group’s resolve, faith, and unity, with Sun Wukong’s quick wit and might often saving the day. Despite their differences and the difficulties they face, the pilgrims learn valuable lessons in compassion, patience, humility, and perseverance. These trials serve not only as physical obstacles but as spiritual tests, refining each disciple’s character and strengthening their bonds.
The pilgrimage is marked by significant trials, from battling the fiery Red Boy and outsmarting the cunning Spider Demons to navigating the treacherous Flaming Mountain and the illusion-filled Tenfold Maze. Each ordeal brings them closer together, teaching them the importance of teamwork, sacrifice, and the pursuit of enlightenment.
Upon reaching the West and passing the final tests set by the Buddha, Tang Sanzang and his disciples are granted the scriptures. Their return to the Tang Empire is triumphant, with each disciple achieving enlightenment and recognition for their service. The sacred texts they bring back promise a new era of spiritual awakening for their homeland.
- Loyalty and Devotion: The loyalty of Sun Wukong, Zhu Bajie, and Sha Wujing to Tang Sanzang is a central theme that underscores the importance of fidelity in the face of adversity. Their unwavering commitment to protect their master and ensure the successful retrieval of the sacred scriptures speaks to the value of loyalty in achieving a higher spiritual purpose.
- Perseverance through Trials: The pilgrims’ journey is fraught with challenges that test their resolve, faith, and endurance. Each trial, whether it be a confrontation with demons or overcoming natural obstacles, symbolizes the inner struggles individuals face on their path to enlightenment.
- The Quest for Enlightenment: At its heart, “Journey to the West” is a spiritual odyssey that mirrors the Buddhist path to enlightenment. The journey to retrieve the scriptures symbolizes the pursuit of wisdom and understanding, essential for liberation from suffering and the cycle of rebirth. The transformations of the characters, especially the disciples, reflect the individual’s journey toward enlightenment, marked by self-discovery, repentance, and spiritual growth.
- The Battle between Good and Evil: The frequent encounters with demons and the celestial trials faced by Tang Sanzang and his disciples embody the eternal struggle between good and evil. This theme is not only external, in the battles with literal demons, but also internal, representing the moral and spiritual conflicts within each character.

- Characters as Symbolic Archetypes: The main characters of “Journey to the West” are rich in symbolic significance. Sun Wukong, with his rebellious nature and transformative journey, symbolizes the untamed mind and the potential for enlightenment through discipline and self-cultivation. Zhu Bajie represents human desires and flaws, highlighting the struggles and potential for redemption despite one’s imperfections. Sha Wujing embodies steadfastness and humility, qualities essential for spiritual progress.
- Events as Metaphors for Spiritual Lessons: Many of the events and trials encountered by the pilgrims are metaphors for spiritual lessons. For example, the crossing of the Flaming Mountain can be seen as a metaphor for overcoming the burning passions and attachments that hinder spiritual growth. The encounters with various demons can represent the overcoming of personal obstacles on the path to enlightenment.
- The Journey Itself: The journey to the West is symbolic of the Buddhist path towards enlightenment. It is fraught with difficulties and distractions, much like the spiritual journey of an individual.
Moral Lessons
- Redemption and the Potential for Change : The characters of “Journey to the West,” especially the disciples of Tang Sanzang, embody the theme of redemption and the belief in the potential for change. Sun Wukong, Zhu Bajie, and Sha Wujing, each banished for their transgressions, find in their journey an opportunity for transformation. Their willingness to protect Tang Sanzang and endure hardships for the sake of obtaining the sacred scriptures illustrates the possibility of redemption, regardless of past misdeeds. This reflects the Buddhist concept of karma and the idea that positive actions can counteract negative past actions, leading to spiritual growth and liberation.
- Virtue and Moral Integrity : Throughout the novel, Tang Sanzang serves as a moral compass, embodying virtue and moral integrity. His compassion, patience, and unwavering commitment to non-violence, even in the face of danger, highlight the importance of upholding one’s principles. Tang Sanzang’s interactions with demons, often opting for understanding and conversion rather than conflict, reinforce the novel’s message that compassion and wisdom are more powerful than force.
- The Pursuit of Knowledge and Enlightenment : “Journey to the West” places great emphasis on the pursuit of knowledge and enlightenment, both as a personal quest and for the benefit of others. The journey to obtain the Buddhist scriptures symbolizes the quest for spiritual knowledge and truth. This quest is not portrayed as easy or straightforward but rather as a path filled with obstacles that require perseverance, sacrifice, and moral fortitude to overcome.
- Humility and Self-Cultivation : Finally, “Journey to the West” teaches the importance of humility and self-cultivation. The characters, particularly Sun Wukong, learn to temper their pride and recognize their limitations. This humility, coupled with a commitment to self-improvement and spiritual cultivation, is portrayed as essential for growth and enlightenment. The novel thus conveys the moral lesson that true strength and wisdom come from understanding oneself, acknowledging one’s flaws, and striving for self-betterment.
SHARE THIS POST
Read this next.

A Spiritual Trek Through Yolyn Am | The Valley of Ice
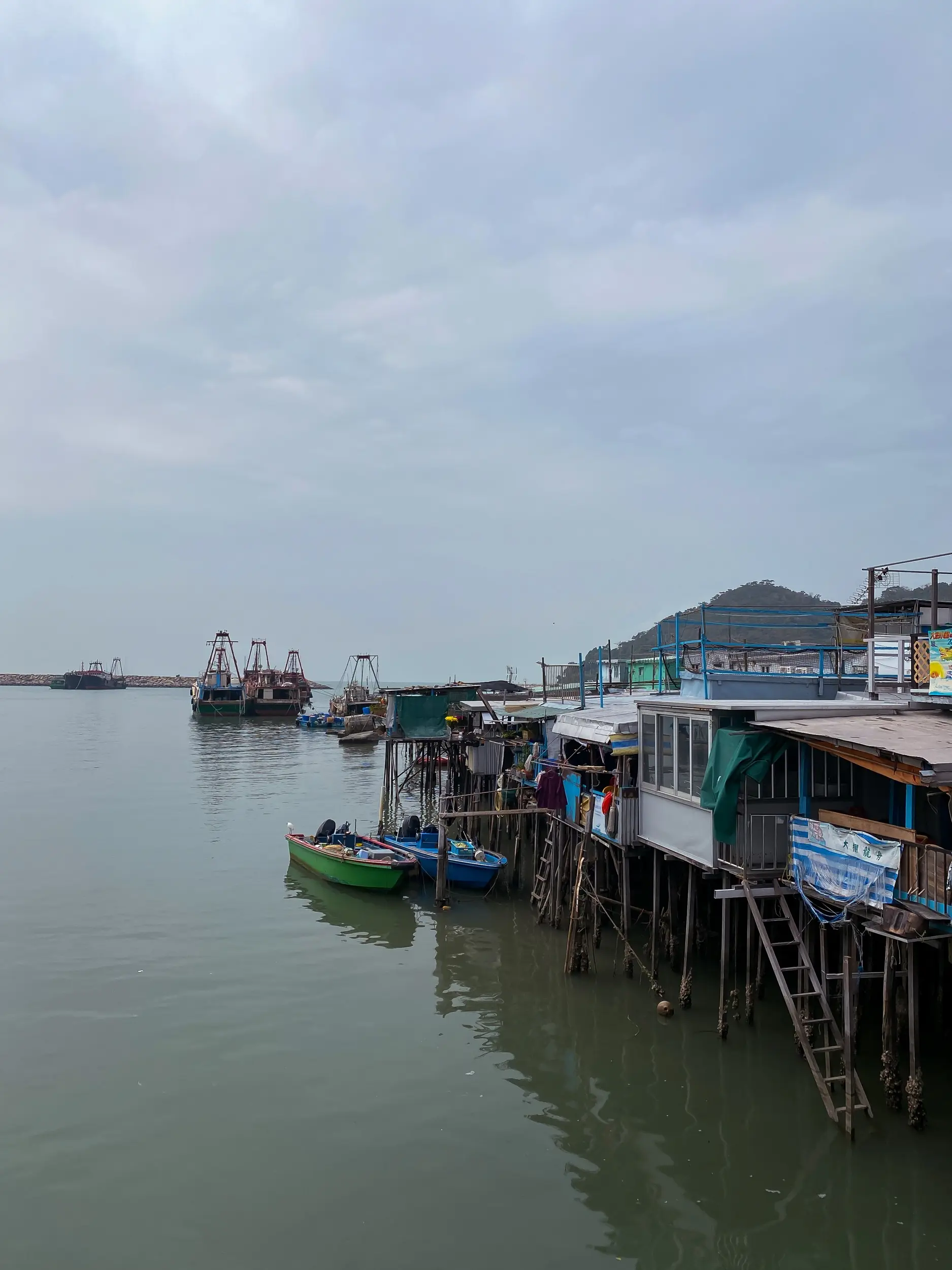

11 Wonderful Things to Do in Tai O Fishing Village
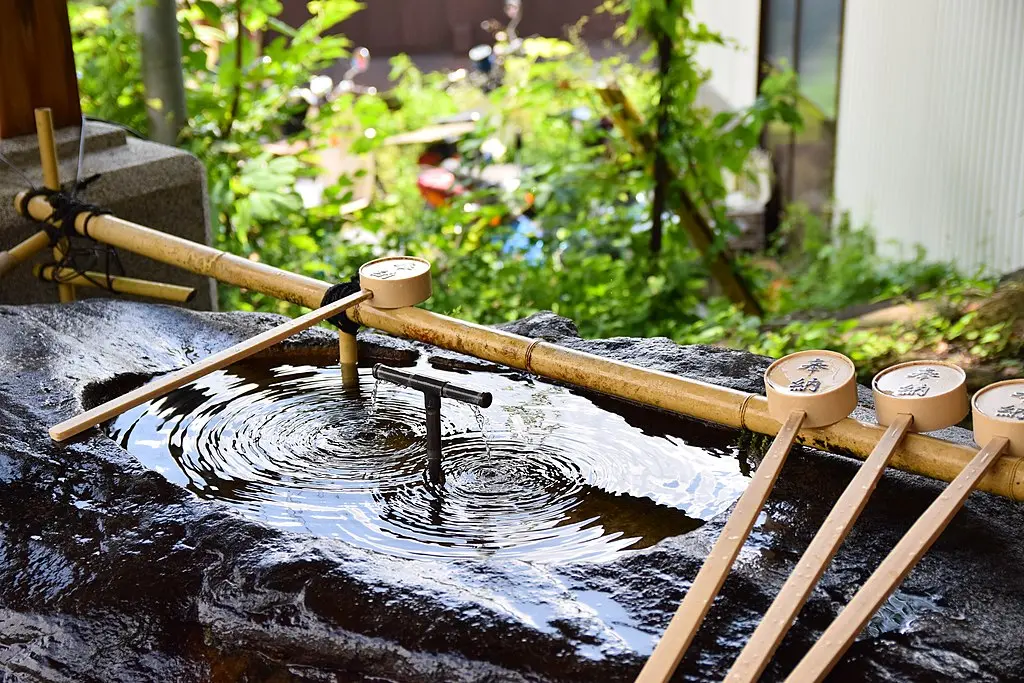


Mt. Mitake Hike | A Spiritual Ascent Amidst Tokyo’s Skies

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Hi, I’m Brandon
A conscious globe-trotter and an avid dreamer, I created this blog to inspire you to walk the Earth.
Through tales of travel, cultural appreciation, and spiritual insights, let’s dive into the Human Experience.
RECENT ARTICLES
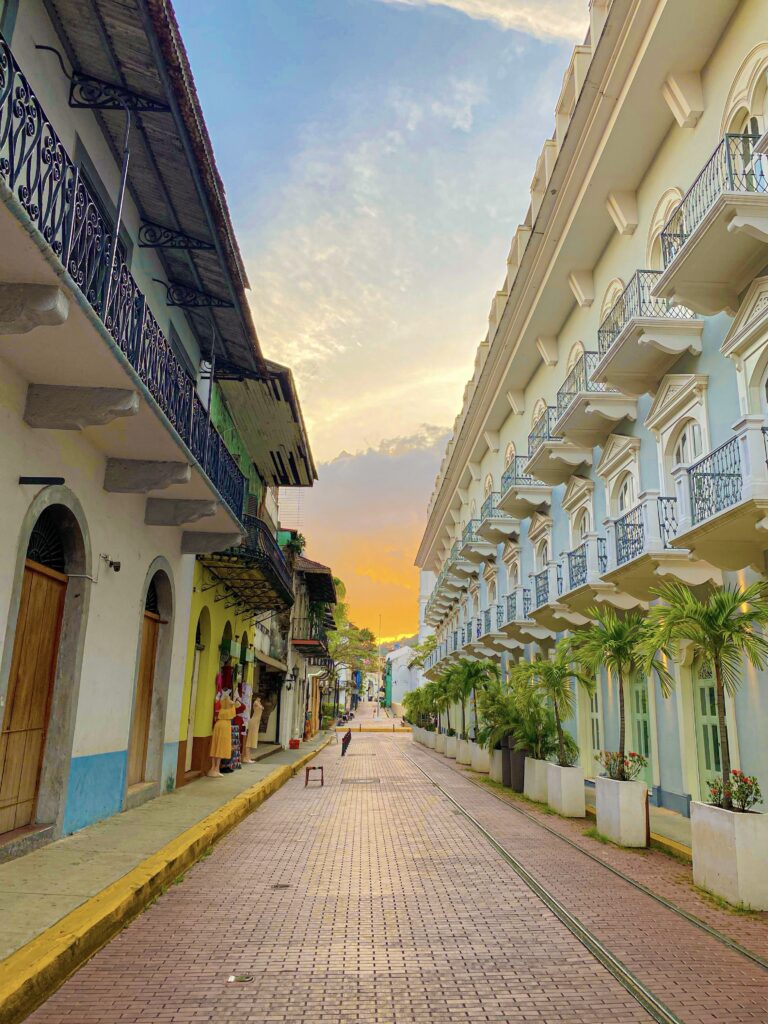

12 Awesome Things to Do in Casco Viejo, Panama

5 Easy Steps to Create a Meaningful Sankalpa

The 4 Stages of Enlightenment in Buddhism | Simplified
Popular articles.

8 Must-See Mosques in Bagerhat | The Ancient Mosque City

19 Amazing Things to Do in Noboribetsu | Japan Travel Guide

How I Got My Shoes Stolen on Jeju Island | Travel Stories

Meet the Ainu People | Japan’s Forgotten Indigenous Culture
Subscribe for the latest blog drops, photography tips, and curious insights about the world.
© 2023 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
- Destinations
- Privacy Policy
Want to get in touch? Feel free to fill in the form below or drop me an e-mail at [email protected]
Journey to the West: Volume I
85 pages • 2 hours read
The Journey to the West: Volume I
A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more. For select classroom titles, we also provide Teaching Guides with discussion and quiz questions to prompt student engagement.
Chapter Summaries & Analyses
Chapters 1-5
Chapters 6-10
Chapters 11-15
Chapters 16-20
Chapters 21-25
Character Analysis
Symbols & Motifs
Important Quotes
Essay Topics
Discussion Questions
Good Versus Evil and the Power of Redemption
Many of the humans, gods, and monsters in the novel all strive for self-improvement. Because Buddhists believe in reincarnation, behavior during one’s lifetime influences what kind of life one will be born into next. When the Monkey King lives among people for the first time, “He saw, however, that the people of the world were all seekers after profit and fame; there was not one who showed concern for his appointed end” (109). While this is predominantly a reference to mortality, it also shows that people were greedy and fame-obsessed before the pilgrim’s quest for dharma.

Don't Miss Out!
Access Study Guide Now
Related Titles
By these authors
Monkey: A Folk Novel of China
Wu Cheng'en, Transl. Arthur Waley
Featured Collections
Chinese Studies
View Collection
Good & Evil
Order & Chaos
Pride & Shame
A Chinese Classic Journeys to the West: Julia Lovell’s Translation of “Monkey King”
By minjie chen october 5, 2021.
:quality(75)/https%3A%2F%2Fdev.lareviewofbooks.org%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2021%2F10%2Fmonkeyking.jpeg)
Monkey King: Journey to the West by Wu Cheng’en
LARB Contributor
LARB Staff Recommendations
Idiom as instrument: on yan lianke’s “hard like water”.
Thomas Chen reviews Yan Lianke’s “Hard Like Water,” translated by Carlos Rojas.
Thomas Chen Aug 31, 2021
A Search for the Soul of the Mainland
Yunte Huang has compiled a 624-doorstop of an anthology.
Liz Carter May 1, 2016
Did you know LARB is a reader-supported nonprofit?
LARB publishes daily without a paywall as part of our mission to make rigorous, incisive, and engaging writing on every aspect of literature, culture, and the arts freely accessible to the public. Help us continue this work with your tax-deductible donation today!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Chapter 3: The Monkey's Story. Monkey decides that his clan needs weapons in case they are attacked again. He goes to a city of soldiers and steals their armaments. All 47,000 monkeys in his clan are now armed but, as their king, Monkey deserves something superior to the weapons of his subjects.
Chapter. Summary. Chapters 1-3. In the small country of Ao-lai, a rock splits open to reveal a stone egg that transforms into a living stone monkey. M... Read More. Chapters 4-7. The Spirit of the Planet Venus takes Monkey to Heaven, where he is assigned to the stables. At a feast celebrating his...
杀杀中文笔记 - 西游记 (Journey to the West; Monkey King) ... Novel Summary Chapter 1. A stone egg on Flower-Fruit Mountain (huaguo shan, 花果山) is conceived by Heaven and Earth and gives birth to a divine monkey. The monkey befriends a clan of primates and quickly gains the title of Handsome Monkey King (meihou wang, 美猴王).
Summary Chapter 15: The Dragon Horse Monkey and Tripitaka reach the banks of the Eagle Grief Stream, where a dragon springs from the water and eats Tripitaka's horse. Tripitaka starts to cry. Without a horse, they'll never reach India. Monkey taunts the dragon and engages him in battle, which ends with the dragon sulking at the bottom of the river. "I don't understand why you are having such ...
The Journey to the West: Volume I (1983), translated and edited by Anthony C. Yu, contains the first 25 chapters of a 100-chapter hero's epic, an allegory designed to impart knowledge on how to behave and what values to extol. Originally published in the late 16th century during the late Ming Dynasty, this epic is "loosely based on the famous pilgrimage of Xuanzang…the monk who went from ...
Chapter 1 begins with the birth of Monkey from a rock on the Mountain of Flowers and Fruit, and witnessed by the Jade Emperor from Heaven. Monkey becomes king of the monkeys when he is the most courageous and leads them safely through a waterfall to their new home -- the Cave of the Water Curtain. He rules for hundreds of years very happily ...
Journey to the West, or Monkey, was written by Wu Ch'eng-en during the Ming dynasty in China. It is loosely based on the historical journey of a monk named Hsuan Tsang, who went to India in the 7th century in search of Buddhist scrolls and scriptures. In this story, the monk, named Tripitaka, undergoes eighty-one trials during his journey with ...
Summary. Last Updated September 5, 2023. Wu Cheng'en's Journey to the West is a meandering, fictionalized account of an actual seventh-century pilgrimage to India made by Xuanzang, a Chinese ...
Monkey: Folk Novel of China is a 1943 translation by Arthur Waley of Wu Ch'êng-ên's novel originally written in Chinese in the 16th century. This summary refers to the American edition. Wu's original novel is more typically translated as Journey to the West in modern scholarship, and Waley's translation excises considerable portions of the original story.
Nov 24, 2023 11:32 AM EST. Journey to the West Analysis. The tale of Monkey and his journey deep into the Buddhist heartland of India is an elaborate tale filled with adventure, allegory, and spiritual insight. Monkey tricks his way in and out of many stressful situations. He is a deviant, mischievous little fellow who can never be trusted.
Chapter 1 Summary. The first human, Pan Gu, is born of yin (the feminine, dark, negative) and yang (the masculine, light, positive) and makes order by separating good and bad. Yang awakens, and so does Yin. A divinely bred monkey, with yin and yang and magic, along with the essences of the universe, is born from a stone.
Summary and Analysis. Tripitaka makes Monkey suffer from the spell while Pigsy eggs him on in Chapter 21, until Monkey goes on his cloud-trapeze spell to Lao Tzu for a grain of his Nine times Sublimated Life Restoring Elixir. Pigsy and Tripitaka mourn the king, while Monkey convinces Lao Tzu that he is not the same troublesome creature he was 500 years ago.
Journey to the West Journey to the West ... Journey to the West Monkey By Wu Ch'êng-ên, translated by Arthur Waley Evergreen Books, 1994 . Chapter 1. There was a rock that since the creation of the world had been worked upon by the pure essence of Heaven and fine savours of Earth, the vigour of sunshine and the grace of moonlight, till at ...
Chapter 27 is the only chapter of Monkey in which Sandy plays a major role. Although he feasts with Monkey and Pigsy at the Immortals' temple in Cart-Slow, he stays mostly on the sidelines keeping Tripitaka safe. He doesn't even get much dialogue. Chapters 22-24 Chapters 28-30.
Explore Journey to the West by Wu Cheng'en. Meet the characters, review Tang Sanzang and Sun Wukong, and study the summary and analysis of the Monkey King's journey.
Journey to the West (Chinese: Xiyou ji 西遊記) is a Chinese novel published in the 16th century during the Ming dynasty and attributed to Wu Cheng'en.It is regarded as one of the greatest Classic Chinese Novels, and has been described as arguably the most popular literary work in East Asia. Arthur Waley's 1942 abridged translation, Monkey, is known in English-speaking countries.
Journey to the West is a Chinese novel published in the 16th century during the Ming dynasty and attributed to Wu Cheng'en. It is one of the Four Great Classical Novels of Chinese literature. In English-speaking countries, the work is widely known as Monkey, the title of Arthur Waley's popular abridged translation.
Chapter 28 Summary. In this final section of the text, the pilgrims achieve their goal and move onto the next phase of their lives. Ten years after leaving China, Tripitaka and his disciples arrive in India. A Taoist Immortal leads them to a mountain, and as they climb upward, they come to a large river with only a thin bridge to cross.
Tripitaka uses the Tight Fillet on Monkey, who promises to be good and obey him, just as Kuan-yin predicted. In Chapter 15, the two travelers have their horse eaten by a dragon. Two deities sent by Kuan-yin, Lu Ting and Lu Chia, as well as the Gold-headed Guardian, descend to guard Tripitaka while Monkey confronts the dragon.
Journey to the West, foremost Chinese comic novel, written by Wu Cheng'en, a novelist and poet of the Ming dynasty (1368-1644). The novel is based on the actual 7th-century pilgrimage of the Buddhist monk Xuanzang (602-664) to India in search of sacred texts. The story itself was already a part of Chinese folk and literary tradition in the form of colloquial stories, a poetic novelette ...
The "Journey to the West" is deeply entwined with the real-life travels of Xuanzang (602-664 CE), whose pilgrimage to India and back took 17 years, a journey undertaken to obtain authentic Buddhist scriptures.. Wu Cheng'en's fictionalized account, however, does more than narrate a religious quest; it weaves a rich story of Chinese myths, Taoist and Buddhist philosophy, and satirical ...
The Journey to the West: Volume I. A modern alternative to SparkNotes and CliffsNotes, SuperSummary offers high-quality Study Guides with detailed chapter summaries and analysis of major themes, characters, and more. For select classroom titles, we also provide Teaching Guides with discussion and quiz questions to prompt student engagement.
Nearly eight decades have passed since Monkey (1943), Arthur Waley's translation of Journey to the West, was published. At that time, China and the United States were thick allies in the midst ...