

Is Time Travel Possible?
We all travel in time! We travel one year in time between birthdays, for example. And we are all traveling in time at approximately the same speed: 1 second per second.
We typically experience time at one second per second. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
NASA's space telescopes also give us a way to look back in time. Telescopes help us see stars and galaxies that are very far away . It takes a long time for the light from faraway galaxies to reach us. So, when we look into the sky with a telescope, we are seeing what those stars and galaxies looked like a very long time ago.
However, when we think of the phrase "time travel," we are usually thinking of traveling faster than 1 second per second. That kind of time travel sounds like something you'd only see in movies or science fiction books. Could it be real? Science says yes!
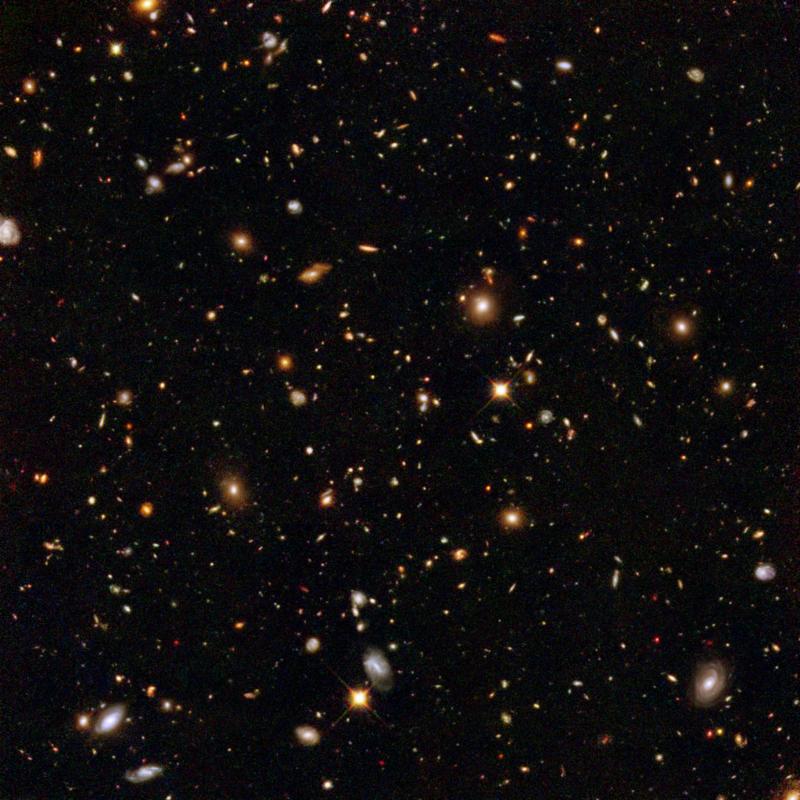

This image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies that are very far away as they existed a very long time ago. Credit: NASA, ESA and R. Thompson (Univ. Arizona)
How do we know that time travel is possible?
More than 100 years ago, a famous scientist named Albert Einstein came up with an idea about how time works. He called it relativity. This theory says that time and space are linked together. Einstein also said our universe has a speed limit: nothing can travel faster than the speed of light (186,000 miles per second).
Einstein's theory of relativity says that space and time are linked together. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
What does this mean for time travel? Well, according to this theory, the faster you travel, the slower you experience time. Scientists have done some experiments to show that this is true.
For example, there was an experiment that used two clocks set to the exact same time. One clock stayed on Earth, while the other flew in an airplane (going in the same direction Earth rotates).
After the airplane flew around the world, scientists compared the two clocks. The clock on the fast-moving airplane was slightly behind the clock on the ground. So, the clock on the airplane was traveling slightly slower in time than 1 second per second.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Can we use time travel in everyday life?
We can't use a time machine to travel hundreds of years into the past or future. That kind of time travel only happens in books and movies. But the math of time travel does affect the things we use every day.
For example, we use GPS satellites to help us figure out how to get to new places. (Check out our video about how GPS satellites work .) NASA scientists also use a high-accuracy version of GPS to keep track of where satellites are in space. But did you know that GPS relies on time-travel calculations to help you get around town?
GPS satellites orbit around Earth very quickly at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. This slows down GPS satellite clocks by a small fraction of a second (similar to the airplane example above).
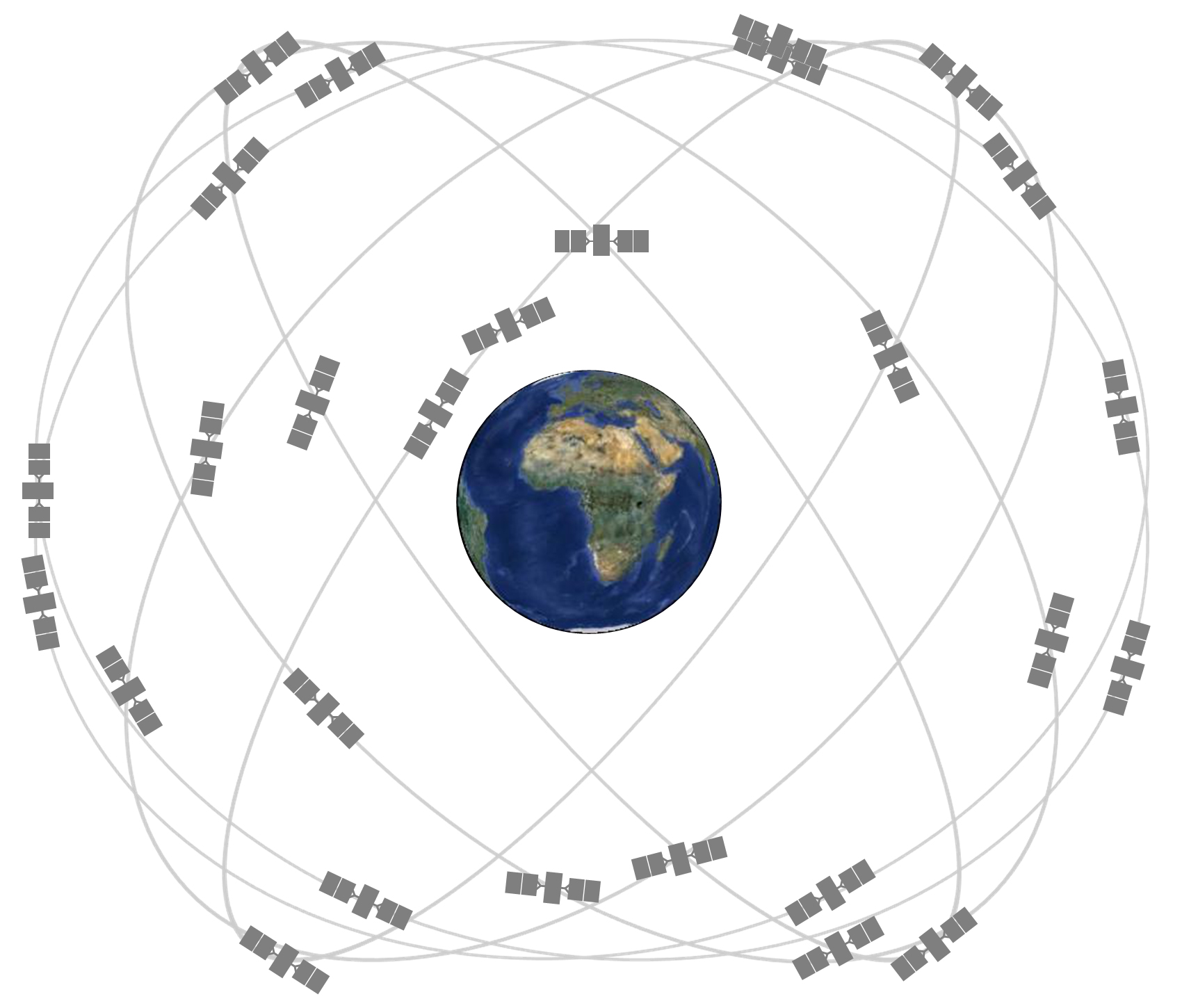
GPS satellites orbit around Earth at about 8,700 miles (14,000 kilometers) per hour. Credit: GPS.gov
However, the satellites are also orbiting Earth about 12,550 miles (20,200 km) above the surface. This actually speeds up GPS satellite clocks by a slighter larger fraction of a second.
Here's how: Einstein's theory also says that gravity curves space and time, causing the passage of time to slow down. High up where the satellites orbit, Earth's gravity is much weaker. This causes the clocks on GPS satellites to run faster than clocks on the ground.
The combined result is that the clocks on GPS satellites experience time at a rate slightly faster than 1 second per second. Luckily, scientists can use math to correct these differences in time.
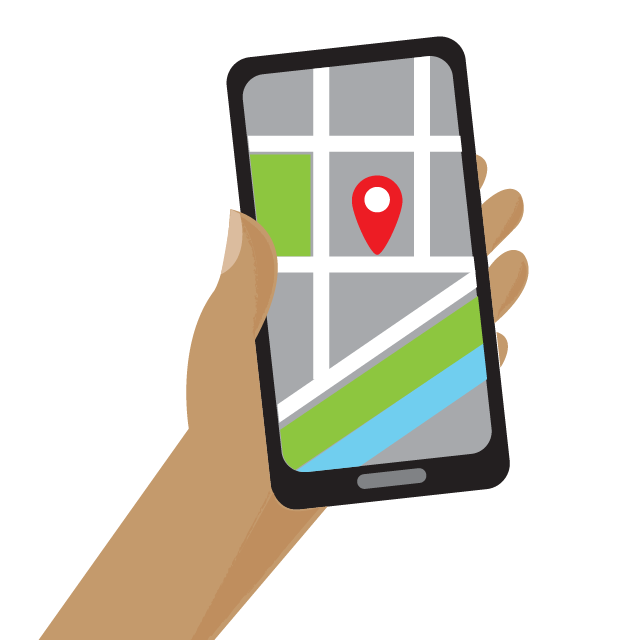
If scientists didn't correct the GPS clocks, there would be big problems. GPS satellites wouldn't be able to correctly calculate their position or yours. The errors would add up to a few miles each day, which is a big deal. GPS maps might think your home is nowhere near where it actually is!
In Summary:
Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
If you liked this, you may like:
- Environment
- Road to Net Zero
- Art & Design
- Film & TV
- Music & On-stage
- Pop Culture
- Fashion & Beauty
- Home & Garden
- Things to do
- Combat Sports
- Horse Racing
- Beyond the Headlines
- Trending Middle East
- Business Extra
- Culture Bites
- Year of Elections
- Pocketful of Dirhams
- Books of My Life
- Iraq: 20 Years On
Nasa’s time travel machine: five facts about the James Webb Space Telescope
World’s most powerful telescope has taken its first set of images.
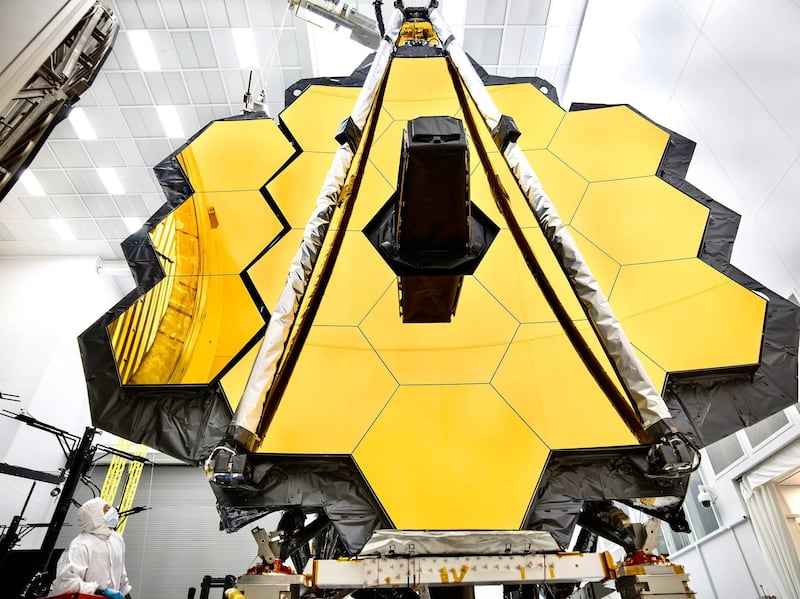

Nasa's James Webb Space Telescope will give astronomers a peek into the early universe. All photos: Nasa

A version of this article first appeared on April 7, 2021
An enormous space telescope has given astronomers a peek into the early cosmos, capturing light of galaxies that formed not long after the birth of the universe.
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the world's most advanced space observatory , was in development for nearly two decades and is expected to create an astronomical revolution.
The $10 billion “time machine” will help astronomers to study what the universe looked like millions of years ago.
It is much more advanced than the Hubble Space Telescope because of its breakthrough technology, design and its planned location in space.
It's here–the deepest, sharpest infrared view of the universe to date: Webb's First Deep Field. Previewed by @POTUS on July 11, it shows galaxies once invisible to us. The full set of @NASAWebb 's first full-color images & data will be revealed July 12: https://t.co/63zxpNDi4I pic.twitter.com/zAr7YoFZ8C — NASA (@NASA) July 11, 2022
Hubble made countless discoveries after it was launched in 1990 and provided millions of images of planets, galaxies, nebulas and stars.
The JWST is equipped with sensitive cameras and spectrographs that can capture light directed into them by its huge golden mirror.
It has been developed by Nasa with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
The National looks at five facts that make the James Webb Space Telescope extra special.
1. It is ‘time travelling’ into the past
The telescope will show us what the universe was like 100 million to 250 million years after its birth. In the Big Bang theory, it is believed the universe came into existence 13.8 billion years ago.
The first image from the telescope, released on July 12, shows the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 , with light that has been travelling for more than 13 billion years.
Hubble has captured this area before, but observations by James Webb show the galaxy cluster in incredible detail.
Nasa has said it wants to look back even further, about 13.5 billion years in the past to make new discoveries.

The telescope will detect infrared light, allowing it to capture an object’s heat source.
The space observatory’s cameras are so sensitive they could spot the heat signature of a bumblebee.
2. Honeycomb mirrors
A telescope’s mirror helps reflect light into its cameras. The better the mirror, the more the observatory will capture.
JWST has 18 primary hexagonal mirrors that together form a honeycomb shape. In total, it measures 6.5 metres in diameter.
The mirror is six times bigger in area than Hubble’s and is 100 times more powerful.
To help reflect infrared light more efficiently, the mirror is covered with a thin coating of gold.
3. Unique orbit
JWST is placed much further out in space and in a different orbit than Hubble, allowing it to see greater distances.

Instead of an orbit around the Earth, the telescope orbits the Sun. It is in line with Earth, but 1.5 million kilometres from the planet and four times farther away than the Moon. This position in space is called a Lagrange point.
The mirror is kept at a temperature of minus 233°C to shield it from the Sun. It has a five-layer sunshield that is the size of a tennis court and which weakens the heat from the host star by more than a million times.
4. Hunt for life
One of the main objectives of the telescope is to study the atmospheres of exoplanets — planets outside the Solar System.
It will look for oxygen present in the atmospheres of planets in distant galaxies.
5. How it launched into space
The school bus-sized telescope, which measures 21 metres by 14.6 metres, had to fold up to fit into the launch rocket.
JWST launched aboard the Ariane 5 rocket , near French Guiana in South America, on Christmas Day, 2021.
The wonders of space — in pictures
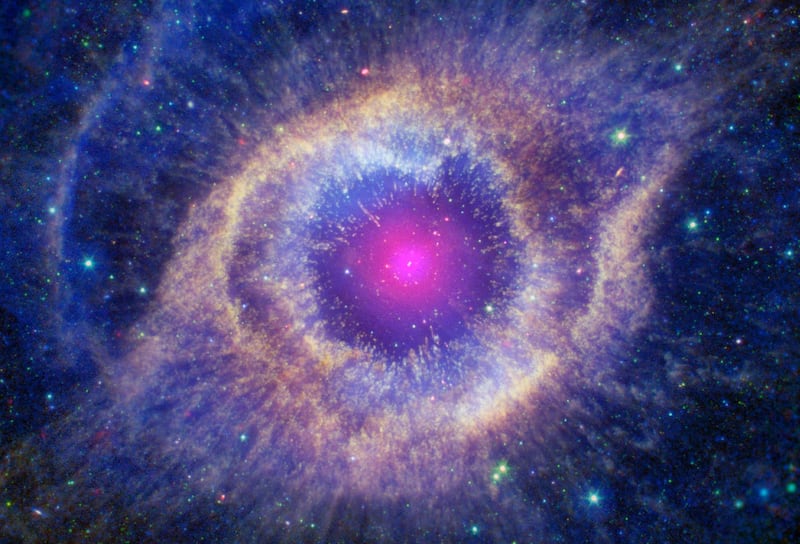

Helix Nebula is a phase when a star like the Sun runs out of fuel, it expands and its outer layers puff off, and then the core of the star shrinks. All photos: Nasa
The UAE Today
The latest news and analysis from the Emirates

Time travel: Is it possible?
Science says time travel is possible, but probably not in the way you're thinking.

Albert Einstein's theory
- General relativity and GPS
- Wormhole travel
- Alternate theories
Science fiction
Is time travel possible? Short answer: Yes, and you're doing it right now — hurtling into the future at the impressive rate of one second per second.
You're pretty much always moving through time at the same speed, whether you're watching paint dry or wishing you had more hours to visit with a friend from out of town.
But this isn't the kind of time travel that's captivated countless science fiction writers, or spurred a genre so extensive that Wikipedia lists over 400 titles in the category "Movies about Time Travel." In franchises like " Doctor Who ," " Star Trek ," and "Back to the Future" characters climb into some wild vehicle to blast into the past or spin into the future. Once the characters have traveled through time, they grapple with what happens if you change the past or present based on information from the future (which is where time travel stories intersect with the idea of parallel universes or alternate timelines).
Related: The best sci-fi time machines ever
Although many people are fascinated by the idea of changing the past or seeing the future before it's due, no person has ever demonstrated the kind of back-and-forth time travel seen in science fiction or proposed a method of sending a person through significant periods of time that wouldn't destroy them on the way. And, as physicist Stephen Hawking pointed out in his book " Black Holes and Baby Universes" (Bantam, 1994), "The best evidence we have that time travel is not possible, and never will be, is that we have not been invaded by hordes of tourists from the future."
Science does support some amount of time-bending, though. For example, physicist Albert Einstein 's theory of special relativity proposes that time is an illusion that moves relative to an observer. An observer traveling near the speed of light will experience time, with all its aftereffects (boredom, aging, etc.) much more slowly than an observer at rest. That's why astronaut Scott Kelly aged ever so slightly less over the course of a year in orbit than his twin brother who stayed here on Earth.
Related: Controversially, physicist argues that time is real
There are other scientific theories about time travel, including some weird physics that arise around wormholes , black holes and string theory . For the most part, though, time travel remains the domain of an ever-growing array of science fiction books, movies, television shows, comics, video games and more.

Einstein developed his theory of special relativity in 1905. Along with his later expansion, the theory of general relativity , it has become one of the foundational tenets of modern physics. Special relativity describes the relationship between space and time for objects moving at constant speeds in a straight line.
The short version of the theory is deceptively simple. First, all things are measured in relation to something else — that is to say, there is no "absolute" frame of reference. Second, the speed of light is constant. It stays the same no matter what, and no matter where it's measured from. And third, nothing can go faster than the speed of light.
From those simple tenets unfolds actual, real-life time travel. An observer traveling at high velocity will experience time at a slower rate than an observer who isn't speeding through space.
While we don't accelerate humans to near-light-speed, we do send them swinging around the planet at 17,500 mph (28,160 km/h) aboard the International Space Station . Astronaut Scott Kelly was born after his twin brother, and fellow astronaut, Mark Kelly . Scott Kelly spent 520 days in orbit, while Mark logged 54 days in space. The difference in the speed at which they experienced time over the course of their lifetimes has actually widened the age gap between the two men.
"So, where[as] I used to be just 6 minutes older, now I am 6 minutes and 5 milliseconds older," Mark Kelly said in a panel discussion on July 12, 2020, Space.com previously reported . "Now I've got that over his head."
General relativity and GPS time travel

The difference that low earth orbit makes in an astronaut's life span may be negligible — better suited for jokes among siblings than actual life extension or visiting the distant future — but the dilation in time between people on Earth and GPS satellites flying through space does make a difference.
Read more: Can we stop time?
The Global Positioning System , or GPS, helps us know exactly where we are by communicating with a network of a few dozen satellites positioned in a high Earth orbit. The satellites circle the planet from 12,500 miles (20,100 kilometers) away, moving at 8,700 mph (14,000 km/h).
According to special relativity, the faster an object moves relative to another object, the slower that first object experiences time. For GPS satellites with atomic clocks, this effect cuts 7 microseconds, or 7 millionths of a second, off each day, according to the American Physical Society publication Physics Central .
Read more: Could Star Trek's faster-than-light warp drive actually work?
Then, according to general relativity, clocks closer to the center of a large gravitational mass like Earth tick more slowly than those farther away. So, because the GPS satellites are much farther from the center of Earth compared to clocks on the surface, Physics Central added, that adds another 45 microseconds onto the GPS satellite clocks each day. Combined with the negative 7 microseconds from the special relativity calculation, the net result is an added 38 microseconds.
This means that in order to maintain the accuracy needed to pinpoint your car or phone — or, since the system is run by the U.S. Department of Defense, a military drone — engineers must account for an extra 38 microseconds in each satellite's day. The atomic clocks onboard don’t tick over to the next day until they have run 38 microseconds longer than comparable clocks on Earth.
Given those numbers, it would take more than seven years for the atomic clock in a GPS satellite to un-sync itself from an Earth clock by more than a blink of an eye. (We did the math: If you estimate a blink to last at least 100,000 microseconds, as the Harvard Database of Useful Biological Numbers does, it would take thousands of days for those 38 microsecond shifts to add up.)
This kind of time travel may seem as negligible as the Kelly brothers' age gap, but given the hyper-accuracy of modern GPS technology, it actually does matter. If it can communicate with the satellites whizzing overhead, your phone can nail down your location in space and time with incredible accuracy.
Can wormholes take us back in time?
General relativity might also provide scenarios that could allow travelers to go back in time, according to NASA . But the physical reality of those time-travel methods is no piece of cake.
Wormholes are theoretical "tunnels" through the fabric of space-time that could connect different moments or locations in reality to others. Also known as Einstein-Rosen bridges or white holes, as opposed to black holes, speculation about wormholes abounds. But despite taking up a lot of space (or space-time) in science fiction, no wormholes of any kind have been identified in real life.
Related: Best time travel movies
"The whole thing is very hypothetical at this point," Stephen Hsu, a professor of theoretical physics at the University of Oregon, told Space.com sister site Live Science . "No one thinks we're going to find a wormhole anytime soon."
Primordial wormholes are predicted to be just 10^-34 inches (10^-33 centimeters) at the tunnel's "mouth". Previously, they were expected to be too unstable for anything to be able to travel through them. However, a study claims that this is not the case, Live Science reported .
The theory, which suggests that wormholes could work as viable space-time shortcuts, was described by physicist Pascal Koiran. As part of the study, Koiran used the Eddington-Finkelstein metric, as opposed to the Schwarzschild metric which has been used in the majority of previous analyses.
In the past, the path of a particle could not be traced through a hypothetical wormhole. However, using the Eddington-Finkelstein metric, the physicist was able to achieve just that.
Koiran's paper was described in October 2021, in the preprint database arXiv , before being published in the Journal of Modern Physics D.

Alternate time travel theories
While Einstein's theories appear to make time travel difficult, some researchers have proposed other solutions that could allow jumps back and forth in time. These alternate theories share one major flaw: As far as scientists can tell, there's no way a person could survive the kind of gravitational pulling and pushing that each solution requires.
Infinite cylinder theory
Astronomer Frank Tipler proposed a mechanism (sometimes known as a Tipler Cylinder ) where one could take matter that is 10 times the sun's mass, then roll it into a very long, but very dense cylinder. The Anderson Institute , a time travel research organization, described the cylinder as "a black hole that has passed through a spaghetti factory."
After spinning this black hole spaghetti a few billion revolutions per minute, a spaceship nearby — following a very precise spiral around the cylinder — could travel backward in time on a "closed, time-like curve," according to the Anderson Institute.
The major problem is that in order for the Tipler Cylinder to become reality, the cylinder would need to be infinitely long or be made of some unknown kind of matter. At least for the foreseeable future, endless interstellar pasta is beyond our reach.
Time donuts
Theoretical physicist Amos Ori at the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa, Israel, proposed a model for a time machine made out of curved space-time — a donut-shaped vacuum surrounded by a sphere of normal matter.
"The machine is space-time itself," Ori told Live Science . "If we were to create an area with a warp like this in space that would enable time lines to close on themselves, it might enable future generations to return to visit our time."
Amos Ori is a theoretical physicist at the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa, Israel. His research interests and publications span the fields of general relativity, black holes, gravitational waves and closed time lines.
There are a few caveats to Ori's time machine. First, visitors to the past wouldn't be able to travel to times earlier than the invention and construction of the time donut. Second, and more importantly, the invention and construction of this machine would depend on our ability to manipulate gravitational fields at will — a feat that may be theoretically possible but is certainly beyond our immediate reach.

Time travel has long occupied a significant place in fiction. Since as early as the "Mahabharata," an ancient Sanskrit epic poem compiled around 400 B.C., humans have dreamed of warping time, Lisa Yaszek, a professor of science fiction studies at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta, told Live Science .
Every work of time-travel fiction creates its own version of space-time, glossing over one or more scientific hurdles and paradoxes to achieve its plot requirements.
Some make a nod to research and physics, like " Interstellar ," a 2014 film directed by Christopher Nolan. In the movie, a character played by Matthew McConaughey spends a few hours on a planet orbiting a supermassive black hole, but because of time dilation, observers on Earth experience those hours as a matter of decades.
Others take a more whimsical approach, like the "Doctor Who" television series. The series features the Doctor, an extraterrestrial "Time Lord" who travels in a spaceship resembling a blue British police box. "People assume," the Doctor explained in the show, "that time is a strict progression from cause to effect, but actually from a non-linear, non-subjective viewpoint, it's more like a big ball of wibbly-wobbly, timey-wimey stuff."
Long-standing franchises like the "Star Trek" movies and television series, as well as comic universes like DC and Marvel Comics, revisit the idea of time travel over and over.
Related: Marvel movies in order: chronological & release order
Here is an incomplete (and deeply subjective) list of some influential or notable works of time travel fiction:
Books about time travel:

- Rip Van Winkle (Cornelius S. Van Winkle, 1819) by Washington Irving
- A Christmas Carol (Chapman & Hall, 1843) by Charles Dickens
- The Time Machine (William Heinemann, 1895) by H. G. Wells
- A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur's Court (Charles L. Webster and Co., 1889) by Mark Twain
- The Restaurant at the End of the Universe (Pan Books, 1980) by Douglas Adams
- A Tale of Time City (Methuen, 1987) by Diana Wynn Jones
- The Outlander series (Delacorte Press, 1991-present) by Diana Gabaldon
- Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban (Bloomsbury/Scholastic, 1999) by J. K. Rowling
- Thief of Time (Doubleday, 2001) by Terry Pratchett
- The Time Traveler's Wife (MacAdam/Cage, 2003) by Audrey Niffenegger
- All You Need is Kill (Shueisha, 2004) by Hiroshi Sakurazaka
Movies about time travel:
- Planet of the Apes (1968)
- Superman (1978)
- Time Bandits (1981)
- The Terminator (1984)
- Back to the Future series (1985, 1989, 1990)
- Star Trek IV: The Voyage Home (1986)
- Bill & Ted's Excellent Adventure (1989)
- Groundhog Day (1993)
- Galaxy Quest (1999)
- The Butterfly Effect (2004)
- 13 Going on 30 (2004)
- The Lake House (2006)
- Meet the Robinsons (2007)
- Hot Tub Time Machine (2010)
- Midnight in Paris (2011)
- Looper (2012)
- X-Men: Days of Future Past (2014)
- Edge of Tomorrow (2014)
- Interstellar (2014)
- Doctor Strange (2016)
- A Wrinkle in Time (2018)
- The Last Sharknado: It's About Time (2018)
- Avengers: Endgame (2019)
- Tenet (2020)
- Palm Springs (2020)
- Zach Snyder's Justice League (2021)
- The Tomorrow War (2021)
Television about time travel:

- Doctor Who (1963-present)
- The Twilight Zone (1959-1964) (multiple episodes)
- Star Trek (multiple series, multiple episodes)
- Samurai Jack (2001-2004)
- Lost (2004-2010)
- Phil of the Future (2004-2006)
- Steins;Gate (2011)
- Outlander (2014-2023)
- Loki (2021-present)
Games about time travel:
- Chrono Trigger (1995)
- TimeSplitters (2000-2005)
- Kingdom Hearts (2002-2019)
- Prince of Persia: Sands of Time (2003)
- God of War II (2007)
- Ratchet and Clank Future: A Crack In Time (2009)
- Sly Cooper: Thieves in Time (2013)
- Dishonored 2 (2016)
- Titanfall 2 (2016)
- Outer Wilds (2019)
Additional resources
Explore physicist Peter Millington's thoughts about Stephen Hawking's time travel theories at The Conversation . Check out a kid-friendly explanation of real-world time travel from NASA's Space Place . For an overview of time travel in fiction and the collective consciousness, read " Time Travel: A History " (Pantheon, 2016) by James Gleik.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Ailsa is a staff writer for How It Works magazine, where she writes science, technology, space, history and environment features. Based in the U.K., she graduated from the University of Stirling with a BA (Hons) journalism degree. Previously, Ailsa has written for Cardiff Times magazine, Psychology Now and numerous science bookazines.
Science and music festival Starmus VII is about to rock Bratislava with a stellar lineup
China's Chang'e 6 mission to collect samples of the far side of the moon enters lunar orbit (video)
How to watch Blue Origin's NS-25 private space tourist mission online May 19
Most Popular
- 2 James Webb Space Telescope sees Orion Nebula in a stunning new light (images)
- 3 NASA astronauts practice 'moonwalking' in the Arizona desert (photos)
- 4 Who is the 'Doctor Who' villain Maestro? And what's their relationship with the Toymaker?
- 5 Boeing's 1st Starliner astronaut launch delayed again, to May 25

Can we time travel? A theoretical physicist provides some answers
Emeritus professor, Physics, Carleton University
Disclosure statement
Peter Watson received funding from NSERC. He is affiliated with Carleton University and a member of the Canadian Association of Physicists.
Carleton University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA.
Carleton University provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
View all partners
- Bahasa Indonesia
Time travel makes regular appearances in popular culture, with innumerable time travel storylines in movies, television and literature. But it is a surprisingly old idea: one can argue that the Greek tragedy Oedipus Rex , written by Sophocles over 2,500 years ago, is the first time travel story .
But is time travel in fact possible? Given the popularity of the concept, this is a legitimate question. As a theoretical physicist, I find that there are several possible answers to this question, not all of which are contradictory.
The simplest answer is that time travel cannot be possible because if it was, we would already be doing it. One can argue that it is forbidden by the laws of physics, like the second law of thermodynamics or relativity . There are also technical challenges: it might be possible but would involve vast amounts of energy.
There is also the matter of time-travel paradoxes; we can — hypothetically — resolve these if free will is an illusion, if many worlds exist or if the past can only be witnessed but not experienced. Perhaps time travel is impossible simply because time must flow in a linear manner and we have no control over it, or perhaps time is an illusion and time travel is irrelevant.

Laws of physics
Since Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity — which describes the nature of time, space and gravity — is our most profound theory of time, we would like to think that time travel is forbidden by relativity. Unfortunately, one of his colleagues from the Institute for Advanced Study, Kurt Gödel, invented a universe in which time travel was not just possible, but the past and future were inextricably tangled.
We can actually design time machines , but most of these (in principle) successful proposals require negative energy , or negative mass, which does not seem to exist in our universe. If you drop a tennis ball of negative mass, it will fall upwards. This argument is rather unsatisfactory, since it explains why we cannot time travel in practice only by involving another idea — that of negative energy or mass — that we do not really understand.
Mathematical physicist Frank Tipler conceptualized a time machine that does not involve negative mass, but requires more energy than exists in the universe .
Time travel also violates the second law of thermodynamics , which states that entropy or randomness must always increase. Time can only move in one direction — in other words, you cannot unscramble an egg. More specifically, by travelling into the past we are going from now (a high entropy state) into the past, which must have lower entropy.
This argument originated with the English cosmologist Arthur Eddington , and is at best incomplete. Perhaps it stops you travelling into the past, but it says nothing about time travel into the future. In practice, it is just as hard for me to travel to next Thursday as it is to travel to last Thursday.
Resolving paradoxes
There is no doubt that if we could time travel freely, we run into the paradoxes. The best known is the “ grandfather paradox ”: one could hypothetically use a time machine to travel to the past and murder their grandfather before their father’s conception, thereby eliminating the possibility of their own birth. Logically, you cannot both exist and not exist.
Read more: Time travel could be possible, but only with parallel timelines
Kurt Vonnegut’s anti-war novel Slaughterhouse-Five , published in 1969, describes how to evade the grandfather paradox. If free will simply does not exist, it is not possible to kill one’s grandfather in the past, since he was not killed in the past. The novel’s protagonist, Billy Pilgrim, can only travel to other points on his world line (the timeline he exists in), but not to any other point in space-time, so he could not even contemplate killing his grandfather.
The universe in Slaughterhouse-Five is consistent with everything we know. The second law of thermodynamics works perfectly well within it and there is no conflict with relativity. But it is inconsistent with some things we believe in, like free will — you can observe the past, like watching a movie, but you cannot interfere with the actions of people in it.
Could we allow for actual modifications of the past, so that we could go back and murder our grandfather — or Hitler ? There are several multiverse theories that suppose that there are many timelines for different universes. This is also an old idea: in Charles Dickens’ A Christmas Carol , Ebeneezer Scrooge experiences two alternative timelines, one of which leads to a shameful death and the other to happiness.
Time is a river
Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius wrote that:
“ Time is like a river made up of the events which happen , and a violent stream; for as soon as a thing has been seen, it is carried away, and another comes in its place, and this will be carried away too.”
We can imagine that time does flow past every point in the universe, like a river around a rock. But it is difficult to make the idea precise. A flow is a rate of change — the flow of a river is the amount of water that passes a specific length in a given time. Hence if time is a flow, it is at the rate of one second per second, which is not a very useful insight.
Theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking suggested that a “ chronology protection conjecture ” must exist, an as-yet-unknown physical principle that forbids time travel. Hawking’s concept originates from the idea that we cannot know what goes on inside a black hole, because we cannot get information out of it. But this argument is redundant: we cannot time travel because we cannot time travel!
Researchers are investigating a more fundamental theory, where time and space “emerge” from something else. This is referred to as quantum gravity , but unfortunately it does not exist yet.
So is time travel possible? Probably not, but we don’t know for sure!
- Time travel
- Stephen Hawking
- Albert Einstein
- Listen to this article
- Time travel paradox
- Arthur Eddington

Compliance Lead

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)
Is time travel possible? Why one scientist says we 'cannot ignore the possibility.'

A common theme in science-fiction media , time travel is captivating. It’s defined by the late philosopher David Lewis in his essay “The Paradoxes of Time Travel” as “[involving] a discrepancy between time and space time. Any traveler departs and then arrives at his destination; the time elapsed from departure to arrival … is the duration of the journey.”
Time travel is usually understood by most as going back to a bygone era or jumping forward to a point far in the future . But how much of the idea is based in reality? Is it possible to travel through time?
Is time travel possible?
According to NASA, time travel is possible , just not in the way you might expect. Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity says time and motion are relative to each other, and nothing can go faster than the speed of light , which is 186,000 miles per second. Time travel happens through what’s called “time dilation.”
Time dilation , according to Live Science, is how one’s perception of time is different to another's, depending on their motion or where they are. Hence, time being relative.
Learn more: Best travel insurance
Dr. Ana Alonso-Serrano, a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Germany, explained the possibility of time travel and how researchers test theories.
Space and time are not absolute values, Alonso-Serrano said. And what makes this all more complex is that you are able to carve space-time .
“In the moment that you carve the space-time, you can play with that curvature to make the time come in a circle and make a time machine,” Alonso-Serrano told USA TODAY.
She explained how, theoretically, time travel is possible. The mathematics behind creating curvature of space-time are solid, but trying to re-create the strict physical conditions needed to prove these theories can be challenging.
“The tricky point of that is if you can find a physical, realistic, way to do it,” she said.
Alonso-Serrano said wormholes and warp drives are tools that are used to create this curvature. The matter needed to achieve curving space-time via a wormhole is exotic matter , which hasn’t been done successfully. Researchers don’t even know if this type of matter exists, she said.
“It's something that we work on because it's theoretically possible, and because it's a very nice way to test our theory, to look for possible paradoxes,” Alonso-Serrano added.
“I could not say that nothing is possible, but I cannot ignore the possibility,” she said.
She also mentioned the anecdote of Stephen Hawking’s Champagne party for time travelers . Hawking had a GPS-specific location for the party. He didn’t send out invites until the party had already happened, so only people who could travel to the past would be able to attend. No one showed up, and Hawking referred to this event as "experimental evidence" that time travel wasn't possible.
What did Albert Einstein invent?: Discoveries that changed the world
Just Curious for more? We've got you covered
USA TODAY is exploring the questions you and others ask every day. From "How to watch the Marvel movies in order" to "Why is Pluto not a planet?" to "What to do if your dog eats weed?" – we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer for you.
Time Travel Probably Isn't Possible—Why Do We Wish It Were?
Time travel exerts an irresistible pull on our scientific and storytelling imagination.
Since H.G. Wells imagined that time was a fourth dimension —and Einstein confirmed it—the idea of time travel has captivated us. More than 50 scientific papers are published on time travel each year, and storytellers continually explore it—from Stephen King’s JFK assassination novel 11/22/63 to the steamy Outlander television series to Woody Allen’s comedy Midnight in Paris . What if we could travel back in time, we wonder, and change history? Assassinate Hitler or marry that high school sweetheart who dumped us? What if we could see what the future has in store?
These are some of the ideas that bestselling author James Gleick explores in his thought-provoking new book, Time Travel: A History. Speaking from his home in New York City, he recalls how Stephen Hawking once sent out invitations to a party that had already taken place ; why the Chinese government has branded time travel as “incorrect” and “frivolous” ; and how the idea of time travel is, ultimately, about our desire to defeat death.
Let’s cut right to the chase: What is time?
Oh, no, you didn’t! [ Laughs. ] In A.D. 400, St. Augustine said—and many people have said the same thing since, either quoting him consciously or unconsciously—“What, then, is time? If no one asks me, I know. If I wish to explain it to one that asks, I know not.” I think that is actually not a quip, but quite profound.
The best way to understand time is to recognize that we actually are very sophisticated about it. Over the past century-plus, we’ve learned a great deal. The physicist John Archibald Wheeler said, “Time is nature’s way to keep everything from happening all at once.” If you look it up in a dictionary, you get stuff like, “The general term for the experience of duration.” But that’s just completely punting because what is duration ?
I try to steer away from aphorisms and dictionary definitions, just to say two things. First, that we have a lot of contradictory ways of talking about time. We think of time as something we waste, spend, or save, as if it’s a quantity. We also think of time as a medium we are passing through every day, a river carrying us along. All of these notions are aspects of a complicated subject that has no bumper sticker answer.
When does the idea of time travel first appear in the West? And how did it impact popular culture?
I assumed, as a person who always read sci-fi a lot when I was a kid, that time travel is an obvious idea we’re born knowing and fantasizing about. And that it must always have been part of human culture, that there must be time travel Greek myths and Chinese legends. But there aren’t! Time travel turns out to be a very new idea that essentially starts with H.G. Wells’s 1895 novel, The Time Machine . Before that nobody thought of putting the words time and travel together. The closest you can come before that is people falling asleep, like Rip Van Winkle, or fantasies like Charles Dickens’s A Christmas Carol .
For Hungry Minds
The beginning of my book is an attempt to answer the question, “Why? Why not before? Why suddenly at the end of the 19 th century was it possible— necessary— for people to dream up this crazy fantasy?” Even though it’s H.G. Wells who does it, people pick up his ball very quickly and run with it. You find it in American science fiction that started appearing in pulp magazines in the 1920s and 1930s, or in the great new modernist literature of Marcel Proust’s In Search of Lost Time , James Joyce, and Virginia Woolf.
All these writers were suddenly making time their explicit subject, twisting time in new ways, inventing new narrative techniques to deal with time, to explore the vagaries of memory or the way our consciousness changes over time.
In 1991, Stephen Hawking wrote a paper called “Chronology Protection Conjecture , ” in which he asked: If time travel is possible, why are we not inundated with tourists from the future? He has a point, doesn’t he?
Yes! He even scheduled a party and sent out an invitation inviting time travelers to come to a party that had taken place in the past. Then he observed that none of them had shown up. [Laughs.] Hawking is one of these physicists who love playing with the idea of time travel. It’s irresistible because it’s so much fun! When he talks about the paradoxes of time travel it’s because he’s reading the same science fiction stories as the rest of us.
The paradoxes started appearing in magazines aimed mostly at young people in the 1920s. Somebody wrote in and said, “Time travel is a weird idea, because what if you go back in time and you kill your grandfather? Then your grandfather never meets your grandmother and you’re never born.” It’s an impossible loop.
Hawking, like other physicists, decided, “Time is my business. What if we take this seriously? Can we express this in physical terms?” I don’t think he succeeded but what he proposed was that the reason these paradoxes can’t happen is because the universe takes care of itself. It can’t happen because it didn’t happen. That’s the simple way of saying what the chronology protection conjecture is.
How have the Internet and other new technologies changed our perception and experience of time?
We are just beginning to see what the Internet is doing to our perception of time. We are living more and more in this networked world in which everything travels at light speed. We are multitasking and experiencing new forms of simultaneity, so the Internet appears to us as a kind of hall of mirrors. It feels as though we’re embedded in an ever expanding present.
Our sense of the past changes because in some ways the past becomes more vivid than ever. We’re looking at the past on our video screens and it’s just as vivid if the movie is about something that happened 20 years ago, as if it is a live stream. We can’t always tell the difference. On the other hand, the past that’s more distant—and isn’t available in video form—starts to seem more remote and fuzzier. Maybe we are forgetting how to visualize the past from reading histories. We’re entering a new period of time confusion, in which we suddenly find ourselves in what looks like an unending present.
In 2011, the Chinese government issued an extraordinary denunciation of the idea of time travel. What was their beef?
They thought it was corrupting and decadent. It’s a reminder that time travel is neither a simple nor innocent idea. It’s very powerful. It enables us to imagine alternative universes, and this is another line that science fiction writers have explored. What if someone was able to go back in time and kill Hitler?
Time travel is also a powerful way of allowing us to imagine what the future might bring. A lot of futurists nowadays tend to be dystopian. Time travel gives us ways of exploring how the worst tendencies of our current societies could grow even worse. That’s what George Orwell did in 1984 . I imagine the Chinese government doesn’t particularly want the equivalent of 1984 to be published in Beijing. [ Laughs. ]
You May Also Like
What's a leap second—and why is it going away for good?

This 2,200-year-old slab bears the world’s first mention of leap year

There’s a better way to wake up. Here’s what experts advise.
More than 50 scientific papers a year are now published on the idea of time travel. why are scientists drawn to the subject.
Scientists live in the same science fictional universe as all the rest of us. Time travel is a sexy and romantic idea that appeals to the physicist as much as it appeals to every teenager. I don’t think scientists are ever going to solve the problem of time travel for us but they still love to talk about wormholes and dark matter.
There’s a fascinating coincidence in the early history that when H.G. Wells needed to set the stage for his time machine hurtling into the future, he decided not to just jump right into his story but set the scene with a framing device—his time traveler lecturing a group of friends on the science of time—in order to justify the possibility of a time machine. His lecture introduces the idea that time is nothing more than a fourth dimension, that traveling through time is analogous to traveling through space. Since we have machines that can take us into any of the three special dimensions, including balloons and elevators, why shouldn’t we have a machine able to travel through the fourth dimension?
A decade later, Einstein burst onto the scene with his theory of relativity in which time is a fourth dimension , just like space. Soon after that, Hermann Minkowski pronounced that, henceforth, we were not going to talk about space and time as separate quantities but as a union of the two, spacetime , a four-dimensional continuum in which the future already exists and the past still exists.
I’m not claiming that Einstein read H.G. Wells 10 years before. But there was something in the air that both scientists and imaginative writers were empowered to visualize time in a new way. Today, that’s the way we visualize it. We’re comfortable talking about time as a fourth dimension.
You quote Ursula K. Le Guin , who writes, “Story is our only boat for sailing on the river of time.” Talk about storytelling and its relationship to time.
One of the things that has happened, along with our heightened awareness of time and its possibilities, is that people who invent narratives have learned very clever new techniques. Literal time travel is only one of them. You don’t actually need to send your hero into the future or into the past to write a story that plays with time in clever new ways. Narrative is also how everybody, not just writers, constructs a vision of our own relationship with time. We imagine the future. We remember the past. When we do that, we’re making up stories.
Psychologists are learning something that great storytellers have known for some time, which is that memory is not like computer retrieval. It’s an active process. Every time we remember something we are remembering it a little bit differently. We’re retelling the story to ourselves.
If time travel is impossible, why do we continue to be so fascinated with the idea?
One of the reasons is we want to go back and undo our mistakes. When you ask yourself, “If I had a time machine, what would I do?” sometimes the answer is, “I would go back to this particular day and do that thing over.” I think one of the great time travel movies is Groundhog Day , the Bill Murray movie where he wakes up every morning and has to live the same day over and over again. He gradually realizes that perhaps fate is telling him he needs to do it over, right. Regret is the time traveler’s energy bar. But that’s not the only motivation for time travel. We also have curiosity about the future and interest in our parents and our children. A lot of time travel fiction is a way of asking questions about what our parents were like, or what our children will be like.
At some point during the four years I worked on this book, I also realized that, in one way or another, every time travel story is about death. Death is either explicitly there in the foreground or lurking in the background because time is a bastard, right? Time is brutal. What does time do to us? It kills us. Time travel is our way of flirting with immortality. It’s the closest we’re going to come to it.
This interview was edited for length and clarity.
Simon Worrall curates Book Talk . Follow him on Twitter or at simonworrallauthor.com .
Related Topics

Why daylight saving time exists—at least for now

Leap year saved our societies from chaos—for now, at least

Does eating close to bedtime make you gain weight? It depends.

Why we sing ‘Auld Lang Syne’ on New Year’s Eve

A Year After Everest Disaster, This Sherpa Isn't Going Back
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

Where Does the Concept of Time Travel Come From?
Time; he's waiting in the wings.

The dream of traveling through time is both ancient and universal. But where did humanity's fascination with time travel begin, and why is the idea so appealing?
The concept of time travel — moving through time the way we move through three-dimensional space — may in fact be hardwired into our perception of time . Linguists have recognized that we are essentially incapable of talking about temporal matters without referencing spatial ones. "In language — any language — no two domains are more intimately linked than space and time," wrote Israeli linguist Guy Deutscher in his 2005 book "The Unfolding of Language." "Even if we are not always aware of it, we invariably speak of time in terms of space, and this reflects the fact that we think of time in terms of space."
Deutscher reminds us that when we plan to meet a friend "around" lunchtime, we are using a metaphor, since lunchtime doesn't have any physical sides. He similarly points out that time can not literally be "long" or "short" like a stick, nor "pass" like a train, or even go "forward" or "backward" any more than it goes sideways, diagonal or down.
Related: Why Does Time Fly When You're Having Fun?
Perhaps because of this connection between space and time, the possibility that time can be experienced in different ways and traveled through has surprisingly early roots. One of the first known examples of time travel appears in the Mahabharata, an ancient Sanskrit epic poem compiled around 400 B.C., Lisa Yaszek, a professor of science fiction studies at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta, told Live Science
In the Mahabharata is a story about King Kakudmi, who lived millions of years ago and sought a suitable husband for his beautiful and accomplished daughter, Revati. The two travel to the home of the creator god Brahma to ask for advice. But while in Brahma's plane of existence, they must wait as the god listens to a 20-minute song, after which Brahma explains that time moves differently in the heavens than on Earth. It turned out that "27 chatur-yugas" had passed, or more than 116 million years, according to an online summary , and so everyone Kakudmi and Revati had ever known, including family members and potential suitors, was dead. After this shock, the story closes on a somewhat happy ending in that Revati is betrothed to Balarama, twin brother of the deity Krishna.
Time is fleeting
To Yaszek, the tale provides an example of what we now call time dilation , in which different observers measure different lengths of time based on their relative frames of reference, a part of Einstein's theory of relativity.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
Such time-slip stories are widespread throughout the world, Yaszek said, citing a Middle Eastern tale from the first century BCE about a Jewish miracle worker who sleeps beneath a newly-planted carob tree and wakes up 70 years later to find it has now matured and borne fruit (carob trees are notorious for how long they take to produce their first harvest). Another instance can be found in an eighth-century Japanese fable about a fisherman named Urashima Tarō who travels to an undersea palace and falls in love with a princess. Tarō finds that, when he returns home, 100 years have passed, according to a translation of the tale published online by the University of South Florida .
In the early-modern era of the 1700 and 1800s, the sleep-story version of time travel grew more popular, Yaszek said. Examples include the classic tale of Rip Van Winkle, as well as books like Edward Belamy's utopian 1888 novel "Looking Backwards," in which a man wakes up in the year 2000, and the H.G. Wells 1899 novel "The Sleeper Awakes," about a man who slumbers for centuries and wakes to a completely transformed London.
Related: Science Fiction or Fact: Is Time Travel Possible ?
In other stories from this period, people also start to be able to move backward in time. In Mark Twain’s 1889 satire "A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur's Court," a blow to the head propels an engineer back to the reign of the legendary British monarch. Objects that can send someone through time begin to appear as well, mainly clocks, such as in Edward Page Mitchell's 1881 story "The Clock that Went Backwards" or Lewis Carrol's 1889 children's fantasy "Sylvie and Bruno," where the characters possess a watch that is a type of time machine .
The explosion of such stories during this era might come from the fact that people were "beginning to standardize time, and orient themselves to clocks more frequently," Yaszek said.
Time after time
Wells provided one of the most enduring time-travel plots in his 1895 novella "The Time Machine," which included the innovation of a craft that can move forward and backward through long spans of time. "This is when we’re getting steam engines and trains and the first automobiles," Yaszek said. "I think it’s no surprise that Wells suddenly thinks: 'Hey, maybe we can use a vehicle to travel through time.'"
Because it is such a rich visual icon, many beloved time-travel stories written after this have included a striking time machine, Yaszek said, referencing The Doctor's blue police box — the TARDIS — in the long-running BBC series "Doctor Who," and "Back to the Future"'s silver luxury speedster, the DeLorean .
More recently, time travel has been used to examine our relationship with the past, Yaszek said, in particular in pieces written by women and people of color. Octavia Butler's 1979 novel "Kindred" about a modern woman who visits her pre-Civil-War ancestors is "a marvelous story that really asks us to rethink black and white relations through history," she said. And a contemporary web series called " Send Me " involves an African-American psychic who can guide people back to antebellum times and witness slavery.
"I'm really excited about stories like that," Yaszek said. "They help us re-see history from new perspectives."
Time travel has found a home in a wide variety of genres and media, including comedies such as "Groundhog Day" and "Bill and Ted's Excellent Adventure" as well as video games like Nintendo's "The Legend of Zelda: Majora's Mask" and the indie game "Braid."
Yaszek suggested that this malleability and ubiquity speaks to time travel tales' ability to offer an escape from our normal reality. "They let us imagine that we can break free from the grip of linear time," she said. "And somehow get a new perspective on the human experience, either our own or humanity as a whole, and I think that feels so exciting to us."
That modern people are often drawn to time-machine stories in particular might reflect the fact that we live in a technological world, she added. Yet time travel's appeal certainly has deeper roots, interwoven into the very fabric of our language and appearing in some of our earliest imaginings.
"I think it's a way to make sense of the otherwise intangible and inexplicable, because it's hard to grasp time," Yaszek said. "But this is one of the final frontiers, the frontier of time, of life and death. And we're all moving forward, we're all traveling through time."
- If There Were a Time Warp, How Would Physicists Find It?
- Can Animals Tell Time?
- Why Does Time Sometimes Fly When You're NOT Having Fun?
Originally published on Live Science .

Adam Mann is a freelance journalist with over a decade of experience, specializing in astronomy and physics stories. He has a bachelor's degree in astrophysics from UC Berkeley. His work has appeared in the New Yorker, New York Times, National Geographic, Wall Street Journal, Wired, Nature, Science, and many other places. He lives in Oakland, California, where he enjoys riding his bike.
30,000 years of history reveals that hard times boost human societies' resilience
'We're meeting people where they are': Graphic novels can help boost diversity in STEM, says MIT's Ritu Raman
A new theory of quantum gravity could explain the biggest puzzle in cosmology, study suggests
Most Popular
- 2 Massive study of 8,000 cats reveals which breeds live longest
- 3 Snake Island: The isle writhing with vipers where only Brazilian military and scientists are allowed
- 4 Some of the oldest stars in the universe found hiding near the Milky Way's edge — and they may not be alone
- 5 Newfound 'glitch' in Einstein's relativity could rewrite the rules of the universe, study suggests
- 2 Snake Island: The isle writhing with vipers where only Brazilian military and scientists are allowed
- 3 32 diseases you can catch from animals
- 4 Does the Milky Way orbit anything?
- 5 'More Neanderthal than human': How your health may depend on DNA from our long-lost ancestors
28 Fascinating Facts About Time
By kerry wolfe | may 2, 2022.

Did you know that a day on Earth used to be around six hours shorter than it is today? Or that Julius Caesar once implemented a 445-day-long year? Learn those fascinating facts about time and more in this list, adapted from an episode of The List Show on YouTube.
1. Every person on Earth is living in the past.
This may sound like the plot to some sci-fi, time-travel thriller, but it’s actually a fact of human biology and the trickiness of time. Our brains don’t perceive events until about 80 milliseconds until after they’ve happened. This fine line between the present and the past is part of the reason why some physicists argue that there’s no such thing as “now” and that the present moment is no more than an illusion.
2. Throughout history, different cultures around the world have experienced time in different ways.
In the Western world, we tend to think of time as linear and flowing from left to right . But this isn’t the case for everyone. Language affects how people conceptualize time, particularly the spatial metaphors they use to describe and map it.
Those who read languages that flow from right to left, such as Arabic and Hebrew, generally view time as flowing in the same direction. The Aymara , who live in the Andes Mountains in South America, consider the future to be behind them, while the past is ahead. In their view, because the future is unknown, it’s behind you, where you can’t see it. Some Indigenous Australian cultures, which rely heavily on direction terms like north, south, east, and west in their languages, visualize the passage of time as moving from east to west. If they’re facing north, for example, the past would be to their right, or east, whereas the future would be to their left, which would be west.
3. Individual people can experience time differently, too.
You’ve probably noticed how time seems to speed up when you’re racing against a deadline or having fun, and how it tends to drag when you’re bored. This is because when you’re focused on something, like a big work project or a party, your brain pays less attention to how time passes . But when you’re bored, or your brain is less stimulated, you become more aware of the passing of time, making it feel slower. One study proposed that dopamine —the neurotransmitter and hormone that helps us feel happy—may be an additional culprit. It showed that increased dopamine production, which happens when you’re enjoying something , may slow down your body’s internal clock, making time feel like it’s flying by.
4. Science has a number of different ways of defining time.
To cover just a couple : There’s astronomical time, which is measured in relation to how long it takes Earth to rotate on its axis. In astronomical time, a second is 1/60th of a minute . And then there’s atomic time, which dictates the numbers that you’ll see on a clock. According to atomic time, one second equals 9,192,631,770 oscillations of a cesium-133 atom. Measuring the vibration of an atom—which, in simple terms, is the gist of what oscillation is —is the most accurate way to track time.
5. We can thank Albert Einstein for a lot of our current understanding of the physics of time.

Rather than viewing time as a set order, he proved that it’s actually relative. For example, according to Einstein’s theory of special relativity , there’s an inverse relationship between your speed and the speed of time. The faster you move, the slower time moves.
This is why someone blasting through space will age slower than the people still hanging out on Earth: Astronaut Scott Kelly was born several minutes after his twin brother, Mark, but after Scott spent 340 days living on the International Space Station, he returned to Earth around an extra 5 milliseconds younger than his “big” brother. Had Scott been traveling at a speed close to the speed of light, that age difference would have become much more pronounced.
6. Einstein’s theory also states that gravity can warp time.
If you’ve seen the 2014 movie Interstellar , this concept may seem familiar . The closer you are to a massive body—which, in the case of Interstellar , is a giant black hole—the slower time would pass for you.
7. Gravity’s effect on time isn’t limited to intergalactic travel.
Here on Earth, gravity can vary for a number of reasons, including your altitude, since you’re changing your distance from the center of the Earth. That means if you put a bunch of synchronized atomic clocks at various altitudes , eventually those clocks would fall out of sync. A clock at the top of Mount Everest and one at sea level would, over the entire 4.5 billion year history of the planet, have diverged by about a day and a half.
8. Gravity is also the reason why our days are getting longer.
Over a billion years ago, a day on Earth lasted around 18 hours . Our days are longer now because the moon’s gravity is causing Earth’s spin to slow down. In Earth’s earlier days, the moon wasn’t as far away, which caused Earth to spin much faster than it currently does.
Longer days also mean shorter years—kind of. The time it takes the Earth to orbit the sun hasn’t changed, but the amount of days within a year has. Back when the dinosaurs ruled 70 million years ago , days were only around 23.5 hours long, and a year was made up of 372 of those slightly shorter days.
9. There are two ways to think of the length of a day on Earth.
Though you probably learned that one day on Earth is 24 hours, it actually takes the planet 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.0916 seconds to rotate on its axis. This is the difference between a solar day and a sidereal day—a solar day is 24 hours, whereas a sidereal day is roughly four minutes shorter. We measure solar time based on the sun’s position in the sky; a sidereal day is measured based on the location of the “fixed” stars. In other words, a sidereal day is the time it takes for a distant star or constellation to appear on the same meridian .
10. Because astronomical time and atomic time don’t always line up, every so often, we get a leap second.
Earth’s spin speed can be a bit unpredictable. Atmospheric winds, Northern Hemisphere winters with heavy snow, and other big weather systems can affect how fast the planet rotates. In order to keep the difference between astronomical time and atomic time to less than .9 seconds, the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service will occasionally announce the need for a leap second .
Most people won’t notice a leap second, but they can be a huge pain for tech companies . Because leap seconds are added irregularly, developers have no way of working them into their codes, which has caused websites like LinkedIn and Reddit to crash in the past. A bug caused by 2012’s leap second created so much chaos on Qantas’s servers, more than 400 flights wound up being delayed.
11. The length of a year on Earth can also get a bit complicated.
The original Roman calendar was a bit of a mess, so much so that in 46 BCE Julius Caesar mandated a 445-day-long year to help bring the calendar back in sync with the seasons.
12. At the same time, Caesar asked the astronomer Sosigenes to help reform the calendar.

Most years were set at 365 days, but to make up for the fact that the earth's revolution around the sun doesn't take exactly 365 days, leap years were implemented . Every four years the month of February was given an extra day to make up for what is a sort of rounding error in the calendar.
13. But Sosigenes made a bit of a miscalculation, so the calendar continued to be a little off.
He thought a year lasted 365.25 days. It’s actually around 365 days, five hours, 48 minutes, and 45 seconds, equivalent to about 365.242 days. This tiny error had some pretty big consequences: By 1577, the Julian calendar was off by 10 days, meaning key Christian holidays were being celebrated on incorrect dates.
Pope Gregory XIII took issue with this and established a commission to get the calendar back on track. In 1582, the Gregorian calendar was created. Rather than having an extra day every four years without exception, years that are divisible by 100—like 1700 or 1900—skip leap year. Unless the year is also divisible by 400, like the year 2000, in which case the Leap Year is back on! Even this system isn’t perfect, though: It has an error of one day in 3236 years.
14. We can thank the railroad industry for standardizing our time zones.
Until the 19th century, towns and villages synchronized their clocks to the local solar noon. This created thousands of local times that all varied and made scheduling transportation a major headache. Train schedules in different cities had to list dozens of arrival and departure times for each train to account for all the mini time zones. On November 18, 1883, railroad companies in the United States and Canada began using a system very similar to the standardized time zones we still use today. In the UK, the railroad companies began using a standard London-based time in 1840.
15. After an engineer named Sandford Fleming missed a train in 1876, he set out to change the way time worked.
Fleming originally proposed a concept he called “Cosmic Time,” in which the world would run off an imaginary clock located at the planet’s center, essentially a line from the center of the planet to the sun. He then suggested splitting the world into 24 time zones labeled with a letter of the alphabet, with each zone spanning 15 degrees of longitude. His original plan to create a standard “Cosmic Time” was rejected, but it did lay the groundwork for a similar standardization, so-called Universal Time . And nations present at the 1884 International Meridian Conference laid the groundwork for dividing the world into 24 time zones, with the Prime Meridian, also known as Longitude 0°, running through Greenwich, England.
16. Even with the advent of standardized time, people still struggled to keep their clocks in sync.
One London family used this to their advantage, and made a living by selling people the time. An astronomer named John Belville would set his pocket watch to the time at the Royal Observatory Greenwich. He would then travel around the city and visit his network of subscribers, who paid to set their own clocks by Belville’s pocket watch. After Belville died in 1856, his wife, and then later their daughter Ruth, carried on the tradition. Ruth continued to sell the time until World War II. By then she was in her eighties, and a couple of factors led to her timely retirement: Improved technology had made her role less important, and the war was making treks around London too dangerous.
17. Time zones can still be a bit complicated.
Big countries like Canada and the United States have multiple time zones, whereas China, another large country, only has one . China adopted the Beijing Standard Time to foster unity, but the effect can feel a bit uncanny—two cities in the country can be at roughly the same latitude, but experience sunrise hours apart, according to their clocks. In some parts of China, for example, the sun doesn’t rise until nearly 10 a.m.
18. Though a lot of people believe daylight saving time was adopted to keep farmers happy, that’s a myth.
The first person to seriously advocate for daylight saving time was an entomologist who wanted more sunlit hours to look for insects after work in the summer. He proposed his idea to a scientific society in New Zealand in 1895.
19. Daylight saving time wasn’t officially implemented until 1916.
Germany became the first country to adopt it in an effort to conserve coal during World War I. The United States didn’t follow suit until 1918 .
20. Daylight saving time ended on a national level after the war, but individual states and municipalities kept it going until World War II.
At the end of World War I, the entire nation went on what was effectively a year-round daylight saving time. After World War II, the entire nation was again picking and choosing daylight saving time. It’s been reported that in Iowa, back in 1964, there were 23 different combinations of dates that communities turned on and off daylight saving time. In 1966, the government officially mandated a standardized daylight saving time for the entire United States, though individual states can opt out.
Until 2007, daylight saving time ended in October. It’s been reported that the candy industry lobbied to wait until after Halloween to change the clocks back an hour.
21. Daylight saving time does more than make people lose an hour of sleep.
In fact, it can have some pretty concerning health effects. Studies have linked daylight saving time with an uptick in heart attacks, car crashes, and mining injuries. The extra hour of daylight is good for koalas, though: Researchers found that koala-car collisions went down by up to 11 percent during daylight saving time.
22. People have been tracking time for thousands of years.
In 2013, archaeologists found what’s thought to be the world's oldest lunar calendar while excavating a field in Scotland. The calendar, which is made of a series of 12 pits that mimic the moon’s phases, dates back to around 8000 BCE.
23. Sundials read differently depending on the hemisphere you’re in.

In the Northern Hemisphere, the sun casts a shadow that moves from north, to east, to south, to west. In the Southern Hemisphere, the shadow moves in the opposite direction. Our concept of “ clockwise ” is based on the way sundials in the Northern Hemisphere told time.
24. An innovative clock was built in China in 1090.
A man named Su Song created a water-powered clock tower that measured time and tracked the movements of the planets and stars in the night sky. Su Song built a giant water wheel within the clock tower. Buckets attached to the wheel would fill with water and then tip once full, causing the wheel to rotate, demarcating time.
25. The Maya had multiple calendars to measure time.
The most familiar is the Long Count Calendar. These calendars measured around 5125 years, beginning around August 3114 BCE. The Long Count calendar’s cycle came to an end around December 21, 2012, sparking a craze of Armageddon conspiracy theories.
26. You’ll find the most accurate clock at the National Institute of Standards and Technology in Boulder, Colorado.
The clock keeps time by measuring the vibration of a single aluminum ion , and should remain accurate for 33 billion years. The clock sitting on your bedside table isn't quite as precise.
27. New clocks are set at 10:10 for a reason.
If you’ve bought a new clock or watch recently, you may have noticed that the default setting was 10:10, give or take a few minutes. There are various theories behind this particular choice of time, but really, it all comes down to aesthetics. Setting the time to around 10:10 allows the hands of an analog clock to be displayed in a neat, symmetrical way that doesn’t obscure any logos in the center of the clock’s face. Clocks were once set to 8:20, and occasionally still are, but the hands’ downward angles can make it look like the timepieces are frowning.
28. Traveling back in time is possible—theoretically, at least.
According to Einstein’s theory, you could travel back in time by moving faster than the speed of light, as long as you could somehow have infinite mass. Since that probably won’t work, you could create “ wormholes ” between two points in space-time. (This would also be tough, since humanity still hasn’t invented the technology to actually build a wormhole.) Or you could try bending space-time by plucking some “cosmic strings.” Two of these theoretical strings, which are thin streams of pure energy that are moving in opposite directions at very near the speed of light, could theoretically warp space-time enough to create a closed time-like curve—also known as a time machine.

Time Travel Facts
Physics of time travel.
Table of Contents
Time travel nears with new trillion-dollar ‘dual-use’ government technology. Visionary new closed timeline curves theory offers a peek into our past.
The idea of going back in time first captivated the popular imagination when H.G. Wells published his book , ‘The Time Machine’ in 1895. But today, this is no longer Star Trek pseudo-science but credible theorization incorporating standard laws of physics. That’s according to Texan, Joseph E. Olson in his article, ‘ Time Travel Tremor ,’ featured in Canada Free Press (June 7, 2010).
How is Time Travel Possible?
Joe insists time travel is infinitely more possible as theorists number-crunch two loose ends from the equations handed down to us by Albert Einstein and Godel’s solution to the ‘Field Equations’ in 1949. It seems even Einstein, himself, admitted the time travel door may be wide open to us yet.
Olson explains, “To the general public the take-home message is this: all that is necessary to complete the Einstein Theory of curved time-space is the charge and the rotation of the cosmological dust.”
The former Houston engineer explains that the two unknowns from that fateful 1949 equation were the spin of the cosmic dust and the net charge of the universal background radiation.
Olson enthuses, “To solve these equations we needed some empirical data. We needed un-disturbed cosmic dust, best collected on the moon, and advanced space-based telescopes to measure the rotation speed and the galactic radio wave radiation.”
The real-world data has painstakingly been put together at great expense as a result of the trillion-dollar space programs of rival Cold War superpowers, the United States and the former Soviet Union. Additional tweaking may now be ongoing here on Earth at the $6 billion Hadron Space Collider in Switzerland.
Top Scientists Seriously Study Time Travel
A long-time outspoken critic of the man-made theory of climate change , this insightful Texan is not shy of controversy. In pitching in with an incredible new angle to humanity’s big dream Olson expects to be labeled by some a ‘conspiracy nut.’ No less an icon of mainstream science, Stephen Hawking, a modern-day Sir Isaac Newton, has waded in to affirm that time travel is feasible in his documentary series on the ‘Discovery Channel.’
British science guru, Hawking admits he kept quiet until now for fear of “being labeled a crank.” Olson has no such fears and the Texan is blasting out on this with both barrels suggesting the public ridicule and the secrecy of successive U.S. governments simply adds fuel to his fire.
Indeed, with trillions of taxpayer dollars accumulated in related research projects with no apparent return on the investment, public speculation readily links projects such as the Hadron particle Collider with the once fanciful musings of H.G. Wells.
Dual Use Technologies
To channel vast amounts of government resources into what would otherwise be a giant cosmological white elephant, Olson identifies the need for policymakers to often couch their time travel research within the context of military defense; what he calls the incorporation of additional ‘dual use’ technologies.
An example of ‘dual use’ technical innovation was the Apollo Moon mission landings, which were seen not just as international kudos for the U.S., but a giant leap towards winning the superpowers’ arms race with the former Soviet Union. Thus the Hadron particle collider may be cloaked in another plausible cover while this hunt for the Holy Grail of science becomes ever more tantalizing.
Olson says, after decades of relentless acquisition of data, we are now about there. The great ‘Theory equation’ could finally be calculated and new technologies developed and refined to implement this new closed timeline curves theory with an actual machine that may cross the time-space curve into our history.
Russian Mathematicians Affirm Time Travel Possible
Olson expects those protective of government secrets will be quick to call him a crank but he’s not concerned. He has plenty of well-credentialed big-hitters supporting his ideas. For example, as reported in the UK’s ‘Independent’ newspaper (February 8, 2008) two Russian mathematicians, Irina Aref’eva and Igor Volovich, have spoken out in support of such a new theory.
The Russians envision the Large Hadron Collider at Cern as the most likely testbed for mankind’s first peek into the past. They suggested 2008 was the most credible “year zero” for time travel because they calculate it was the ideal location for plausible tiny “wormholes” in space that could allow some form of time travel.
Where future developments will lead we can only guess, because as Olson says, whoever seeks to exploit this technology will be guarding it very jealously and will be loathe to want to share it.
References:
- Connor, S., ‘The Big Question: Is time travel possible, and is there any chance that it will ever take place?’ Science Editor, The Independent ( February 8, 2008)
- Godel, K., An example of a new type of cosmological solutions of Einstein’s field equations of gravitation, (1949); Oxford University Press.
- Olson, J., ‘Time Travel Tremor,’ Canada Free Press (June 7, 2010)
- Overbye, D., ‘Large Hadron Collider,’ New York Times , (June 8, 2010)
- Matyszczyk, C. ‘Hawking: Time Travel Will Happen,’ (May 2, 2010); Cnet News
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.


- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Time Travel
There is an extensive literature on time travel in both philosophy and physics. Part of the great interest of the topic stems from the fact that reasons have been given both for thinking that time travel is physically possible—and for thinking that it is logically impossible! This entry deals primarily with philosophical issues; issues related to the physics of time travel are covered in the separate entries on time travel and modern physics and time machines . We begin with the definitional question: what is time travel? We then turn to the major objection to the possibility of backwards time travel: the Grandfather paradox. Next, issues concerning causation are discussed—and then, issues in the metaphysics of time and change. We end with a discussion of the question why, if backwards time travel will ever occur, we have not been visited by time travellers from the future.
1.1 Time Discrepancy
1.2 changing the past, 2.1 can and cannot, 2.2 improbable coincidences, 2.3 inexplicable occurrences, 3.1 backwards causation, 3.2 causal loops, 4.1 time travel and time, 4.2 time travel and change, 5. where are the time travellers, other internet resources, related entries, 1. what is time travel.
There is a number of rather different scenarios which would seem, intuitively, to count as ‘time travel’—and a number of scenarios which, while sharing certain features with some of the time travel cases, seem nevertheless not to count as genuine time travel: [ 1 ]
Time travel Doctor . Doctor Who steps into a machine in 2024. Observers outside the machine see it disappear. Inside the machine, time seems to Doctor Who to pass for ten minutes. Observers in 1984 (or 3072) see the machine appear out of nowhere. Doctor Who steps out. [ 2 ] Leap . The time traveller takes hold of a special device (or steps into a machine) and suddenly disappears; she appears at an earlier (or later) time. Unlike in Doctor , the time traveller experiences no lapse of time between her departure and arrival: from her point of view, she instantaneously appears at the destination time. [ 3 ] Putnam . Oscar Smith steps into a machine in 2024. From his point of view, things proceed much as in Doctor : time seems to Oscar Smith to pass for a while; then he steps out in 1984. For observers outside the machine, things proceed differently. Observers of Oscar’s arrival in the past see a time machine suddenly appear out of nowhere and immediately divide into two copies of itself: Oscar Smith steps out of one; and (through the window) they see inside the other something that looks just like what they would see if a film of Oscar Smith were played backwards (his hair gets shorter; food comes out of his mouth and goes back into his lunch box in a pristine, uneaten state; etc.). Observers of Oscar’s departure from the future do not simply see his time machine disappear after he gets into it: they see it collide with the apparently backwards-running machine just described, in such a way that both are simultaneously annihilated. [ 4 ] Gödel . The time traveller steps into an ordinary rocket ship (not a special time machine) and flies off on a certain course. At no point does she disappear (as in Leap ) or ‘turn back in time’ (as in Putnam )—yet thanks to the overall structure of spacetime (as conceived in the General Theory of Relativity), the traveller arrives at a point in the past (or future) of her departure. (Compare the way in which someone can travel continuously westwards, and arrive to the east of her departure point, thanks to the overall curved structure of the surface of the earth.) [ 5 ] Einstein . The time traveller steps into an ordinary rocket ship and flies off at high speed on a round trip. When he returns to Earth, thanks to certain effects predicted by the Special Theory of Relativity, only a very small amount of time has elapsed for him—he has aged only a few months—while a great deal of time has passed on Earth: it is now hundreds of years in the future of his time of departure. [ 6 ] Not time travel Sleep . One is very tired, and falls into a deep sleep. When one awakes twelve hours later, it seems from one’s own point of view that hardly any time has passed. Coma . One is in a coma for a number of years and then awakes, at which point it seems from one’s own point of view that hardly any time has passed. Cryogenics . One is cryogenically frozen for hundreds of years. Upon being woken, it seems from one’s own point of view that hardly any time has passed. Virtual . One enters a highly realistic, interactive virtual reality simulator in which some past era has been recreated down to the finest detail. Crystal . One looks into a crystal ball and sees what happened at some past time, or will happen at some future time. (Imagine that the crystal ball really works—like a closed-circuit security monitor, except that the vision genuinely comes from some past or future time. Even so, the person looking at the crystal ball is not thereby a time traveller.) Waiting . One enters one’s closet and stays there for seven hours. When one emerges, one has ‘arrived’ seven hours in the future of one’s ‘departure’. Dateline . One departs at 8pm on Monday, flies for fourteen hours, and arrives at 10pm on Monday.
A satisfactory definition of time travel would, at least, need to classify the cases in the right way. There might be some surprises—perhaps, on the best definition of ‘time travel’, Cryogenics turns out to be time travel after all—but it should certainly be the case, for example, that Gödel counts as time travel and that Sleep and Waiting do not. [ 7 ]
In fact there is no entirely satisfactory definition of ‘time travel’ in the literature. The most popular definition is the one given by Lewis (1976, 145–6):
What is time travel? Inevitably, it involves a discrepancy between time and time. Any traveller departs and then arrives at his destination; the time elapsed from departure to arrival…is the duration of the journey. But if he is a time traveller, the separation in time between departure and arrival does not equal the duration of his journey.…How can it be that the same two events, his departure and his arrival, are separated by two unequal amounts of time?…I reply by distinguishing time itself, external time as I shall also call it, from the personal time of a particular time traveller: roughly, that which is measured by his wristwatch. His journey takes an hour of his personal time, let us say…But the arrival is more than an hour after the departure in external time, if he travels toward the future; or the arrival is before the departure in external time…if he travels toward the past.
This correctly excludes Waiting —where the length of the ‘journey’ precisely matches the separation between ‘arrival’ and ‘departure’—and Crystal , where there is no journey at all—and it includes Doctor . It has trouble with Gödel , however—because when the overall structure of spacetime is as twisted as it is in the sort of case Gödel imagined, the notion of external time (“time itself”) loses its grip.
Another definition of time travel that one sometimes encounters in the literature (Arntzenius, 2006, 602) (Smeenk and Wüthrich, 2011, 5, 26) equates time travel with the existence of CTC’s: closed timelike curves. A curve in this context is a line in spacetime; it is timelike if it could represent the career of a material object; and it is closed if it returns to its starting point (i.e. in spacetime—not merely in space). This now includes Gödel —but it excludes Einstein .
The lack of an adequate definition of ‘time travel’ does not matter for our purposes here. [ 8 ] It suffices that we have clear cases of (what would count as) time travel—and that these cases give rise to all the problems that we shall wish to discuss.
Some authors (in philosophy, physics and science fiction) consider ‘time travel’ scenarios in which there are two temporal dimensions (e.g. Meiland (1974)), and others consider scenarios in which there are multiple ‘parallel’ universes—each one with its own four-dimensional spacetime (e.g. Deutsch and Lockwood (1994)). There is a question whether travelling to another version of 2001 (i.e. not the very same version one experienced in the past)—a version at a different point on the second time dimension, or in a different parallel universe—is really time travel, or whether it is more akin to Virtual . In any case, this kind of scenario does not give rise to many of the problems thrown up by the idea of travelling to the very same past one experienced in one’s younger days. It is these problems that form the primary focus of the present entry, and so we shall not have much to say about other kinds of ‘time travel’ scenario in what follows.
One objection to the possibility of time travel flows directly from attempts to define it in anything like Lewis’s way. The worry is that because time travel involves “a discrepancy between time and time”, time travel scenarios are simply incoherent. The time traveller traverses thirty years in one year; she is 51 years old 21 years after her birth; she dies at the age of 100, 200 years before her birth; and so on. The objection is that these are straightforward contradictions: the basic description of what time travel involves is inconsistent; therefore time travel is logically impossible. [ 9 ]
There must be something wrong with this objection, because it would show Einstein to be logically impossible—whereas this sort of future-directed time travel has actually been observed (albeit on a much smaller scale—but that does not affect the present point) (Hafele and Keating, 1972b,a). The most common response to the objection is that there is no contradiction because the interval of time traversed by the time traveller and the duration of her journey are measured with respect to different frames of reference: there is thus no reason why they should coincide. A similar point applies to the discrepancy between the time elapsed since the time traveller’s birth and her age upon arrival. There is no more of a contradiction here than in the fact that Melbourne is both 800 kilometres away from Sydney—along the main highway—and 1200 kilometres away—along the coast road. [ 10 ]
Before leaving the question ‘What is time travel?’ we should note the crucial distinction between changing the past and participating in (aka affecting or influencing) the past. [ 11 ] In the popular imagination, backwards time travel would allow one to change the past: to right the wrongs of history, to prevent one’s younger self doing things one later regretted, and so on. In a model with a single past, however, this idea is incoherent: the very description of the case involves a contradiction (e.g. the time traveller burns all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976, and does not burn all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976). It is not as if there are two versions of the past: the original one, without the time traveller present, and then a second version, with the time traveller playing a role. There is just one past—and two perspectives on it: the perspective of the younger self, and the perspective of the older time travelling self. If these perspectives are inconsistent (e.g. an event occurs in one but not the other) then the time travel scenario is incoherent.
This means that time travellers can do less than we might have hoped: they cannot right the wrongs of history; they cannot even stir a speck of dust on a certain day in the past if, on that day, the speck was in fact unmoved. But this does not mean that time travellers must be entirely powerless in the past: while they cannot do anything that did not actually happen, they can (in principle) do anything that did happen. Time travellers cannot change the past: they cannot make it different from the way it was—but they can participate in it: they can be amongst the people who did make the past the way it was. [ 12 ]
What about models involving two temporal dimensions, or parallel universes—do they allow for coherent scenarios in which the past is changed? [ 13 ] There is certainly no contradiction in saying that the time traveller burns all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976 in universe 1 (or at hypertime A ), and does not burn all her diaries at midnight on her fortieth birthday in 1976 in universe 2 (or at hypertime B ). The question is whether this kind of story involves changing the past in the sense originally envisaged: righting the wrongs of history, preventing subsequently regretted actions, and so on. Goddu (2003) and van Inwagen (2010) argue that it does (in the context of particular hypertime models), while Smith (1997, 365–6; 2015) argues that it does not: that it involves avoiding the past—leaving it untouched while travelling to a different version of the past in which things proceed differently.
2. The Grandfather Paradox
The most important objection to the logical possibility of backwards time travel is the so-called Grandfather paradox. This paradox has actually convinced many people that backwards time travel is impossible:
The dead giveaway that true time-travel is flatly impossible arises from the well-known “paradoxes” it entails. The classic example is “What if you go back into the past and kill your grandfather when he was still a little boy?”…So complex and hopeless are the paradoxes…that the easiest way out of the irrational chaos that results is to suppose that true time-travel is, and forever will be, impossible. (Asimov 1995 [2003, 276–7]) travel into one’s past…would seem to give rise to all sorts of logical problems, if you were able to change history. For example, what would happen if you killed your parents before you were born. It might be that one could avoid such paradoxes by some modification of the concept of free will. But this will not be necessary if what I call the chronology protection conjecture is correct: The laws of physics prevent closed timelike curves from appearing . (Hawking, 1992, 604) [ 14 ]
The paradox comes in different forms. Here’s one version:
If time travel was logically possible then the time traveller could return to the past and in a suicidal rage destroy his time machine before it was completed and murder his younger self. But if this was so a necessary condition for the time trip to have occurred at all is removed, and we should then conclude that the time trip did not occur. Hence if the time trip did occur, then it did not occur. Hence it did not occur, and it is necessary that it did not occur. To reply, as it is standardly done, that our time traveller cannot change the past in this way, is a petitio principii . Why is it that the time traveller is constrained in this way? What mysterious force stills his sudden suicidal rage? (Smith, 1985, 58)
The idea is that backwards time travel is impossible because if it occurred, time travellers would attempt to do things such as kill their younger selves (or their grandfathers etc.). We know that doing these things—indeed, changing the past in any way—is impossible. But were there time travel, there would then be nothing left to stop these things happening. If we let things get to the stage where the time traveller is facing Grandfather with a loaded weapon, then there is nothing left to prevent the impossible from occurring. So we must draw the line earlier: it must be impossible for someone to get into this situation at all; that is, backwards time travel must be impossible.
In order to defend the possibility of time travel in the face of this argument we need to show that time travel is not a sure route to doing the impossible. So, given that a time traveller has gone to the past and is facing Grandfather, what could stop her killing Grandfather? Some science fiction authors resort to the idea of chaperones or time guardians who prevent time travellers from changing the past—or to mysterious forces of logic. But it is hard to take these ideas seriously—and more importantly, it is hard to make them work in detail when we remember that changing the past is impossible. (The chaperone is acting to ensure that the past remains as it was—but the only reason it ever was that way is because of his very actions.) [ 15 ] Fortunately there is a better response—also to be found in the science fiction literature, and brought to the attention of philosophers by Lewis (1976). What would stop the time traveller doing the impossible? She would fail “for some commonplace reason”, as Lewis (1976, 150) puts it. Her gun might jam, a noise might distract her, she might slip on a banana peel, etc. Nothing more than such ordinary occurrences is required to stop the time traveller killing Grandfather. Hence backwards time travel does not entail the occurrence of impossible events—and so the above objection is defused.
A problem remains. Suppose Tim, a time-traveller, is facing his grandfather with a loaded gun. Can Tim kill Grandfather? On the one hand, yes he can. He is an excellent shot; there is no chaperone to stop him; the laws of logic will not magically stay his hand; he hates Grandfather and will not hesitate to pull the trigger; etc. On the other hand, no he can’t. To kill Grandfather would be to change the past, and no-one can do that (not to mention the fact that if Grandfather died, then Tim would not have been born). So we have a contradiction: Tim can kill Grandfather and Tim cannot kill Grandfather. Time travel thus leads to a contradiction: so it is impossible.
Note the difference between this version of the Grandfather paradox and the version considered above. In the earlier version, the contradiction happens if Tim kills Grandfather. The solution was to say that Tim can go into the past without killing Grandfather—hence time travel does not entail a contradiction. In the new version, the contradiction happens as soon as Tim gets to the past. Of course Tim does not kill Grandfather—but we still have a contradiction anyway: for he both can do it, and cannot do it. As Lewis puts it:
Could a time traveler change the past? It seems not: the events of a past moment could no more change than numbers could. Yet it seems that he would be as able as anyone to do things that would change the past if he did them. If a time traveler visiting the past both could and couldn’t do something that would change it, then there cannot possibly be such a time traveler. (Lewis, 1976, 149)
Lewis’s own solution to this problem has been widely accepted. [ 16 ] It turns on the idea that to say that something can happen is to say that its occurrence is compossible with certain facts, where context determines (more or less) which facts are the relevant ones. Tim’s killing Grandfather in 1921 is compossible with the facts about his weapon, training, state of mind, and so on. It is not compossible with further facts, such as the fact that Grandfather did not die in 1921. Thus ‘Tim can kill Grandfather’ is true in one sense (relative to one set of facts) and false in another sense (relative to another set of facts)—but there is no single sense in which it is both true and false. So there is no contradiction here—merely an equivocation.
Another response is that of Vihvelin (1996), who argues that there is no contradiction here because ‘Tim can kill Grandfather’ is simply false (i.e. contra Lewis, there is no legitimate sense in which it is true). According to Vihvelin, for ‘Tim can kill Grandfather’ to be true, there must be at least some occasions on which ‘If Tim had tried to kill Grandfather, he would or at least might have succeeded’ is true—but, Vihvelin argues, at any world remotely like ours, the latter counterfactual is always false. [ 17 ]
Return to the original version of the Grandfather paradox and Lewis’s ‘commonplace reasons’ response to it. This response engenders a new objection—due to Horwich (1987)—not to the possibility but to the probability of backwards time travel.
Think about correlated events in general. Whenever we see two things frequently occurring together, this is because one of them causes the other, or some third thing causes both. Horwich calls this the Principle of V-Correlation:
if events of type A and B are associated with one another, then either there is always a chain of events between them…or else we find an earlier event of type C that links up with A and B by two such chains of events. What we do not see is…an inverse fork—in which A and B are connected only with a characteristic subsequent event, but no preceding one. (Horwich, 1987, 97–8)
For example, suppose that two students turn up to class wearing the same outfits. That could just be a coincidence (i.e. there is no common cause, and no direct causal link between the two events). If it happens every week for the whole semester, it is possible that it is a coincidence, but this is extremely unlikely . Normally, we see this sort of extensive correlation only if either there is a common cause (e.g. both students have product endorsement deals with the same clothing company, or both slavishly copy the same influencer) or a direct causal link (e.g. one student is copying the other).
Now consider the time traveller setting off to kill her younger self. As discussed, no contradiction need ensue—this is prevented not by chaperones or mysterious forces, but by a run of ordinary occurrences in which the trigger falls off the time traveller’s gun, a gust of wind pushes her bullet off course, she slips on a banana peel, and so on. But now consider this run of ordinary occurrences. Whenever the time traveller contemplates auto-infanticide, someone nearby will drop a banana peel ready for her to slip on, or a bird will begin to fly so that it will be in the path of the time traveller’s bullet by the time she fires, and so on. In general, there will be a correlation between auto-infanticide attempts and foiling occurrences such as the presence of banana peels—and this correlation will be of the type that does not involve a direct causal connection between the correlated events or a common cause of both. But extensive correlations of this sort are, as we saw, extremely rare—so backwards time travel will happen about as often as you will see two people wear the same outfits to class every day of semester, without there being any causal connection between what one wears and what the other wears.
We can set out Horwich’s argument this way:
- If time travel were ever to occur, we should see extensive uncaused correlations.
- It is extremely unlikely that we should ever see extensive uncaused correlations.
- Therefore time travel is extremely unlikely to occur.
The conclusion is not that time travel is impossible, but that we should treat it the way we treat the possibility of, say, tossing a fair coin and getting heads one thousand times in a row. As Price (1996, 278 n.7) puts it—in the context of endorsing Horwich’s conclusion: “the hypothesis of time travel can be made to imply propositions of arbitrarily low probability. This is not a classical reductio, but it is as close as science ever gets.”
Smith (1997) attacks both premisses of Horwich’s argument. Against the first premise, he argues that backwards time travel, in itself, does not entail extensive uncaused correlations. Rather, when we look more closely, we see that time travel scenarios involving extensive uncaused correlations always build in prior coincidences which are themselves highly unlikely. Against the second premise, he argues that, from the fact that we have never seen extensive uncaused correlations, it does not follow that we never shall. This is not inductive scepticism: let us assume (contra the inductive sceptic) that in the absence of any specific reason for thinking things should be different in the future, we are entitled to assume they will continue being the same; still we cannot dismiss a specific reason for thinking the future will be a certain way simply on the basis that things have never been that way in the past. You might reassure an anxious friend that the sun will certainly rise tomorrow because it always has in the past—but you cannot similarly refute an astronomer who claims to have discovered a specific reason for thinking that the earth will stop rotating overnight.
Sider (2002, 119–20) endorses Smith’s second objection. Dowe (2003) criticises Smith’s first objection, but agrees with the second, concluding overall that time travel has not been shown to be improbable. Ismael (2003) reaches a similar conclusion. Goddu (2007) criticises Smith’s first objection to Horwich. Further contributions to the debate include Arntzenius (2006), Smeenk and Wüthrich (2011, §2.2) and Elliott (2018). For other arguments to the same conclusion as Horwich’s—that time travel is improbable—see Ney (2000) and Effingham (2020).
Return again to the original version of the Grandfather paradox and Lewis’s ‘commonplace reasons’ response to it. This response engenders a further objection. The autoinfanticidal time traveller is attempting to do something impossible (render herself permanently dead from an age younger than her age at the time of the attempts). Suppose we accept that she will not succeed and that what will stop her is a succession of commonplace occurrences. The previous objection was that such a succession is improbable . The new objection is that the exclusion of the time traveler from successfully committing auto-infanticide is mysteriously inexplicable . The worry is as follows. Each particular event that foils the time traveller is explicable in a perfectly ordinary way; but the inevitable combination of these events amounts to a ring-fencing of the forbidden zone of autoinfanticide—and this ring-fencing is mystifying. It’s like a grand conspiracy to stop the time traveler from doing what she wants to do—and yet there are no conspirators: no time lords, no magical forces of logic. This is profoundly perplexing. Riggs (1997, 52) writes: “Lewis’s account may do for a once only attempt, but is untenable as a general explanation of Tim’s continual lack of success if he keeps on trying.” Ismael (2003, 308) writes: “Considered individually, there will be nothing anomalous in the explanations…It is almost irresistible to suppose, however, that there is something anomalous in the cases considered collectively, i.e., in our unfailing lack of success.” See also Gorovitz (1964, 366–7), Horwich (1987, 119–21) and Carroll (2010, 86).
There have been two different kinds of defense of time travel against the objection that it involves mysteriously inexplicable occurrences. Baron and Colyvan (2016, 70) agree with the objectors that a purely causal explanation of failure—e.g. Tim fails to kill Grandfather because first he slips on a banana peel, then his gun jams, and so on—is insufficient. However they argue that, in addition, Lewis offers a non-causal—a logical —explanation of failure: “What explains Tim’s failure to kill his grandfather, then, is something about logic; specifically: Tim fails to kill his grandfather because the law of non-contradiction holds.” Smith (2017) argues that the appearance of inexplicability is illusory. There are no scenarios satisfying the description ‘a time traveller commits autoinfanticide’ (or changes the past in any other way) because the description is self-contradictory (e.g. it involves the time traveller permanently dying at 20 and also being alive at 40). So whatever happens it will not be ‘that’. There is literally no way for the time traveller not to fail. Hence there is no need for—or even possibility of—a substantive explanation of why failure invariably occurs, and such failure is not perplexing.
3. Causation
Backwards time travel scenarios give rise to interesting issues concerning causation. In this section we examine two such issues.
Earlier we distinguished changing the past and affecting the past, and argued that while the former is impossible, backwards time travel need involve only the latter. Affecting the past would be an example of backwards causation (i.e. causation where the effect precedes its cause)—and it has been argued that this too is impossible, or at least problematic. [ 18 ] The classic argument against backwards causation is the bilking argument . [ 19 ] Faced with the claim that some event A causes an earlier event B , the proponent of the bilking objection recommends an attempt to decorrelate A and B —that is, to bring about A in cases in which B has not occurred, and to prevent A in cases in which B has occurred. If the attempt is successful, then B often occurs despite the subsequent nonoccurrence of A , and A often occurs without B occurring, and so A cannot be the cause of B . If, on the other hand, the attempt is unsuccessful—if, that is, A cannot be prevented when B has occurred, nor brought about when B has not occurred—then, it is argued, it must be B that is the cause of A , rather than vice versa.
The bilking procedure requires repeated manipulation of event A . Thus, it cannot get under way in cases in which A is either unrepeatable or unmanipulable. Furthermore, the procedure requires us to know whether or not B has occurred, prior to manipulating A —and thus, it cannot get under way in cases in which it cannot be known whether or not B has occurred until after the occurrence or nonoccurrence of A (Dummett, 1964). These three loopholes allow room for many claims of backwards causation that cannot be touched by the bilking argument, because the bilking procedure cannot be performed at all. But what about those cases in which it can be performed? If the procedure succeeds—that is, A and B are decorrelated—then the claim that A causes B is refuted, or at least weakened (depending upon the details of the case). But if the bilking attempt fails, it does not follow that it must be B that is the cause of A , rather than vice versa. Depending upon the situation, that B causes A might become a viable alternative to the hypothesis that A causes B —but there is no reason to think that this alternative must always be the superior one. For example, suppose that I see a photo of you in a paper dated well before your birth, accompanied by a report of your arrival from the future. I now try to bilk your upcoming time trip—but I slip on a banana peel while rushing to push you away from your time machine, my time travel horror stories only inspire you further, and so on. Or again, suppose that I know that you were not in Sydney yesterday. I now try to get you to go there in your time machine—but first I am struck by lightning, then I fall down a manhole, and so on. What does all this prove? Surely not that your arrival in the past causes your departure from the future. Depending upon the details of the case, it seems that we might well be entitled to describe it as involving backwards time travel and backwards causation. At least, if we are not so entitled, this must be because of other facts about the case: it would not follow simply from the repeated coincidental failures of my bilking attempts.
Backwards time travel would apparently allow for the possibility of causal loops, in which things come from nowhere. The things in question might be objects—imagine a time traveller who steals a time machine from the local museum in order to make his time trip and then donates the time machine to the same museum at the end of the trip (i.e. in the past). In this case the machine itself is never built by anyone—it simply exists. The things in question might be information—imagine a time traveller who explains the theory behind time travel to her younger self: theory that she herself knows only because it was explained to her in her youth by her time travelling older self. The things in question might be actions. Imagine a time traveller who visits his younger self. When he encounters his younger self, he suddenly has a vivid memory of being punched on the nose by a strange visitor. He realises that this is that very encounter—and resignedly proceeds to punch his younger self. Why did he do it? Because he knew that it would happen and so felt that he had to do it—but he only knew it would happen because he in fact did it. [ 20 ]
One might think that causal loops are impossible—and hence that insofar as backwards time travel entails such loops, it too is impossible. [ 21 ] There are two issues to consider here. First, does backwards time travel entail causal loops? Lewis (1976, 148) raises the question whether there must be causal loops whenever there is backwards causation; in response to the question, he says simply “I am not sure.” Mellor (1998, 131) appears to claim a positive answer to the question. [ 22 ] Hanley (2004, 130) defends a negative answer by telling a time travel story in which there is backwards time travel and backwards causation, but no causal loops. [ 23 ] Monton (2009) criticises Hanley’s counterexample, but also defends a negative answer via different counterexamples. Effingham (2020) too argues for a negative answer.
Second, are causal loops impossible, or in some other way objectionable? One objection is that causal loops are inexplicable . There have been two main kinds of response to this objection. One is to agree but deny that this is a problem. Lewis (1976, 149) accepts that a loop (as a whole) would be inexplicable—but thinks that this inexplicability (like that of the Big Bang or the decay of a tritium atom) is merely strange, not impossible. In a similar vein, Meyer (2012, 263) argues that if someone asked for an explanation of a loop (as a whole), “the blame would fall on the person asking the question, not on our inability to answer it.” The second kind of response (Hanley, 2004, §5) is to deny that (all) causal loops are inexplicable. A second objection to causal loops, due to Mellor (1998, ch.12), is that in such loops the chances of events would fail to be related to their frequencies in accordance with the law of large numbers. Berkovitz (2001) and Dowe (2001) both argue that Mellor’s objection fails to establish the impossibility of causal loops. [ 24 ] Effingham (2020) considers—and rebuts—some additional objections to the possibility of causal loops.
4. Time and Change
Gödel (1949a [1990a])—in which Gödel presents models of Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity in which there exist CTC’s—can well be regarded as initiating the modern academic literature on time travel, in both philosophy and physics. In a companion paper, Gödel discusses the significance of his results for more general issues in the philosophy of time (Gödel 1949b [1990b]). For the succeeding half century, the time travel literature focussed predominantly on objections to the possibility (or probability) of time travel. More recently, however, there has been renewed interest in the connections between time travel and more general issues in the metaphysics of time and change. We examine some of these in the present section. [ 25 ]
The first thing that we need to do is set up the various metaphysical positions whose relationships with time travel will then be discussed. Consider two metaphysical questions:
- Are the past, present and future equally real?
- Is there an objective flow or passage of time, and an objective now?
We can label some views on the first question as follows. Eternalism is the view that past and future times, objects and events are just as real as the present time and present events and objects. Nowism is the view that only the present time and present events and objects exist. Now-and-then-ism is the view that the past and present exist but the future does not. We can also label some views on the second question. The A-theory answers in the affirmative: the flow of time and division of events into past (before now), present (now) and future (after now) are objective features of reality (as opposed to mere features of our experience). Furthermore, they are linked: the objective flow of time arises from the movement, through time, of the objective now (from the past towards the future). The B-theory answers in the negative: while we certainly experience now as special, and time as flowing, the B-theory denies that what is going on here is that we are detecting objective features of reality in a way that corresponds transparently to how those features are in themselves. The flow of time and the now are not objective features of reality; they are merely features of our experience. By combining answers to our first and second questions we arrive at positions on the metaphysics of time such as: [ 26 ]
- the block universe view: eternalism + B-theory
- the moving spotlight view: eternalism + A-theory
- the presentist view: nowism + A-theory
- the growing block view: now-and-then-ism + A-theory.
So much for positions on time itself. Now for some views on temporal objects: objects that exist in (and, in general, change over) time. Three-dimensionalism is the view that persons, tables and other temporal objects are three-dimensional entities. On this view, what you see in the mirror is a whole person. [ 27 ] Tomorrow, when you look again, you will see the whole person again. On this view, persons and other temporal objects are wholly present at every time at which they exist. Four-dimensionalism is the view that persons, tables and other temporal objects are four-dimensional entities, extending through three dimensions of space and one dimension of time. On this view, what you see in the mirror is not a whole person: it is just a three-dimensional temporal part of a person. Tomorrow, when you look again, you will see a different such temporal part. Say that an object persists through time if it is around at some time and still around at a later time. Three- and four-dimensionalists agree that (some) objects persist, but they differ over how objects persist. According to three-dimensionalists, objects persist by enduring : an object persists from t 1 to t 2 by being wholly present at t 1 and t 2 and every instant in between. According to four-dimensionalists, objects persist by perduring : an object persists from t 1 to t 2 by having temporal parts at t 1 and t 2 and every instant in between. Perduring can be usefully compared with being extended in space: a road extends from Melbourne to Sydney not by being wholly located at every point in between, but by having a spatial part at every point in between.
It is natural to combine three-dimensionalism with presentism and four-dimensionalism with the block universe view—but other combinations of views are certainly possible.
Gödel (1949b [1990b]) argues from the possibility of time travel (more precisely, from the existence of solutions to the field equations of General Relativity in which there exist CTC’s) to the B-theory: that is, to the conclusion that there is no objective flow or passage of time and no objective now. Gödel begins by reviewing an argument from Special Relativity to the B-theory: because the notion of simultaneity becomes a relative one in Special Relativity, there is no room for the idea of an objective succession of “nows”. He then notes that this argument is disrupted in the context of General Relativity, because in models of the latter theory to date, the presence of matter does allow recovery of an objectively distinguished series of “nows”. Gödel then proposes a new model (Gödel 1949a [1990a]) in which no such recovery is possible. (This is the model that contains CTC’s.) Finally, he addresses the issue of how one can infer anything about the nonexistence of an objective flow of time in our universe from the existence of a merely possible universe in which there is no objectively distinguished series of “nows”. His main response is that while it would not be straightforwardly contradictory to suppose that the existence of an objective flow of time depends on the particular, contingent arrangement and motion of matter in the world, this would nevertheless be unsatisfactory. Responses to Gödel have been of two main kinds. Some have objected to the claim that there is no objective flow of time in his model universe (e.g. Savitt (2005); see also Savitt (1994)). Others have objected to the attempt to transfer conclusions about that model universe to our own universe (e.g. Earman (1995, 197–200); for a partial response to Earman see Belot (2005, §3.4)). [ 28 ]
Earlier we posed two questions:
Gödel’s argument is related to the second question. Let’s turn now to the first question. Godfrey-Smith (1980, 72) writes “The metaphysical picture which underlies time travel talk is that of the block universe [i.e. eternalism, in the terminology of the present entry], in which the world is conceived as extended in time as it is in space.” In his report on the Analysis problem to which Godfrey-Smith’s paper is a response, Harrison (1980, 67) replies that he would like an argument in support of this assertion. Here is an argument: [ 29 ]
A fundamental requirement for the possibility of time travel is the existence of the destination of the journey. That is, a journey into the past or the future would have to presuppose that the past or future were somehow real. (Grey, 1999, 56)
Dowe (2000, 442–5) responds that the destination does not have to exist at the time of departure: it only has to exist at the time of arrival—and this is quite compatible with non-eternalist views. And Keller and Nelson (2001, 338) argue that time travel is compatible with presentism:
There is four-dimensional [i.e. eternalist, in the terminology of the present entry] time-travel if the appropriate sorts of events occur at the appropriate sorts of times; events like people hopping into time-machines and disappearing, people reappearing with the right sorts of memories, and so on. But the presentist can have just the same patterns of events happening at just the same times. Or at least, it can be the case on the presentist model that the right sorts of events will happen, or did happen, or are happening, at the rights sorts of times. If it suffices for four-dimensionalist time-travel that Jennifer disappears in 2054 and appears in 1985 with the right sorts of memories, then why shouldn’t it suffice for presentist time-travel that Jennifer will disappear in 2054, and that she did appear in 1985 with the right sorts of memories?
Sider (2005) responds that there is still a problem reconciling presentism with time travel conceived in Lewis’s way: that conception of time travel requires that personal time is similar to external time—but presentists have trouble allowing this. Further contributions to the debate whether presentism—and other versions of the A-theory—are compatible with time travel include Monton (2003), Daniels (2012), Hall (2014) and Wasserman (2018) on the side of compatibility, and Miller (2005), Slater (2005), Miller (2008), Hales (2010) and Markosian (2020) on the side of incompatibility.
Leibniz’s Law says that if x = y (i.e. x and y are identical—one and the same entity) then x and y have exactly the same properties. There is a superficial conflict between this principle of logic and the fact that things change. If Bill is at one time thin and at another time not so—and yet it is the very same person both times—it looks as though the very same entity (Bill) both possesses and fails to possess the property of being thin. Three-dimensionalists and four-dimensionalists respond to this problem in different ways. According to the four-dimensionalist, what is thin is not Bill (who is a four-dimensional entity) but certain temporal parts of Bill; and what is not thin are other temporal parts of Bill. So there is no single entity that both possesses and fails to possess the property of being thin. Three-dimensionalists have several options. One is to deny that there are such properties as ‘thin’ (simpliciter): there are only temporally relativised properties such as ‘thin at time t ’. In that case, while Bill at t 1 and Bill at t 2 are the very same entity—Bill is wholly present at each time—there is no single property that this one entity both possesses and fails to possess: Bill possesses the property ‘thin at t 1 ’ and lacks the property ‘thin at t 2 ’. [ 30 ]
Now consider the case of a time traveller Ben who encounters his younger self at time t . Suppose that the younger self is thin and the older self not so. The four-dimensionalist can accommodate this scenario easily. Just as before, what we have are two different three-dimensional parts of the same four-dimensional entity, one of which possesses the property ‘thin’ and the other of which does not. The three-dimensionalist, however, faces a problem. Even if we relativise properties to times, we still get the contradiction that Ben possesses the property ‘thin at t ’ and also lacks that very same property. [ 31 ] There are several possible options for the three-dimensionalist here. One is to relativise properties not to external times but to personal times (Horwich, 1975, 434–5); another is to relativise properties to spatial locations as well as to times (or simply to spacetime points). Sider (2001, 101–6) criticises both options (and others besides), concluding that time travel is incompatible with three-dimensionalism. Markosian (2004) responds to Sider’s argument; [ 32 ] Miller (2006) also responds to Sider and argues for the compatibility of time travel and endurantism; Gilmore (2007) seeks to weaken the case against endurantism by constructing analogous arguments against perdurantism. Simon (2005) finds problems with Sider’s arguments, but presents different arguments for the same conclusion; Effingham and Robson (2007) and Benovsky (2011) also offer new arguments for this conclusion. For further discussion see Wasserman (2018) and Effingham (2020). [ 33 ]
We have seen arguments to the conclusions that time travel is impossible, improbable and inexplicable. Here’s an argument to the conclusion that backwards time travel simply will not occur. If backwards time travel is ever going to occur, we would already have seen the time travellers—but we have seen none such. [ 34 ] The argument is a weak one. [ 35 ] For a start, it is perhaps conceivable that time travellers have already visited the Earth [ 36 ] —but even granting that they have not, this is still compatible with the future actuality of backwards time travel. First, it may be that time travel is very expensive, difficult or dangerous—or for some other reason quite rare—and that by the time it is available, our present period of history is insufficiently high on the list of interesting destinations. Second, it may be—and indeed existing proposals in the physics literature have this feature—that backwards time travel works by creating a CTC that lies entirely in the future: in this case, backwards time travel becomes possible after the creation of the CTC, but travel to a time earlier than the time at which the CTC is created is not possible. [ 37 ]
- Adams, Robert Merrihew, 1997, “Thisness and time travel”, Philosophia , 25: 407–15.
- Arntzenius, Frank, 2006, “Time travel: Double your fun”, Philosophy Compass , 1: 599–616. doi:10.1111/j.1747-9991.2006.00045.x
- Asimov, Isaac, 1995 [2003], Gold: The Final Science Fiction Collection , New York: Harper Collins.
- Baron, Sam and Colyvan, Mark, 2016, “Time enough for explanation”, Journal of Philosophy , 113: 61–88.
- Belot, Gordon, 2005, “Dust, time and symmetry”, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 56: 255–91.
- Benovsky, Jiri, 2011, “Endurance and time travel”, Kriterion , 24: 65–72.
- Berkovitz, Joseph, 2001, “On chance in causal loops”, Mind , 110: 1–23.
- Black, Max, 1956, “Why cannot an effect precede its cause?”, Analysis , 16: 49–58.
- Brier, Bob, 1973, “Magicians, alarm clocks, and backward causation”, Southern Journal of Philosophy , 11: 359–64.
- Carlson, Erik, 2005, “A new time travel paradox resolved”, Philosophia , 33: 263–73.
- Carroll, John W., 2010, “Context, conditionals, fatalism, time travel, and freedom”, in Time and Identity , Joseph Keim Campbell, Michael O’Rourke, and Harry S. Silverstein, eds., Cambridge MA: MIT Press, 79–93.
- Craig, William L., 1997, “Adams on actualism and presentism”, Philosophia , 25: 401–5.
- Daniels, Paul R., 2012, “Back to the present: Defending presentist time travel”, Disputatio , 4: 469–84.
- Deutsch, David and Lockwood, Michael, 1994, “The quantum physics of time travel”, Scientific American , 270(3): 50–6.
- Dowe, Phil, 2000, “The case for time travel”, Philosophy , 75: 441–51.
- –––, 2001, “Causal loops and the independence of causal facts”, Philosophy of Science , 68: S89–S97.
- –––, 2003, “The coincidences of time travel”, Philosophy of Science , 70: 574–89.
- Dummett, Michael, 1964, “Bringing about the past”, Philosophical Review , 73: 338–59.
- Dwyer, Larry, 1977, “How to affect, but not change, the past”, Southern Journal of Philosophy , 15: 383–5.
- Earman, John, 1995, Bangs, Crunches, Whimpers, and Shrieks: Singularities and Acausalities in Relativistic Spacetimes , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Effingham, Nikk, 2020, Time Travel: Probability and Impossibility , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Effingham, Nikk and Robson, Jon, 2007, “A mereological challenge to endurantism”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 85: 633–40.
- Ehring, Douglas, 1997, “Personal identity and time travel”, Philosophical Studies , 52: 427–33.
- Elliott, Katrina, 2019, “How to Know That Time Travel Is Unlikely Without Knowing Why”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 100: 90–113.
- Fulmer, Gilbert, 1980, “Understanding time travel”, Southwestern Journal of Philosophy , 11: 151–6.
- Gilmore, Cody, 2007, “Time travel, coinciding objects, and persistence”, in Oxford Studies in Metaphysics , Dean W. Zimmerman, ed., Oxford: Clarendon Press, vol. 3, 177–98.
- Goddu, G.C., 2003, “Time travel and changing the past (or how to kill yourself and live to tell the tale)”, Ratio , 16: 16–32.
- –––, 2007, “Banana peels and time travel”, Dialectica , 61: 559–72.
- Gödel, Kurt, 1949a [1990a], “An example of a new type of cosmological solutions of Einstein’s field equations of gravitation”, in Kurt Gödel: Collected Works (Volume II), Solomon Feferman, et al. (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 190–8; originally published in Reviews of Modern Physics , 21 (1949): 447–450.
- –––, 1949b [1990b], “A remark about the relationship between relativity theory and idealistic philosophy”, in Kurt Gödel: Collected Works (Volume II), Solomon Feferman, et al. (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 202–7; originally published in P. Schilpp (ed.), Albert Einstein: Philosopher-Scientist , La Salle: Open Court, 1949, 555–562.
- Godfrey-Smith, William, 1980, “Travelling in time”, Analysis , 40: 72–3.
- Gorovitz, Samuel, 1964, “Leaving the past alone”, Philosophical Review , 73: 360–71.
- Grey, William, 1999, “Troubles with time travel”, Philosophy , 74: 55–70.
- Hafele, J. C. and Keating, Richard E., 1972a, “Around-the-world atomic clocks: Observed relativistic time gains”, Science , 177: 168–70.
- –––, 1972b, “Around-the-world atomic clocks: Predicted relativistic time gains”, Science , 177: 166–8.
- Hales, Steven D., 2010, “No time travel for presentists”, Logos & Episteme , 1: 353–60.
- Hall, Thomas, 2014, “In Defense of the Compossibility of Presentism and Time Travel”, Logos & Episteme , 2: 141–59.
- Hanley, Richard, 2004, “No end in sight: Causal loops in philosophy, physics and fiction”, Synthese , 141: 123–52.
- Harrison, Jonathan, 1980, “Report on analysis ‘problem’ no. 18”, Analysis , 40: 65–9.
- Hawking, S.W., 1992, “Chronology protection conjecture”, Physical Review D , 46: 603–11.
- Holt, Dennis Charles, 1981, “Time travel: The time discrepancy paradox”, Philosophical Investigations , 4: 1–16.
- Horacek, David, 2005, “Time travel in indeterministic worlds”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 423–36.
- Horwich, Paul, 1975, “On some alleged paradoxes of time travel”, Journal of Philosophy , 72: 432–44.
- –––, 1987, Asymmetries in Time: Problems in the Philosophy of Science , Cambridge MA: MIT Press.
- Ismael, J., 2003, “Closed causal loops and the bilking argument”, Synthese , 136: 305–20.
- Keller, Simon and Nelson, Michael, 2001, “Presentists should believe in time-travel”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 79: 333–45.
- Kiourti, Ira, 2008, “Killing baby Suzy”, Philosophical Studies , 139: 343–52.
- Le Poidevin, Robin, 2003, Travels in Four Dimensions: The Enigmas of Space and Time , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2005, “The Cheshire Cat problem and other spatial obstacles to backwards time travel”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 336–52.
- Lewis, David, 1976, “The paradoxes of time travel”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 13: 145–52.
- Loss, Roberto, 2015, “How to Change the Past in One-Dimensional Time”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 96: 1–11.
- Luminet, Jean-Pierre, 2011, “Time, topology, and the twin paradox”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Time , Craig Callender (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199298204.003.0018
- Markosian, Ned, 2004, “Two arguments from Sider’s Four-Dimensionalism ”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 68: 665–73.
- Markosian, Ned, 2020, “The Dynamic Theory of Time and Time Travel to the Past”, Disputatio , 12: 137–65.
- Maudlin, Tim, 2012, Philosophy of Physics: Space and Time , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Meiland, Jack W., 1974, “A two-dimensional passage model of time for time travel”, Philosophical Studies , 26: 153–73.
- Mellor, D.H., 1998, Real Time II , London: Routledge.
- Meyer, Ulrich, 2012, “Explaining causal loops”, Analysis , 72: 259–64.
- Miller, Kristie, 2005, “Time travel and the open future”, Disputatio , 1: 223–32.
- –––, 2006, “Travelling in time: How to wholly exist in two places at the same time”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 36: 309–34.
- –––, 2008, “Backwards causation, time, and the open future”, Metaphysica , 9: 173–91.
- Monton, Bradley, 2003, “Presentists can believe in closed timelike curves”, Analysis , 63: 199–202.
- –––, 2009, “Time travel without causal loops”, Philosophical Quarterly , 59: 54–67.
- Nerlich, Graham, 1981, “Can time be finite?”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 62: 227–39.
- Ney, S.E., 2000, “Are grandfathers an endangered species?”, Journal of Philosophical Research , 25: 311–21.
- Price, Huw, 1996, Time’s Arrow & Archimedes’ Point: New Directions for the Physics of Time , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Putnam, Hilary, 1975, “It ain’t necessarily so”, in Mathematics, Matter and Method , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, vol. 1 of Philosophical Papers , 237–49.
- Reinganum, Marc R., 1986, “Is time travel impossible? A financial proof”, Journal of Portfolio Management , 13: 10–2.
- Riggs, Peter J., 1991, “A critique of Mellor’s argument against ‘backwards’ causation”, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 42: 75–86.
- –––, 1997, “The principal paradox of time travel”, Ratio , 10: 48–64.
- Savitt, Steven, 1994, “The replacement of time”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 74: 463–73.
- –––, 2005, “Time travel and becoming”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 413–22.
- Sider, Theodore, 2001, Four-Dimensionalism: An Ontology of Persistence and Time , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- –––, 2002, “Time travel, coincidences and counterfactuals”, Philosophical Studies , 110: 115–38.
- –––, 2004, “Replies to Gallois, Hirsch and Markosian”, Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 68: 674–87.
- –––, 2005, “Traveling in A- and B- time”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 329–35.
- Simon, Jonathan, 2005, “Is time travel a problem for the three-dimensionalist?”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 353–61.
- Slater, Matthew H., 2005, “The necessity of time travel (on pain of indeterminacy)”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 362–9.
- Smart, J.J.C., 1963, “Is time travel possible?”, Journal of Philosophy , 60: 237–41.
- Smeenk, Chris and Wüthrich, Christian, 2011, “Time travel and time machines”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Time , Craig Callender (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, online ed. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199298204.003.0021
- Smith, Joseph Wayne, 1985, “Time travel and backward causation”, Cogito , 3: 57–67.
- Smith, Nicholas J.J., 1997, “Bananas enough for time travel?”, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science , 48: 363–89.
- –––, 1998, “The problems of backward time travel”, Endeavour , 22(4): 156–8.
- –––, 2004, “Review of Robin Le Poidevin Travels in Four Dimensions: The Enigmas of Space and Time ”, Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 82: 527–30.
- –––, 2005, “Why would time travellers try to kill their younger selves?”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 388–95.
- –––, 2011, “Inconsistency in the A-theory”, Philosophical Studies , 156: 231–47.
- –––, 2015, “Why time travellers (still) cannot change the past”, Revista Portuguesa de Filosofia , 71: 677–94.
- –––, 2017, “I’d do anything to change the past (but I can’t do ‘that’)”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 54: 153–68.
- van Inwagen, Peter, 2010, “Changing the past”, in Oxford Studies in Metaphysics (Volume 5), Dean W. Zimmerman (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 3–28.
- Vihvelin, Kadri, 1996, “What time travelers cannot do”, Philosophical Studies , 81: 315–30.
- Vranas, Peter B.M., 2005, “Do cry over spilt milk: Possibly you can change the past”, Monist (Special Issue on Time Travel), 88: 370–87.
- –––, 2009, “Can I kill my younger self? Time travel and the retrosuicide paradox”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 90: 520–34.
- –––, 2010, “What time travelers may be able to do”, Philosophical Studies , 150: 115–21.
- Wasserman, Ryan, 2018, Paradoxes of Time Travel , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Williams, Donald C., 1951, “The myth of passage”, Journal of Philosophy , 48: 457–72.
- Wright, John, 2006, “Personal identity, fission and time travel”, Philosophia , 34: 129–42.
- Yourgrau, Palle, 1999, Gödel Meets Einstein: Time Travel in the Gödel Universe , Chicago: Open Court.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Time Travel , entry by Joel Hunter (Truckee Meadows Community College) in the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy .
causation: backward | free will: divine foreknowledge and | identity: over time | location and mereology | temporal parts | time | time machines | time travel: and modern physics
Copyright © 2024 by Nicholas J.J. Smith < nicholas . smith @ sydney . edu . au >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

- [ November 30, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: December 2022 Night Sky
- [ November 22, 2022 ] James Webb Telescope Turns Its Attention To The Kuiper Belt News & Events
- [ November 1, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: November 2022 Night Sky
- [ October 4, 2022 ] Are Wormholes Fact or Fiction? General Astronomy
- [ October 1, 2022 ] The Night Sky This Month: October 2022 Night Sky
5 Bizarre Paradoxes Of Time Travel Explained
December 20, 2014 James Miller Astronomy Lists , Time Travel 58

There is nothing in Einstein’s theories of relativity to rule out time travel , although the very notion of traveling to the past violates one of the most fundamental premises of physics, that of causality. With the laws of cause and effect out the window, there naturally arises a number of inconsistencies associated with time travel, and listed here are some of those paradoxes which have given both scientists and time travel movie buffs alike more than a few sleepless nights over the years.
Types of Temporal Paradoxes
The time travel paradoxes that follow fall into two broad categories:
1) Closed Causal Loops , such as the Predestination Paradox and the Bootstrap Paradox, which involve a self-existing time loop in which cause and effect run in a repeating circle, but is also internally consistent with the timeline’s history.
2) Consistency Paradoxes , such as the Grandfather Paradox and other similar variants such as The Hitler paradox, and Polchinski’s Paradox, which generate a number of timeline inconsistencies related to the possibility of altering the past.
1: Predestination Paradox
A Predestination Paradox occurs when the actions of a person traveling back in time become part of past events, and may ultimately cause the event he is trying to prevent to take place. The result is a ‘temporal causality loop’ in which Event 1 in the past influences Event 2 in the future (time travel to the past) which then causes Event 1 to occur.
This circular loop of events ensures that history is not altered by the time traveler, and that any attempts to stop something from happening in the past will simply lead to the cause itself, instead of stopping it. Predestination paradoxes suggest that things are always destined to turn out the same way and that whatever has happened must happen.
Sound complicated? Imagine that your lover dies in a hit-and-run car accident, and you travel back in time to save her from her fate, only to find that on your way to the accident you are the one who accidentally runs her over. Your attempt to change the past has therefore resulted in a predestination paradox. One way of dealing with this type of paradox is to assume that the version of events you have experienced are already built into a self-consistent version of reality, and that by trying to alter the past you will only end up fulfilling your role in creating an event in history, not altering it.
– Cinema Treatment
In The Time Machine (2002) movie, for instance, Dr. Alexander Hartdegen witnesses his fiancee being killed by a mugger, leading him to build a time machine to travel back in time to save her from her fate. His subsequent attempts to save her fail, though, leading him to conclude that “I could come back a thousand times… and see her die a thousand ways.” After then traveling centuries into the future to see if a solution has been found to the temporal problem, Hartdegen is told by the Über-Morlock:
“You built your time machine because of Emma’s death. If she had lived, it would never have existed, so how could you use your machine to go back and save her? You are the inescapable result of your tragedy, just as I am the inescapable result of you .”
- Movies : Examples of predestination paradoxes in the movies include 12 Monkeys (1995), TimeCrimes (2007), The Time Traveler’s Wife (2009), and Predestination (2014).
- Books : An example of a predestination paradox in a book is Phoebe Fortune and the Pre-destination Paradox by M.S. Crook.
2: Bootstrap Paradox
A Bootstrap Paradox is a type of paradox in which an object, person, or piece of information sent back in time results in an infinite loop where the object has no discernible origin, and exists without ever being created. It is also known as an Ontological Paradox, as ontology is a branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of being or existence.
– Information : George Lucas traveling back in time and giving himself the scripts for the Star War movies which he then goes on to direct and gain great fame for would create a bootstrap paradox involving information, as the scripts have no true point of creation or origin.
– Person : A bootstrap paradox involving a person could be, say, a 20-year-old male time traveler who goes back 21 years, meets a woman, has an affair, and returns home three months later without knowing the woman was pregnant. Her child grows up to be the 20-year-old time traveler, who travels back 21 years through time, meets a woman, and so on. American science fiction writer Robert Heinlein wrote a strange short story involving a sexual paradox in his 1959 classic “All You Zombies.”
These ontological paradoxes imply that the future, present, and past are not defined, thus giving scientists an obvious problem on how to then pinpoint the “origin” of anything, a word customarily referring to the past, but now rendered meaningless. Further questions arise as to how the object/data was created, and by whom. Nevertheless, Einstein’s field equations allow for the possibility of closed time loops, with Kip Thorne the first theoretical physicist to recognize traversable wormholes and backward time travel as being theoretically possible under certain conditions.
- Movies : Examples of bootstrap paradoxes in the movies include Somewhere in Time (1980), Bill and Ted’s Excellent Adventure (1989), the Terminator movies, and Time Lapse (2014). The Netflix series Dark (2017-19) also features a book called ‘A Journey Through Time’ which presents another classic example of a bootstrap paradox.
- Books : Examples of bootstrap paradoxes in books include Michael Moorcock’s ‘Behold The Man’, Tim Powers’ The Anubis Gates, and Heinlein’s “By His Bootstraps”
3: Grandfather Paradox
The Grandfather Paradox concerns ‘self-inconsistent solutions’ to a timeline’s history caused by traveling back in time. For example, if you traveled to the past and killed your grandfather, you would never have been born and would not have been able to travel to the past – a paradox.
Let’s say you did decide to kill your grandfather because he created a dynasty that ruined the world. You figure if you knock him off before he meets your grandmother then the whole family line (including you) will vanish and the world will be a better place. According to theoretical physicists, the situation could play out as follows:
– Timeline protection hypothesis: You pop back in time, walk up to him, and point a revolver at his head. You pull the trigger but the gun fails to fire. Click! Click! Click! The bullets in the chamber have dents in the firing caps. You point the gun elsewhere and pull the trigger. Bang! Point it at your grandfather.. Click! Click! Click! So you try another method to kill him, but that only leads to scars that in later life he attributed to the world’s worst mugger. You can do many things as long as they’re not fatal until you are chased off by a policeman.
– Multiple universes hypothesis: You pop back in time, walk up to him, and point a revolver at his head. You pull the trigger and Boom! The deed is done. You return to the “present,” but you never existed here. Everything about you has been erased, including your family, friends, home, possessions, bank account, and history. You’ve entered a timeline where you never existed. Scientists entertain the possibility that you have now created an alternate timeline or entered a parallel universe.
- Movies : Example of the Grandfather Paradox in movies include Back to the Future (1985), Back to the Future Part II (1989), and Back to the Future Part III (1990).
- Books : Example of the Grandfather Paradox in books include Dr. Quantum in the Grandfather Paradox by Fred Alan Wolf , The Grandfather Paradox by Steven Burgauer, and Future Times Three (1944) by René Barjavel, the very first treatment of a grandfather paradox in a novel.
4: Let’s Kill Hitler Paradox
Similar to the Grandfather Paradox which paradoxically prevents your own birth, the Killing Hitler paradox erases your own reason for going back in time to kill him. Furthermore, while killing Grandpa might have a limited “butterfly effect,” killing Hitler would have far-reaching consequences for everyone in the world, even if only for the fact you studied him in school.
The paradox itself arises from the idea that if you were successful, then there would be no reason to time travel in the first place. If you killed Hitler then none of his actions would trickle down through history and cause you to want to make the attempt.
- Movies/Shows : By far the best treatment for this notion occurred in a Twilight Zone episode called Cradle of Darkness which sums up the difficulties involved in trying to change history, with another being an episode of Dr Who called ‘Let’s Kill Hitler’.
- Books : Examples of the Let’s Kill Hitler Paradox in books include How to Kill Hitler: A Guide For Time Travelers by Andrew Stanek, and the graphic novel I Killed Adolf Hitler by Jason.
5: Polchinski’s Paradox
American theoretical physicist Joseph Polchinski proposed a time paradox scenario in which a billiard ball enters a wormhole, and emerges out the other end in the past just in time to collide with its younger version and stop it from going into the wormhole in the first place.
Polchinski’s paradox is taken seriously by physicists, as there is nothing in Einstein’s General Relativity to rule out the possibility of time travel, closed time-like curves (CTCs), or tunnels through space-time. Furthermore, it has the advantage of being based upon the laws of motion, without having to refer to the indeterministic concept of free will, and so presents a better research method for scientists to think about the paradox. When Joseph Polchinski proposed the paradox, he had Novikov’s Self-Consistency Principle in mind, which basically states that while time travel is possible, time paradoxes are forbidden.
However, a number of solutions have been formulated to avoid the inconsistencies Polchinski suggested, which essentially involves the billiard ball delivering a blow that changes its younger version’s course, but not enough to stop it from entering the wormhole. This solution is related to the ‘timeline-protection hypothesis’ which states that a probability distortion would occur in order to prevent a paradox from happening. This also helps explain why if you tried to time travel and murder your grandfather, something will always happen to make that impossible, thus preserving a consistent version of history.
- Books: Paradoxes of Time Travel by Ryan Wasserman is a wide-ranging exploration of time and time travel, including Polchinski’s Paradox.
Are Self-Fulfilling Prophecies Paradoxes?
A self-fulfilling prophecy is only a causality loop when the prophecy is truly known to happen and events in the future cause effects in the past, otherwise the phenomenon is not so much a paradox as a case of cause and effect. Say, for instance, an authority figure states that something is inevitable, proper, and true, convincing everyone through persuasive style. People, completely convinced through rhetoric, begin to behave as if the prediction were already true, and consequently bring it about through their actions. This might be seen best by an example where someone convincingly states:
“High-speed Magnetic Levitation Trains will dominate as the best form of transportation from the 21st Century onward.”
Jet travel, relying on diminishing fuel supplies, will be reserved for ocean crossing, and local flights will be a thing of the past. People now start planning on building networks of high-speed trains that run on electricity. Infrastructure gears up to supply the needed parts and the prediction becomes true not because it was truly inevitable (though it is a smart idea), but because people behaved as if it were true.
It even works on a smaller scale – the scale of individuals. The basic methodology for all those “self-help” books out in the world is that if you modify your thinking that you are successful (money, career, dating, etc.), then with the strengthening of that belief you start to behave like a successful person. People begin to notice and start to treat you like a successful person; it is a reinforcement/feedback loop and you actually become successful by behaving as if you were.
Are Time Paradoxes Inevitable?
The Butterfly Effect is a reference to Chaos Theory where seemingly trivial changes can have huge cascade reactions over long periods of time. Consequently, the Timeline corruption hypothesis states that time paradoxes are an unavoidable consequence of time travel, and even insignificant changes may be enough to alter history completely.
In one story, a paleontologist, with the help of a time travel device, travels back to the Jurassic Period to get photographs of Stegosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Ceratosaurus, and Allosaurus amongst other dinosaurs. He knows he can’t take samples so he just takes magnificent pictures from the fixed platform that is positioned precisely to not change anything about the environment. His assistant is about to pick a long blade of grass, but he stops him and explains how nothing must change because of their presence. They finish what they are doing and return to the present, but everything is gone. They reappear in a wild world with no humans and no signs that they ever existed. They fall to the floor of their platform, the only man-made thing in the whole world, and lament “Why? We didn’t change anything!” And there on the heel of the scientist’s shoe is a crushed butterfly.
The Butterfly Effect is also a movie, starring Ashton Kutcher as Evan Treborn and Amy Smart as Kayleigh Miller, where a troubled man has had blackouts during his youth, later explained by him traveling back into his own past and taking charge of his younger body briefly. The movie explores the issue of changing the timeline and how unintended consequences can propagate.
Scientists eager to avoid the paradoxes presented by time travel have come up with a number of ingenious ways in which to present a more consistent version of reality, some of which have been touched upon here, including:
- The Solution: time travel is impossible because of the very paradox it creates.
- Self-healing hypothesis: successfully altering events in the past will set off another set of events which will cause the present to remain the same.
- The Multiverse or “many-worlds” hypothesis: an alternate parallel universe or timeline is created each time an event is altered in the past.
- Erased timeline hypothesis : a person traveling to the past would exist in the new timeline, but have their own timeline erased.
Related Posts
© Copyright 2023 Astronomy Trek

Universe is everything!
Social link.
Time Travel
If you ask anyone about time travel, you will get fascinating answers, as it’s a fascinating subject. Time travel back into the past or forward into the future is the stuff of science fiction and always has been. There are many TV show’s and movies dedicated to time travel, as it’s so interesting to try and understand the possibilities. One great movie to check out is called ‘back to the future’
So time travel naturally all starts with time. We know that time exists as we created it, as we know that things have been happening since well, the dawn of time!! Ever since the universe was created by the big bang , time has been happening, and everything that has come before us up to this very present day is because of time. So we travel in time every day, and that means that time travel is real and is something that exists when you look at it like that, as we are always travelling in time.

The big question is? Can we travel back through time to events that have already happened, or can we travel forward through time to events that have not happened yet? That has always been the great wonder. The answer is, we do not know, and there has been no evidence ever to prove travelling back or forward in time.
One of the greatest and most famous physicists Stephen Hawking who is a master on the subject believes that it’s almost impossible to travel back in time. It makes sense when you think about it. It’s in the past and it has already happened. How could you go back? So we can park time travel back in time. It’s likely to never happen.

Time travel into the future though. That’s different! That just may be possible. And here’s why.
Hawking’s theory is that if we discover how to travel really fast, up to even half the speed of light in a specially made train around the world for a period of time, of about 100 years into the future, or about a week in real time for the passengers on board, the passengers after a week of really fast travel would end up 100 years into the future from when the train first took off. It’s possible in theory and It would be fascinating one day to see, however this is also only a theory.
It is a good theory though when you think about it as time on board the train would slow down so much even though the train is going so fast. It may just happen one day when technology allows us to move so fast in time.
Q&A Corner
Q. What is time travel?
Q. Who is Stephen Hawking?
Q. Is it possible In theory to travel back in time?
Q. Is it possible in theory to travel forward in forward?
Q. Name the famous movie in the article that is all about time travel?
Download questions about time travel here: time travel (answers are on this page)
For further reading and more information on time travel visit www.easyscienceforkids.com/time travel
Train ride to the future
5 thoughts on “Time Travel”
One day in the future I will oneday try to make this possible!
wow this is cool
this is very useful.
http://ytscinema.website2.me/ytscinema
Glad it was helpful.
It is perfect time to make some plans for the long run and it is time to be happy. I have learn this submit and if I may I want to recommend you some interesting issues or advice. Perhaps you could write subsequent articles relating to this article. I wish to read more things about it!
http://www.google.com.qa/url?q=https://singviola2.hatenablog.com/entry/Motion_Free
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Enter Captcha Here : *
Black Holes: The Universe's Secret Hideouts
Imagine you're on a space adventure, flying past stars and planets, when you come across the universe's best-kept secret: black holes! These cosmic hideouts are so strong that they can…
How Mathematics Is Used for Space Exploration?
Exploring the vastness of space has always been a dream for humanity, a dream that turns into reality through the advancements in technology and meticulous application of mathematics. Just as…

How Planets Were Discovered? An Interesting Guide
Source: unsplash.com Have you ever looked up at the night sky and wondered how many planets are there? Well, scientists say we have a total of 8 planets in our…
JWST DISCLOSES DISTANT “GALAXY” IS SIX-WAY GALACTIC CRASH
Looking deep into the past, the JWST’s ardent detectors are revealing extraordinary details of some of the oldest structures of the universe. Previously fuzzy images become sharp at the telescope's…
- Solar System
- Space Exploration
- Constellations
- Science Blog
- Our Cookie Collection policy
- Video Disclaimer
- Website and Blog Disclaimer
- Terms Of Services
- Privacy Policy
- Español NEW
Time travel facts for kids
Time travel is the idea of going back in time to the past or forward to the future. We always travel forward, to the future. Time travel to the past is not known to be possible, but it is much used in fiction. The Time Machine (1895) by H. G. Wells was one of the first and most famous stories of time travel. Much later, the American movie " Back to the Future " tells a fictional story about a professor who builds a machine that can take people into the future or back in the past.
The popular British TV program Doctor Who is about an alien who has adventures by time travelling. Another TV show about time travel is the series Charmed . Instead of using machines and science, this one uses magic to go to other times and places.
Some series that are not mainly about time travel have episodes about it, for example Star Trek and Stargate and The Flash .
Related pages
- General relativity
- Special relativity
Images for kids

Transversal time dilation . The blue dots represent a pulse of light. Each pair of dots with light "bouncing" between them is a clock. For each group of clocks, the other group appears to be ticking more slowly, because the moving clock's light pulse has to travel a larger distance than the stationary clock's light pulse. That is so, even though the clocks are identical and their relative motion is perfectly reciprocal.

Statue of Rip Van Winkle in Irvington, New York
- This page was last modified on 16 October 2023, at 16:53. Suggest an edit .
6 Mind-blowing facts about time travel
Time Travel has been one of the most fascinating topics since HG Wells published his book ‘The Time Machine.’
The concept existed even before that but it was during that time the topic went into a heated debate related to the possibility of it.
Let’s have a look at some of the time travel facts:
1. Time Is The Fourth Dimension
Simply stated, the first three dimensions are used to specify an object’s location/movement in space (forward-backwards, left-right and up-down), while the fourth dimension locates its position in time.
All four dimensions are used to specify completely the location or dynamism of an object in space. Collectively the four dimensions are inseparably interlinked and known as space-time.


2. A Time Traveller to the Past Cannot Change History
According to people who claim to have taken retrocognitive time trips, you may see people and buildings from past times. You may be aware that the weather has suddenly changed.
You may see many things that no longer exist in the present. But you will not be able to touch or pick up any objects you see. And the people you see in the past will not speak or even see you. They exist in their time, you exist in yours–and the two never seem to interact.
This is quite a different picture from the one presented in the movie Back to the Future and its sequels. Not only does Marty interact with everyone he meets in the past, but he also interferes with history to the extent that his brother and sister become “erased” from the future.
In real-time travel, no such possibility exists.
3. Retrocognitive Time Travel Is Difficult to Prove
Unfortunately, the biggest problem with retrocognitive time travel is that people can’t prove that they actually traveled to the past.
For example, Mr. Dawson had only his own testimony to prove that he had seen a store from his childhood.
After all, he hadn’t walked into the store and picked up a few items to bring back to the present as proof that the trip took place.
4. Three Dimensional Creatures
Being three-dimensional creatures (possessing length, width, and height), humans are unable to see the fourth dimension as our physical world is constructed within these three physical dimensions.
We might feel or intuit time’s presence, but we can never actually detect it with our three-dimensional senses because it extends beyond our universe.
Humans only perceive the fourth dimension time as memories lodged at variable intervals, the result of which is our apparent perception of time moving forward in a straight line.
However, time still exists as a dimension, and objects can cross it in a similar way as they do the others, although three-dimensional like humans can only move in one direction forward through time.
If we could see an object’s fourth-dimensional space-time (or world-line) it may resemble a spaghetti-like line stretching from the past to the future showing the spatial location of the object at every instant in time.
5. Time And The Speed Of Light
A property of light is that it always travels at the same constant speed in a vacuum of 186,000 miles a second (700 million mph) and you can’t go any faster.
The reason for this is that mass increases with speed all the way to infinity and so an infinite amount of energy would then be needed to travel beyond the speed of light.
6. Time Travel to the Future Is Called Precognition
Travel to the future is called precognition, or “knowledge of future events before they happen.” You can travel to the future to gain a glimpse of what will happen to you, usually, or to someone you know.
You won’t find yourself beaming aboard the Starship Enterprise, though, or even the space shuttle Endeavor .
Neither will you find yourself in some future city trying to find or avoid a “terminator.”
Also, Check 7 More Interesting facts about time travel
Sangam Adhikari
High on Entertainment and Sports, Filling my gaps in Technology and Science
The 5 best IPTV service providers in 2020
Oneplus to ditch the pop-up camera in 2020, you may also like, interesting facts about social psychology, 5 less known amazing facts of tom and..., 5 interesting facts about gordon ramsay you didn’t..., 7 scientific photos that are hard to believe, the 5 unknown facts about outer space people..., 7 interesting facts about time travel, the pale blue dot, some fascinating science facts that will blow your..., leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Nomadic Matt's Travel Site
Travel Better, Cheaper, Longer
United States Travel Guide
Last Updated: April 14, 2024

The United States isn’t a popular destination for backpackers and budget travelers. Most overseas tourists come here for a short vacation, visit one or two cities, and then head home. They usually stick to the big coastal cities or places like Disney.
And it wasn’t until COVID that Americans en-masse bothered to hop in their cars and explore their backyard.
The U.S. is massive country that lacks a lot of tourist infrastructure or good cross-country transportation. Hostels haven’t quite caught on, trains don’t go to many places, and we don’t offer working holiday visas to attract young working backpackers. In short, it’s hard to get around.
However, the United States has a lot to offer: stunning national parks, gorgeous landscapes, incredible and diverse culture, world-class music, and a variety of delicious cuisine that varies from region to region.
I think the U.S. is one of the best destinations in the world to road trip . I’ve done several multi-month road trips across the United States . While the coastal cities are fun, the U.S. really reveals itself in the middle and countryside (it’s much more affordable there too). It’s in the nooks and crannies of America that you get a sense of its quirks.
But even if you aren’t spending months visiting the country in a car, there’s still a lot you can do via train, bus, or plane.
This travel guide to the United States can help you navigate the country, save money, and get off the beaten path.
Table of Contents
- Things to See and Do
- Typical Costs
- Suggested Budget
- Money-Saving Tips
- Where to Stay
- How to Get Around
- How to Stay Safe
- Best Places to Book Your Trip
- Related Blogs on the United States
Click Here for City Guides
Top 5 things to see and do in the united states.

1. Explore New York City
The city that never sleeps is one of the greatest cities in the world. There’s nothing you can’t do or see and you’ll find every language and food from around the world here. From world-class museums and art galleries to innovative theater performances to unique restaurants to the expansive Central Park, you can fill a lifetime of activities here. You can take the ferry to Ellis Island, see the Statue of Liberty, hang with the hipsters in Brooklyn, see a Yankees game, and so, so much more. Check out my detailed guide for everything you need to do .
2. Visit the Grand Canyon
Words can’t describe how epicly beautiful the Grand Canyon is. It’s simply breathtaking. Most people just look out at the canyon from the overlook at the top, but its vast size and beauty are best appreciated with a hike down to the Colorado River so try to do that if you have time (make the time). The canyon itself is 6,000 feet deep, and you can find plenty of hikes to take you further into the canyon that will give you a chance to experience it in more detail. For a shorter hike, Grandview Trail to the first overlook at Coconino Saddle and back is only a couple of miles. If you have a whole day to spend and want to challenge yourself, try the 12.5 miles from Bright Angel Trail to Plateau Point. Just be sure to bring plenty of water!
3. Discover Austin
The warm weather, lively honky-tonks, funky house bars on Rainey Street, amazing walking and biking trails, tons of outdoor activities — Austin is great (I lived there for many years). You can always find great live music on 6th Street. On a hot day, Barton Springs pool is the perfect place to cool off, there’s always something to do, the food scene gets better and better, and everyone is very welcoming. It’s one of the best cities in the U.S., boasting a combination of nature, city, and delicious food. Be sure to binge on BBQ while you’re here!
4. Visit Glacier National Park
This is my favorite national park in the country. It’s home to gorgeous snow-topped mountains, a beautiful lake from which to admire said mountains, large glaciers, and hiking trails galore. It is one of the most mind-blowing places I’ve seen on my adventures. There are more than 700 miles of hiking trails in the park that provide everyone an opportunity to explore the landscape. Park rangers offer various programs and guided tours are also available. There are spots for fishing and additional trails for biking and horseback riding. (If you plan to visit multiple national parks while traveling throughout the United States, it’s worth it to get the America the Beautiful Park Pass, which costs just $80 USD and provides entry to all the national parks for a year.)
5. Drive the Pacific Coast Highway
The Pacific Coast is considered one of the most scenic landscapes in the world, offering sheer cliffs, forests descending to the shoreline, miles of beaches, and giant redwoods. The Pacific Coast Highway (PCH) runs 1,650 miles from San Diego, California to Seattle, Washington taking you from the warm, sunny beaches to the lush temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest. Highway 1 thorough California is one of the longest historic state highways in the country. The California portion alone route takes 10 hours without stopping but I recommend dedicating at least several days to enjoy all the great stops along the way.
Other Things to See and Do in the United States
NOTE: There’s a lot to do in the United States and you can spend months traveling around the country . I could write an entire book on the places to visit! This is just a list to give you some ideas. Be sure to check out some of my other articles and city specific guides (scroll to the bottom of this guide for links) for more suggestions.
1. Have fun in Memphis
Gritty and industrial, Memphis appears like its best days are behind it. But don’t let the rough exterior fool you — the city is home to some killer food and a vibrant blues music scene. It is a cool city with boisterous and friendly locals. I love the vibe here. There’s Graceland (Elvis’s home) for fans of the King, a big waterfront for walking, and the phenomenal Museum of Civil Rights (it’s huge, so don’t rush it!). The city is going through a big revival right now. To use a cliché, it’s a hidden gem as most people, to their detriment, skip over it.
2. Discover Asheville
Asheville is full of tasty craft beer, great restaurants, and plenty of outdoor loving residents. The beautiful Smoky Mountains are a short drive away, Asheville Botanical Gardens are right near the university, and the gigantic Biltmore estate (the largest privately-owned home in the U.S. and once home to George Vanderbilt) is on the outskirts of the city. (If you’ve ever seen Downton Abbey, that’s what the house is like!) The town has a lot of parks and there are a lot of beautiful biking and hiking trails that you can get to from the center of town.
3. Explore Redwood National Park
Along the Pacific Coast is Redwood National Park, a huge expanse of towering redwood trees filled with picnic areas, places to camp, and miles upon miles of hiking trails. Trails range from easy to strenuous, and there are many loops that head out to nearby beaches. The trees range from 200-240 feet tall. It’s utterly beautiful, awe-inspiring, and humbling in every way. Admission is free, though the three adjoining state parks (Prairie Creek Redwoods State Park, Del Norte Coast Redwoods State Park, and Jedediah Smith Redwoods State Park) each charge $10 USD.
4. Explore Denver
Known as the Mile High City (the city is one mile above sea level), Denver offers a mix of outdoor ruggedness and big-city living. It has a huge craft beer scene, excellent restaurants (including, Sushi Sasa, one of my favorite sushi restaurants), a large international airport with lots of connections, and is close to the mountains. There are a lot of interesting museums, including the Denver Art Museum, Meow Wolf Denver, and the Clifford Still Museum. There’s plenty of art outside of the museums as well and there are walking tours available to show you around, if you prefer that to exploring on your own. It’s clean, lively, and the locals are incredibly friendly.
5. Get off-the-beaten-path in Natchez
I was surprised by Natchez . I didn’t know anything about it when it was recommended as a place to see historic 19th-century homes. These mansions were built by white plantation owners wanting to escape the summer heat and socialize with each other. As cotton became king, the houses became ever larger and more elaborate. Today, the homes are historic monuments you can tour while enjoying a view of the Mississippi River. It’s far off the beaten path and you’ll need a car to visit but it’s worth the trek.
6. Visit Savannah
Sitting on Georgia’s coast, Savannah escaped the wrath of the Civil War, allegedly because General Sherman thought it was too pretty to be destroyed. With streets lined with Spanish moss-covered oaks, large and inviting parks, and a bustling waterfront, Savannah is a wonderful place to experience the slow pace of the South. There are a number of interesting historical sites like the Bonaventure Cemetery and Factors Row. The city is full of small squares and sprawling parks where you can enjoy a stroll or a picnic. And nearby Tybee Island is a draw for many visitors due to its sandy beaches and slow pace of life.
7. Dive into Nashville’s music scene
Nashville is one of the fastest-growing cities in the U.S. It’s got a wonderful music scene (duh), a growing cocktail bar culture, and some world-class down-home Southern restaurants. There’s not a lot of “touristy stuff” to do here, but what makes this city one of my favorites are the music, the food, the wildly friendly people, and the positive energy the city seems to exude. When you’re here, plan to spend a few hours at the Tennessee State Museum. It goes into detail about the state’s history (and it’s more exciting than you might think!).
8. Catch some rays in sunny San Diego
I love San Diego. San Diego’s weather is almost always perfect, leading to a permanently happy population that’s friendly and outgoing and that loves the outdoors. From hiking, days at the beach, or running, people here love to get out and enjoy the sun. The downtown Gaslamp area — as well as the famous Pacific Beach — is full of trendy restaurants, bustling bars, and some seriously life-changing taco stalls.
9. Get tipsy in California’s Wine Country
California is home to some of the best wine in the world, and a visit to the Sonoma or Napa Valley shouldn’t be missed. While Sonoma is cheaper than Napa, both these destinations are meant for splashing out. Take a tour, book a cozy vineyard Airbnb, and enjoy a relaxing few days learning about the region’s wines. Tastings usually cost between $15-20 USD. If you go to Sonoma, check out Three Fat Guys winery. They have phenomenal reds.
10. Hike around Lake Tahoe
Lake Tahoe is impressive and beautiful. Ringed by tiny mountain communities, this is a terrific place for hiking and boating in the summer and skiing in the winter. For fun in the sun, be sure to spend some time lounging at Kings Beach. For hikes, check out the Rubicon Trail (16 miles/25.7 kilometers) or the Cascade Falls Trail (1.4 miles/2.2 kilometers). You can’t really go wrong here.
11. Anywhere in Montana
A lot has been written about how stunning Montana is, but words cannot do this state justice. To me, it’s the most beautiful state in the Union, filled with wondrous mountains and hills as far as the eye can see. It’s a nature-lover’s paradise and there is a huge craft beer scene here too, with tons of local breweries all around the state. If you want nature, good food, friendly locals, and just quiet, Montana is it!
12. Relax in Cape Cod
I spent a lot of summers on the Cape since I grew up in Boston. You’ll find plenty of small beach towns along the coast (Provincetown and Hyannis being the most famous but I also love Chatham, Falmouth, Wellfleet, and Brewster). There’s not a lot to “do” but if you’re looking for seafood, beaches, boardwalks, and that perfect family vacation, visit the Cape! Just avoid the weekends when it gets a little too crowded.
13. Explore Deadwood
Tucked away in western South Dakota, this town was famous during the Old West days (noteworthy enough to be the focus of the eponymous HBO series). Wyatt Earp, Calamity Jane, Wild Bill Hickok, and many other infamous gunslingers all spent time here. Sort of kitschy and re-created, it’s nonetheless a very cool place where you can experience a taste of the old frontier days. It’s also conveniently located near the Black Hills and Mount Rushmore so you can use it as a base for exploring the region.
14. Be surprised by Kansas City
I really loved this city, which features some of the world’s best BBQ and a lively downtown core. There’s a detailed and enlightening jazz museum here, as well as the eye-opening Negro Leagues Baseball Museum (that’s the actual name). This is yet another super underrated and under-visited destination.
15. Stay weird in Portland
Portland , Oregon is incredible. Here you’ll find an impressive food truck scene, cool bespoke bars and cocktail lounges, a craft beer scene that’s religion to residents, relaxing parks (including a peaceful Japanese garden), a vibrant art scene, and hiking in the nearby mountains. Portland is just an awesome city, especially in the summer when the weather is perfect and there are festivals and events galore.
16. Hike our national parks
America has 63 national parks as well as countless state and local parks. These parks highlight the best of the American wilderness. Yellowstone, Yosemite, Glacier, Zion, Byrce, the Smokey Mountains, Rocky Mountain Park, the Badlands — the list goes on. Make sure you visit as many national parks as you can to get a sense of the grand and diverse landscape that is the United States. You can use this government map to find a park near you! If you plan to visit multiple parks, get the America the Beautiful Park Pass, which costs just $80 USD and gets you free entry to all the national parks for a year.
17. Admire the architecture in Chicago
One of my favorite cities in the world, Chicago is full of amazing architecture, great parks, delicious and hearty food, and a fun nightlife. One of the best ways to see the city’s unique architecture is on a river cruise. There are multiple operators and prices start around $45. Don’t miss trying deep-dish pizza (it was invented here, along with stuffed-crust pizza) and seeing the iconic “Bean” sculpture in Millennium Park. Additionally, check out the city’s famous pier, aquarium, and waterfront park. The city also hosts one of the biggest St. Patrick’s Day celebrations in the country.
18. Enjoy Lively New Orleans
This French-influenced city has incredible seafood and Cajun cuisine and even better live music. A visit to New Orleans is a must for any jazz or blues fan. Live music is available seven nights a week. Frenchman Street is one of the best places to go (my favorite venue is the Spotted Cat). There are also tons of amazing walking tours that highlight the city’s unique culture and history (including ghost and voodoo tours). Nature lovers will enjoy wandering through the massive oak trees in City Park where you can also visit the city’s Botanical Gardens, which are open year-round. Admission is $12. Plus, there’s incredible independent bookstores, creole food, art museums, and the simply incredible and informative World War 2 museum. Don’t skip roaming the redone and revitalized Bywater district too. It’s a bit hipster. If you plan on celebrating Mardi Gras in NOLA , book early. Accommodations fill up fast.
19. Get some sun in Hawaii
Closer to Asia than the United States, Hawaii is America’s slice of South Pacific paradise. White sands beaches, clear blue water, tropical jungle, and great surf — Hawaii has it all! Don’t miss the otherworldly landscapes of Hawai’i Volcanoes National Park, the somber memorial at Pearl Harbor, and the hikes at Diamond Head and the Lanikai Pillbox Trail near Honolulu. There are a ton of opportunities for snorkeling and scuba diving where you get a chance to see manta rays, sea turtles, and plenty of colorful fish. Waimea Canyon and the Napali coast on the island of Kauai are places you can get up close and personal with the natural landscape. There are helicopter and boat tours or, if you’re up for a challenge, you can hike the iconic Kalalau Trail. Every island has its own vibe so, if you can, visit more than one.
20. Check out Boston
The birthplace of the revolution (and my hometown), no one leaves Boston disappointed. It’s a big city, but its lack of high-rises, as well as its cobblestone streets and brick buildings, give the city a small-town feel. The Freedom Trail, which covers all the main historic stops, is a must because it gives you a look at the city’s historic past. Be sure to lounge in the Boston Common and catch a Red Sox game at Fenway Park too (the city is big on sports).
21. Visit the nation’s capital
The country’s capital is home to many of the best museums in the country. And, given the large number of international embassy workers here, it’s unsurprising one of the most international cities in the country. You can find food from anywhere in the world thanks to all the embassies in the city. Plus, there’s a vibrant music and cocktail scene. Don’t miss the National Mall and all its monuments, the Holocaust Museum, and the various Smithsonian Museums (some of the best are the Air and Space Museum, the Museum of the American Indian, the African American Museum, the National Zoo, the Smithsonian Castle, and the American Art Museum). If you visit in the spring, you’ll get to see the cherry blossoms bloom along the Mall.
22. Learn about Mt. Rushmore
Completed in 1941, this historic monument in the Black Hills of South Dakota is a lot smaller than you expect, but it makes a good stop while driving. Originally, the indigenous Lakota Sioux inhabited this area, however, when gold was found in the hills, white settlers forcibly removed them from their homeland. At the Wounded Knee massacre, U.S. forces killed over 250 indigenous women and children. Decades later, Rushmore was built, much to the dismay of the local indigenous population, who consider the land to be sacred. Take a guided tour to learn more about this iconic monument’s complex and tragic history.
23. Be a kid at Disney World
Sure, it’s cheesy . Yes, it’s built for kids. True, it’s not authentic. But despite all that, Disney World is still a fun time and they have a lot of rides for adults too. I recently went back as an adult and there’s a lot to do there: they have some good restaurants, and Disney Springs has a fun nightlife. If you are in Florida, take a stop for a few days. Indulge your inner child. Tickets cost around $110 USD per day and go up from there.
24. Hike the Appalachian Mountains
Stretching the east coast of America, these mountains are almost 500 million years old and offer great hiking, camping, and trekking. For a multi-month adventure, hike the 2,190-mile (3,524-kilometer) Appalachian Trail which covers the entire mountain range and takes 5-7 months to complete. You can also do day hikes or weekend hikes of its various sections if you want a more manageable outdoor getaway.
25. Unwind in Put-In-Bay
One of the coolest, not-so-hidden places in the U.S. is this group of islands in Lake Erie. Widely known to Midwesterners (but unknown to most everyone else), South Bass Island is home to Put-in-Bay, where Midwest hospitality meets Caribbean vibes (you ride around in golf carts and bars have sand as floors). My favorite spot is Mojito Bay, an outdoor tiki bar with sand floors and swings for bar seats that offers up more than 25 different mojitos. These places get very wild on the weekends too.
26. Explore Maine
Tucked away up in the northeast, Maine evokes images of endless shorelines, wild forests, iconic lighthouses, and lots and lots of lobster dinners. It’s often overlooked yet it’s incredibly beautiful and perfect for a short road trip. Don’t miss trying lobster rolls (a regional favorite) and hiking in Acadia National Park. Portland has some great eateries (such as Duckfat and Eventide Oyster Co.) and picturesque historic lighthouses, including Maine’s oldest operating lighthouse, the Portland Head Light, which opened in 1791 when George Washington was president. Additionally, tiny Bangor is home to tons of breweries and Moosehead State Park is an incredible place to go hiking for a few days. And you can’t go wrong stopping in any of the quintessential New England fishing villages up and down the coast. Maine is one of the best states in the union!
27. Take a road trip
The only good way to see this vast and diverse landscape and the small towns that populate it is with a road trip . I highly suggest renting a car and driving across the U.S. It’s an amazing experience. I’ve done several coast-to-coast trips as well as regional trips around New England , California , and the South . It’s the best way to see the country and you can do it for under $50 USD a day.
For the best rental car deals, use Discover Cars .
28. Take a tour
You can find all sorts of amazing walking tours, bike tours, and food tours all around the country. They’re a great way to get an in-depth look at the city you’re in with the help of an expert local guide. Take Walks is my go-to walking tour company when I’m looking for something thorough and insightful (and fun). They can get you behind the scenes and are much more comprehensive than your average free walking tour.
For information on specific cities in the United States, check out these city guides:
- Austin Travel Guide
- Boston Travel Guide
- Chicago Travel Guide
- Hawaii Travel Guide
- Las Vegas Travel Guide
- Los Angeles Travel Guide
- Miami Travel Guide
- New York Travel Guide
- Philadelphia Travel Guide
- San Francisco Travel Guide
- Seattle Travel Guide
- Washington D.C. Travel Guide
United States Travel Costs

Accommodation – Hostels can be found in most major cities, though options are generally slim in the country. A bed in a dorm room with 4-6 beds usually costs between $35-55 USD per night. Rooms with more beds are marginally cheaper (they start around $25-30 USD per night). Private rooms are usually $75-125 USD. Expect prices on the higher end in bigger cities and during peak season. Free Wi-Fi is standard and most hostels also have self-catering facilities. Hostels with free breakfast are rare.
If you plan on camping, expect to pay at least $20-30 USD per night for a basic tent plot for two without electricity.
Cheap motels usually start around $60-75 USD per night and can be found along any highway. Expect basic amenities like TV, Wi-Fi, and AC. Some have pools.
Budget two-star hotels start at $90 USD per night. But, in major cities like NYC, LA, or Chicago, they start closer to $125 USD. The U.S. is very vast and prices fluctuate a lot depending on what region you’re in so check out the specific city guides listed above for more detailed information on accommodation. The United States is too diverse to pin down a specific number!
Airbnb is available around the country, with private rooms starting at $40 USD per night, though for good rooms, you’ll likely pay closer to $60 USD. For an entire home/apartment, expect to pay at least $100 USD per night. Prices in large cities are usually double. Again, there’s a lot of variation depending on where you’re going so check out the city guides for more specific prices!
Food – From seafood in New England to BBQ in the South to Tex-Mex and organic whole foods in the West to German influenced food in the Midwest, there is no singular food culture in the US. Every region has its own staples, which means you’ll never get bored of eating your way around the country.
Since the country is so big, prices for food vary a lot. What is $5 USD in Kansas is probably $15 USD in New York City. Below are some country averages but, if visiting a big metropolis/coastal city, add about 25% to the price.
Grab-and-go sandwiches usually cost around $10 USD while fast food costs $10-12 USD for a combo meal. Meals from food trucks will cost between $10-15 USD. Mid-range casual restaurants cost between $25-30 USD for a meal and drink. At some place a little nicer (think white table cloth), expect to spend at least $60 USD per person on dinner. Prices go up from there and the sky is the limit. Again, consult the city and destination guides for specific prices.
You can generally find takeout pizzas for around $10-15 USD while Chinese and Thai cuisine start around $10-12 USD for a main dish.
Beer is around $6-8 USD, a glass of wine is $8-10 USD, and cocktails start at $14 USD in most cities (about $20 USD in NYC though!). A latte/cappuccino is $4-5 USD and bottled water is $2 USD.
If you cook your own food, expect to pay about $60-80 USD per week for basic staples like rice, pasta, vegetables, and some meat.
Backpacking the United States Suggested Budgets
How much does it cost to visit the United States? Well, how much you spend largely depends on where in the United States you’re going to visit. For example, New York City is much more expensive than Memphis and San Francisco is going to hit your budget harder than Boise. The South is cheaper than the North and the interior states are cheaper than the coasts. The comparisons are endless! However, this overview can give you a basic look at what to expect based on your travel style and assuming you’re going to mix cheap and expensive destinations.
On a backpacking budget of $75 USD per day, you can stay in a hostel dorm, cook your meals, use public transportation to get around, limit your drinking, and do free activities like walking tours, hiking, and hanging out at beaches. If you plan on drinking, add another $10-20 USD per day. If you can camp or Couchsurf, you can likely get this down to $50-60 USD per day.
On a mid-range budget of $210 USD per day, you can stay in a private Airbnb or motel, eat out for most meals, enjoy some drinks, take the occasional taxi to get around, and do more paid activities like museum visits and food tours.
On an upscale budget of $350 USD or more per day, you can stay in a midrange hotel, eat out for all your meals, drink more, rent a car to get around, and do as many guided tours and activities as you want. This is just the ground floor for luxury though. The sky is the limit!
You can use the chart below to get some idea of how much you need to budget daily, depending on your travel style. Keep in mind these are daily averages – some days you’ll spend more, some days you’ll spend less (you might spend less every day). We just want to give you a general idea of how to make your budget. Prices are in USD.
United States Travel Guide: Money-Saving Tips
There are plenty of ways to save money when you travel the U.S. but it varies a lot by region (as I’ve been repeating). The general tips below can help you get started but, for more specific tips, visit my city guides.
- Take a free tour – Taking a free walking tour is the best way to get introduced to a new place, and most major cities in the U.S. have free walking tours. You get to see the main sights and ask all your questions to a local guide. Just be sure to tip your guide at the end!
- Take the bus – The cheapest way to get around the U.S. is by bus. Bus fares cost as little as $1 USD, though 2-3-hour journeys start around $30 USD. Between cities, the best companies are Megabus, Greyhound, and FlixBus.
- Redeem hotel points – Be sure to sign up for hotel credit cards before you go and use those points when you travel. This is especially helpful in big cities. Be aware that most hotels charge parking fees if you have a car.
- Get a U.S. Park Pass – This national park pass lets you into all the national parks for free so you don’t have to keep paying admission. The annual fee is $80 USD and it pays for itself after four parks.
- Cook – The United States has some of the cheapest groceries in the developed world, while eating out here can add up quickly once you factor in a tip and tax (which varies by state). Grocery shopping can about $60 USD per week and is way cheaper and healthier than eating out every day. Cook and save!
- Stay with a local – Couchsurfing lets you stay with a local for free, cutting your accommodation costs drastically. You’ll get to spend time with a local who can share their tips and advice while sharing your own travel stories and culture. You can also use the app to meet people for activities (coffee, museum visits, etc.) if you don’t feel comfortable staying with a stranger.
- Camp – Most campsites start around $20-30 USD per night for a tent — much cheaper than a hostel. You can use nps.gov to find campsites run by the National Park Service. You can also camp for free in National Forests or Bureau Land Management (BLM) lands (search for “dispersed camping” options). Just be sure to respect the environment and follow Leave No Trace principles when camping.
- Use city tourism cards – City tourism cards allow you to see a large number of attractions (and often include free public transportation) for one low price, usually $75–100 USD. If you plan on seeing a lot, these can save you a ton.
- Share your ride – If you have a car, taking on riders can be a way to lower your costs. On my first trip across the U.S., I offered rides to people I met in hostels. On another trip, I had friends and readers join me along the way. You can post ads on Craigslist and at hostels to find riders. This not only makes the trip more enjoyable but lowers your gas costs too. If you don’t have a car, you can use look for rides in the same places.
- Stay at roadside hotels – There are a plethora of cheap roadside hotels such as Motel 6 and Super 8 to the rescue. Rooms start around $60-75 USD a night (plus tax). They’re great when you’re traveling with someone and can split the cost.
- Find free museums and events – Inquire at tourism offices, use Google, or ask hotel or hostel staff for information about free events and museums. Many museums offer free or discounted admission times throughout the week.
- Get free water or free refills – If you order a drink, most restaurants allow free refills while you eat your meal or refills at a low cost. If you ask, tap water is usually provided for free.
- Save on gas – If you’re on a road trip, use the app GasBuddy to find cheap gas near you. Also, sign up for gas station loyalty programs as they can save you money on fill ups.
Where to Stay in the United States
Hostels are not all that plentiful across the United States yet. Generally, those that do exist are clean, social, and fun. You’ll find a lot of budget hotels wherever you go. here are some of my recommended places to stay around the USA (the cities guides will have even more suggestions):
- HI Hostel (Boston)
- The Revolution Hotel (Boston)
- HI Hostel (Chicago)
- The Arlo (Chicago)
- Banana Bungalow (Los Angeles)
- Hollywood Historic Hotel Los Angeles
- Hostel Memphis (Memphis)
- Hu Hotel (Memphis)
- Freehand (Miami)
- Hotel Ocean (Miami)
- HI New Orleans (New Orleans)
- Villa Convento (New Orleans)
- The Local (New York City)
- Heritage Hotel (New York City)
- ITH Adventure Hostel (San Diego)
- Old Town Inn (San Diego)
- The Green Tortoise (San Francisco)
- SW Hotel (San Francisco)
- The Green Tortoise (Seattle)
- MarQueen Hotel (Seattle)
How to Get Around the United States

City transportation – Most U.S. cities have public transportation, including metro systems and buses. Fares cost around $2-3 USD for a single journey, but there are usually packaged options for visitors. For example, you can get a 7-day unlimited MetroCard in New York City for $34 USD, which covers both buses and the subway system, while San Francisco offers a 7-day transit pass for $41 USD.
Outside of major cities, subways are rare. Some of the smaller cities have trams. Everywhere has a bus though and that’s usually the best way to get around.
Taxis – Taxis are metered with charges starting around $3 USD plus $2-3 USD per mile. This is one of the most expensive ways to get around, however, so I’d skip it unless you have no other choice.
Ridesharing – Uber and Lyft are generally cheaper than taxis and are the best way to get around a city if you don’t want to take a bus or pay for a taxi.
Intercity Bus – Taking the bus is one of the cheapest options for getting around the country, with fares as low as $1 USD if you book far enough in advance. Popular bus companies include:
A 4-5-hour bus ride from New York to Washington D.C. starts at $30 USD, while the 7-hour journey from Chicago to Detroit starts at $27 USD. Austin to New Orleans is around $54 USD. Booking early can save you upwards of 50% so try to plan ahead if you’re going to be taking the bus.
To find bus routes and prices, use BusBud .
Flying – Flying is your quickest option for long distance. You can occasionally find sales for as little as $100 USD so it’s worth it to check several websites ahead of time to see what deals are on. Post-COVID, fares are a lot higher than they were in the past. But if you find a deal, book in advance, or go off season, you can usually get a cheap fare. Sample one-way fares include San Francisco to Maui for $100-150 USD, Seattle to Austin for $85-115 USD, or New York to L.A. for $250 USD (round trip). However, prices can easily double if booked last minute.
For more information on how to find a cheap flight, check out this article .
Train – Amtrak is the rail provider for the United States, but it’s not the quickest or most affordable way to travel. They have routes all around the country ( here’s their route map ) and offer a cross-country pass for $499 USD. The USA Rail Pass gives you 30 days of travel over 10 segments, which averages out to around $50 USD per leg.
If you have a valid student ID you can save 15% on your tickets.
As for prices, A 20-hour train ride from Chicago to New Orleans costs around $110 USD, while a multi-day trip from New York to Los Angeles is around $280 USD. Book in advance to find the best deals. Shorter trips lasting 2-4 hours are usually under $40 USD.
Car rental – Roadtripping is a great way to explore the country, and car rentals can be found for as little as $35 USD for a multi-day rental. Renters need to be at least 21 years old. For the best rental car deals, use Discover Cars .
Hitchhiking – Hitchhiking in the United States is common and safe. Dress respectably, smile while making eye contact with drivers, and use a cardboard sign to tell people where you’re headed. Be prepared for long bouts of no pick-ups, especially if you’re traveling through more rural areas. Pack plenty of water and a light meal or two, like sandwiches and fruit. Hitchwiki is a great resource for additional hitchhiking tips.
When to Go to the United States
Since the United States is such a large country, the climate and temperature change drastically from coast to coast and from north to south.
The northern states have clearly defined seasons. In cities like Chicago, Boston, and New York, winter can bring heavy snowfall and more severe temperatures. Coastal areas like Seattle and Portland, Oregon, tend to be milder. Spring can start as late as May in the northernmost parts of the country, but this is a good time to visit because the weather begins to warm up and the busy tourist season hasn’t started yet. Summers are gorgeous and temperatures climb into the 80s°F (30s°C). It’s also the busiest time of year for tourism. Autumn is a wonderful time to visit the northern states because many parts of this region have a lot of trees. Temperatures have cooled, crowds have dwindled, and the changing leaves offer an something extra to enjoy.
The southern states have less defined seasons. In the southwest, winters tend to be dry and mild. In the southeast, temperatures are mild but places like and Memphis can be rainy. Spring is a wonderful time to visit this part of the country because temperatures are warm but not stifling. Summers get incredibly hot and humid in the southeast. In the desert areas of the southwest, like Las Vegas, temperatures can soar well above 104°F (40°C) on some days. Autumn cools things off across the southern states, but can also bring severe weather in the southeast. .
Ultimately, the best time to travel to the United States depends on where you’re headed and what kind of activities you’d like to do. Visit our city guides for more specific information on when to go.
How to Stay Safe in the United States
The United States is a massive country and “safety” changes a lot depending on where you go and what you do. Generally, the US safe place to travel around — even if you’re traveling solo.
Violent attacks tend to be confined to certain areas (especially where drug and gang violence are a problem). You may encounter petty crime, like theft, especially around popular tourist landmarks and in larger cities, especially on the west coast where theft is a much more common problem. Keep an eye on your belongings at all times, especially while taking crowded public transportation.
Gun violence and mass shootings tend to dominate headlines when they happen. However, the chances of it happening to you are slim. Do not let this discourage you from exploring the United States. The U.S. is very big and very, very diverse. And, due to this size, there is a lot of cultural (and political) variation. Despite what you hear, crime in America is low. (There was far more crime in the US in the 1990s!). For more information, read this post, “ Is it Safe to Visit the United States?”
If you rent a vehicle, don’t leave any valuables in it overnight. Take common sense safety measures and you’ll be fine.
Moreover, be sure to read about common travel scams to avoid here .
When hiking, always bring water and sunscreen. Be sure to check the weather before you depart and dress accordingly.
Solo female travelers should generally feel safe but all the standard safety cautions apply. For specific tips, I would read one of the many incredible solo female travel blogs on the web. They’ll give you tips and advice that I can’t.
If you do experience an emergency, dial 911 for assistance.
Always trust your gut instinct. Make copies of your personal documents, including your passport and ID.
The most important piece of advice I can offer is to purchase good travel insurance. Travel insurance protects you against illness, injury, theft, and cancellations. It’s comprehensive protection in case anything goes wrong. I never go on a trip without it as I’ve had to use it many times in the past. You can use the widget below to find the policy right for you:
United States Travel Guide: The Best Booking Resources
These are my favorite companies to use when I travel. They consistently have the best deals, offer world-class customer service and great value, and overall, are better than their competitors. They are the companies I use the most and are always the starting point in my search for travel deals.
- Skyscanner – Skyscanner is my favorite flight search engine. They search small websites and budget airlines that larger search sites tend to miss. They are hands down the number one place to start.
- Hostelworld – This is the best hostel accommodation site out there with the largest inventory, best search interface, and widest availability.
- Booking.com – The best all around booking site that constantly provides the cheapest and lowest rates. They have the widest selection of budget accommodation. In all my tests, they’ve always had the cheapest rates out of all the booking websites.
- Get Your Guide – Get Your Guide is a huge online marketplace for tours and excursions. They have tons of tour options available in cities all around the world, including everything from cooking classes, walking tours, street art lessons, and more!
- SafetyWing – Safety Wing offers convenient and affordable plans tailored to digital nomads and long-term travelers. They have cheap monthly plans, great customer service, and an easy-to-use claims process that makes it perfect for those on the road.
- LifeStraw – My go-to company for reusable water bottles with built-in filters so you can ensure your drinking water is always clean and safe.
- Unbound Merino – They make lightweight, durable, easy-to-clean travel clothing.
- Top Travel Credit Cards – Points are the best way to cut down travel expenses. Here’s my favorite point earning credit cards so you can get free travel!
United States Travel Guide: Related Articles
Want more info? Check out all the articles I’ve written on United States travel and continue planning your trip:

Where to Stay in San Francisco: The Best Neighborhoods for Your Visit

The 12 Best Things to Do in Chicago

The 5 Best Hotels in San Francisco

How to Experience Milwaukee Like a Local

The 7 Best Hotels in New York City

The 7 Best Hotels in Miami
Get my best stuff sent straight to you, pin it on pinterest.
- Where To Stay
- Transportation
- Booking Resources
- Related Blogs
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
The huge solar storm is keeping power grid and satellite operators on edge

Geoff Brumfiel
Willem Marx

NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm. Solar Dynamics Observatory hide caption
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm.
Planet Earth is getting rocked by the biggest solar storm in decades – and the potential effects have those people in charge of power grids, communications systems and satellites on edge.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration says there have been measurable effects and impacts from the geomagnetic storm that has been visible as aurora across vast swathes of the Northern Hemisphere. So far though, NOAA has seen no reports of major damage.

The Picture Show
Photos: see the northern lights from rare, solar storm.
There has been some degradation and loss to communication systems that rely on high-frequency radio waves, NOAA told NPR, as well as some preliminary indications of irregularities in power systems.
"Simply put, the power grid operators have been busy since yesterday working to keep proper, regulated current flowing without disruption," said Shawn Dahl, service coordinator for the Boulder, Co.-based Space Weather Prediction Center at NOAA.
NOAA Issues First Severe Geomagnetic Storm Watch Since 2005

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
- Amazon Alexa
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
"Satellite operators are also busy monitoring spacecraft health due to the S1-S2 storm taking place along with the severe-extreme geomagnetic storm that continues even now," Dahl added, saying some GPS systems have struggled to lock locations and offered incorrect positions.
NOAA's GOES-16 satellite captured a flare erupting occurred around 2 p.m. EDT on May 9, 2024.
As NOAA had warned late Friday, the Earth has been experiencing a G5, or "Extreme," geomagnetic storm . It's the first G5 storm to hit the planet since 2003, when a similar event temporarily knocked out power in part of Sweden and damaged electrical transformers in South Africa.
The NOAA center predicted that this current storm could induce auroras visible as far south as Northern California and Alabama.
Extreme (G5) geomagnetic conditions have been observed! pic.twitter.com/qLsC8GbWus — NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (@NWSSWPC) May 10, 2024
Around the world on social media, posters put up photos of bright auroras visible in Russia , Scandinavia , the United Kingdom and continental Europe . Some reported seeing the aurora as far south as Mallorca, Spain .
The source of the solar storm is a cluster of sunspots on the sun's surface that is 17 times the diameter of the Earth. The spots are filled with tangled magnetic fields that can act as slingshots, throwing huge quantities of charged particles towards our planet. These events, known as coronal mass ejections, become more common during the peak of the Sun's 11-year solar cycle.
A powerful solar storm is bringing northern lights to unusual places
Usually, they miss the Earth, but this time, NOAA says several have headed directly toward our planet, and the agency predicted that several waves of flares will continue to slam into the Earth over the next few days.
While the storm has proven to be large, predicting the effects from such incidents can be difficult, Dahl said.
Shocking problems
The most disruptive solar storm ever recorded came in 1859. Known as the "Carrington Event," it generated shimmering auroras that were visible as far south as Mexico and Hawaii. It also fried telegraph systems throughout Europe and North America.

Stronger activity on the sun could bring more displays of the northern lights in 2024
While this geomagnetic storm will not be as strong, the world has grown more reliant on electronics and electrical systems. Depending on the orientation of the storm's magnetic field, it could induce unexpected electrical currents in long-distance power lines — those currents could cause safety systems to flip, triggering temporary power outages in some areas.
my cat just experienced the aurora borealis, one of the world's most radiant natural phenomena... and she doesn't care pic.twitter.com/Ee74FpWHFm — PJ (@kickthepj) May 10, 2024
The storm is also likely to disrupt the ionosphere, a section of Earth's atmosphere filled with charged particles. Some long-distance radio transmissions use the ionosphere to "bounce" signals around the globe, and those signals will likely be disrupted. The particles may also refract and otherwise scramble signals from the global positioning system, according to Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist with NOAA. Those effects can linger for a few days after the storm.
Like Dahl, Steenburgh said it's unclear just how bad the disruptions will be. While we are more dependent than ever on GPS, there are also more satellites in orbit. Moreover, the anomalies from the storm are constantly shifting through the ionosphere like ripples in a pool. "Outages, with any luck, should not be prolonged," Steenburgh said.

What Causes The Northern Lights? Scientists Finally Know For Sure
The radiation from the storm could have other undesirable effects. At high altitudes, it could damage satellites, while at low altitudes, it's likely to increase atmospheric drag, causing some satellites to sink toward the Earth.
The changes to orbits wreak havoc, warns Tuija Pulkkinen, chair of the department of climate and space sciences at the University of Michigan. Since the last solar maximum, companies such as SpaceX have launched thousands of satellites into low Earth orbit. Those satellites will now see their orbits unexpectedly changed.
"There's a lot of companies that haven't seen these kind of space weather effects before," she says.
The International Space Station lies within Earth's magnetosphere, so its astronauts should be mostly protected, Steenburgh says.
In a statement, NASA said that astronauts would not take additional measures to protect themselves. "NASA completed a thorough analysis of recent space weather activity and determined it posed no risk to the crew aboard the International Space Station and no additional precautionary measures are needed," the agency said late Friday.

People visit St Mary's lighthouse in Whitley Bay to see the aurora borealis on Friday in Whitley Bay, England. Ian Forsyth/Getty Images hide caption
People visit St Mary's lighthouse in Whitley Bay to see the aurora borealis on Friday in Whitley Bay, England.
While this storm will undoubtedly keep satellite operators and utilities busy over the next few days, individuals don't really need to do much to get ready.
"As far as what the general public should be doing, hopefully they're not having to do anything," Dahl said. "Weather permitting, they may be visible again tonight." He advised that the largest problem could be a brief blackout, so keeping some flashlights and a radio handy might prove helpful.
I took these photos near Ranfurly in Central Otago, New Zealand. Anyone can use them please spread far and wide. :-) https://t.co/NUWpLiqY2S — Dr Andrew Dickson reform/ACC (@AndrewDickson13) May 10, 2024
And don't forget to go outside and look up, adds Steenburgh. This event's aurora is visible much further south than usual.
A faint aurora can be detected by a modern cell phone camera, he adds, so even if you can't see it with your eyes, try taking a photo of the sky.
The aurora "is really the gift from space weather," he says.
- space weather
- solar flares
- solar storm

17 Fascinating Facts That Prove the Bible Is More Than Just a Book
Posted: May 19, 2024 | Last updated: May 19, 2024

For billions of people around the world, the Bible is more than just a book – it’s the divinely inspired Word of God. This ancient text has shaped the course of history, inspired countless works of art and literature, and transformed the lives of those who read it. But even for those who have studied the Bible for years, there are still many fascinating facts and details that are often overlooked. Check out these 17 facts about the Bible that demonstrate its miraculous nature and its enduring power to speak to the human heart.

The Bible is the Best-Selling Book of All Time
Did you know that the Bible is the best-selling book in history? It’s estimated that over 5 billion copies have been sold worldwide, far surpassing any other book. This fact alone testifies to the Bible’s enduring relevance and its ability to speak to people across cultures and generations. No other book has had such a profound impact on the world, and its continued popularity is a testament to its timeless wisdom and divine inspiration.

The Bible Was Written by Over 40 Different Authors
One of the most remarkable things about the Bible is that it was written by over 40 different authors, spanning a period of over 1,500 years. These authors came from all walks of life – from kings and prophets to fishermen and tent-makers – and yet their writings form a cohesive and unified message. This diversity of authorship is a powerful evidence of the Bible’s divine inspiration, as it would be impossible for so many different people to create such a consistent and compelling work without the guidance of the Holy Spirit.

The Bible Contains 66 Books
The Bible is not just one book, but a collection of 66 different books, divided into two main sections: the Old Testament and the New Testament. The Old Testament contains 39 books, while the New Testament contains 27. Each of these books has its own unique style, purpose, and message, yet they all work together to tell the grand story of God’s love and redemption for humanity. This incredible diversity and unity is another evidence of the Bible’s divine origin.

The Bible Was Written in Three Different Languages
The Bible was originally written in three different languages: Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek. The Old Testament was primarily written in Hebrew, with some portions in Aramaic, while the New Testament was written in Greek. Despite these linguistic differences, the Bible’s message remains consistent and clear across all translations and versions. This is a testament to the Holy Spirit’s ability to preserve the integrity of God’s Word, even as it is translated and shared across the world.

The Bible Contains Many Different Literary Genres
The Bible is not just a history book or a collection of moral teachings – it contains many different literary genres, including poetry, prophecy, parables, letters, and more. This diversity of genres reflects the many different ways in which God has chosen to communicate with humanity, and it highlights the Bible’s ability to speak to us on many different levels – emotionally, intellectually, and spiritually. Whether we’re seeking comfort, guidance, or inspiration, the Bible has something to offer for every situation and every need.

The Bible Has Been Translated into Over 2,000 Languages
The Bible is the most translated book in the world, with portions of it available in over 2,000 different languages. This incredible feat of translation is a testament to the Bible’s universal appeal and its ability to speak to people of all cultures and backgrounds. No matter where you go in the world, you can find people who have been touched by the power of God’s Word, and who have found hope, healing, and salvation through its pages.

The Bible Contains Many Prophecies That Have Been Fulfilled
One of the most compelling evidences of the Bible’s divine inspiration is the many prophecies it contains that have been fulfilled throughout history. From the rise and fall of empires to the birth and death of Jesus Christ, the Bible contains countless predictions that have come to pass with stunning accuracy. These fulfilled prophecies are a powerful reminder that the Bible is not just a collection of human writings, but a divinely inspired message from God himself.

The Bible Has Survived Countless Attempts to Destroy It
Throughout history, there have been many attempts to destroy or suppress the Bible, from the ancient Roman persecution of Christians to the modern-day censorship of the Bible in certain countries. Yet despite these efforts, the Bible has endured and even thrived, spreading its message of hope and salvation to countless people around the world. This resilience is a testament to the Bible’s divine protection and its enduring power to transform lives.

The Bible Contains Many Scientific Insights
While the Bible is not primarily a scientific text, it contains many insights that align with modern scientific discoveries. From the creation of the universe to the complexity of the human body, the Bible offers a perspective on the natural world that is both ancient and remarkably accurate. These scientific insights are another evidence of the Bible’s divine inspiration, as they demonstrate a knowledge and understanding that goes beyond what was known at the time the Bible was written.

The Bible Has Inspired Many Great Works of Art and Literature
The Bible has been a source of inspiration for countless artists, writers, and musicians throughout history. From the paintings of Michelangelo and Rembrandt to the poetry of John Milton and the music of Johann Sebastian Bach, the Bible has inspired some of the greatest works of art and literature in human history. This enduring influence is a testament to the Bible’s ability to capture the human imagination and to speak to the deepest longings of the human heart.

The Bible Contains Many Hidden Treasures and Mysteries
Despite its age and its familiarity, the Bible still contains many hidden treasures and mysteries waiting to be discovered. From the symbolism of the Old Testament to the parables of Jesus, the Bible is a text that rewards careful study and reflection. As we dig deeper into its pages, we can uncover new insights and revelations that speak to our lives and our struggles in profound and unexpected ways. This ongoing discovery is a testament to the Bible’s depth and complexity, and to its ability to speak to us in fresh and relevant ways, no matter how many times we read it.

The Bible Has the Power to Transform Lives
Perhaps the most remarkable thing about the Bible is its power to transform lives. Countless people throughout history have found hope, healing, and purpose through the pages of this ancient text. From the lowest depths of despair to the highest heights of joy, the Bible has been a source of comfort, guidance, and inspiration for millions of people around the world. This transformative power is the ultimate evidence of the Bible’s divine origin, as no mere human book could have such a profound and lasting impact on the human soul.

The Bible Reveals the Character and Nature of God
At its core, the Bible is a revelation of the character and nature of God. From the creation of the world to the redemption of humanity, the Bible tells the story of a God who is loving, just, and merciful, and who desires to have a personal relationship with each one of us. Through the pages of the Bible, we can come to know God in a deeper and more intimate way, and we can discover the incredible depths of his love and grace for us.

The Bible Offers Hope and Comfort in Times of Trouble
In a world that is often filled with pain, suffering, and uncertainty, the Bible offers a source of hope and comfort that is unparalleled. From the promises of God’s faithfulness to the assurance of eternal life, the Bible contains countless messages of encouragement and support for those who are struggling. Whether we are facing illness, loss, or other trials, the Bible reminds us that we are never alone, and that God is always with us, working all things together for our good.

The Bible is a Living and Active Word
The Bible is not just a static collection of ancient writings – it is a living and active word that continues to speak to us today. Through the power of the Holy Spirit, the Bible can come alive in our hearts and minds, revealing new truths and insights that are relevant to our lives and our struggles. This dynamic nature of the Bible is a testament to its divine inspiration, as it demonstrates the ongoing work of God in the world and in our lives.

The Bible is the Ultimate Source of Truth and Wisdom
In a world that is often confused and conflicted about what is true and what is right, the Bible stands as the ultimate source of truth and wisdom. From the Ten Commandments to the Sermon on the Mount, the Bible contains timeless principles and teachings that can guide us in every area of life. As we study and apply these truths to our lives, we can find the clarity, purpose, and direction that we need to navigate the challenges and opportunities of life.

The Bible Points Us to Jesus Christ
Finally, and most importantly, the Bible points us to Jesus Christ, the Son of God and the Savior of the world. From the Old Testament’s prophecies to the New Testament’s teachings, the Bible reveals Jesus as the ultimate revelation of God’s love and grace for humanity. Through his life, death, and resurrection, Jesus offers us the gift of salvation and the hope of eternal life, and he invites us to follow him and to become a part of his kingdom. This is the ultimate message of the Bible, and it is a message that has the power to change our lives forever.

15 Things The Bible Says To Look For In The Last Days

21 Things You’ve Been Told About Sin That Aren’t Quite Right
More for You
Did a 14-year-old prank caller just blow up Michael Cohen’s testimony in Trump’s hush money trial?
It’s time to bring back the world’s greatest fighter jet – from the 1990s
Selena Gomez Wears Stunning Off-The-Shoulder Gown to Cannes Film Festival Premiere
Bronny James Measures 3 Inches Shorter At Combine Than USC
Applebee's Forced to Close 35 More Locations in 2024
Here is the average income for retirees in the US — how do you compare?
Giant lake suddenly returns 130 years after vanishing
What Is the Anduril Roadrunner? America's Latest Game-Changing Weapon
The New Math of Driving Your Car Till the Wheels Fall Off
I'm a Senior. When Can I Stop Paying Property Taxes?
Crockett to Greene: ‘Don’t come for me’
Severe storms hit Kansas, triggering tornadoes and dust storm
‘Friends’ star Courteney Cox says Matthew Perry ‘visits me a lot,’ still feels sense he is ‘around, for sure’
3 Reasons Why The US Has Never Sold Its F-22 Raptor Fighter Jets To Allies
5 Expenses Parents Should Stop Covering for Their Adult Children
The 10 states with the worst roads in America—and the 5 states with the best
5 Things You Need To Stop Doing If Your Car Has An Automatic Transmission
Chicago teen earns doctoral degree at age 17
Should You Buy Nvidia Stock Before Wednesday?
Caitlin Clark News: Fever Star Makes WNBA History in Just Three Games
By clicking Sign In, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Sign In Up with your social account
We won't post to any of your accounts
Your password must include:
- Min 8 characters
- Min 1 lowercase character
- Min 1 uppercase character
- Min 1 number
Get Woman's World Magazine
Save up to 65%.

Woman's World
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Do Not Sell
‘Back to the Future’: 10 Shocking Behind-the-Scenes Facts About the Classic Time Travel Adventure
Put some plutonium in your DeLorean and travel back to 1985!
Share this:
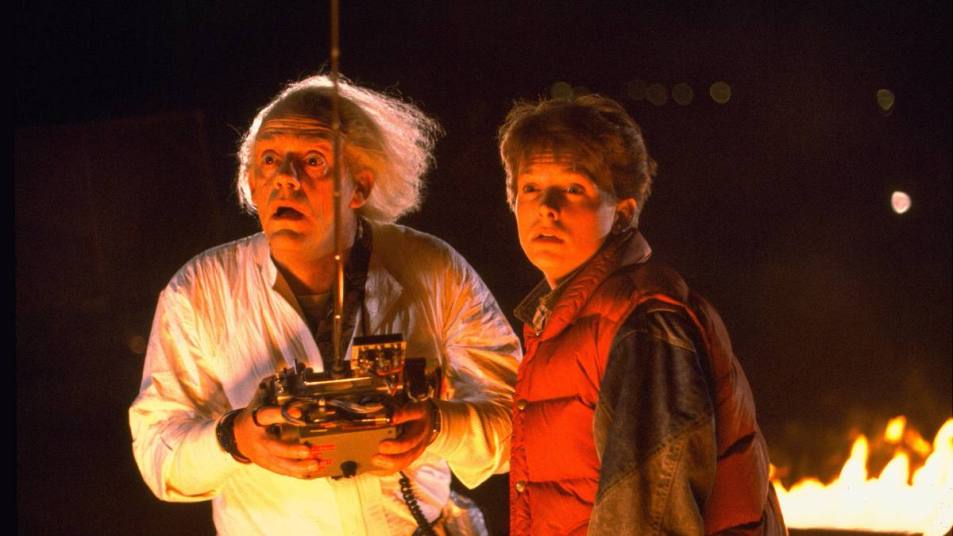

Great scott! — we traveled back in time to 1985 and uncovered the 10 most shocking Back to the Future trivia facts. From what Michael J. Fox really thought about the plot, which catchphrases were improvised and who really wanted to film just one more movie, we found it all out. Keep reading to find out all of that out and more.
Back to The Future follows Marty McFly ( Michael J. Fox ) a kid from 1985, who accidentally gets sent back to 1955 in the time-traveling DeLorean created by his friend, Dr. Emmett Brown ( Christopher Lloyd ). While there, he accidentally interrupts his parents’ first meeting and must race against time to try and get them back together before he ceases to exist.
Wanting to watch the film? It is avaliable for streaming on Amazon Prime Video.
MUST READ: Michael J Fox Movies: The Celebrated Star’s 10 Most Iconic Roles, Ranked
1. The movie had been rejected many times before

Before Universal Pictures bought the rights to Back to The Future, the script by Bob Gale and Robert Zemeckis was rejected 44 times, because people thought it wasn’t as risqué as other teen movies of the time.
Coincidentally, Disney turned it down because they thought it was too risqué.
2. Michael J. Fox didn’t actually sing: Back to The Future trivia

After finally getting his parents back together, Marty (Fox) celebrates by singing “Jonny B Goode.” But, despite playing Marty, Fox was not the one singing — it was actually musician Mark Campbell , a member of the 1980s band Jack Mack and the Heart Attack .
MUST READ: 10 Christopher Lloyd Movies and TV Shows, Ranked – And Where to Watch Them
3. Fox’s filming schedule was very intense

Fox was filming both Family Ties and Back to The Future at the same time. He would film Family Ties in the morning, and then head over to Back to The Future at night, and be there until around 3 or 4 in the morning. Then, he would go home to sleep for a few hours before waking up and doing it all again.
“ I was running on adrenaline ,” Fox admitted in 2023. “I barely knew where I was and I didn’t really know what I was doing. That served the film [ Back to The Future ], because Marty’s supposed to be disoriented.”
MUST READ: ‘Family Ties’ Cast Then and Now — You Won’t Believe How Much They’ve Changed!
4. Some parts of the film had to be reviewed by The White House

After he is sent back in time, Marty tells Doc (Lloyd) that Ronald Reagan was the president in 1985. In response, Doc makes a joke about how he found it hard to believe that 1955 movie star Ronald Reagan went on to become president of The United States of America.
That whole exchange was sent to the White House because the studio was worried that President Reagan was going to be offended, but it turned out to be the exact opposite. Regan reportedly loved it and asked his staff to rewind the whole scene because he found it so funny.
5. Fox wasn’t originally cast as Marty: Back to The Future trivia

Due to his very busy filming schedule for Family Ties , Fox wasn’t originally available to play Marty. At first, C. Thomas Howell was cast but was replaced by Eric Stoltz two weeks later. Stoltz was reported to be a very serious method actor — in fact, he made all of the cast and crew call him Marty even though the cameras weren’t rolling.
Stoltz was soon let go, and Fox joined the cast after coming to an agreement with the Family Ties team. “Eric Stoltz is a wonderful actor, but he lacked a certain comedic sense that is inherent in Michael,” Lloyd said in 2023. “Initially, I was worried because we’d been shooting for six weeks, and it meant going back and redoing all my scenes. I thought I might not be as good. But Michael made me better.”
MUST READ : 15 Shocking Behind-the-Scenes Secrets About ‘Melrose Place’ + Rumors of a Reboot!
6. Fox thinks the whole concept of the movie is a bit odd

Despite playing the lead role in the film, Fox found the plot of it a bit odd, specifically the part where Marty’s mother, Lorraine ( Lea Thompson ), has a massive crush on her son after he gets sent back in time.
“There’s something about it that people still respond to because it’s so weird,” Fox says. “Not to be crude, but it’s a movie about almost f—–g your mom and she’s totally ready for it. Even at the time, I realized it was bizarre — plus Lea [Thompson] was pretty cute.”
7. The DeLorean was selected for a very specific reason

Doc Brown uses a DeLorean for his time machine. The reason was that production thought it looked the most space-like, and it would help the residents of 1955 believe Marty was an alien.
Coincidentally, the film was almost called Space Man From Pluto .
MUST READ : ‘The Karate Kid’ Turns 40 This Year — See the Cast Then and Now
8. The idea for the film came from a yearbook: Back to The Future trivia

After screenwriter Bob Gale discovered his father’s high school yearbook, he began to wonder if the two would have been friends, and that brought the whole Marty McFly going back in time and befriending his own father idea to life.
9. Christoper Lloyd wanted to do one more movie

There are two Back to The Future sequels : One where Doc, Marty and Jennifer ( Elisabeth Shu e ) travel to 2015, entitled Back to the Future Part II (1989), and the other one ( Back to the Future Part III, released in 1990 ) set in the Wild West. Surprisingly, Lloyd wanted to do one more where the two go to ancient Rome, but sadly it never happened.
MUST READ : ‘Adventures in Babysitting’: See the Cast Then and Now!
10. Tom Wilson coined two of Biff’s catchphrases

Two of Biff’s ( Tom Wilson ) most well known lines are “make like a tree and get outta here” and “butthead.” Well, those were actually improvised by Wilson and production loved them so much, they left them in the final film.

Deal of the Day
For all things 1980s, click here !
More in Movies

8 Patriotic Movies That Are Perfect Viewing for Memorial Day — Plus, How to Watch Them

12 Shocking Facts About Marilyn Monroe’s Hit Classic ‘Gentlemen Prefer Blondes’

Professional Dog Walker Approved Shoes for Your Next Doggy Stroll

Clara Bow — The Tragic and Triumphant Life of Hollywood’s First ‘It’ Girl

‘Housesitter’: 8 Hilarious Facts About the Wacky Film Starring Goldie Hawn and Steve Martin

‘Adventures in Babysitting’: See the Cast Then and Now!
Introducing our product reviews team, and how we review.

‘The Long, Long Trailer’: The Lucille Ball and Desi Arnaz Film Turns 70 — Take An Inside Look

The 10 Best Goldie Hawn Movies Ranked, Plus Where to Watch Them

The ‘Earthquake’ Movie: A Look Back at the 1974 Charlton Heston, Ava Gardner Thriller

QVC Promo Code for New Customers Plus Get Free Shipping This Weekend!

‘Funny Face’: 16 Wild Facts About the 1957 Audrey Hepburn and Fred Astaire Musical
Sorry, we did not find any matching results.
We frequently add data and we're interested in what would be useful to people. If you have a specific recommendation, you can reach us at [email protected] .
We are in the process of adding data at the state and local level. Sign up on our mailing list here to be the first to know when it is available.
Search tips:
• Check your spelling
• Try other search terms
• Use fewer words
Dates to know for the 2024 presidential election
The 2024 presidential election will take place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024. Presidential primaries and caucuses are scheduled to begin in January and will run through June.
Published Fri, March 1, 2024 by the USAFacts Team
Every four years, Americans elect a president on the first Tuesday in November . Beginning in January of the election year, voters participate in primaries and caucuses , influencing which presidential candidates are on the November ballot.
When is the 2024 presidential election?
The 2024 presidential election will take place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024 .
When are the presidential primaries and caucuses?
In 2024, presidential primaries and caucuses began in January and will run through June. Two states — Iowa and New Hampshire — hold a caucus and primary in January. Three states — South Carolina, Nevada, and Michigan — hold primaries and caucuses in February.
Twenty-eight states and Washington, DC, hold primaries and caucuses in March, seven states begin in April, and five states begin in May. The final four states — Montana, New Jersey, New Mexico, and South Dakota, hold primaries in June.
Political parties and state law determine caucus and primary dates. Because of variations in laws and bylaws, caucuses and primaries happen over several months, and not all on a single day.
Often, primaries and caucuses for different political parties happen on the same day, but sometimes, they are separated by days, or even months. The Idaho Republican caucus, for example, is scheduled for March 2, 2024, and the Idaho Democratic caucus is scheduled for May 23, 2024. Alternatively, the Utah Democratic primary and Republican caucus are both scheduled for March 5.

Get facts first
Unbiased, data-driven insights in your inbox each week
You are signed up for the facts!
What’s the difference between a primary and a caucus?
The purpose of these contests is not to directly select a presidential candidate, but rather to determine how many delegates will vote in support of a candidate at each political party’s national convention. Delegates are awarded either proportionally or winner-take-all, depending on the rules of the political party.
In a primary, voters participate by casting ballots for their preferred candidate. The ballots are counted, and the number of delegates for the state’s political party are awarded to the winning candidate. Those delegates then attend the political party’s national convention and count toward the candidate’s delegate count.
A caucus is a meeting of voters who are members of a political party. The members split into groups based on which candidate they support. From there, each group tries to persuade others to join their group and support their candidate.
In 2024, four states will hold only caucuses, 41 states and Washington, DC, will hold only primaries, and five states will hold both.

What is Super Tuesday? When is it?
In 2024, Super Tuesday is Tuesday, March 5 . On this date, Alabama, Alaska, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Iowa, Maine, Massachusetts, Minnesota, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, and Virginia will all hold presidential primaries and caucuses. It’s often a turning point in the presidential race, as it can provide candidates with insurmountable delegate counts.
When is the Republican National Convention?
The Republican National Convention will take place from July 15-18, 2024, in Milwaukee .
When is the Democratic National Convention?
The Democratic National Convention will take place from August 19-22, 2024, in Chicago .
What is a national convention?
Political parties hold national convention s to select their presidential and vice-presidential nominees. This is done by state delegates, who are selected through state primaries and caucuses and attend the national convention to confirm their candidate choice. To become the presidential nominee, a candidate typically must win the most delegates.
When are the 2024 presidential debates?
Presidential candidates from both major parties, and occasionally other parties, participate in debates. These are usually scheduled in September and October of the election year.
Read more about how runoff elections work and get the data directly in your inbox by signing up for our email newsletter .
Explore more of USAFacts
Related articles, the october 2019 democratic debate and the data behind it.

For a nonpartisan state of the nation, try The State of the Union in Numbers

Data on six topics from the vice presidential debate

Data on four topics from the final presidential debate

Related Data

Voting-age population during elections
255.46 million

Percent of people who always or sometimes vote in local elections
Data delivered to your inbox.
Keep up with the latest data and most popular content.
SIGN UP FOR THE NEWSLETTER

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In Summary: Yes, time travel is indeed a real thing. But it's not quite what you've probably seen in the movies. Under certain conditions, it is possible to experience time passing at a different rate than 1 second per second. And there are important reasons why we need to understand this real-world form of time travel.
Einstein found that the faster you move through space, the slower you move through time — you age more slowly, in other words. One of the key ideas in relativity is that nothing can travel ...
It has been developed by Nasa with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. The National looks at five facts that make the James Webb Space Telescope extra special. 1. It is 'time travelling' into the past. The telescope will show us what the universe was like 100 million to 250 million years after its birth.
An observer traveling at high velocity will experience time at a slower rate than an observer who isn't speeding through space. While we don't accelerate humans to near-light-speed, we do send ...
Vox asks James Gleick, author of Time Travel: A History about the origins of the time travel and Hitler question. Time is a river. Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius wrote that: "Time is like a river ...
Albert Einstein's theory of relativity says time and motion are relative to each other, and nothing can go faster than the speed of light, which is 186,000 miles per second. Time travel happens ...
Time travel exerts an irresistible pull on our scientific and storytelling imagination. Since H.G. Wells imagined that time was a fourth dimension —and Einstein confirmed it—the idea of time ...
In this weekly series, Life's Little Mysteries rates the plausibility of popular science fiction concepts. In the first "Back to the Future" movie, all it took to travel through time was 1.21 ...
One of the first known examples of time travel appears in the Mahabharata, an ancient Sanskrit epic poem compiled around 400 B.C., Lisa Yaszek, a professor of science fiction studies at the ...
1. Every person on Earth is living in the past. This may sound like the plot to some sci-fi, time-travel thriller, but it's actually a fact of human biology and the trickiness of time. Our ...
Joe insists time travel is infinitely more possible as theorists number-crunch two loose ends from the equations handed down to us by Albert Einstein and Godel's solution to the 'Field Equations' in 1949. It seems even Einstein, himself, admitted the time travel door may be wide open to us yet. Olson explains, "To the general public the ...
The first page of The Time Machine published by Heinemann. Time travel is the hypothetical activity of traveling into the past or future.Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. In fiction, time travel is typically achieved through the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine.The idea of a time machine was popularized by H ...
Explore the fascinating world of time travel through these 25 mind-bending facts and theories that delve into its scientific plausibility, fictional depictio...
Milky Way: A space crew would experience 3.2 seconds of time while crossing the 300,000 light years distance to the center of our galaxy. Andromeda Galaxy: Located 2.2 million light-years away, the journey, as far as the crew are concerned, would last 3.5 minutes. Virgo Cluster: Located 40 million light-years away, the crew would experience a ...
Time Travel. First published Thu Nov 14, 2013; substantive revision Fri Mar 22, 2024. There is an extensive literature on time travel in both philosophy and physics. Part of the great interest of the topic stems from the fact that reasons have been given both for thinking that time travel is physically possible—and for thinking that it is ...
1: Predestination Paradox. A Predestination Paradox occurs when the actions of a person traveling back in time become part of past events, and may ultimately cause the event he is trying to prevent to take place. The result is a 'temporal causality loop' in which Event 1 in the past influences Event 2 in the future (time travel to the past ...
Fact 1: Time Travel to the Past Is Called Retrocognition. Psychologists, parapsychologists, and other researchers have a technical name for backward time travel. They call it retrocognition, which simply means "knowledge about the past." Retrocognition occurs when a person somehow "travels" to the past. A retrocognitive time traveler does not ...
The answer is, we do not know, and there has been no evidence ever to prove travelling back or forward in time. One of the greatest and most famous physicists Stephen Hawking who is a master on the subject believes that it's almost impossible to travel back in time. It makes sense when you think about it. It's in the past and it has already ...
Kids Encyclopedia Facts. Time travel is the idea of going back in time to the past or forward to the future. We always travel forward, to the future. Time travel to the past is not known to be possible, but it is much used in fiction. The Time Machine (1895) by H. G. Wells was one of the first and most famous stories of time travel.
Let's have a look at some of the time travel facts: 1. Time Is The Fourth Dimension. Simply stated, the first three dimensions are used to specify an object's location/movement in space (forward-backwards, left-right and up-down), while the fourth dimension locates its position in time. All four dimensions are used to specify completely the ...
10 General Relativity. Einstein's theory of general relativity; is a true masterpiece in the world of physics. And lucky for us, it provides the foundation for understanding the possibility of time travel. In a nutshell, Einstein's theory states that time and space are interconnected, forming spacetime.
United States Travel Costs. Accommodation - Hostels can be found in most major cities, though options are generally slim in the country. A bed in a dorm room with 4-6 beds usually costs between $35-55 USD per night. Rooms with more beds are marginally cheaper (they start around $25-30 USD per night).
The huge solar storm is keeping power grid and satellite operators on edge. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of solar flares early Saturday afternoon. The National Oceanic and ...
An All-Encompassing Study Offers a Clear Answer. For billions of people around the world, the Bible is more than just a book - it's the divinely inspired Word of God. This ancient text has ...
3. Fox's filming schedule was very intense. Michael J Fox (1985) Universal Pictures / Handout/Getty. Fox was filming both Family Ties and Back to The Future at the same time. He would film Family Ties in the morning, and then head over to Back to The Future at night, and be there until around 3 or 4 in the morning.
Dates to know for the 2024 presidential election. The 2024 presidential election will take place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024. Presidential primaries and caucuses are scheduled to begin in January and will run through June. Published Fri, March 1, 2024 by the USAFacts Team. Every four years, Americans elect a president on the first Tuesday in ...
Key Facts. A celestial event called Solar Cycle 25 —the cycle the sun goes through around every 11 years—has been the cause of geomagnetic storms that have resulted in recent sightings of the ...